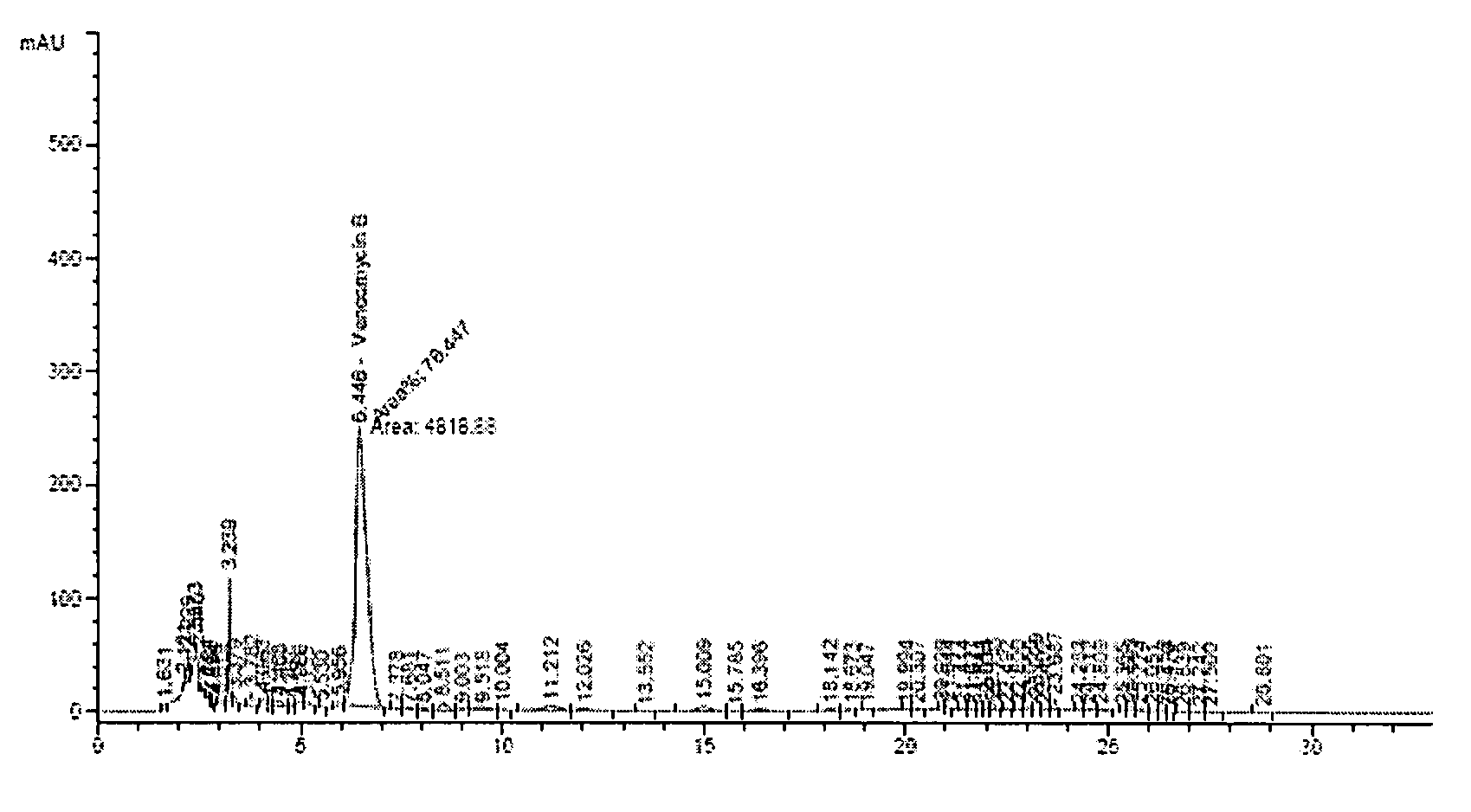
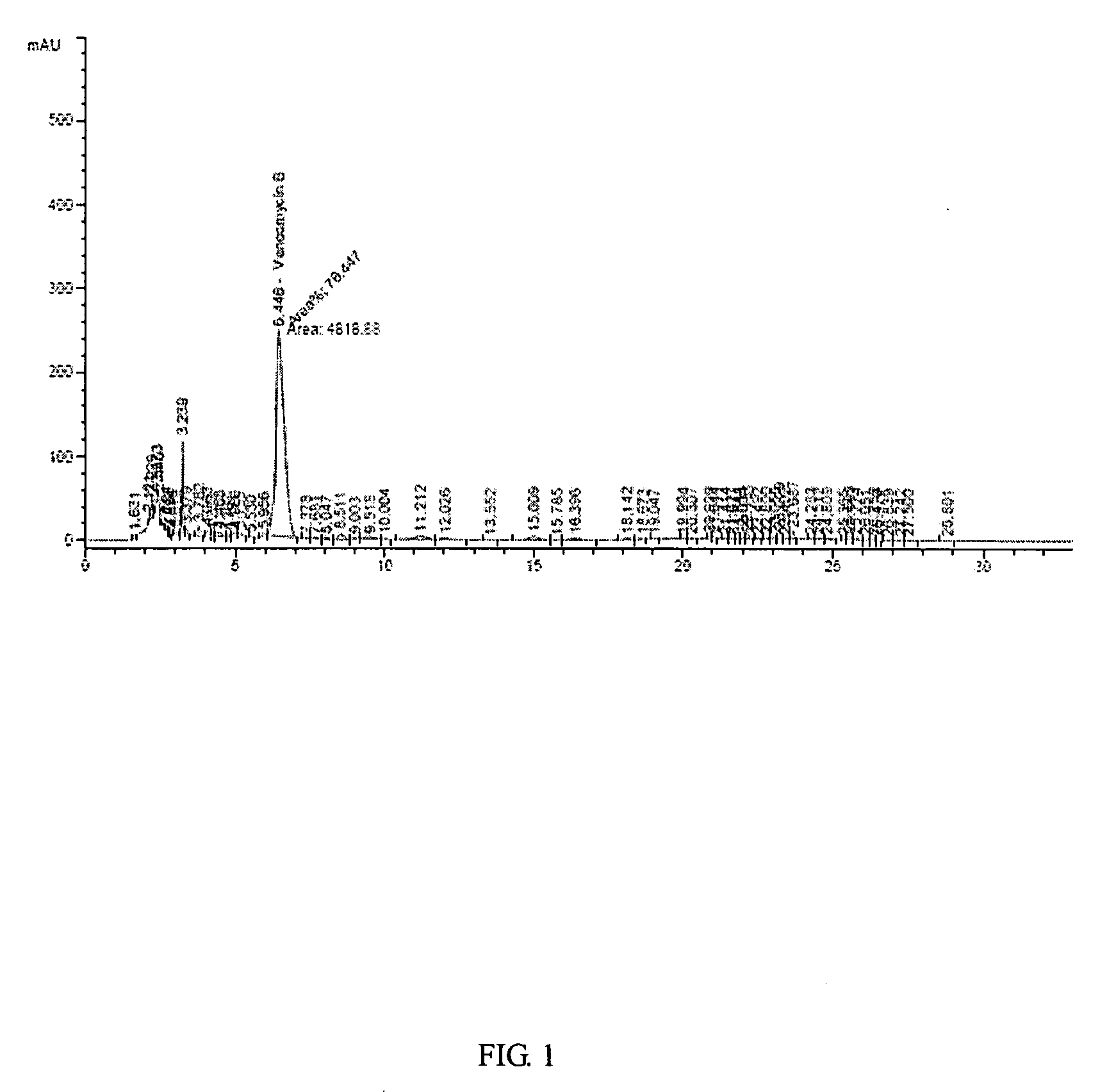
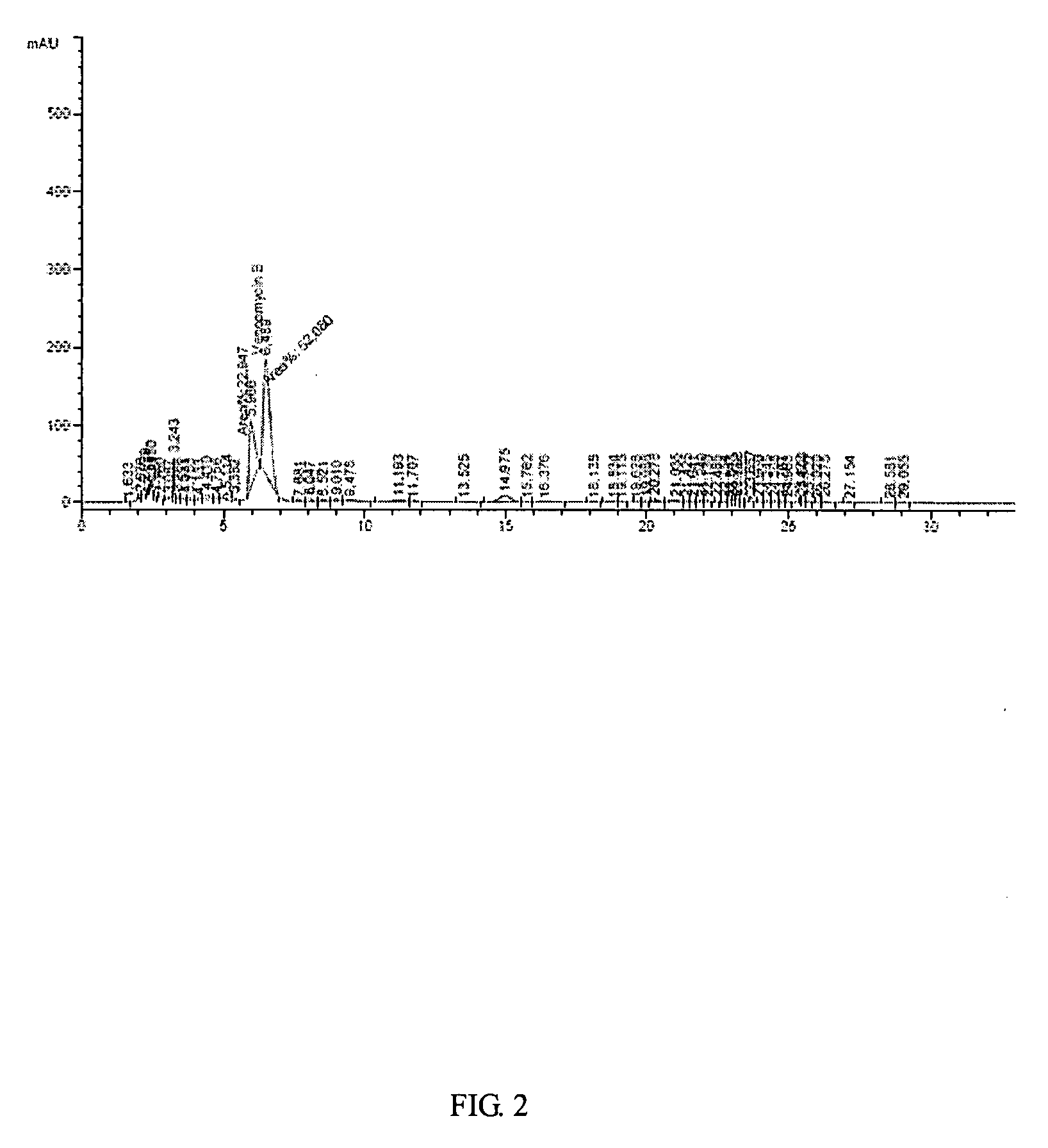
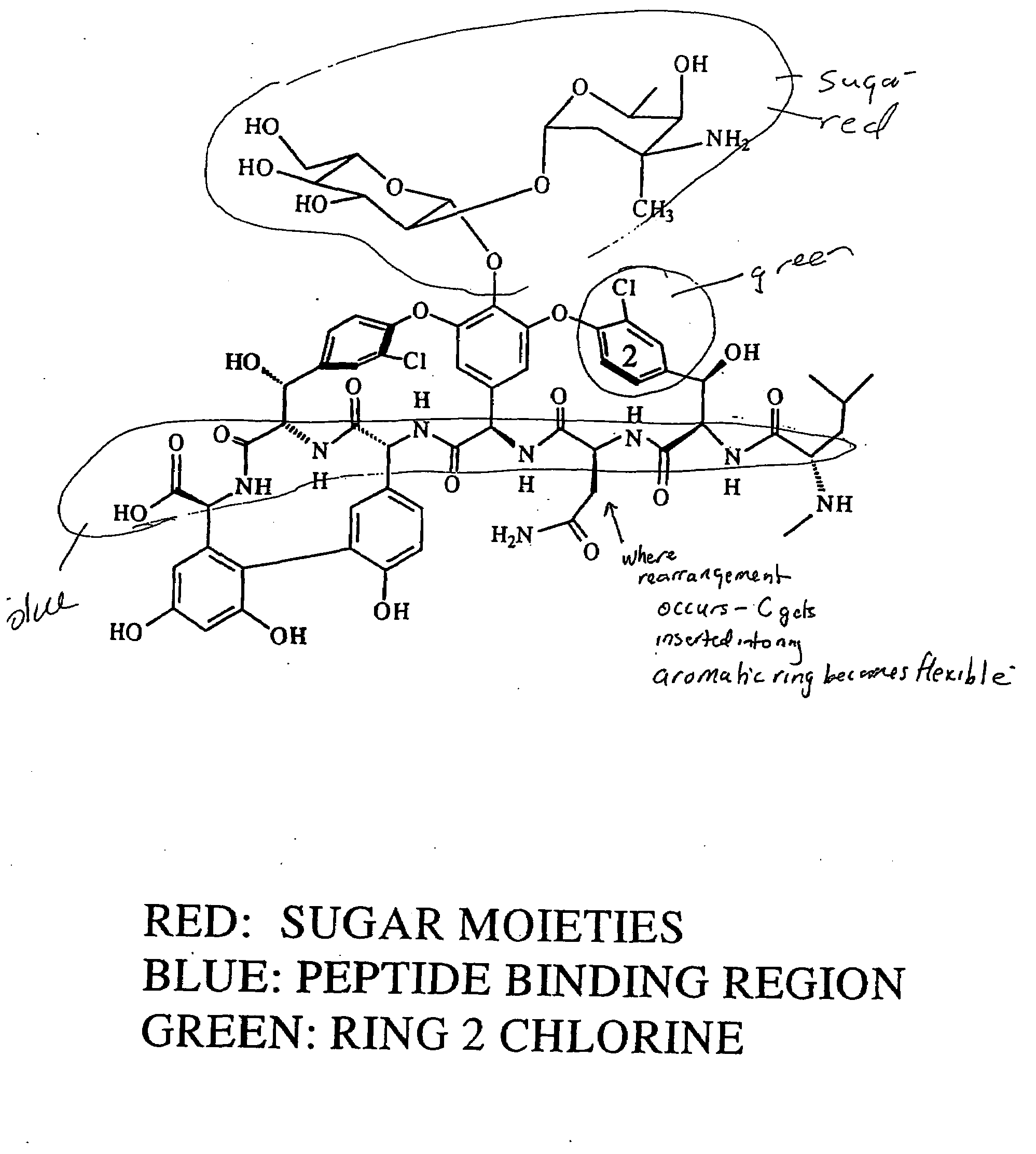
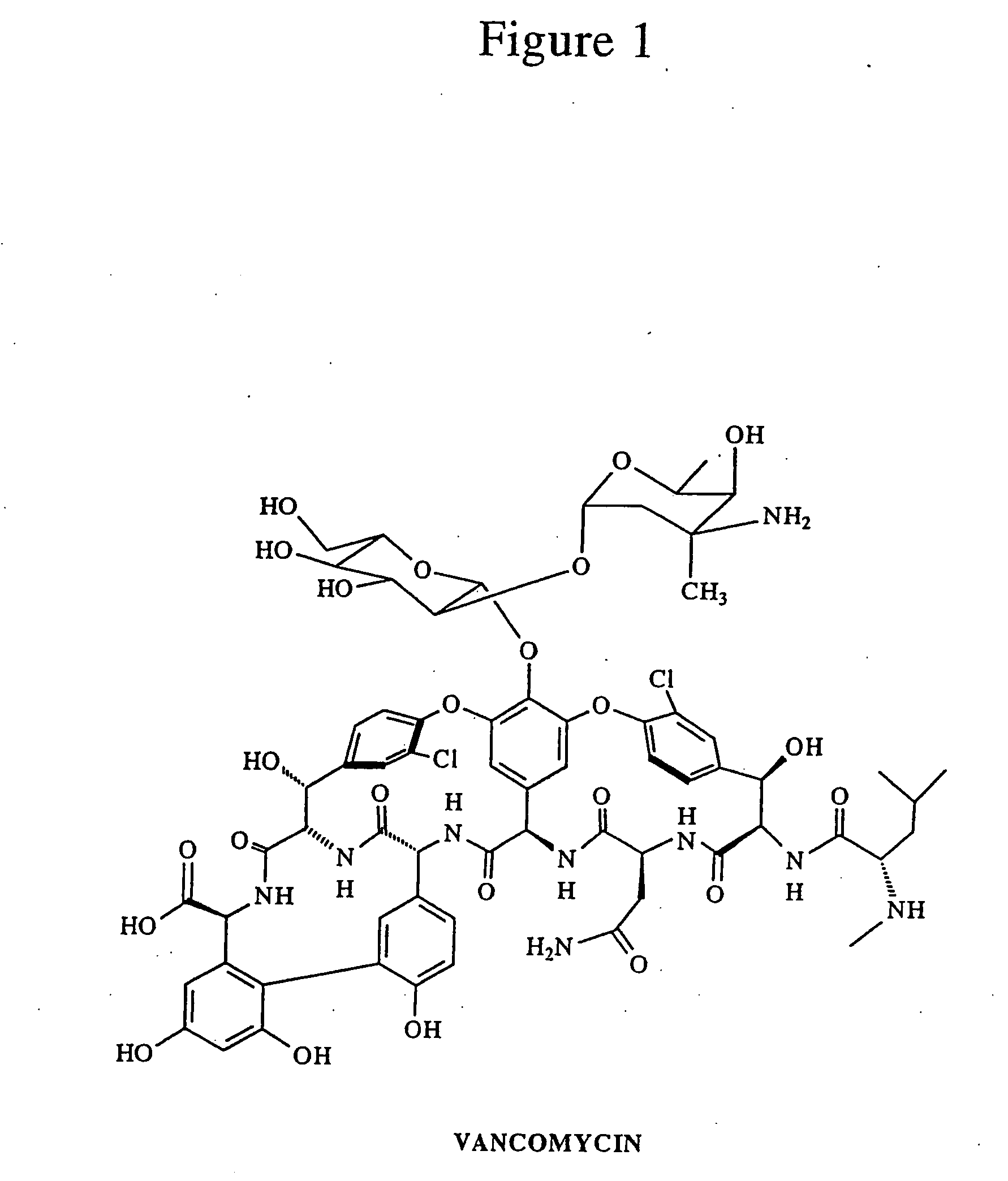
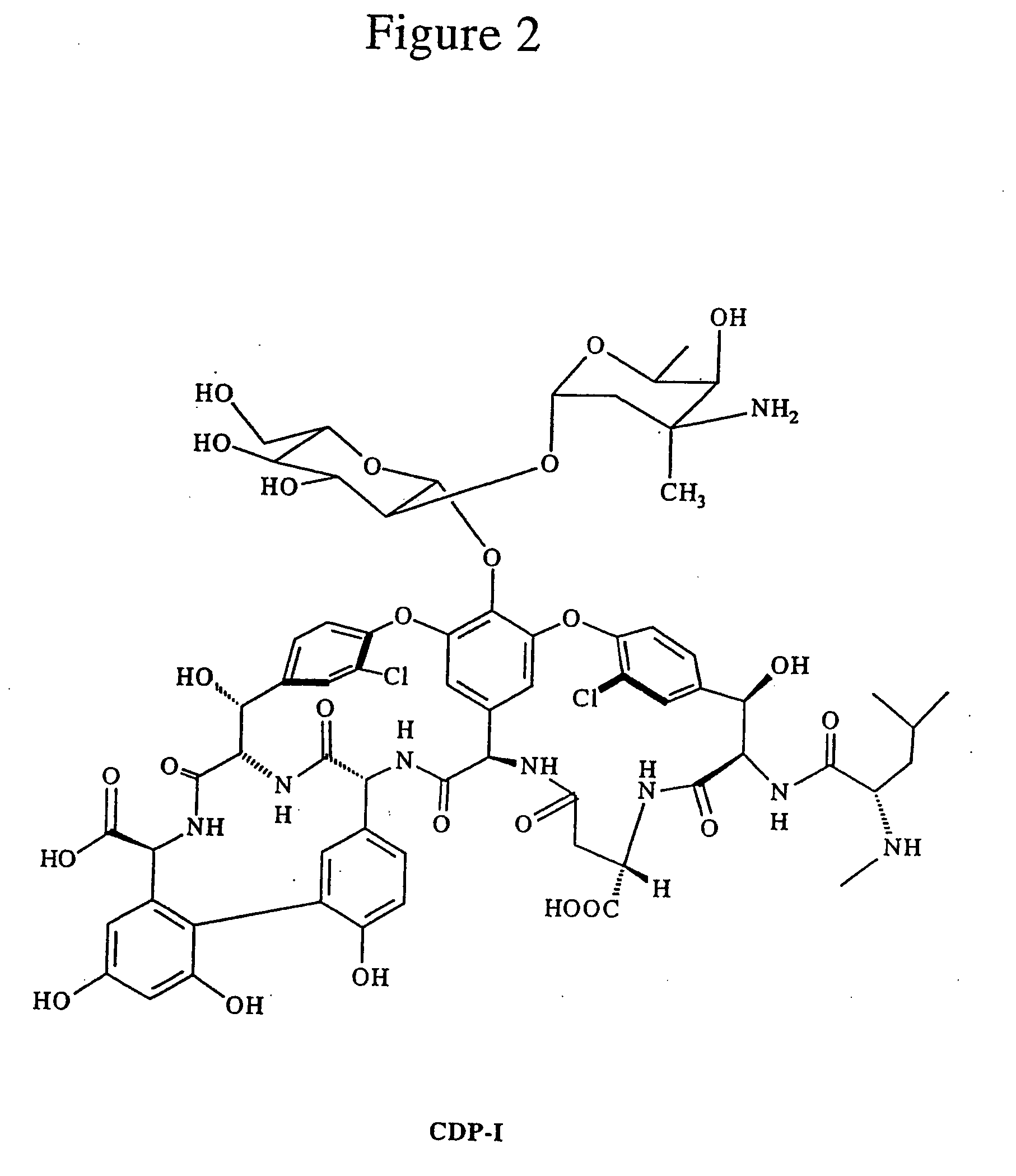
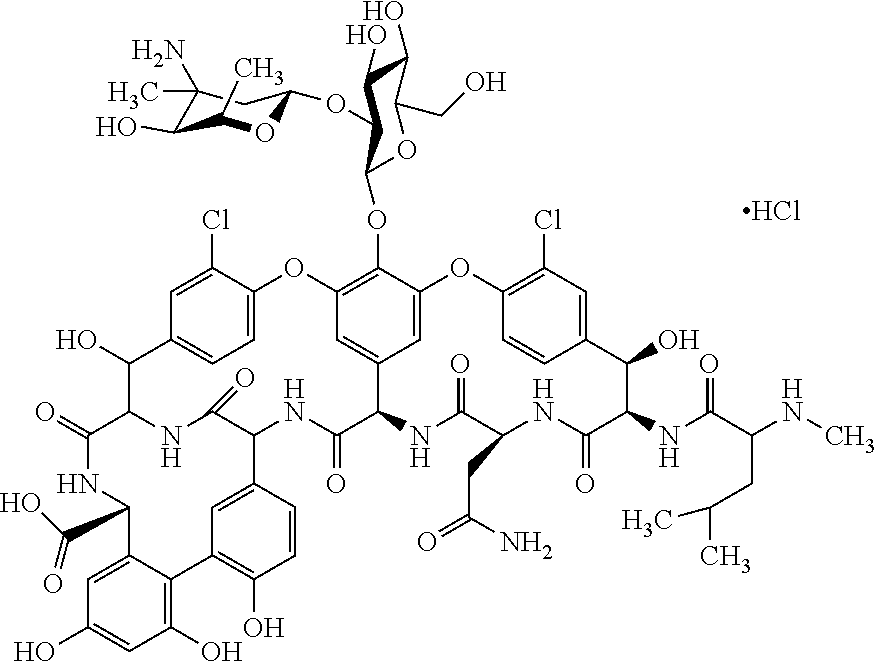
Patents
Literature
131 results about "Vancomycinum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods for characterizing and restoring gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota
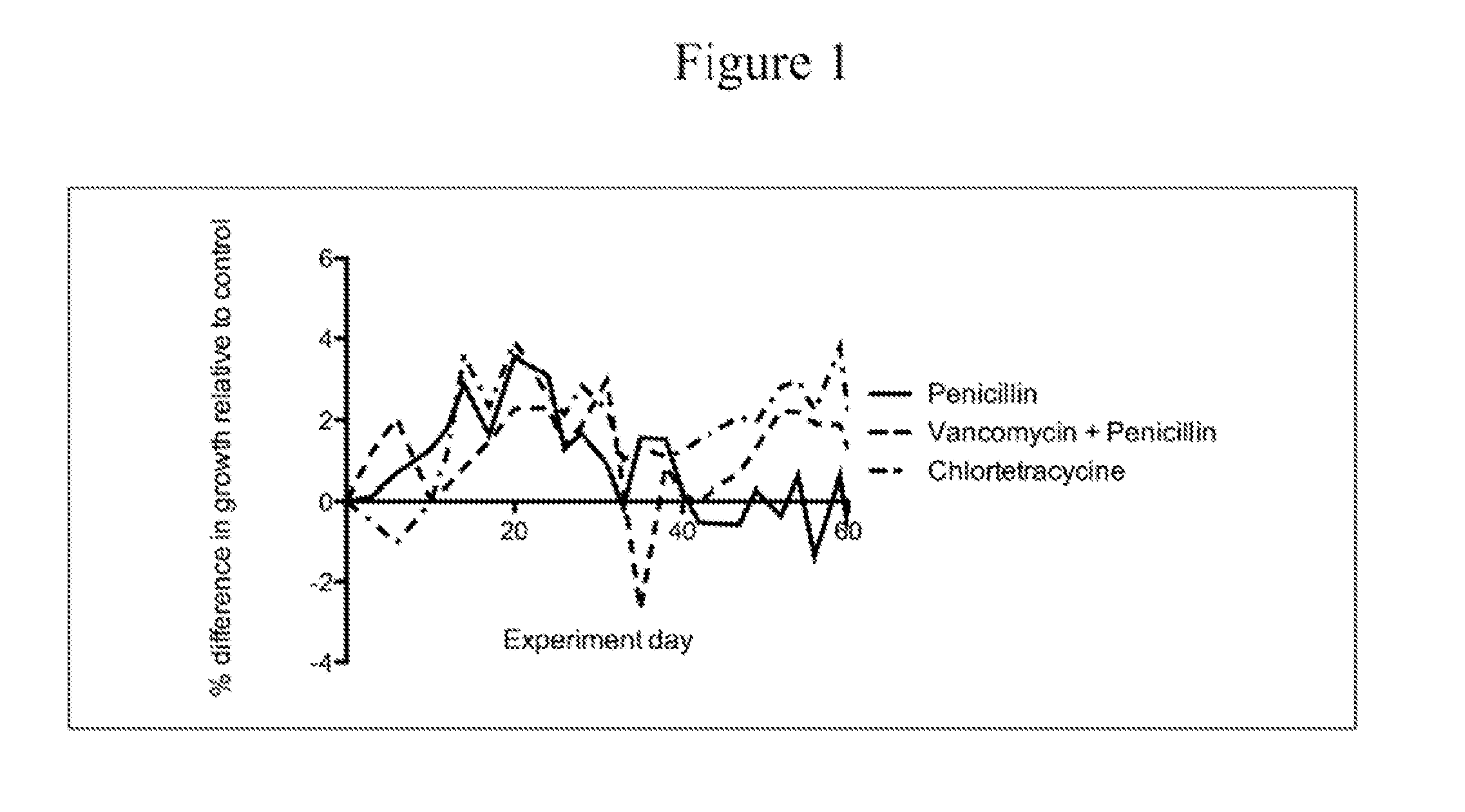
