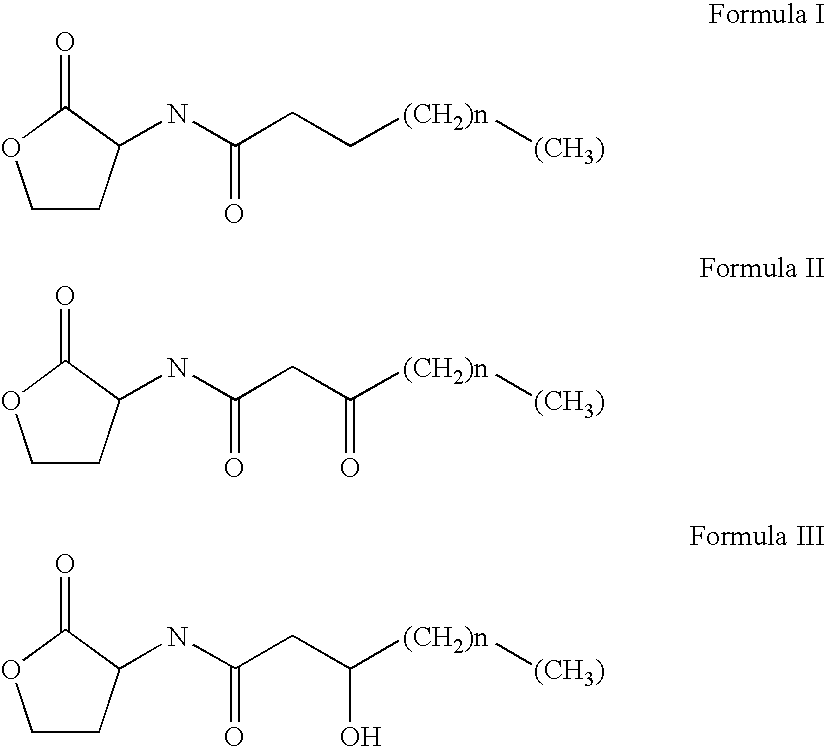
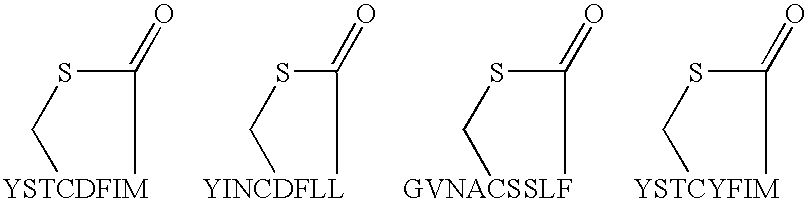
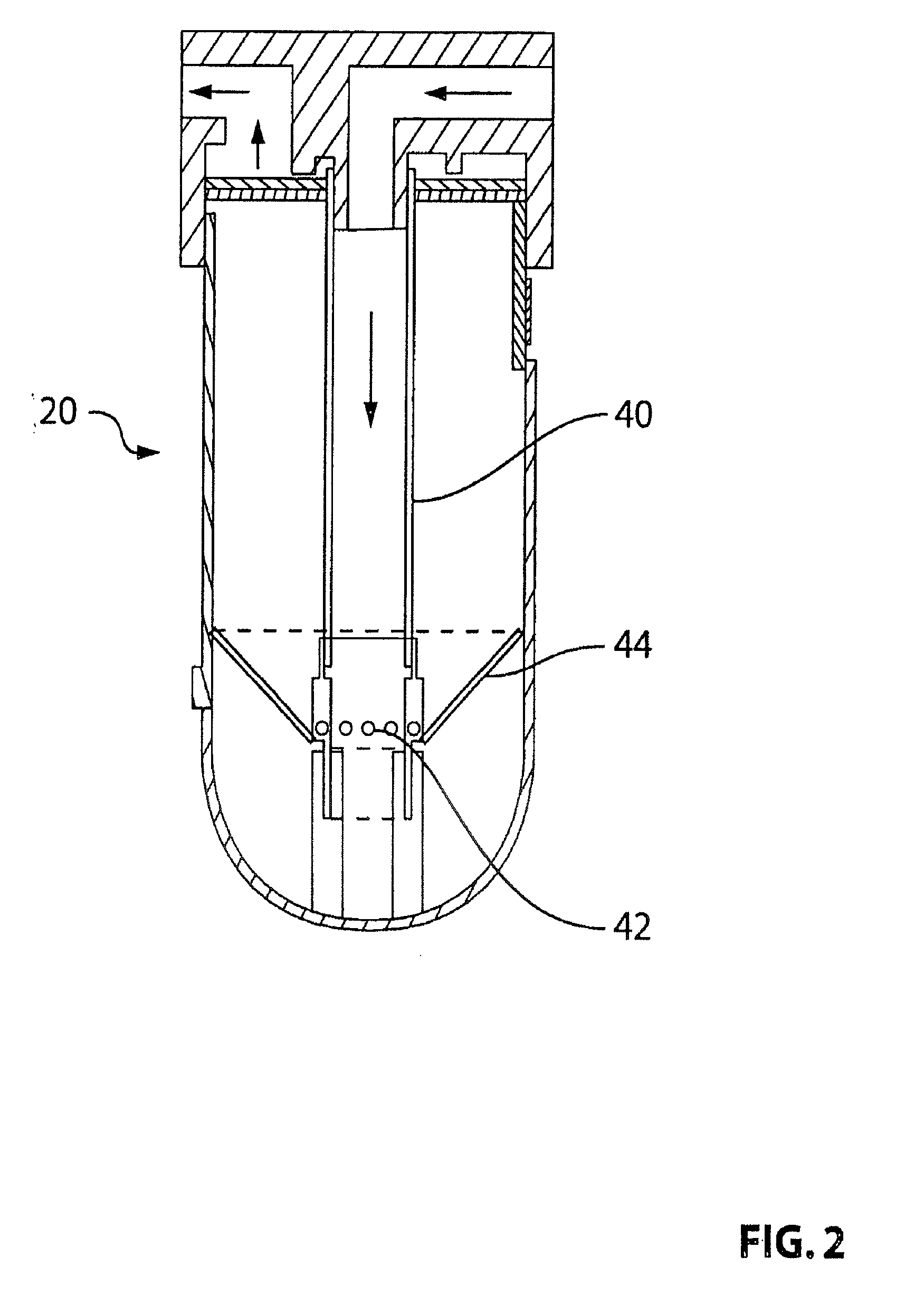
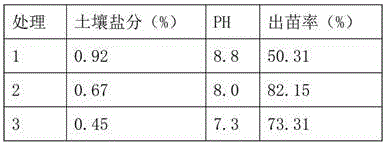
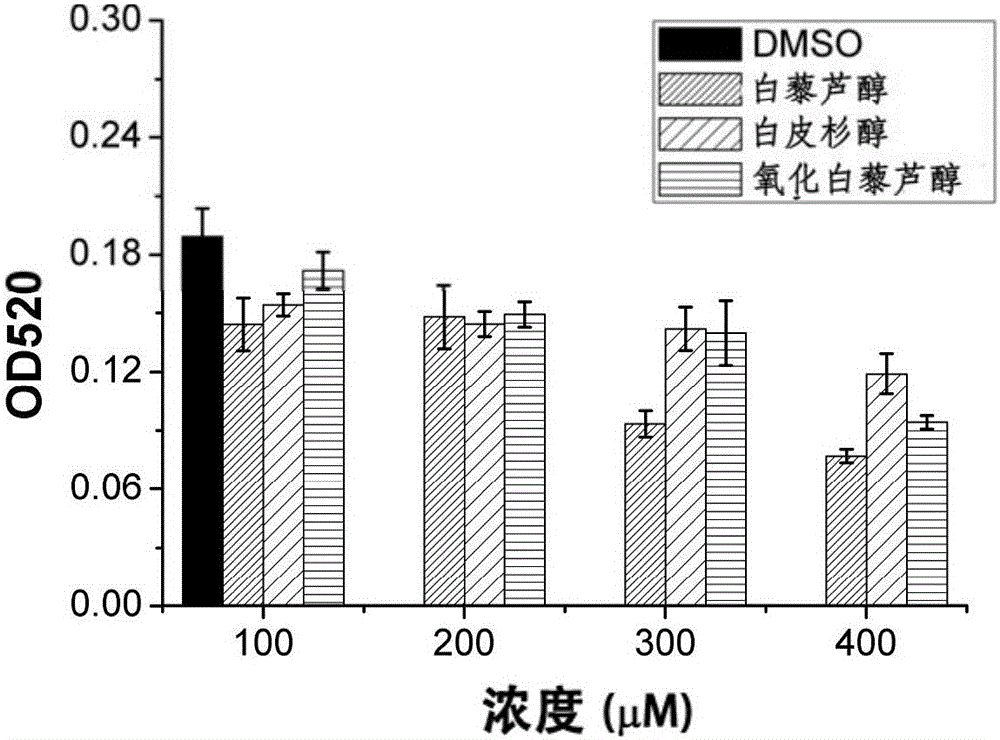
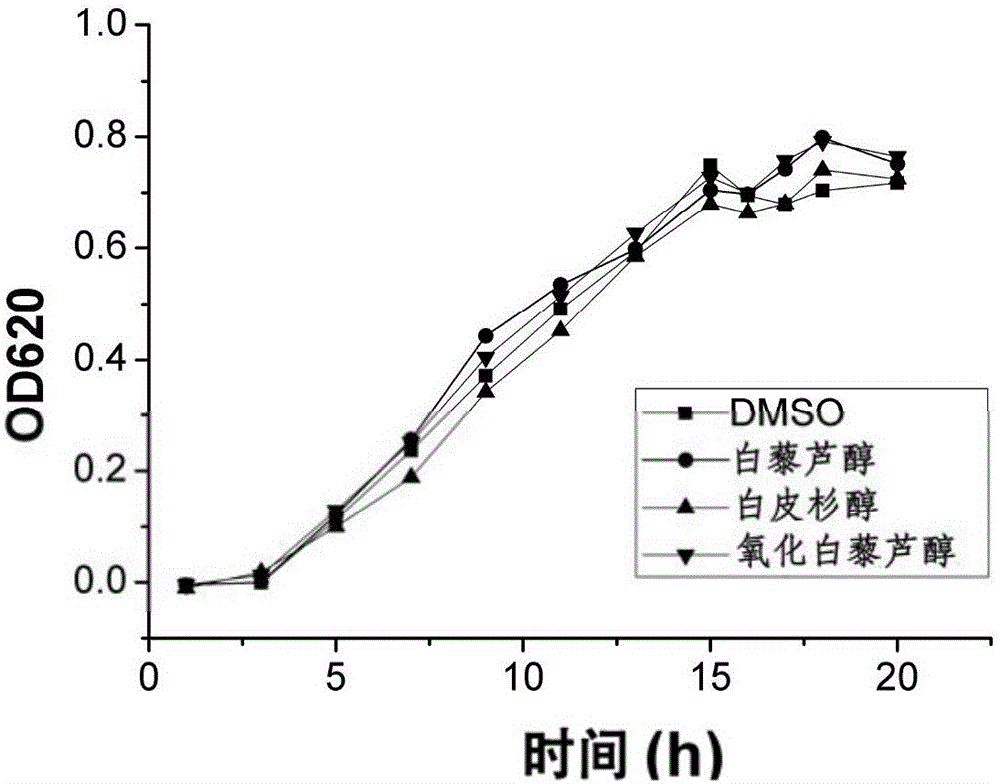
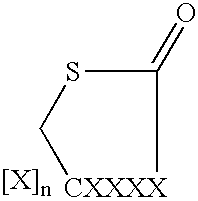Patents
Literature
47 results about "Opportunistic pathogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Opportunistic pathogen. an organism that exists harmlessly as part of the normal human body environment and does not become a health threat until the body's immune system fails. op·por·tu·nis·tic path·o·gen. Organism capable of causing disease only when the host's resistance is lowered by other diseases or drugs.
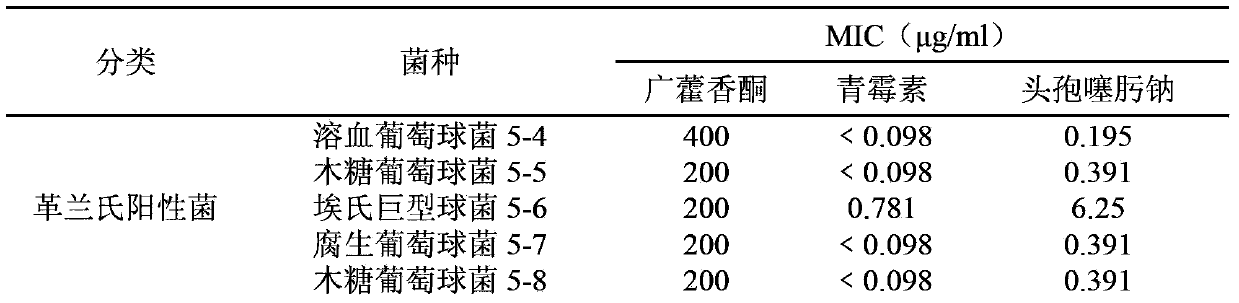
New application of patchouli alcohol
ActiveCN103156826AStrong inhibitory activityEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to an application of patchouli alcohol in preparation of antibacterial drugs, healthcare food, food, cosmetics, disinfectors or daily chemical articles. The invention also provides the antibacterial drugs, healthcare food, food, cosmetics, disinfectors or daily chemical articles. The patchouli alcohol has good antibacterial activity on pathogenic bacteria or conditional pathogen, can be used for effectively treating bacterium infectious diseases and simultaneously can also effectively antagonize methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis drug-resistance bacteria; and the pharmacodynamics activity of the patchouli alcohol is even equivalent to that of vancomycin, thus the possibility is provided for slowing down or avoiding the occurrence of the drug-resistance bacteria.
