Method for detecting harm degree of postoperative cytomegalovirus infection of kidney transplantation patient
A cytomegalovirus, harmful degree of technology, applied in animal cells, vertebrate cells, blood/immune system cells, etc., can solve problems that must be treated in time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
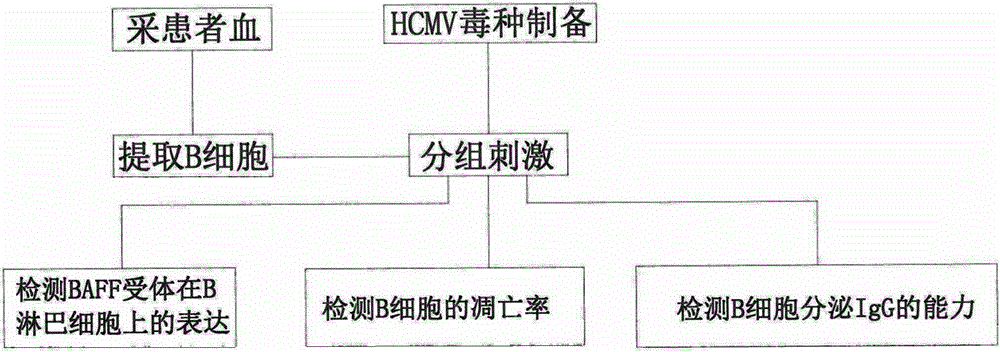
[0032] This embodiment is a detection method for assessing the degree of harm caused by cytomegalovirus infection for patients with type 1 kidney transplantation after surgery, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0033] Step a, blood collection, collecting 20 mL of heparin sodium anticoagulated peripheral blood from a patient undergoing a kidney transplantation.
[0034] Step b, CD19 + Acquisition and analysis of B lymphocytes, mononuclear cells were separated with lymphocyte separation medium (Ficoll) (purchased from Tianjin Haoyang Biological Company), and CD19 in peripheral blood was sorted with magnetic beads + B lymphocytes. Magnetic bead sorting of cells involves the following substeps:
[0035] (1) Take an appropriate amount of mononuclear cell suspension, centrifuge at 100g for 5 minutes, and discard the supernatant;
[0036] (2) by every 10 7 Add 80 μl MACS buffer to each cell, gently blow off the cells, and mix well;
[0037] (3) Add 20 μl ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] This embodiment is a detection method for assessing the degree of harm caused by cytomegalovirus infection in patients with second kidney transplantation after surgery, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps: .
[0093] Step a, blood collection, collecting 20mL of heparin sodium anticoagulated peripheral blood from patients with second kidney transplantation.
[0094] Step b, CD19 + Acquisition and analysis of B lymphocytes, separation of mononuclear cells with lymphocyte separation medium (Ficoll), separation of CD19 in peripheral blood with magnetic beads + B lymphocytes. Magnetic bead sorting of cells involves the following substeps:
[0095] (1) Take an appropriate amount of mononuclear cell suspension, centrifuge at 100g for 5 minutes, and discard the supernatant;
[0096] (2) by every 10 7 Add 80 μl MACS buffer to each cell, gently blow off the cells, and mix well;
[0097] (3) Add 20 μl CD19 magnetic beads per 80 μl MACS buffer, mix well, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com