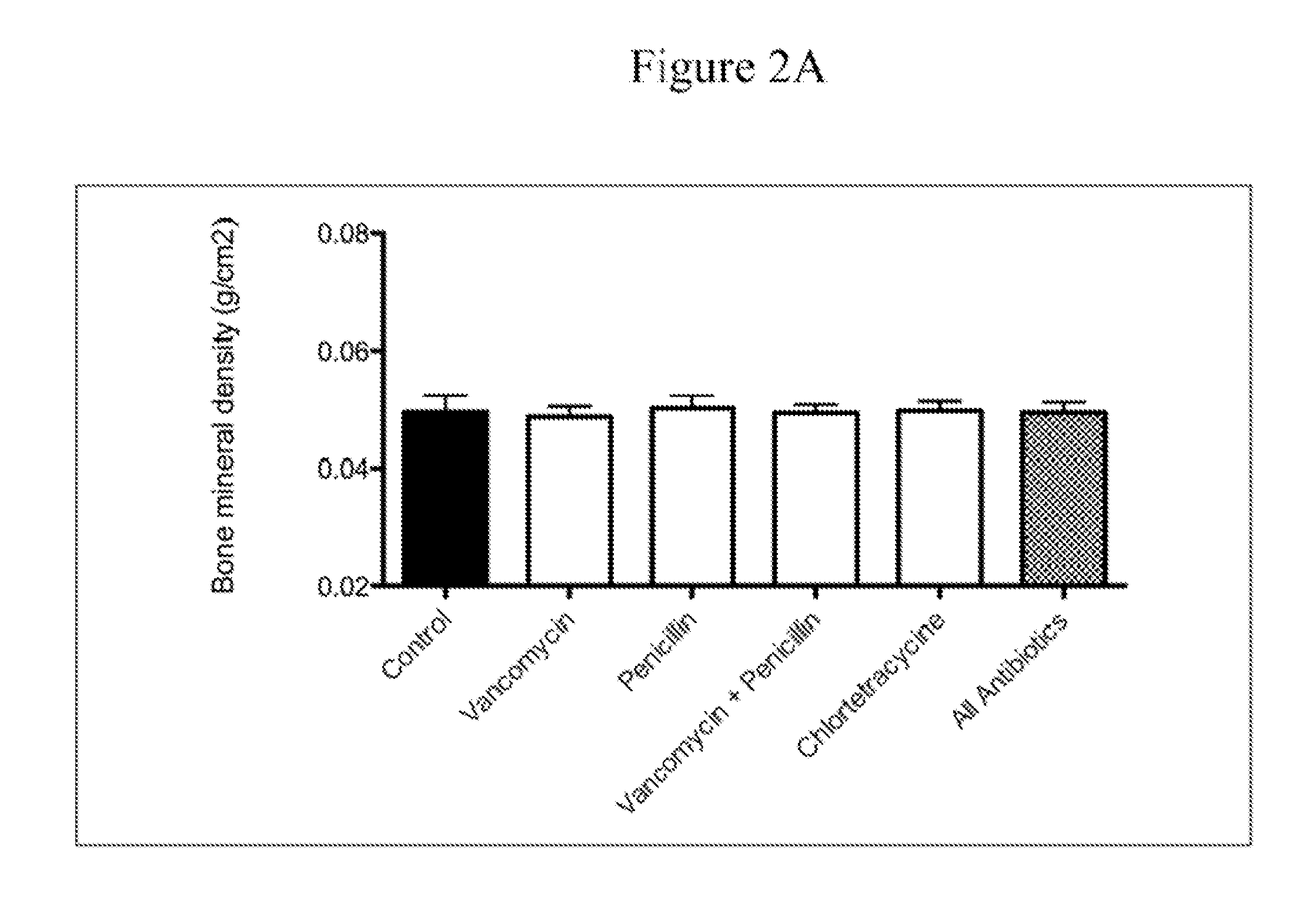
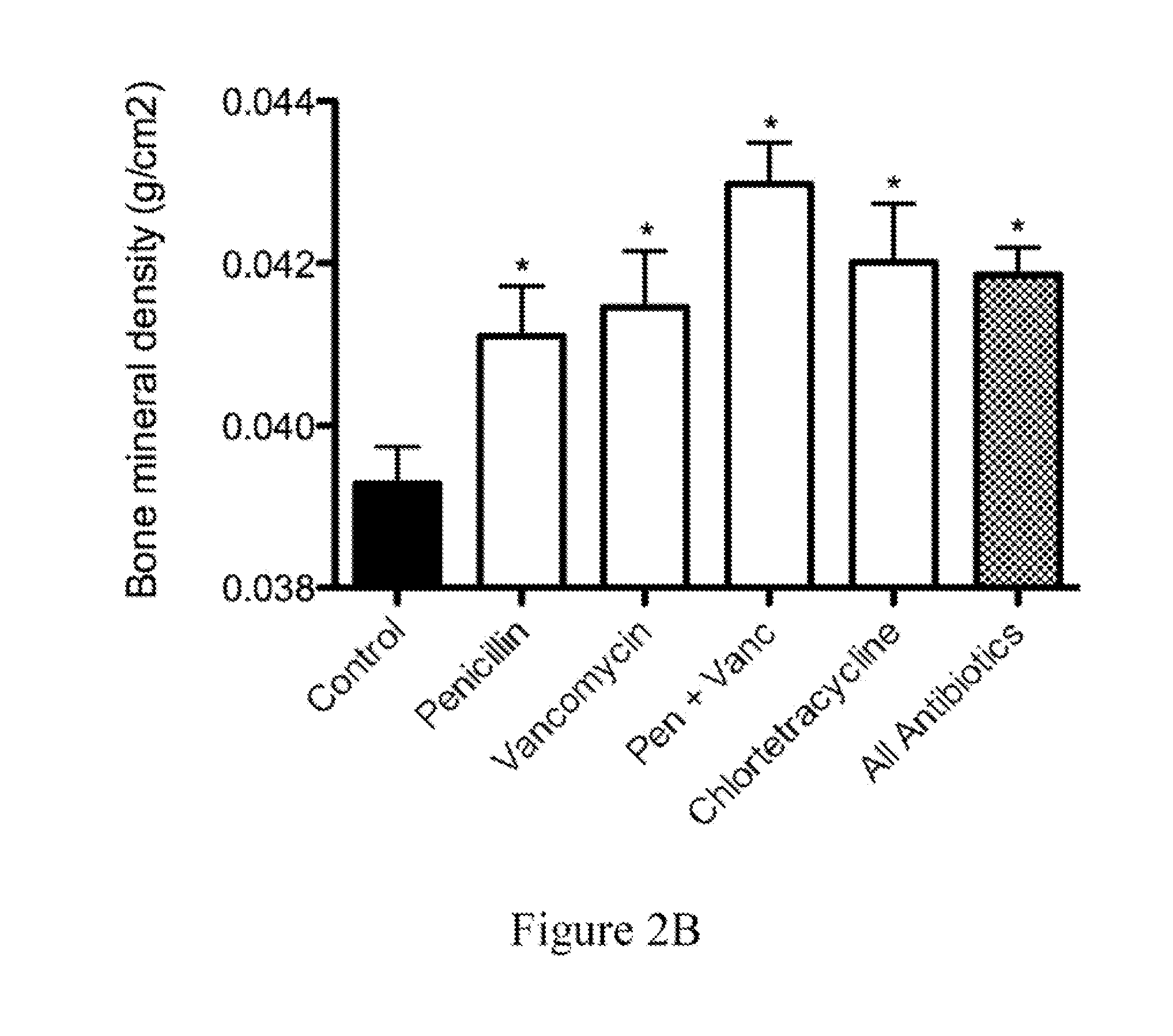
ActiveUS20100074872A1Growth inhibitionFacilitate calorie uptakeBiocideMetabolism disorderBacteroidesDisease
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated with antibiotic treatment and various disease conditions (such as asthma, allergy, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), eosinophilic esophagitis, gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinomas (GEJAC), infections due