Owner:CHENGDU HUASUN GRP INC LTD +1
Lactobacillus jensenii for preventing and curing bacterial vaginosis
The invention discloses lactobacillus jensenii and application thereof. The lactobacillus jensenii is particularly lactobacillus jensenii IMJ-1, and the file No. of the lactobacillus jensenii IMJ-1 in the General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee is CGMCC No. 6558. The lactobacillus jensenii IMJ-1 CGMCC No.6558 has high H2O2 generation capability, can effectively suppress breeding of external pathogenic bacteria and other conditional pathogenic bacteria, and has a high binding function to epithelial cells of vagina, and accordingly, breeding of bacteria strains on the vaginal epithelium is guranteed. Besides, the lactobacillus jensenii IMJ-1 CGMCC No. 6558 has a certain application prospect in preventing and curing bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:北京益生苑生物科技有限公司
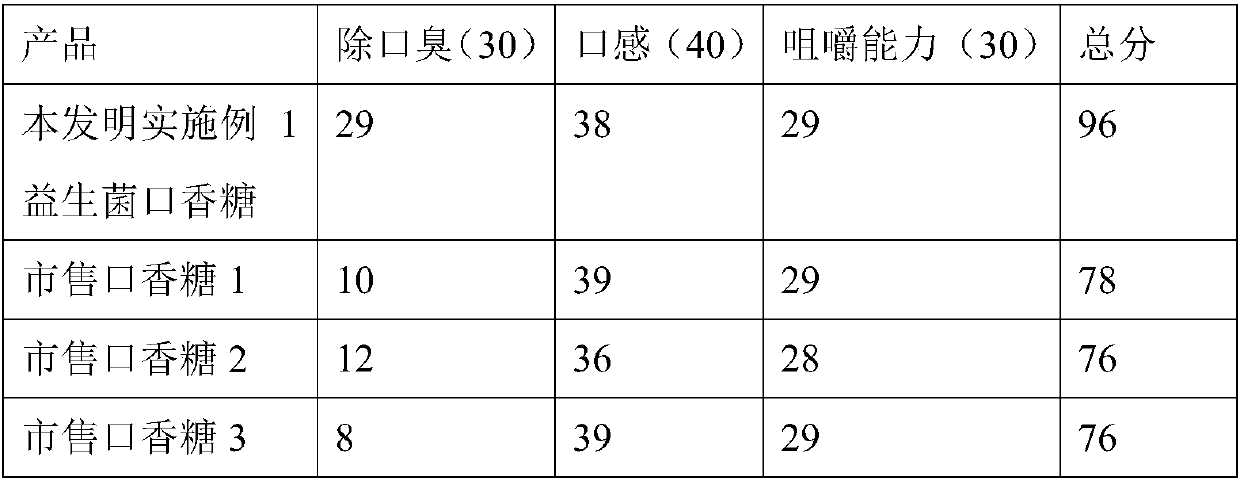
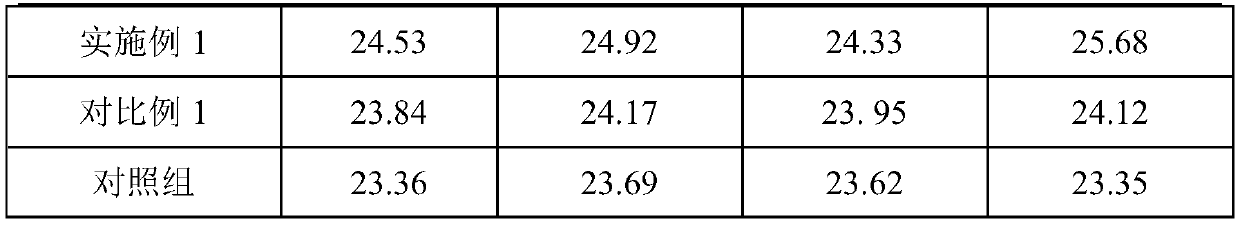
Probiotic chewing gum preparation method
InactiveCN108670982AFresh breathExercise masticatory musclesAntipyreticDigestive systemDiseaseRetention time
The invention provides a probiotic chewing gum preparation method. By means of a probiotic embedding technology, survivability of probiotics in chewing gum is kept, and long-time storage is facilitated; by means of the characteristic of long chewing gum chewing time, retention time of probiotics in the oral cavity is prolonged; furthermore, the characteristic that the probiotics can antagonize pathogenic bacteria is utilized to inhibit and kill opportunistic pathogens in the oral cavity; finally, the purposes of preventing and treating oral diseases of ozostomia, pulpitis, periapical periodontitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, acute necrotic ulcerative periodontitis, stomatitis and the like are achieved. In addition, the probiotics can enter gastrointestinal tracts along with saliva to promote host gastrointestinal tract flora health and has recovering and treating effects on symptoms of unacclimatization, anorexia, diarrhea and the like of flora disorder diseases.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Methods for the treatment of an infectious bacterial disease with an anti-lactone or lactone derived signal molecules antibody
InactiveUS20060165704A1Limit and prevent down-regulationPrevent diseaseAntibacterial agentsBiocideDisease monitoringVirulent characteristics
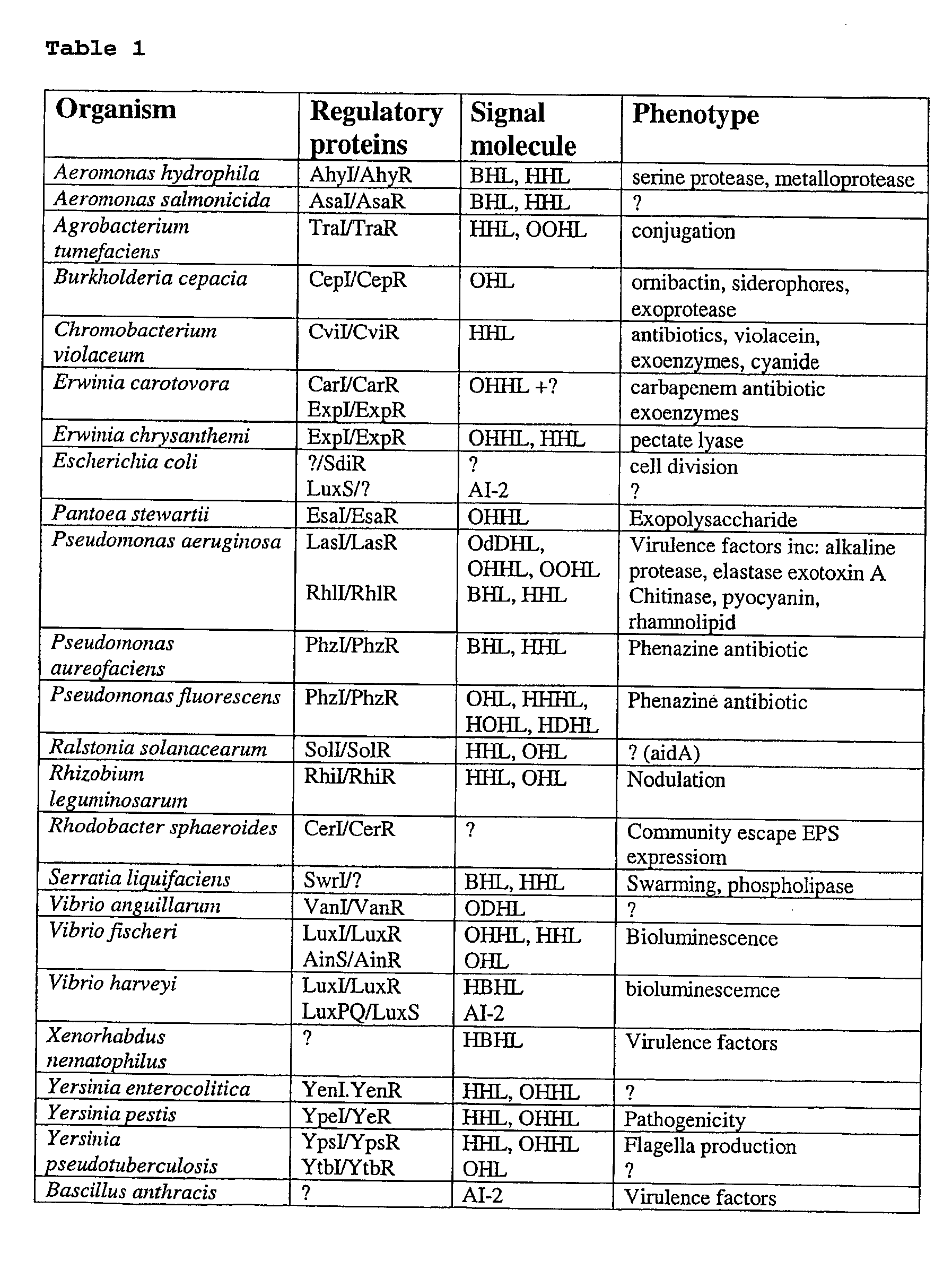
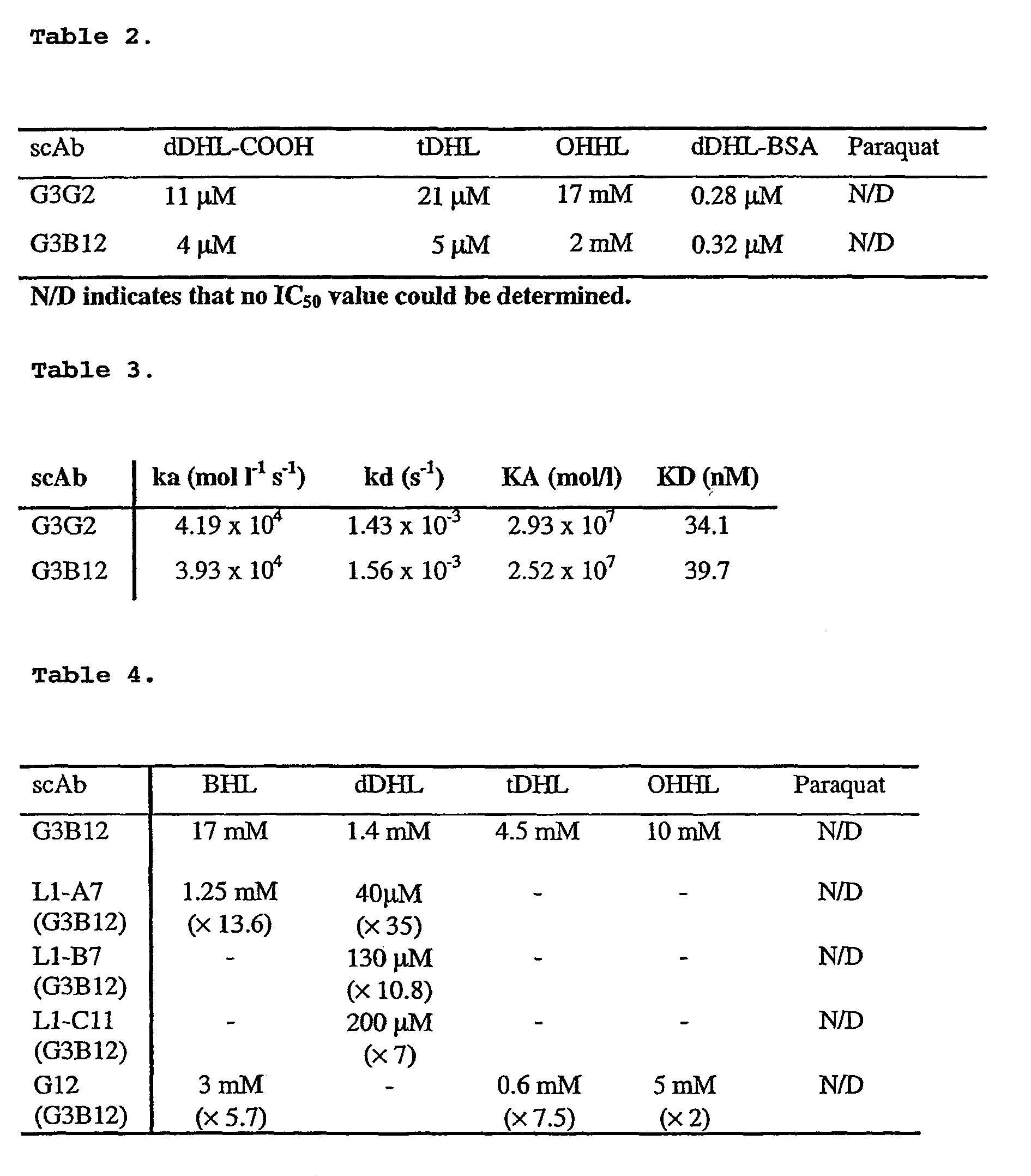
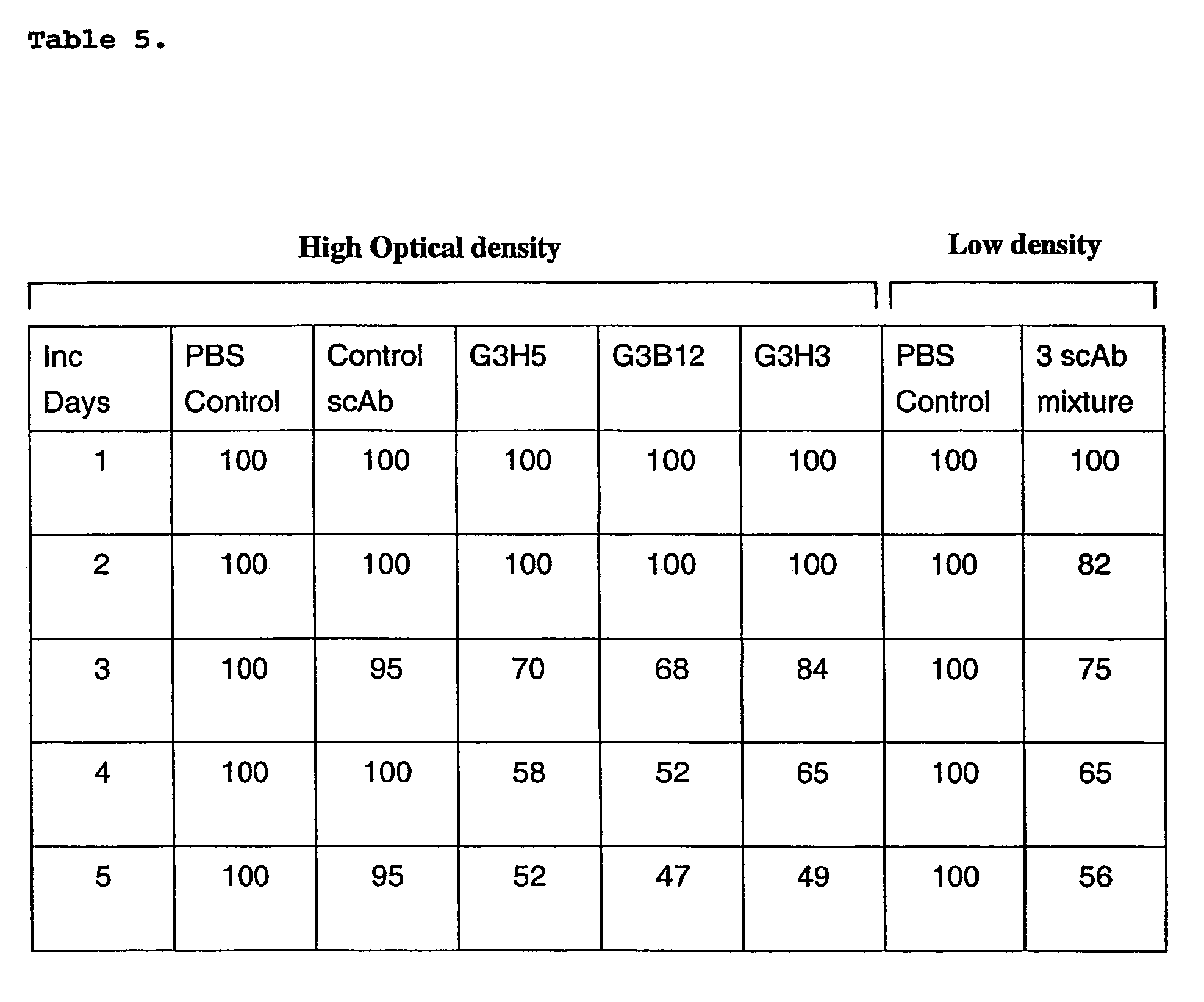
The present invention relates to methods for the control of virulence of infectious bacteria by modulating the extra-cellular concentration of bacterial cell signalling molecules. Derivatives of cell signalling molecules are conjugated to suitable carrier proteins and used to isolate high affinity receptors recognising the native signal molecule(s). By binding to signalling molecules, the receptors reduce and maintain extra-cellular concentrations of signal molecules below the threshold level that would otherwise result in certain opportunistic pathogens adopting a virulent form, and can transform virulent organisms to non-virulent states. These receptors have applications for the treatment of individuals with susceptibility to infection, the treatment of patients with existing infections, in disease monitoring and management, and in related applications where the host for infection is an animal or plant.