to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, etc.) and related diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of live bacterial inoculants that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
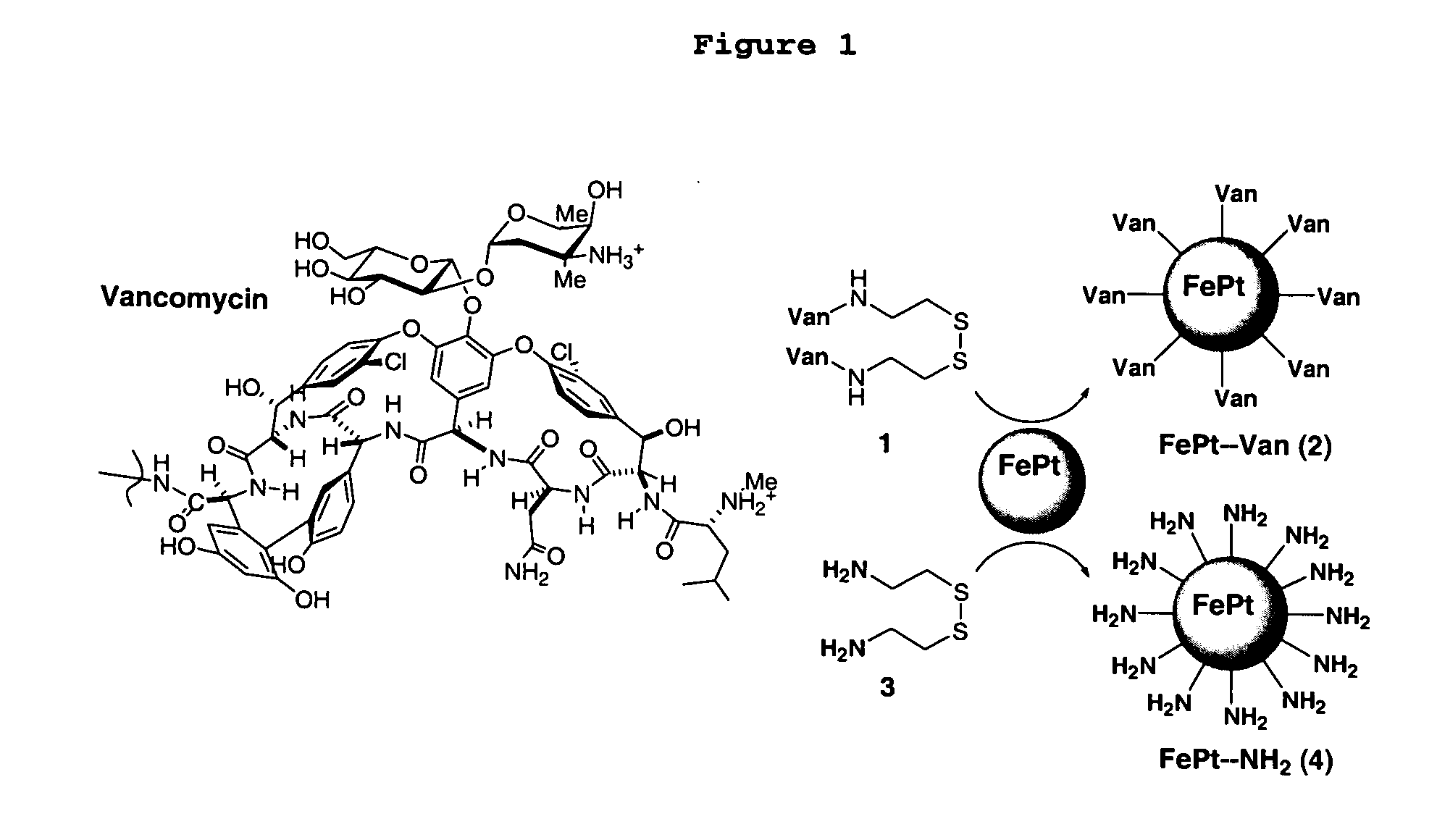
Biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for pathogen detection
InactiveUS20060292555A1High sensitivityEasy to reportNanotechMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetite NanoparticlesBiology
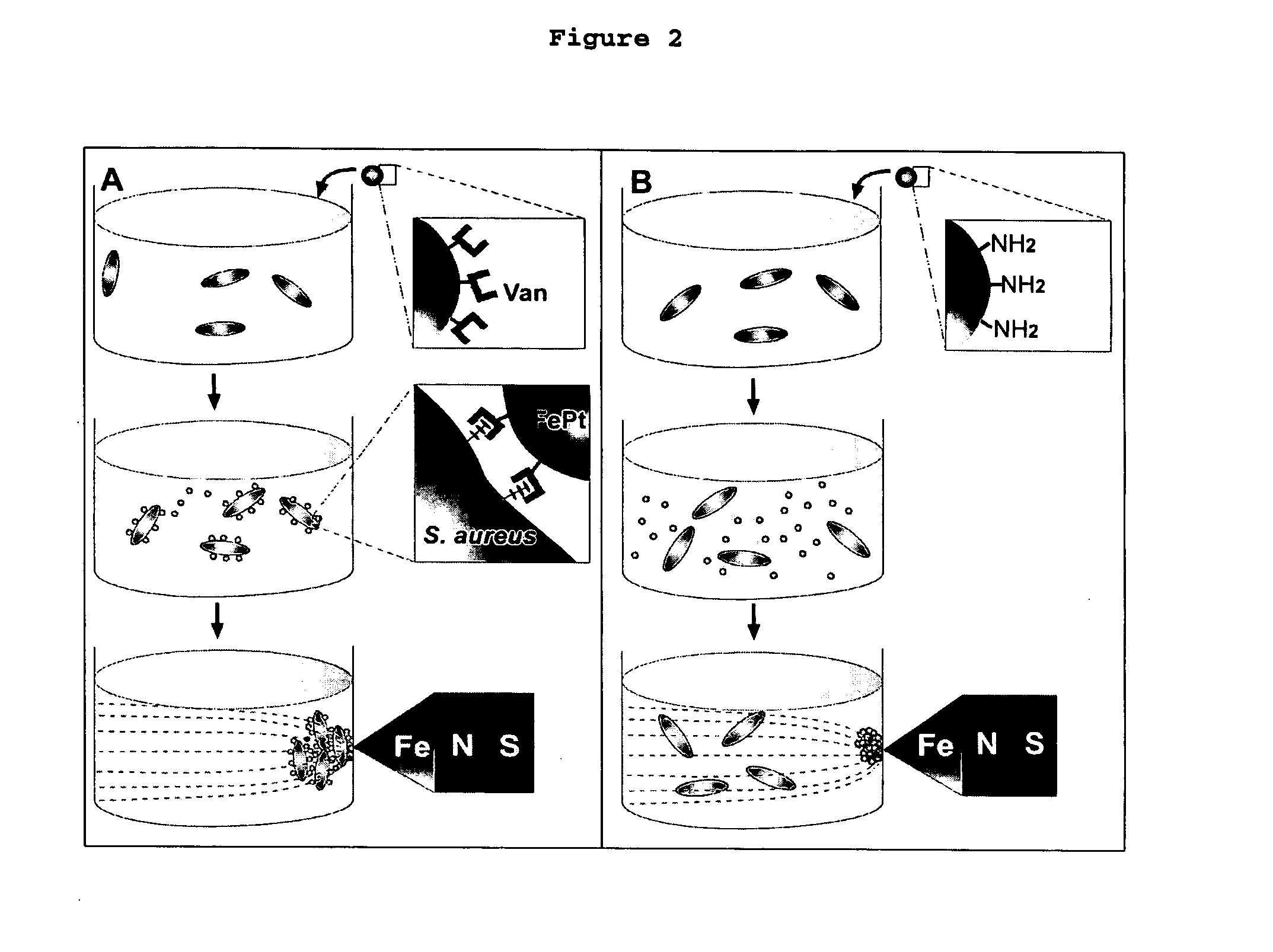