Owner:HAPTOGEN
Lactobacillus curvatus and pharmaceutical application thereof
ActiveCN104673702AStrong adhesionProduce efficientlyAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacterial vaginosisVaginal epithelium
The invention discloses lactobacillus curvatus and pharmaceutical application thereof. The lactobacillus curvatus provided by the invention specifically is lactobacillus curvatus IMC-79 which has a relatively strong capability of generating H2O2 and can effectively inhibit the growth of external pathogenic bacteria and other conditioned pathogens; and meanwhile, the lactobacillus curvatus IMC-79 also has a relatively strong effect of adhering vaginal epithelial cells to ensure that a strain is fixedly planted on the vaginal epithelium. The lactobacillus curvatus IMC-79 provided by the invention has a certain application prospect in the aspect of preventing and treating bacterial vaginal diseases.
Owner:北京博园新里科技有限公司
Lactobacillus crispatus for preventing and treating female urogenital tract infection and application thereof
ActiveCN111893057AImprove antibacterial propertiesStrong adhesionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAntibiosisVaginal epithelium
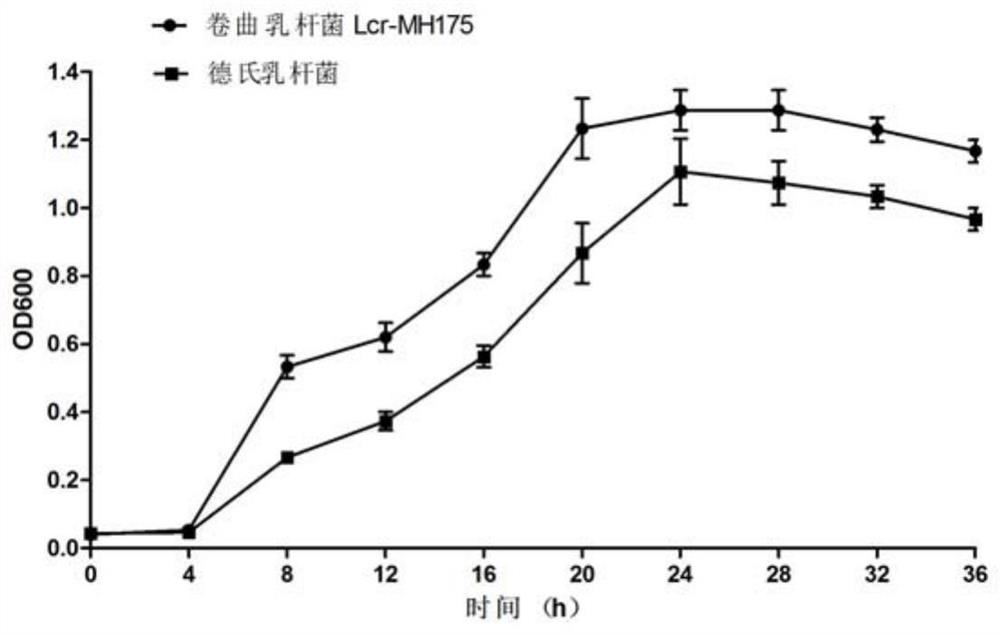
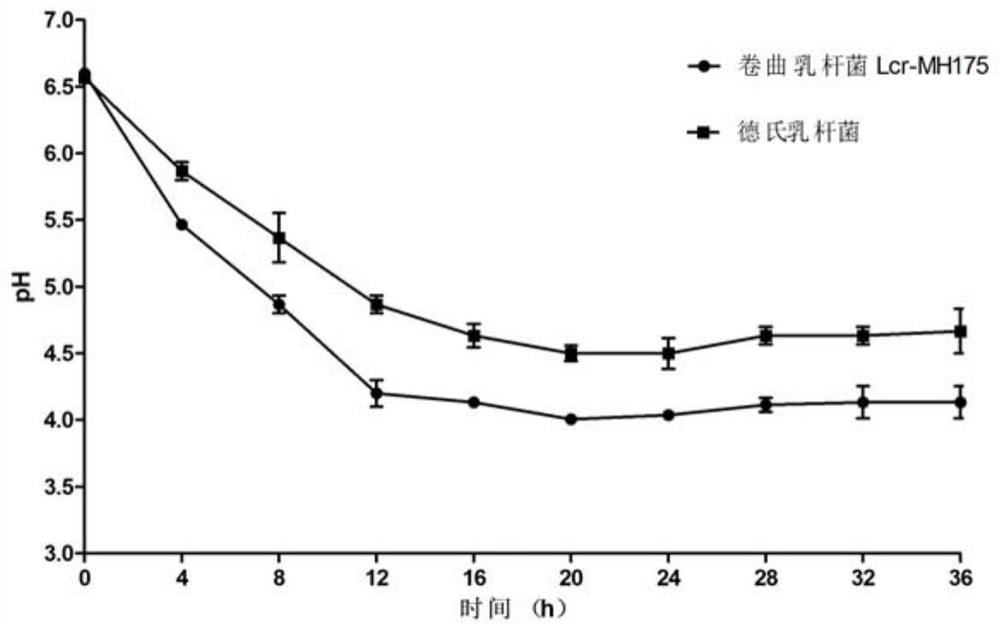
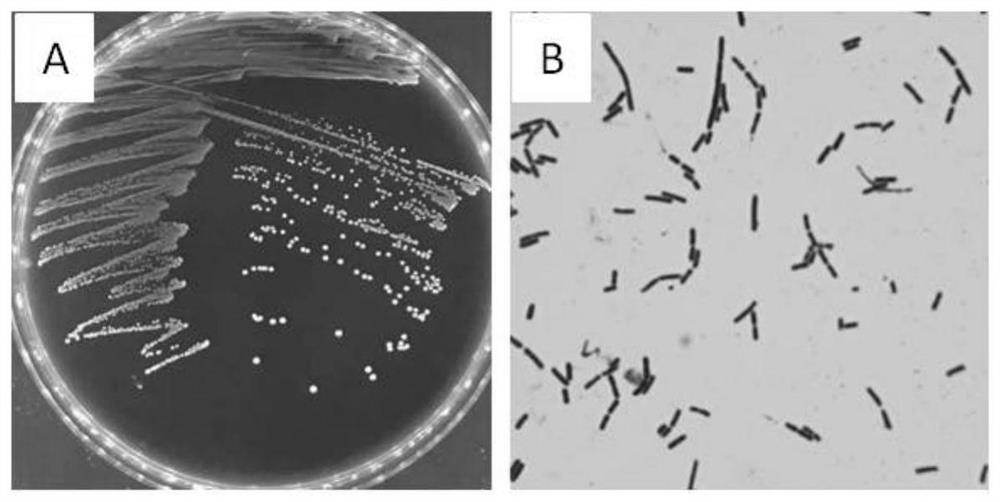
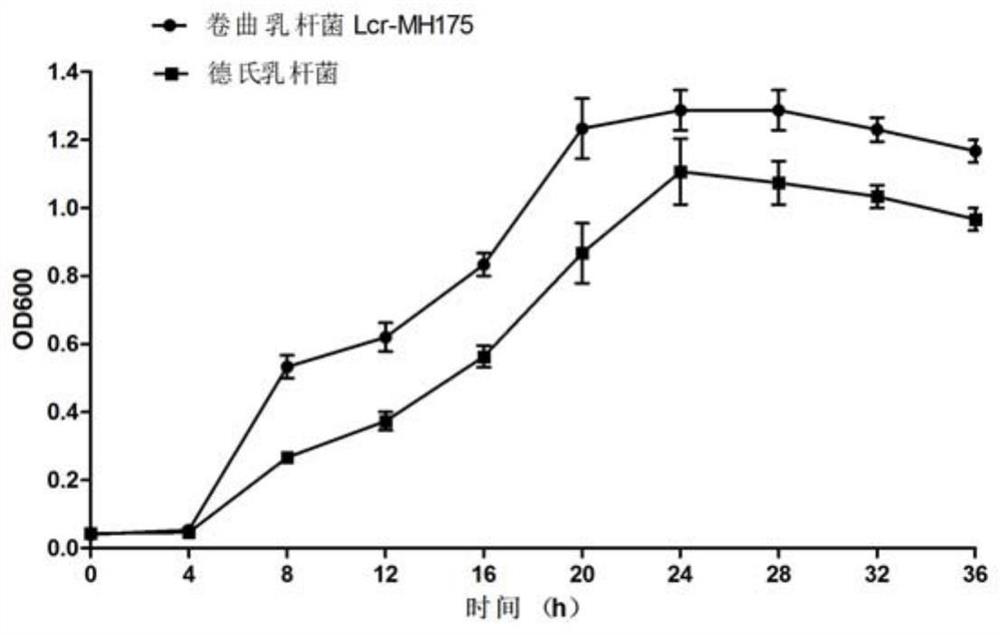
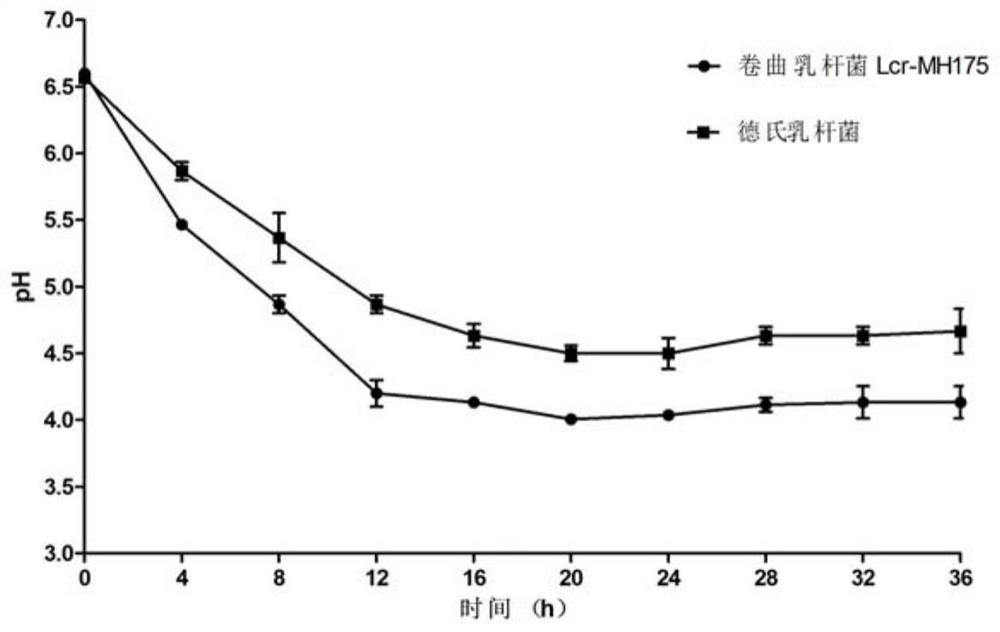
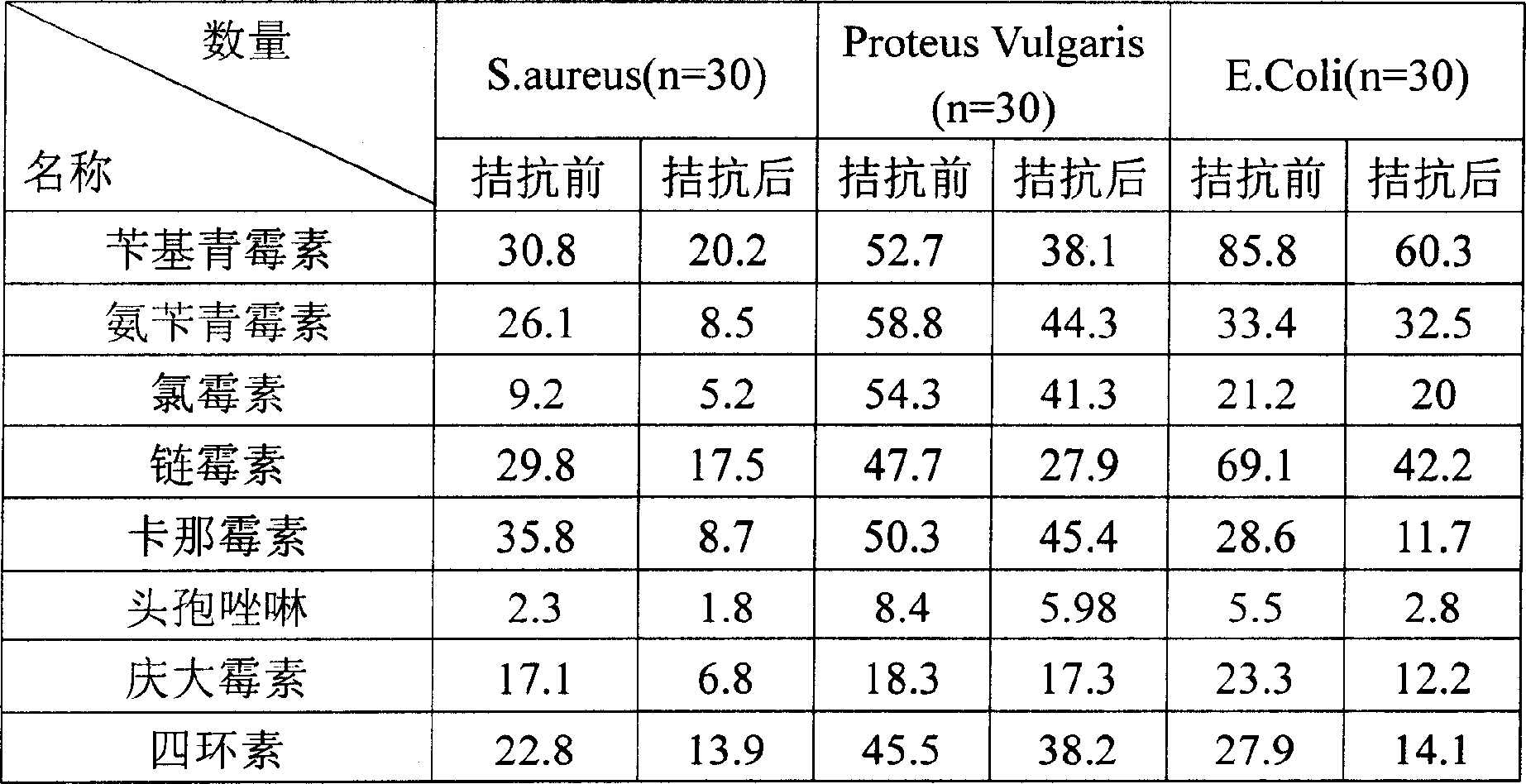
The invention discloses lactobacillus crispatus Lcr-MH175 for preventing and treating female urogenital tract infection. The preservation number of the Lcr-MH175 is CGMCC No. 15938. The lactobacilluscrispatus Lcr-MH175 provided by the invention has relatively strong antibacterial ability, can effectively inhibit growth of external pathogenic bacteria and pathogenic bacteria under other conditions, and also has a relatively strong adhesion effect on Hela cells so as to ensure the colonization of the strain on vaginal epithelium. The lactobacillus crispatus Lcr-MH175 provided by the invention has a certain application prospect in the aspect of urogenital tract infection prevention and treatment.
Owner:哈尔滨美华生物技术股份有限公司
Methods for the treatment of an infectious bacterial disease with an anti-lactone or lactone derived signal molecules antibody
InactiveUS7812134B2Reduce bacterial infectionImprove life expectancyAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaDisease monitoringBacteroides
Owner:HAPTOGEN
Control of Subterranean Termites
InactiveUS20140026468A1Effective controlIncrease consumptionBiocideDead animal preservationAureobasidium sp.Toxicant
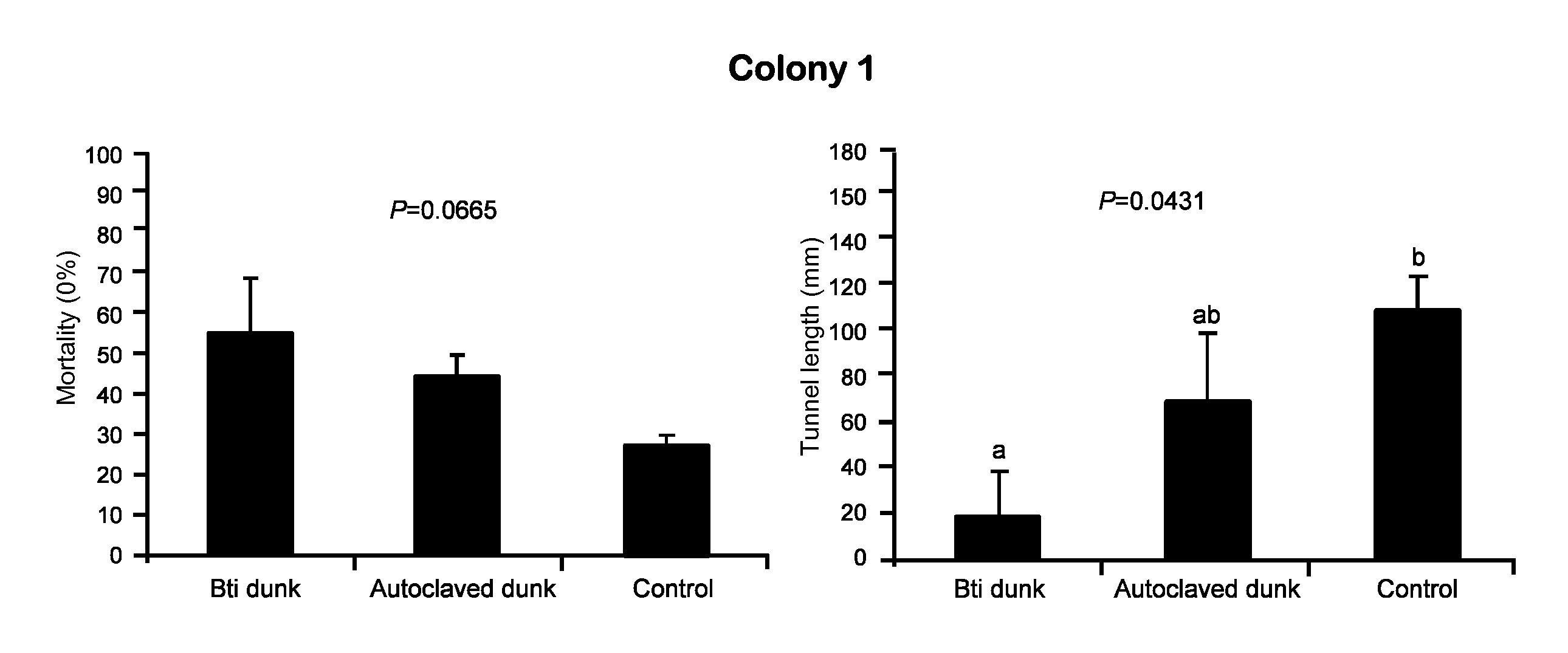
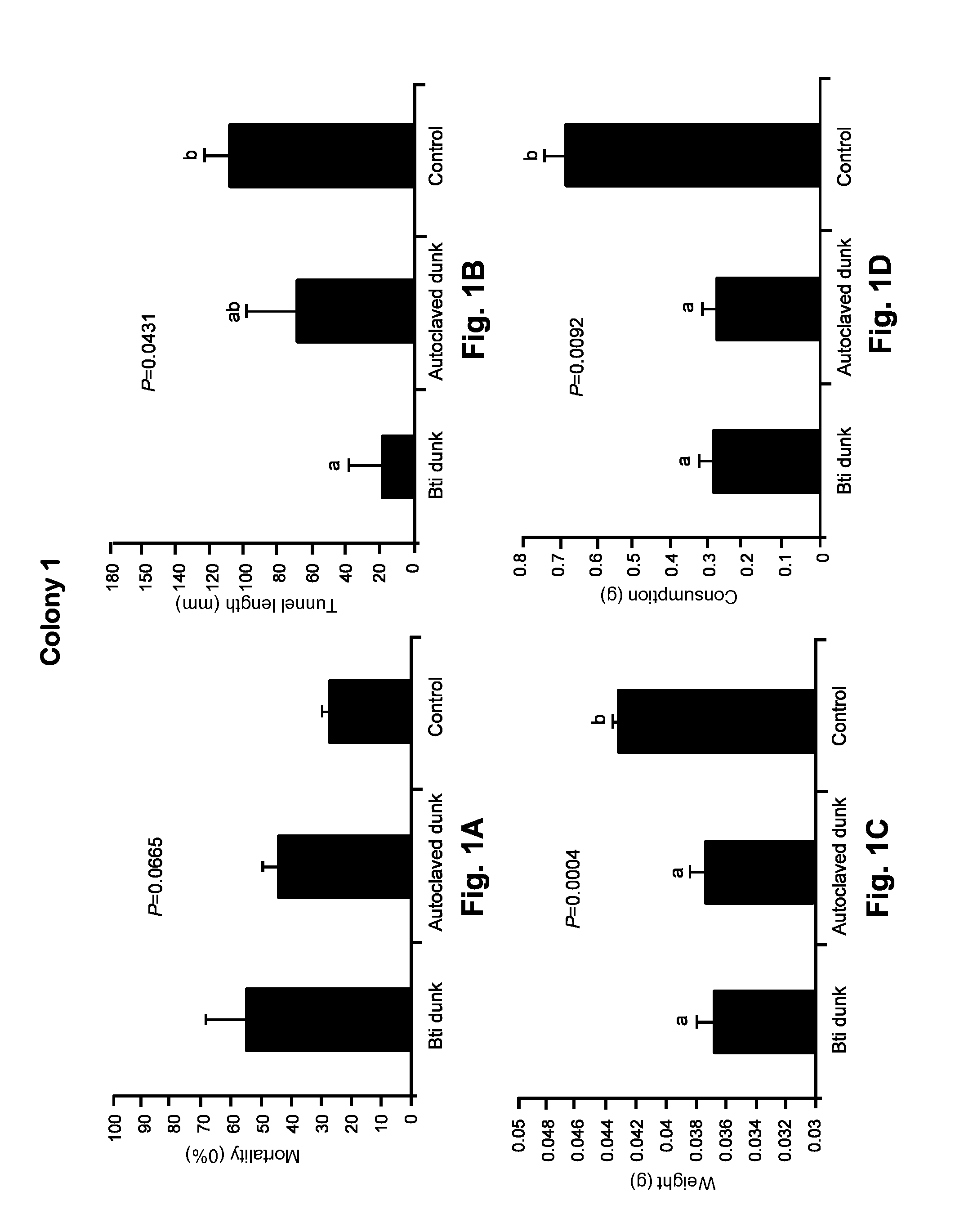
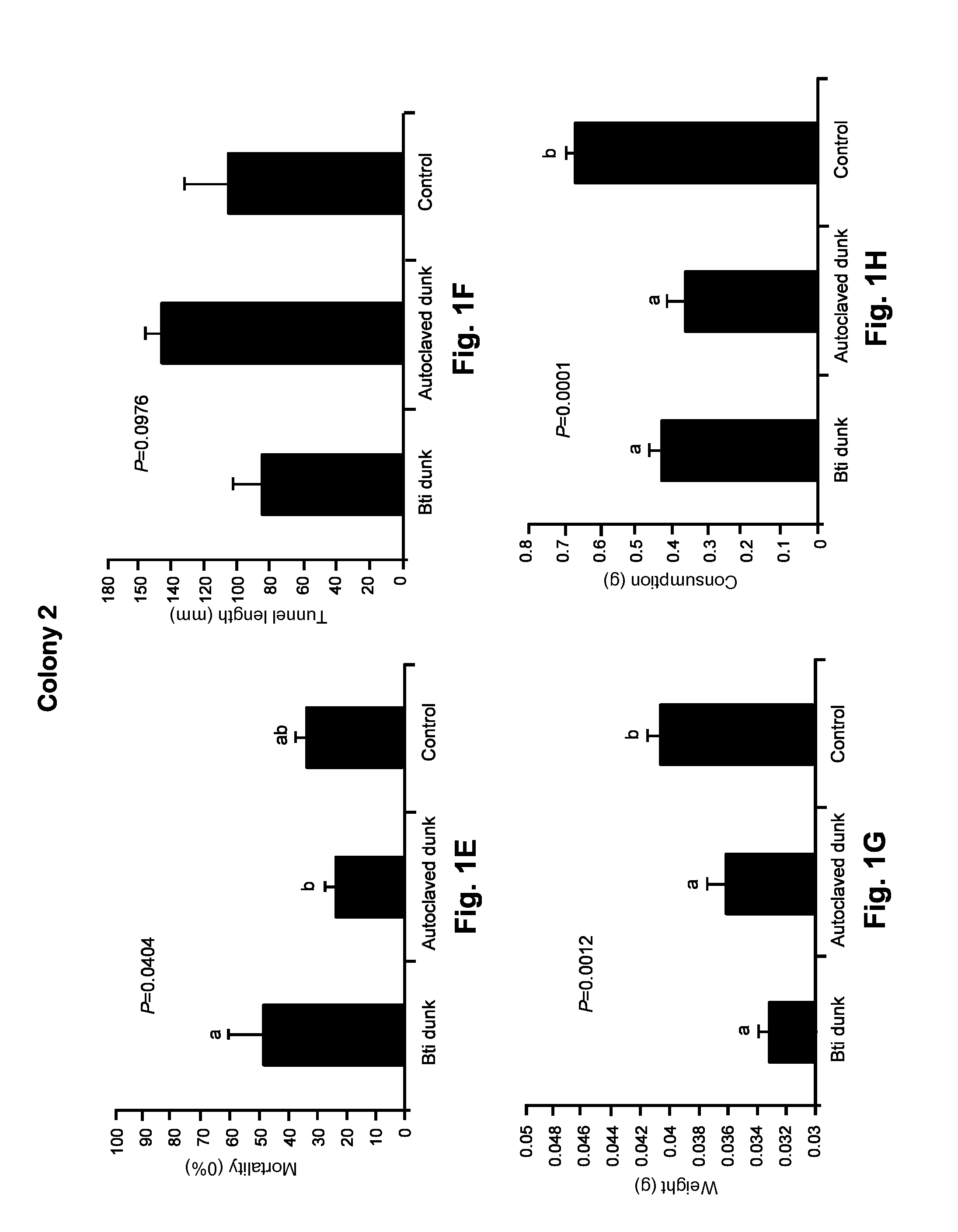
A biological control is disclosed for termites, including subterranean termites such as C. formosanus, comprising a mixture of a chitin synthesis inhibitor such as lufenuron with a pathogen or opportunistic pathogen. The combination greatly enhances the effectiveness above that of the individual components. For example, P. aeruginosa is commonly found in association with termites, but it is not normally harmful to termites. However, in the presence of lufenuron, P. aeruginosa becomes an opportunistic pathogen that kills termites. As another example, B. thuringiensis, which otherwise has shown only limited effectiveness against termites, has greatly enhanced lethality in combination with lufenuron. In another aspect a termite toxicant is administered to termites in a clay-based bait. Clay acts as an attractant for subterranean termites such as C. formosanus, and a clay bait can increase a colony's consumption of a toxicant.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Raw water after-treatment method in aquatic breeding plant in summer and autumn
InactiveCN104761082AReduce usageImprove sterilization effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentAmmoniacal nitrogenPathogenic bacteria
The invention provides a raw water after-treatment method in an aquatic breeding plant in summer and autumn, aiming at the conditions of high bacteria density, high sulfide content and high ammonia nitrogen content in raw water in the aquatic breeding plant in summer and autumn. With the adoption of ferrate pretreatment and hydrogen persulfate matched treatment, the amount of the hydrogen persulfate is reduced, and the sterilization effect of the ferrate is enhanced. According to the water treated by the method disclosed by the invention, the number of pathogenic bacteria in the water condition is 103 bacteria per ml or below, the sulfide content is in a safe concentration range, and when the water is used for breeding, the seed quality and the survival rate of the aquatic breeding plant can be obviously improved, the dependence on antibiotics in the breeding and cultivating link is alleviated or avoided, and the edible security of cultured products is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF FUJIAN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Microbial organic fertilizer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108947679AAchieve reuseAdaptableBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaAnaerobic bacteriaFermentation
The invention relates to the field of bacterial manure, in particular to a microbial organic fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding bacillus subtilis into flax plant degumming waste liquor for aerobic fermentation; and stopping oxygen supply and inoculating an EM culture for anaerobic fermentation to obtain the microbial organic fertilizer. By taking the flax plant degumming waste liquor as a raw material and adding bacillus subtilis for aerobic fermentation, the bacillus subtilis can form an advantageous population quickly soas to inhibit growth of pathogenic bacteria or other infectious microbes; in the thallus growing process, active substances such as subtilin, polymyxin, nystatin and gramicidin are generated to play an obvious inhibiting role to pathogenic bacteria or endogenously infected conditioned pathogens. By adding the ME culture for anaerobic fermentation, the anaerobic EM bacteria are fermented to generate organic acids, so that the pH is reduced to form a slight acidic environment. In addition, the EM bacteria are compound cultures. Multiple probiotics are fermented, and the organic fertilizer applied to soil can form a symbiotic and stable bacterial colony environment, so that the effect is more lasting.