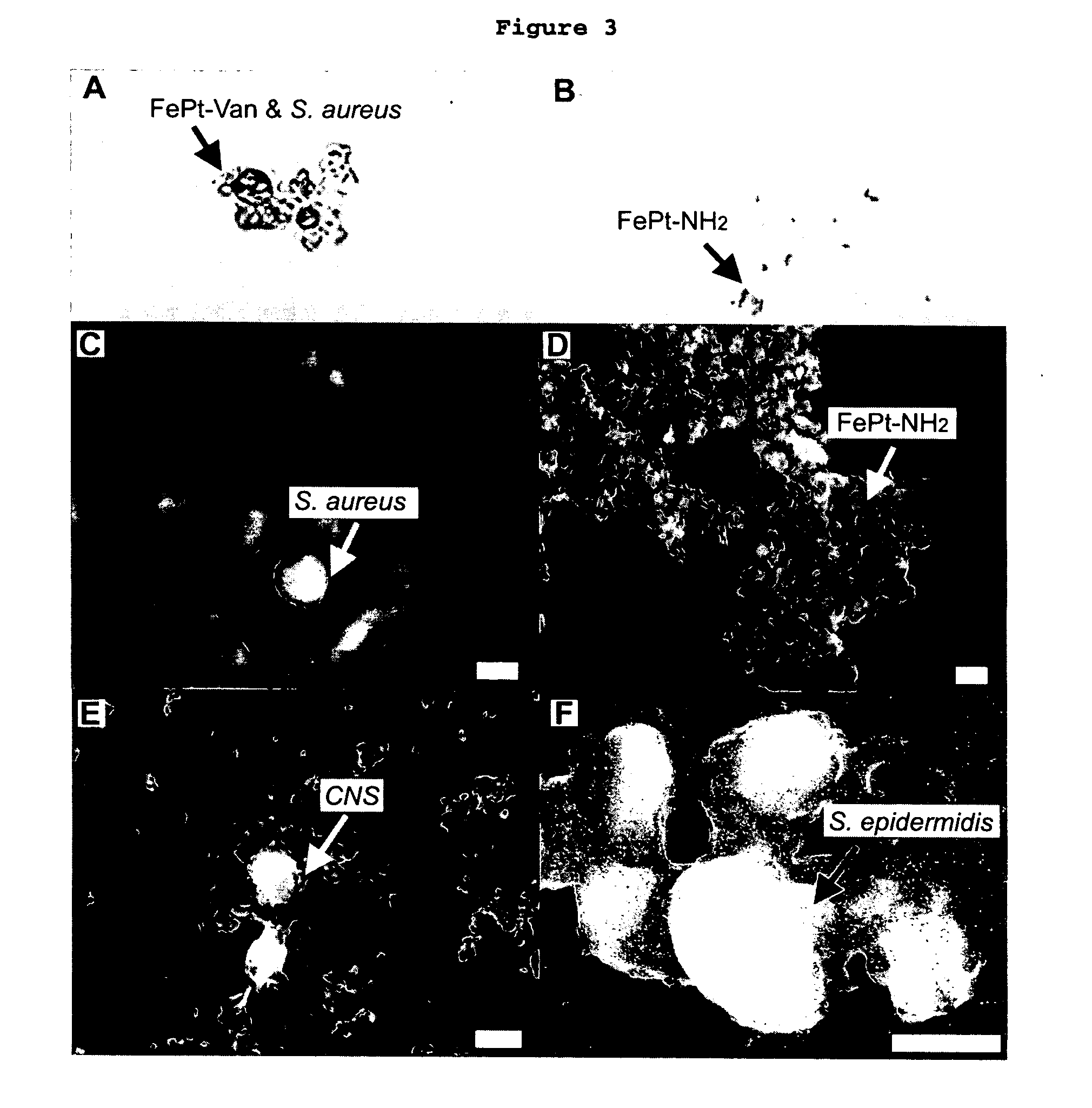
This invention provides a method of detecting pathogens comprising the steps of: (a) contacting a sufficient amount of biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles with an appropriate sample for an appropriate period of time to permit the formation of complexes between the pathogens in the sample and the nanoparticles; (b) using a magnetic field to aggregate said complexes; and (c) detecting said complexes. The method may further comprise the