Owner:江西线元生物科技有限公司
Bacillus subtilis, its combination preparation and method for preparing combination preparation
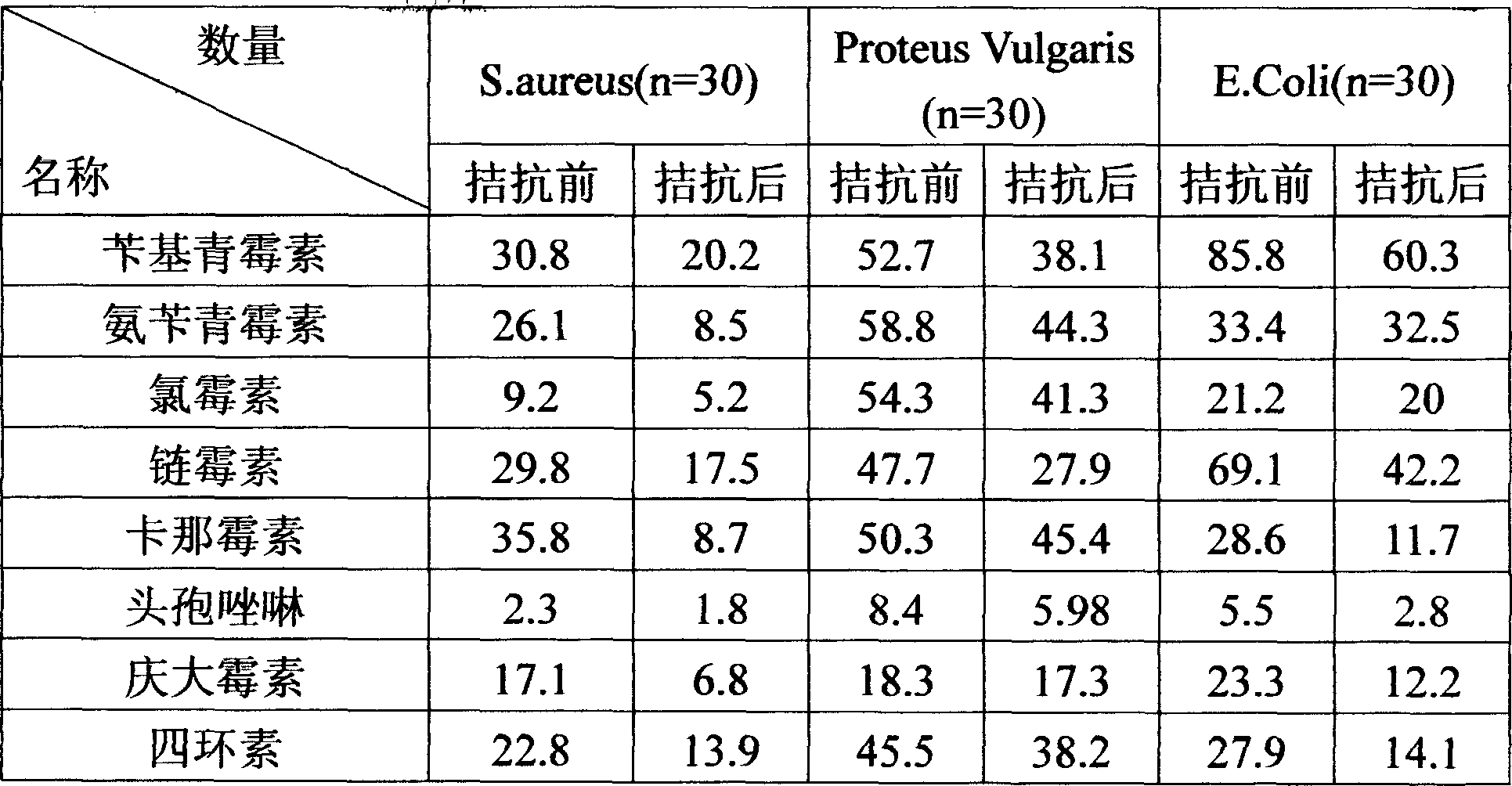
The invention relates to a bacilli, its compound preparation and the preparing method for the compound preparation. Its name is Bacillus subtilis LY-35, which is preserved in the general microbe center of Micro Germ conservation Management committee of China, and its conservation number is:CGMCC N0.1222. The preparation is a mixture of lambda phage of culture of bacilli and staphylococcus, streptococcus, colibacillus, bacillus proteus, pseudomonad, salmonella, pasteurella and klebsiella, can cure and prevent all kinds of illness caused by conditional pathogen,is a micro biological preparation which can be used by being mixed with antibiotics or replace antibiotics without any remainder and pollution, with good curative effect and safety.
Owner:烟台绿云生物工程研究院有限公司
Method for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis complex through multi-crossover amplification and biosensing
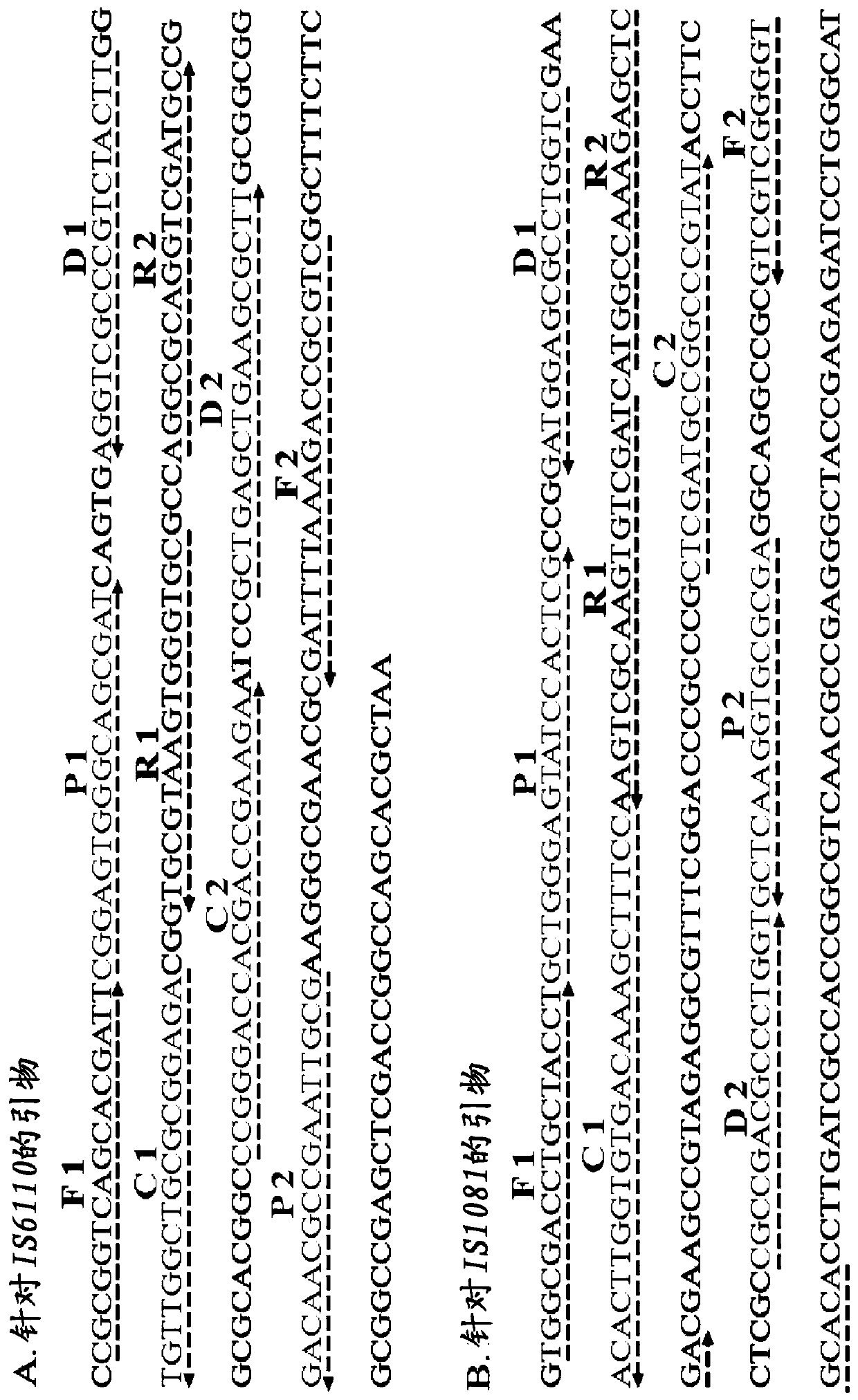
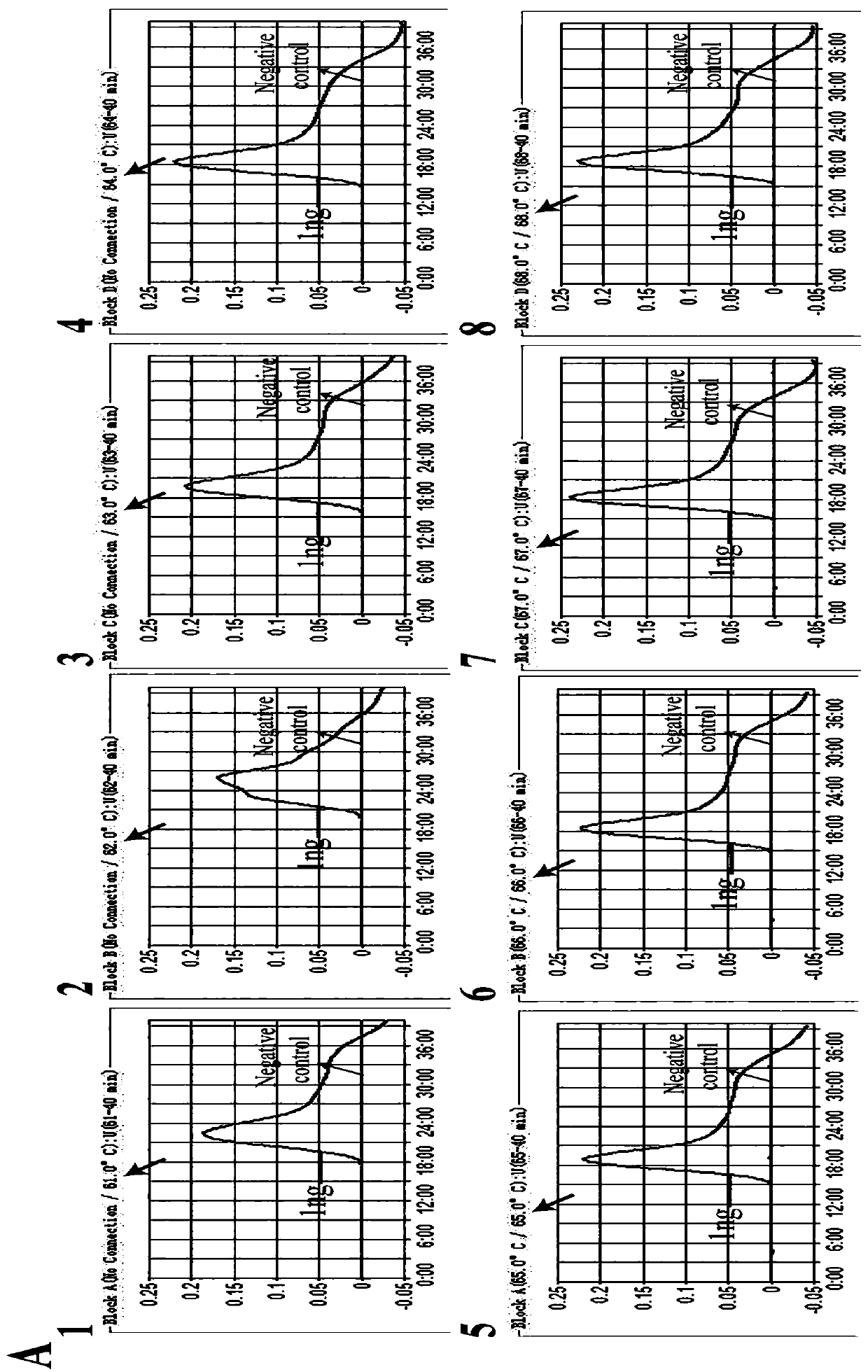
InactiveCN109811036AConvenient multi-cross isothermal amplification methodThe multiple-crossover isothermal amplification method is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesOpportunistic pathogenMycobacterium
The invention discloses a method for detecting a target gene through multi-crossover constant-temperature amplification and nano-biosensing (MCDA-LFB), which can simultaneously detect specific genes IS6110 and IS1081 of a mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC). The invention also discloses a specific primer combination which aims at the two genes and is applied to the method. The whole MCDA amplification can be completed within 30 minutes by the multi-crossover constant-temperature amplification method, the detection range for the two genes is 10 ng to 10 fg, and accordingly, extremely highsensitivity is achieved; only members belonging to the MTBC can have positive results through MTBC-MCDA-LFB tests, non-specific amplification of other common pathogens and opportunistic pathogens does not occur, and accordingly, the method has extremely high specificity.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
New application of pogostone or derivatives of pogostone
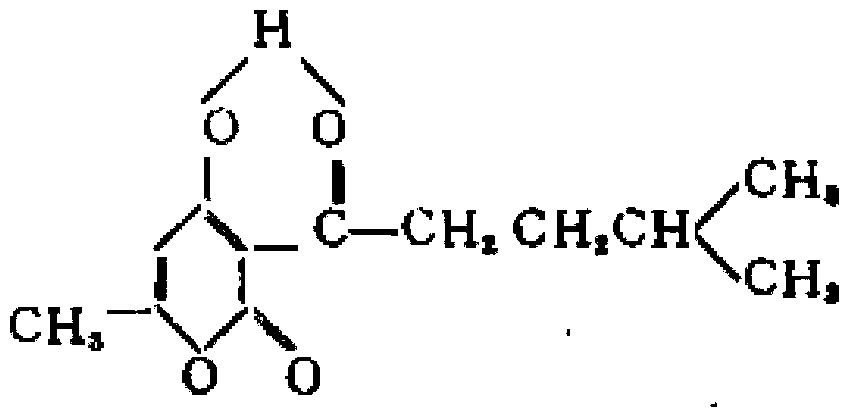
ActiveCN103416403AOvercoming the pitfalls of drug resistanceEffective againstAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyChemical products
The invention provides the application of pogostone or derivatives of the pogostone in preparation of antibacterial health food, food, cosmetics, sanitizers or daily chemical products. The invention further provides an antibacterial health food, food, a cosmetic, a sanitizer or a daily chemical product. The pogostone has favorable inhibitory activity to staphylococcus and other pathogenic bacteria or conditioned pathogen, can be used for effective treatment of bacterial infections, and can be effectively against methicillin-resistant drug-resistance bacteria, so that a new choice for clinical medication is provided.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
Combining waterborne bionutrients with scale particles and use of a waterborne particle remover to remove the combined particles from the water
InactiveUS20070068875A1Eliminate scalingSuppress bio-organic contaminationOther chemical processesSpecific water treatment objectivesEvaporationBiofouling
An automatic, self-regulating method of water treatment for use in water circulating towers in which water is evaporated, and make up water is added, with components which synergistically function to cut chemical, energy, water, corrosion, pollution, and maintenance costs, by passing the water through a Water Conditioning unit to prevent adhering evaporation scale deposits along with their content of concentrated biofouling nutrients from forming on the flooded surfaces of the tower and its associated water flow circuit, adding a trace level of iodine to the input make-up water to enhance the further disinfection of nutrient-deprived surfaces from any residual biofilm and chance pathogen contaminations, and adding a trace level addition of zinc ions in the water such as by an assured treatment feeder to the input make-up flow for inhibiting residual iodine-resistant algal and bacterial organisms of hazard for restoring bionutrient tower conditions, such as within sun-lit environments, and apparatus for carrying out the foregoing method.