additional step of removing said complexes. The biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles are preferably a conjugate of vancomycin and FePt. The pathogens may be bacteria or viruses, and the sample may be a solid, liquid, or gas. Detection may involve conventional fluorescence assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), optical microscope, electron microscope, or a combination thereof. The sensitivity of detection for the method is at least as low as 10 colony forming units (cfu) of the pathogens in one milliliter of solution within one hour.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
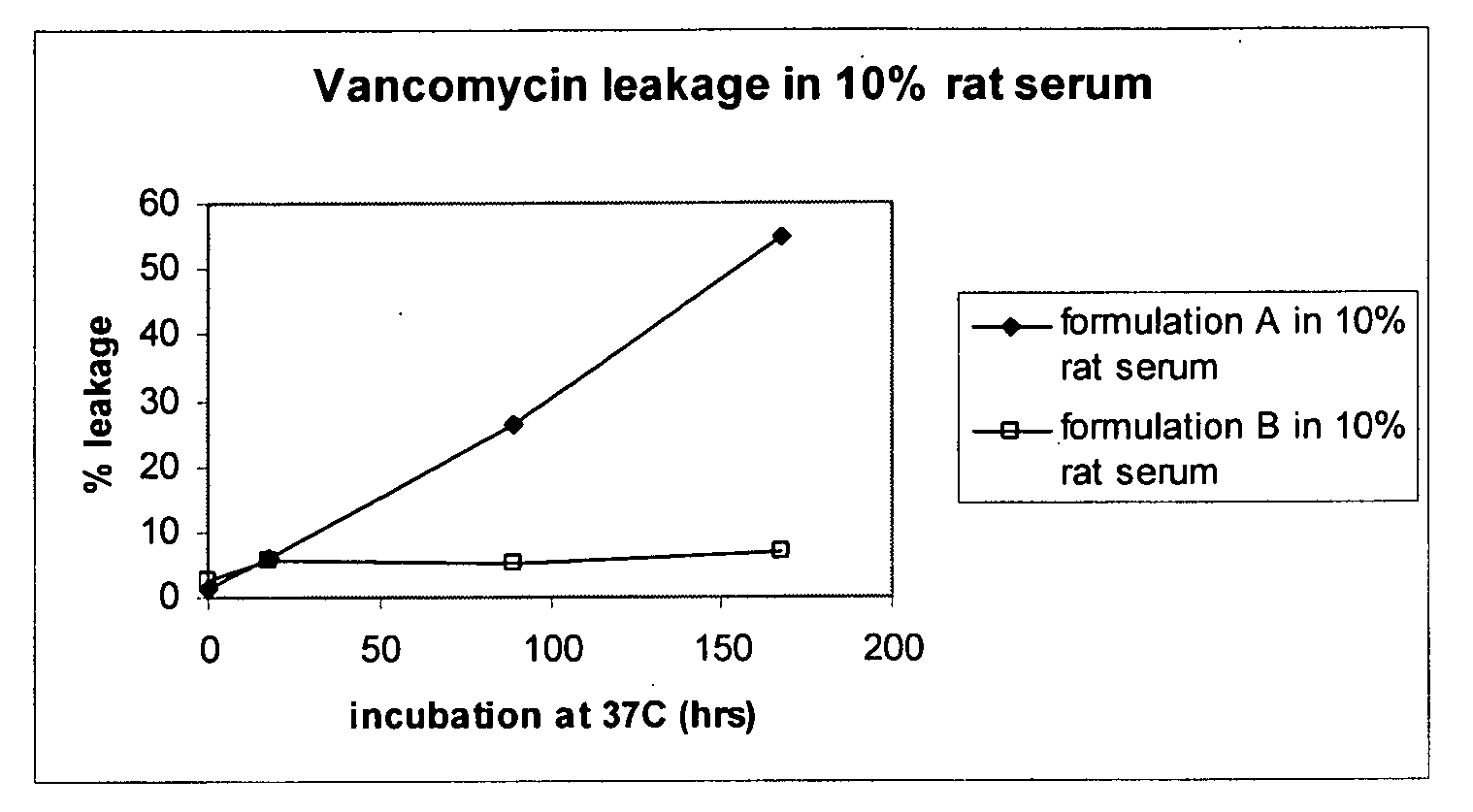
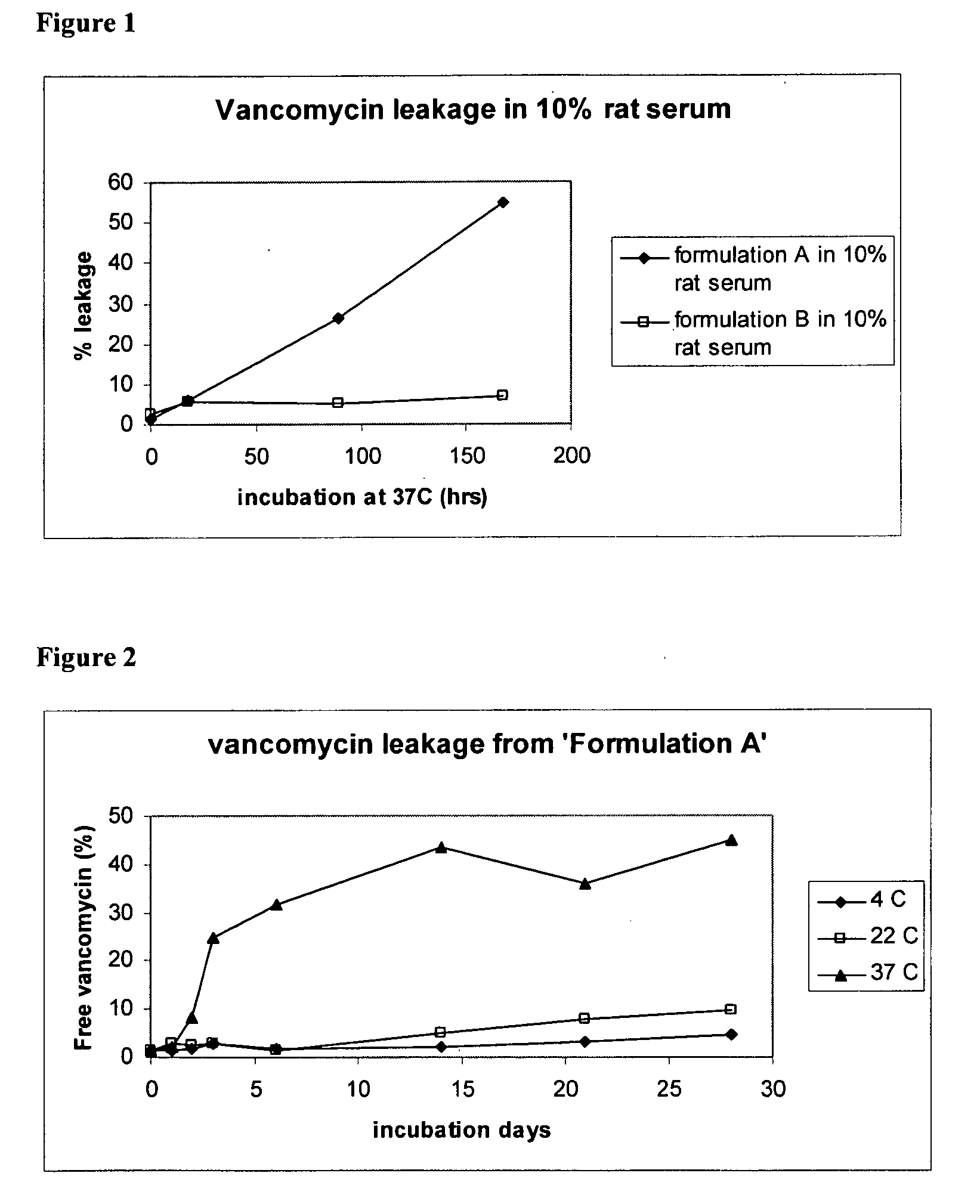
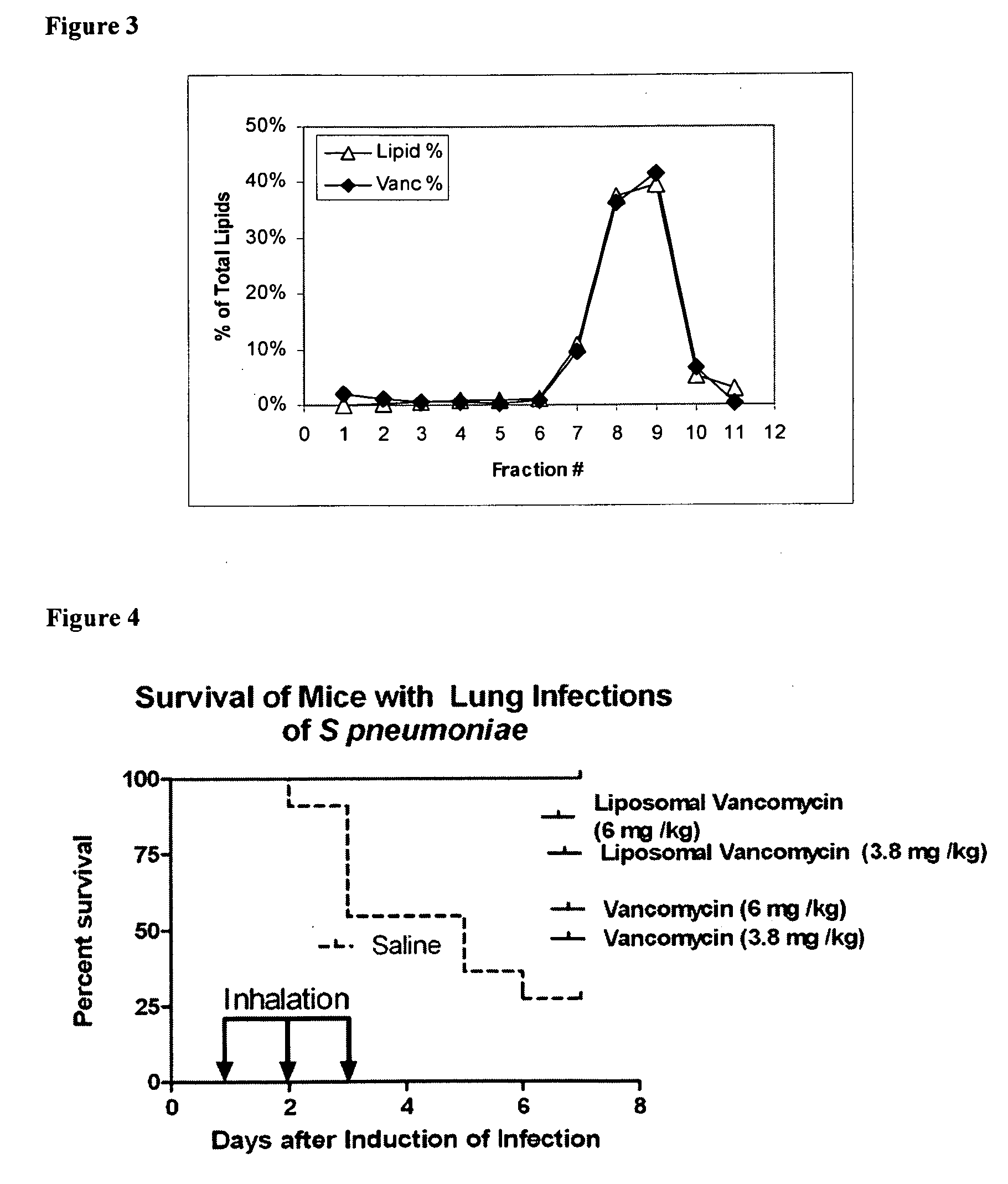
Liposomal Vancomycin Formulations
The present disclosure relates in part to liposomal vancomycin compositions having low lipid to drug ratios and high concentration of vancomycin. The present disclosure also relates in part to methods of making such compositions.