Owner:ENVIROTOWER
Organic soil conditioner and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106281348AReduce compactionSimple structureBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesSludgeMushroom
The invention provides an organic soil conditioner and a preparation method thereof. The organic soil conditioner is prepared by adding vermiculite, mushroom residues, rice hull powder and bacillus subtilis to municipal sludge, carrying out aerobic composting fermentation and then carrying out low temperature drying and grinding. The organic soil conditioner provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the organic soil conditioner can effectively relieve soil hardening caused by applying excessive chemical fertilizers, improve the soil structure, store water to preserve soil moisture, improve the soil permeability and water-bearing property and supplement K, Mg, Ca, Fe and trace elements, such as Mn, Cu, Zn and Si, in soil; and the active substances generated in the bacillus subtilis thalli growth process, such as subtilin, polymyxin, nystatin and gramicidin, have obvious inhibiting effects on pathogens or opportunistic pathogens causing endogenous infection, thus reducing the occurrence rates of crop diseases.
Owner:新疆天物生态环保股份有限公司
Medical humidification liquid having bacteriostasis function
InactiveCN102941034AGood hygroscopicityImprove thermal stabilityBiocideTransportation and packagingPhenolic content in teaEthylic acid
The invention discloses a medical humidification liquid having a bacteriostasis function and relates to the medical field. The medical humidification liquid having a bacteriostasis function comprises epsilon-polylysine and distilled water, wherein 0.01 to 0.5g of epsilon-polylysine is added into each 100ml of distilled water. The medical humidification liquid having a bacteriostasis function also comprises a bacteriostatic agent which is sodium chloride, citric acid, glycine, acetic acid, alcohol or tea polyphenol. The medical humidification liquid having a bacteriostasis function is a safe and efficient reagent having no toxic and side effects and has good effects in oxygen humidification and clinical care. The medical humidification liquid having a bacteriostasis function has a simple formula and a low price, can be preserved easily, can kill and inhibit pathogenic bacteria and conditioned pathogens in an oxygen humidification liquid, has low replacement frequency, has good effects of disinfection and humidification, provides a comfortable patient oxygen inhalation environment after humidification, and improves clinical care work efficiency.
Owner:曹青春
Application of stilbene compounds in inhibiting pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing system
InactiveCN106109448AInhibition of swarm movementInhibitionAntibacterial agentsHydroxy compound active ingredientsOxyresveratrolOpportunistic pathogen
The invention discloses an application of three stilbene compounds, namely resveratrol, piceatannol and oxyresveratrol, in inhibiting a pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing system. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the most common opportunistic pathogens which can cause serious acquired infection, and the quorum sensing system of the pseudomonas aeruginosa can regulate and control the generation of various virulence factors. In a sub-lethal concentration, the three stilbene compounds, namely the resveratrol, the piceatannol and the oxyresveratrol, can significantly inhibit the swarming of the pseudomonas aeruginosa and the generation of the virulence factor, namely pyocyanine, under the precondition of avoiding influence on the growth of the bacterium (the pseudomonas aeruginosa). The three stilbene compounds, namely the resveratrol, the piceatannol and the oxyresveratrol, can be prepared into pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing inhibitors so as to effectively inhibit quorum sensing and prevent bacterium infection; and the inhibitors have an important practical value in clinical bacteriostatic application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of a strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in preventing and relieving ulcerative colitis
ActiveCN112625964BEasily damagedIncrease richnessMilk preparationBacteriaInflammatory factorsLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention discloses the application of a strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in preventing and relieving ulcerative colitis, and belongs to the technical field of functional microorganisms. Lactobacillus rhamnosus can tolerate the human gastrointestinal environment, significantly reduce weight loss during ulcerative colitis, improve stool texture and blood in the stool, improve colonic mucosal damage, reduce MPO activity, and reduce the pro-inflammatory factor TNF-α in the colon , IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ content, up-regulate the transcription levels of colon tight junction-related proteins Claudin-3, ZO-1, ZO-2 and Occludin, antimicrobial peptides Reg3g, Reg3b and mucin MUC2, increase the transcription level of short chain The abundance of fatty acid-producing bacteria Coprococcus, Faecalibacterium and the content of short-chain fatty acids increased the abundance of beneficial bacteria Lactobacillus and decreased the abundance of opportunistic pathogen Acinetobacter, increasing the richness and diversity of intestinal flora.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Healthy soap for inhibiting germ reproduction and preventing germ transmission and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101602986AEfficient decontaminationStrong anti-bacterialSoap detergents with inorganic compounding agentsCooling soapMedicineStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a healthy soap for inhibiting germ reproduction and preventing germ transmission and a preparation method thereof. Germs exist everywhere, and people can contact with germs at any time in the daily life; although most germs have no harm on the health of human beings, germs can result in a bad effect on human beings on specified conditions, namely conditioned pathogen, and even make people ill. The invention is a block healthy soap prepared with the method that corresponding minor ingredients are added into soap base, pancreatic enzyme, KF-88 and essence. The invention has the efficacy of disinfecting, sterilizing, decontaminating, quickly removing epidermis pathogenic bacterium (hepatitis virus, staphylococcus aureus and the like) and various kinds of reproduction, shack and infectious bacteria, effectively inhibiting various germs from reproducing and preventing germs transmission.
Owner:周菊彦
Method to mitigate morbidity and mortality in virally induced forms of ACE2 receptor pathology progressing to SARS or ARDS.
InactiveUS20210315910A1Reduce infectionMaximize resultTetracycline active ingredientsMucoid impactionBronchial epithelium
ACE receptors are affected in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome related coronaviruses. ACE genes are directly related to the morbidity and mortality of those with cystic fibrosis. The thick, sticky mucus in the respiratory, and digestive systems, is seen in the inherited disease cystic fibrosis. Viral induced sticky mucus in the respiratory and digestive systems can also be appreciated as a response to viral pathogens where the cycle of mucus production in vivo induces the recruitment of more mucus production to the extent that cellular damage occurs within the lower respiratory track requiring intubation as a life saving measure. In the most severe cases mechanical intubation fails due to the fact that no control over the recruitment of mucus production was achieved at the onset. SARS pathology shows inflammatory exudation in the alveoli and interstitial tissue, with hyperplasia of fibrous tissue and fibrosis. Inherited cystic fibrosis pathology shows atelectasis, mucoid impaction, acute and chronic inflammation, bronchiectasis, cyst formation, and fibrosis widespread. A virally induced disorder in relations to ACE2 receptors can be treated successfully at the early onset with inherited cystic fibrosis disease mimicking techniques with the efforts of minimizing the activity and utilization of the ACE2 receptor. Cystic fibrosis lung infections, and opportunistic pathogens contribute to chronic airway inflammation that is characterized by neutrophil / macrophage infiltration, cytokine release and ceramide accumulation. In terms of virally induced forms off ACE2 receptor pathologies, as it related to coronavirus such as Covid 19, presumably ceramide precursors which aid in intracellular transport of the virus into the cell via inflammation and remodeling is present in alveolar tissues of the lung in patients with cystic fibrosis while the same pathology occurs in patients with virally induced forms of ACE2 pathology which to often progresses to SARS or ARDS.
Owner:STAFFORD VIVI ROBYN
Extraction method of dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs as well as application thereof in adjusting intestinal flora
InactiveCN110025015ASimple processHigh yieldFood dryingFood ingredient functionsIntestinal fermentationFeces
The invention provides an extraction method of dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs. The method can be used to produce high purity dietary fiber in large quantity from the sweet potato dregs, a by-product of sweet potato processing, the process is simple, and productivity is high. The invention also provides an application of the dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs in adjusting intestinal flora, and a simulation experiment of intestinal fermentation in vitro shows that the dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs can improve the colonization ability of intestinal beneficial bacteria and reducethe colonization ability of opportunistic pathogens, and that the effect of prebiotics on the dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs is significant; an animal level experiment shows that, after beingfed the dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs for 28 D, abundance of intestinal flora at phylum, genus and OTU classification level in rats has significant changes, the water content of colon feces rises, the pH of contents drops, the short chain fatty acid content of colon feces rises. Moreover, both villus height and recess depth of small intestine change, the consequence of the experiments showthat the dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs not only improves the health level of intestinal flora, but also enhances the absorption and digestion function of small intestine.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of spray reagent for preventing avian influenza of livestock and poultry
InactiveCN108079057AHigh expressionEasy to recycleAerosol deliveryAntiviralsLiver and kidneyMetabolite
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal drugs and particularly relates to a preparation method of a spray reagent for preventing avian influenza of livestock and poultry. According to the spray reagent disclosed by the invention, a Chinese herbal probiotic preparation can protect respiratory mucosa and can be also used as a disinfectant for improving the environment of the livestockand poultry; the aim of disinfecting is achieved by using an antagonistic action of probiotics and metabolite thereof to pathogenic bacteria and conditioned pathogen. Chinese herbal medicines and theprobiotics have a synergistic effect, and further the capability of diffusion propagation of the avian influenza is weakened; in addition, the avian influenza is prevented and treated by a spray mode, so that the damage to liver and kidney caused by long-term administration is avoided.
Owner:袁春华
Biological agent for preventing strawberry powdery mildew and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110477023AEasy to solveEasy to manageBiocidePlant growth regulatorsHigh resistanceInsect pest
The invention relates to a biological agent for preventing and treating strawberry powdery mildew and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of disease prevention and treatment. The biological agent is mainly composed of Harpin protein, bacillus subtilis fermentation liquid and an adsorption carrier component, and not only can prevent and protect strawberry powdery mildew, but alsocan cure and protect strawberry powdery mildew. The Harpin protein can enable plants to generate disease-resistant, insect-pest-resistant and stress-resistant effects, and active substances generatedin the growth process of the bacillus subtilis have an obvious inhibiting effect on pathogenic bacteria or conditioned pathogenic bacteria of endogenous infection, so that prevention and treatment ofpowdery mildew of strawberries are facilitated. In addition, the biological agent can provide nutrition for crops, automatically adjust vegetative growth and reproductive growth of the crops and improve the yield of the crops. The Harpin protein in the biological agent is high-resistance immune protein, can provide nutrition for crops, can promote plant growth and is beneficial to increase of crop yield.
Owner:嘉特(烟台)生态农业科技研发有限公司
Composition for regulating immunological activity in intestine and use thereof
ActiveUS20160151371A1Avoid symptomsEfficient use ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideIntestinal structureBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
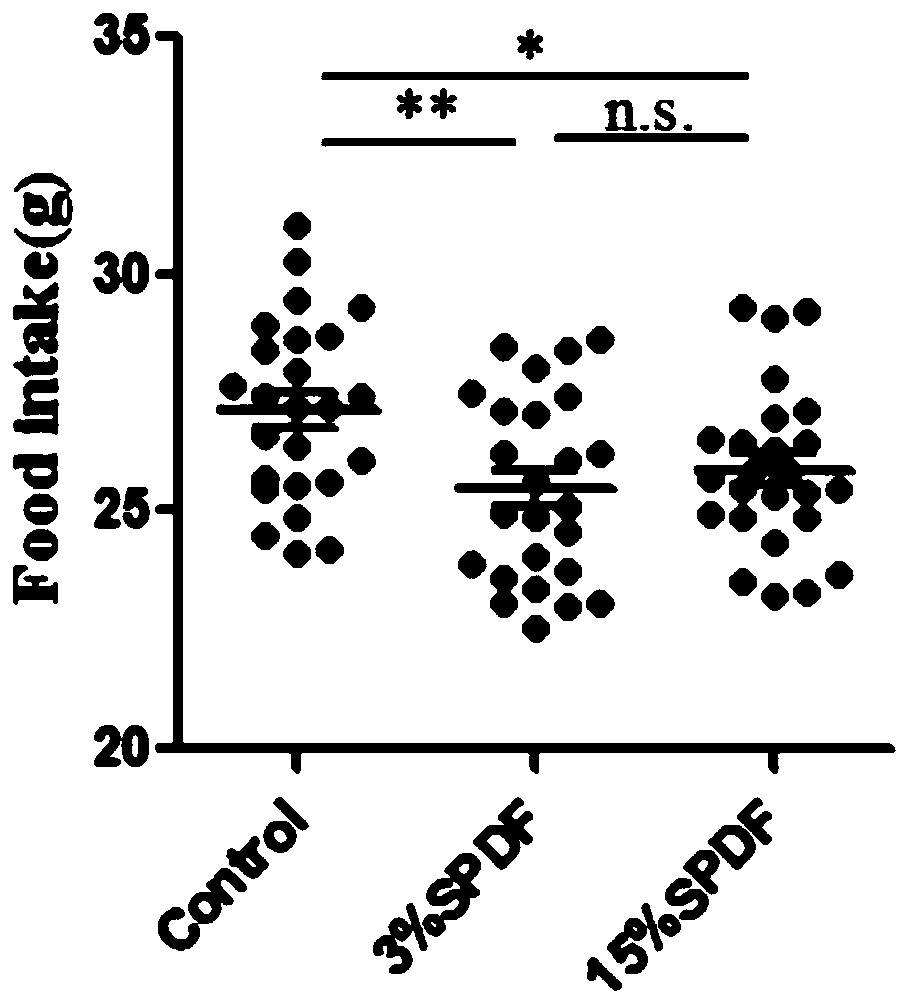
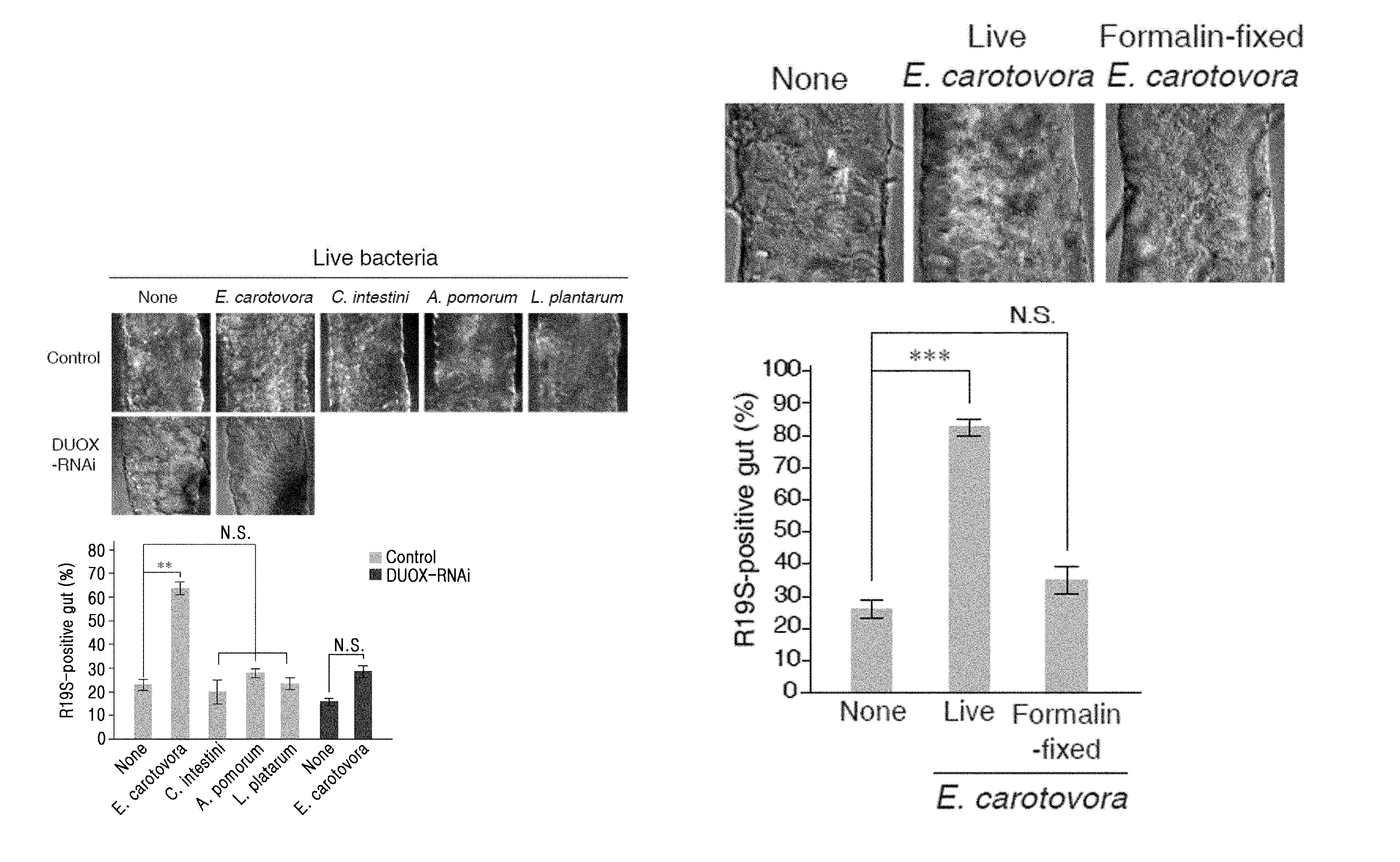
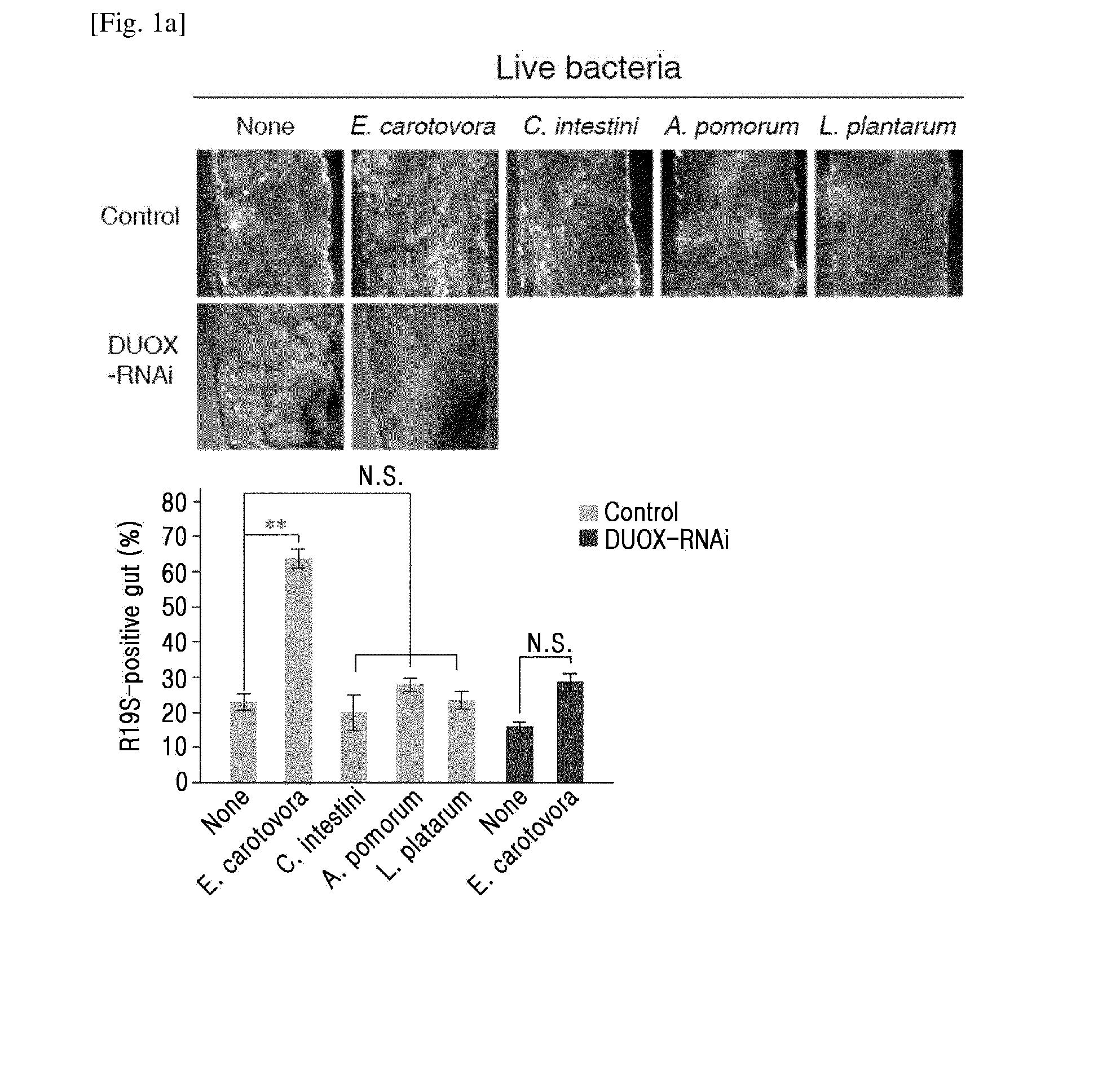
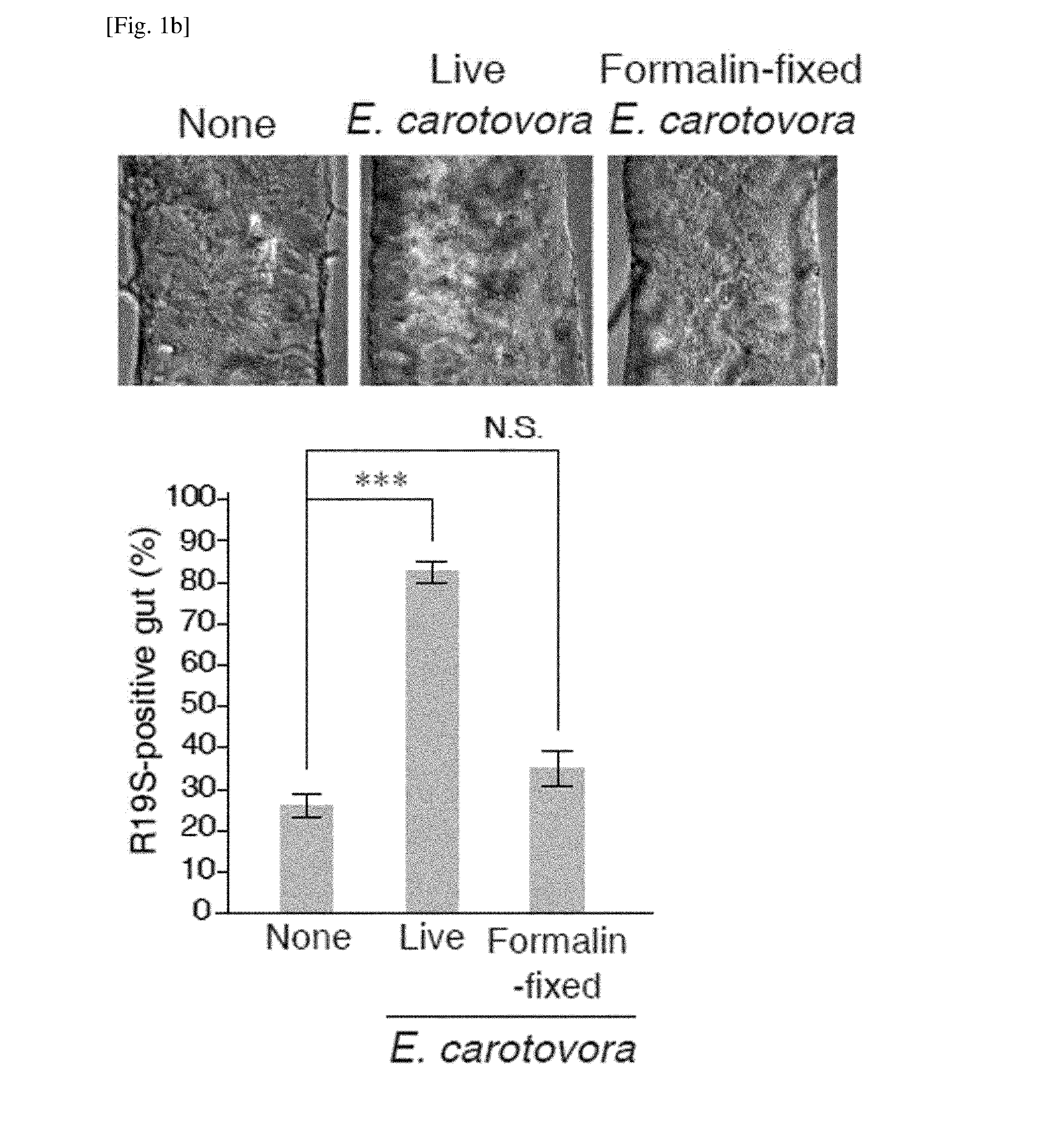
The present invention relates to an antimicrobial composition for uracil non-secretory (URA−) bacteria, comprising uracil, uracil precursors, uracil analogs, or uracil-secreting opportunistic pathogens as an active ingredient; and a composition for preventing cell damage caused by uracil-secretory (URA+) bacteria, comprising ROS scavengers as an active ingredient. The present invention also relates to food or feed for antimicrobial activity and preventing cell damage, comprising said composition; a method for controlling dual oxidase (DUOX) activation, the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), or the level thereof; a method for producing cells, wherein DUOX activation, the generation of ROS, or the level thereof are controlled; and a method for providing information on gut pathogenicity in isolated bacteria. The composition of the present invention has effects for preventing symptoms caused by bacteria according to a mechanism which has been unknown in the art. Further, the present invention can be efficiently utilized for establishing prevention and treatment strategies for symptoms caused by bacteria later, as therapeutic strategies can be readily established by bacterial classification based on criteria that can be easily confirmed.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Composition containing schizophyllan and bifida yeast and application thereof in preparation of skin care products
InactiveCN111494239APromote Microecological BalanceGood for repairing micro-damagesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a composition containing schizophyllan and bifida yeast. The composition containing schizophyllan and bifida yeast is composed of the following raw materials by weight: 4-10 parts of schizophyllan, 2-8 parts of bifida ferment lysate, 0.4-1 part of an aloe vera extract, 1-10 parts of a hamamelis virginiana extract, 0.2-0.5 part of 1, 2-hexanediol, 0.2-0.5 part of p-hydroxyacetophenone and 65-85 parts of a dispersing agent. The composition disclosed by the invention has a function of regulating skin micro-ecological balance, and has good effects of conditioning various skin symptom diseases and repairing micro-damaged skin cells; the composition provided by the invention can effectively promote proliferation of skin resident probiotics, and has an inhibition effect onskin resident harmful bacteria and conditioned pathogens, so that probiotics are in a dominant position, and skin micro-ecological balance is promoted.
Owner:广州市拓瑞科技有限公司
A strain of Lactobacillus crispatus for preventing and treating women's urogenital tract infection and its application
The invention discloses a strain of Lactobacillus crispatus Lcr-MH175 used for preventing and treating urogenital tract infection in women, and its preservation number is CGMCC No.15938. The Lactobacillus crispatus Lcr-MH175 provided by the invention has strong antibacterial ability, can effectively inhibit the growth of foreign pathogenic bacteria and other conditional pathogenic bacteria; at the same time, it has strong adhesion to Hela cells, ensuring that the bacterial strain is Colonization of the vaginal epithelium. The Lactobacillus crispatus Lcr‑MH175 provided by the present invention has a certain application prospect in the prevention and treatment of urogenital tract infection.
Owner:哈尔滨美华生物技术股份有限公司
Bacillus subtilis, composite preparation, and method for preparing the composite preparation
InactiveCN1796542AIncreased sensitivityNo side effectsBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsEscherichia coliDisease
This invention describes a bacillus subtilis and the process for preparing its compound pharmaceutics. The bacillus subtilis is conserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms, the name is: Bacillus subtilis LY-35 and the conservation number is: CGMCC No. 1222. The pharmaceutics is a compound of the bacteriophages of such pathogens as bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus, Streptocoaus, colibacillus, proteus, pseudomonas, salmonella, shigella, pasteurella and klebsiella. The pharmaceutics can prevent and treat the diseases caused by pathogens, and can be a non-polluted, high therapeutic effectiveness and safe substitute for antibiotics.
Owner:烟台绿云生物工程研究院有限公司
Health evaluation method taking intestinal flora characteristics as core
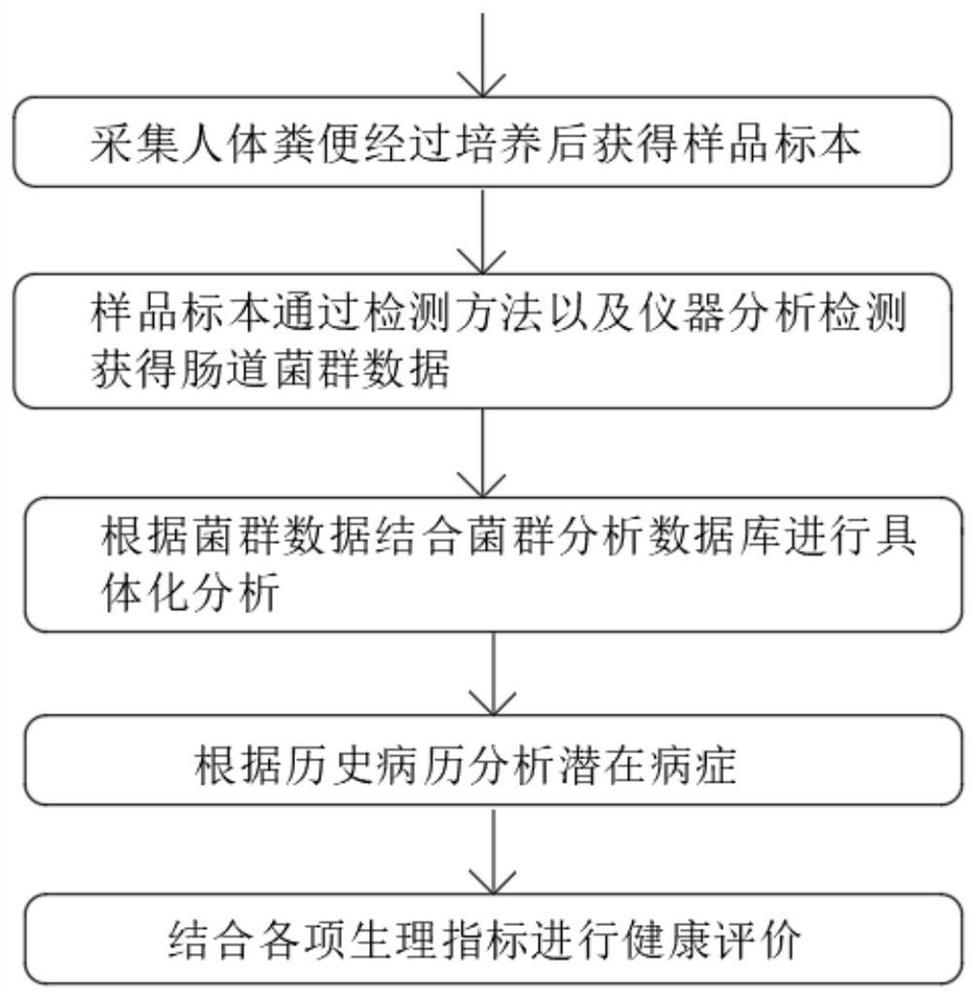
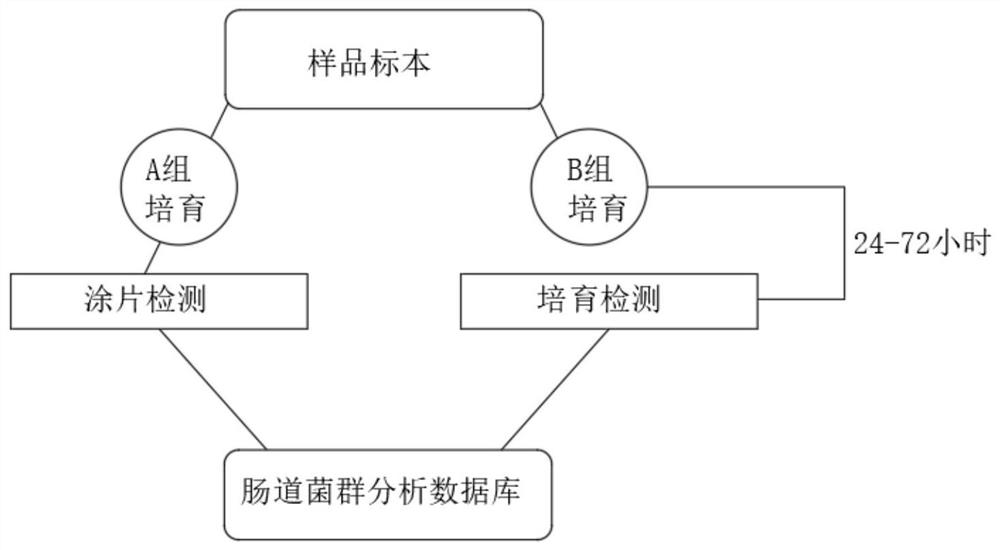
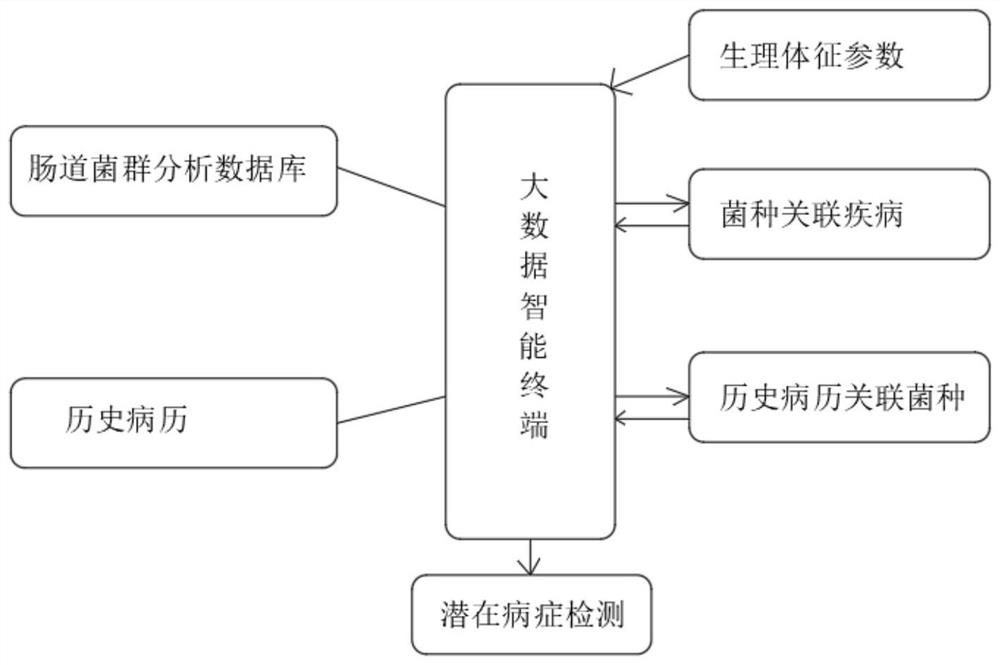
PendingCN113130074AHigh simulationHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical recordDisease
The invention discloses a health evaluation method taking intestinal flora characteristics as a core. The health evaluation method comprises the following steps: collecting a human excrement sample, and culturing to obtain a sample specimen; analyzing and detecting the sample by a detection method and an instrument to obtain intestinal flora data; performing specific analysis according to the flora data in combination with a flora analysis database; analyzing potential diseases according to historical medical records; and carrying out the health evaluation in combination with various physiological indexes. According to the health evaluation method, data obtained by a smear detection method and a culture detection method are obtained, wherein the data comprises types and quantity of microorganisms, and further comprises proportion data of beneficial bacteria, pathogenic bacteria and conditioned pathogenic bacteria; the data is inputted into a database, the data is matched with corresponding diseases, and then historical diseases and physiological indexes are inputted; the disease most likely to be obtained is analyzed by using big data, and inspection is emphasized, so potential diseases are checked by adopting a mode of combining intestinal flora inspection and computer big data analysis.
Owner:厦门惠达医疗科技有限公司
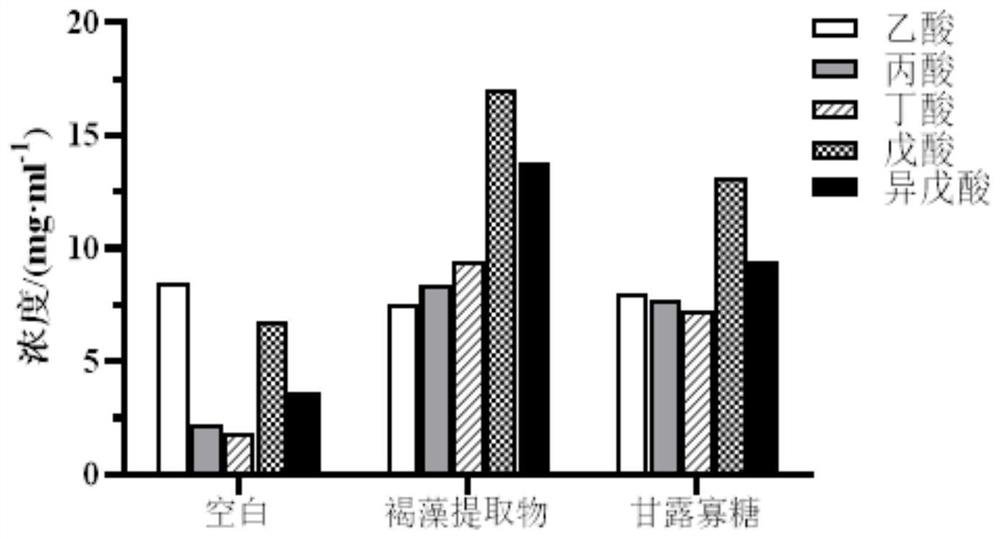
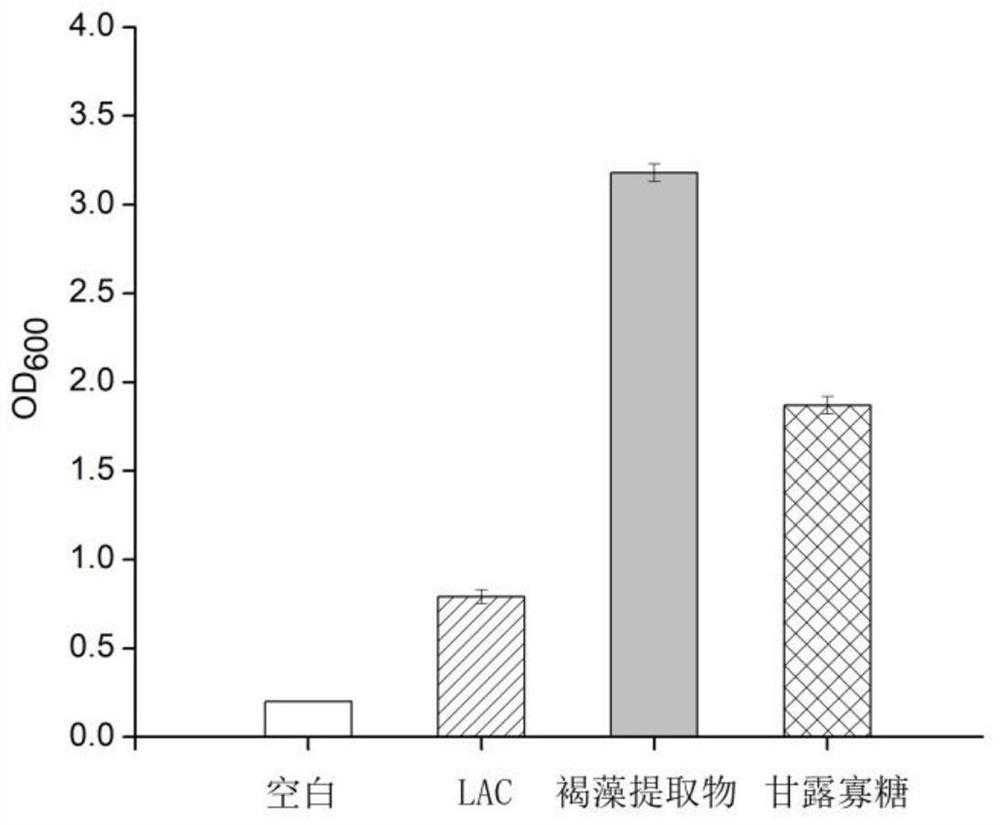
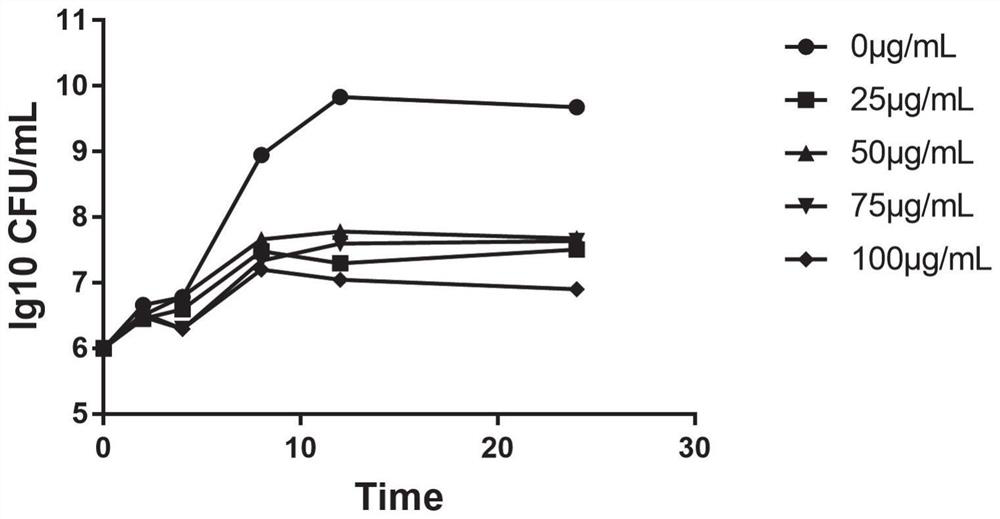
Composition based on brown algae extract and lactobacillus reuteri and application of composition
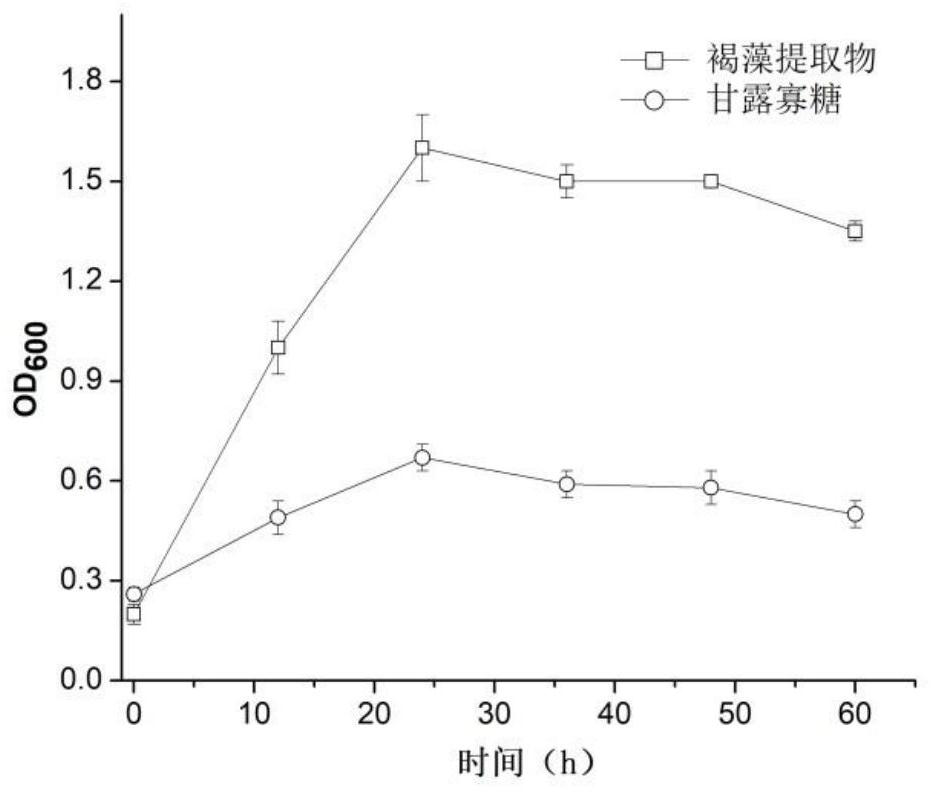
ActiveCN113209141APromote growthImprove the ability to produce short-chain fatty acidsMetabolism disorderDigestive systemBiotechnologyFasting glucose
The invention discloses a composition based on brown algae extract and lactobacillus reuteri and application of the composition. The composition disclosed by the invention is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 30 to 97 parts of brown algae extract and 3 to 70 parts of lactobacillus reuteri. The combination of the brown algae extract and the lactobacillus reuteri can promote field planting of the lactobacillus reuteri in intestinal tracts, and the field planting rate is remarkably increased. The combination of the brown algae extract and the lactobacillus reuteri can significantly reduce the fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin concentration of type 2 diabetes model mice, improve the insulin secretion amount, significantly improve the abundance of beneficial bacteria such as bifidobacterium and lactobacillus in intestines, reduce the abundance of conditioned pathogenic bacteria such as enterococcus and proteobacteria. Good application prospects are realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of desloratadine in the preparation of anti-multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii preparations
ActiveCN111920810BEnhanced inhibitory effectRich in active substancesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial drugLoratadine
The invention provides the application of desloratadine in preparing anti-multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii preparations. Acinetobacter baumannii, as an opportunistic pathogen with strong vitality, is a common pathogen of nosocomial infection. Because Acinetobacter baumannii is inherently resistant to common antibiotics, it is prone to drug resistance. The purpose of the present invention is to provide promising active substances for the development of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii therapeutic drugs, and according to the research results of the present invention, desloratadine has a good inhibitory effect on multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii , is expected to be used as an active substance in the development of related antibacterial drugs.
Owner:MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG PROVINCE SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com