Owner:INSMED INC
New application of patchouli alcohol
ActiveCN103156826AStrong inhibitory activityEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to an application of patchouli alcohol in preparation of antibacterial drugs, healthcare food, food, cosmetics, disinfectors or daily chemical articles. The invention also provides the antibacterial drugs, healthcare food, food, cosmetics, disinfectors or daily chemical articles. The patchouli alcohol has good antibacterial activity on pathogenic bacteria or conditional pathogen, can be used for effectively treating bacterium infectious diseases and simultaneously can also effectively antagonize methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis drug-resistance bacteria; and the pharmacodynamics activity of the patchouli alcohol is even equivalent to that of vancomycin, thus the possibility is provided for slowing down or avoiding the occurrence of the drug-resistance bacteria.
Owner:CHENGDU HUASUN GRP INC LTD +1
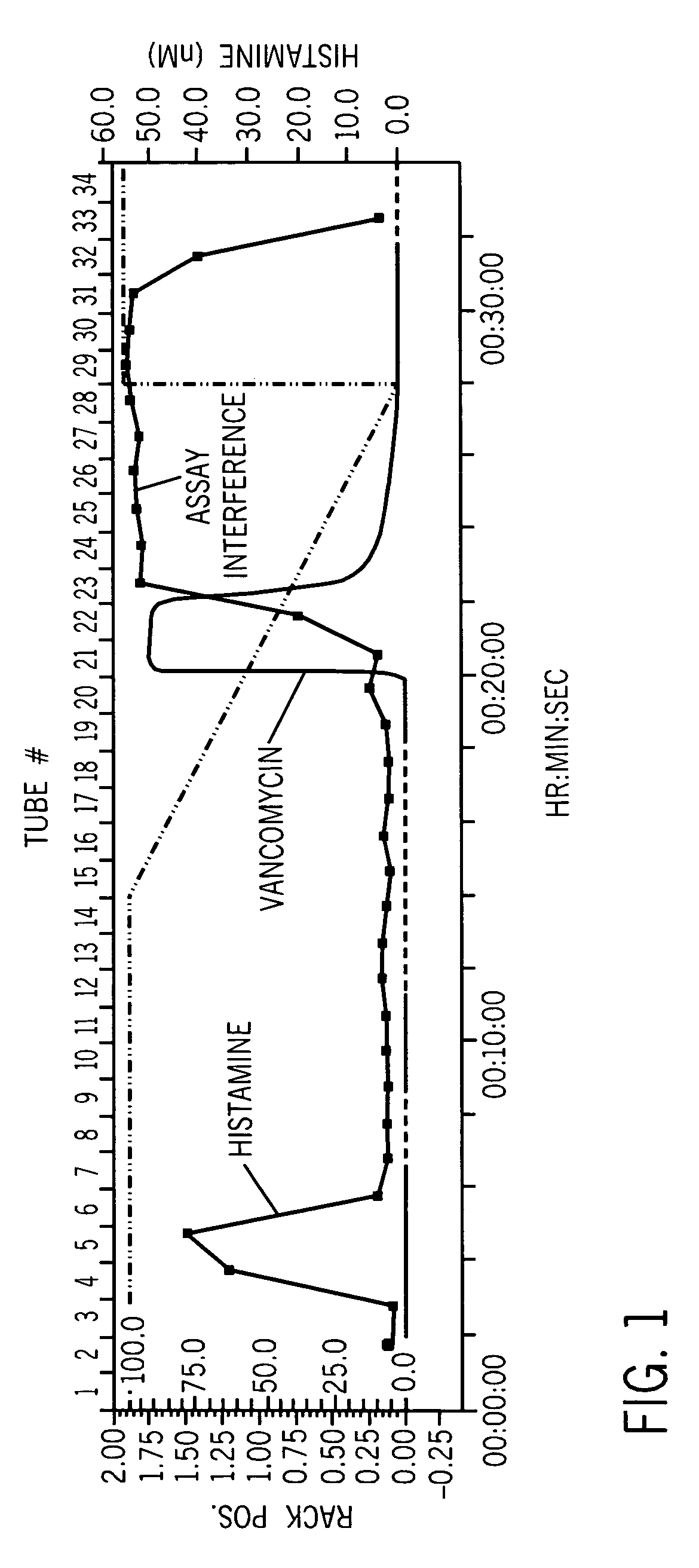
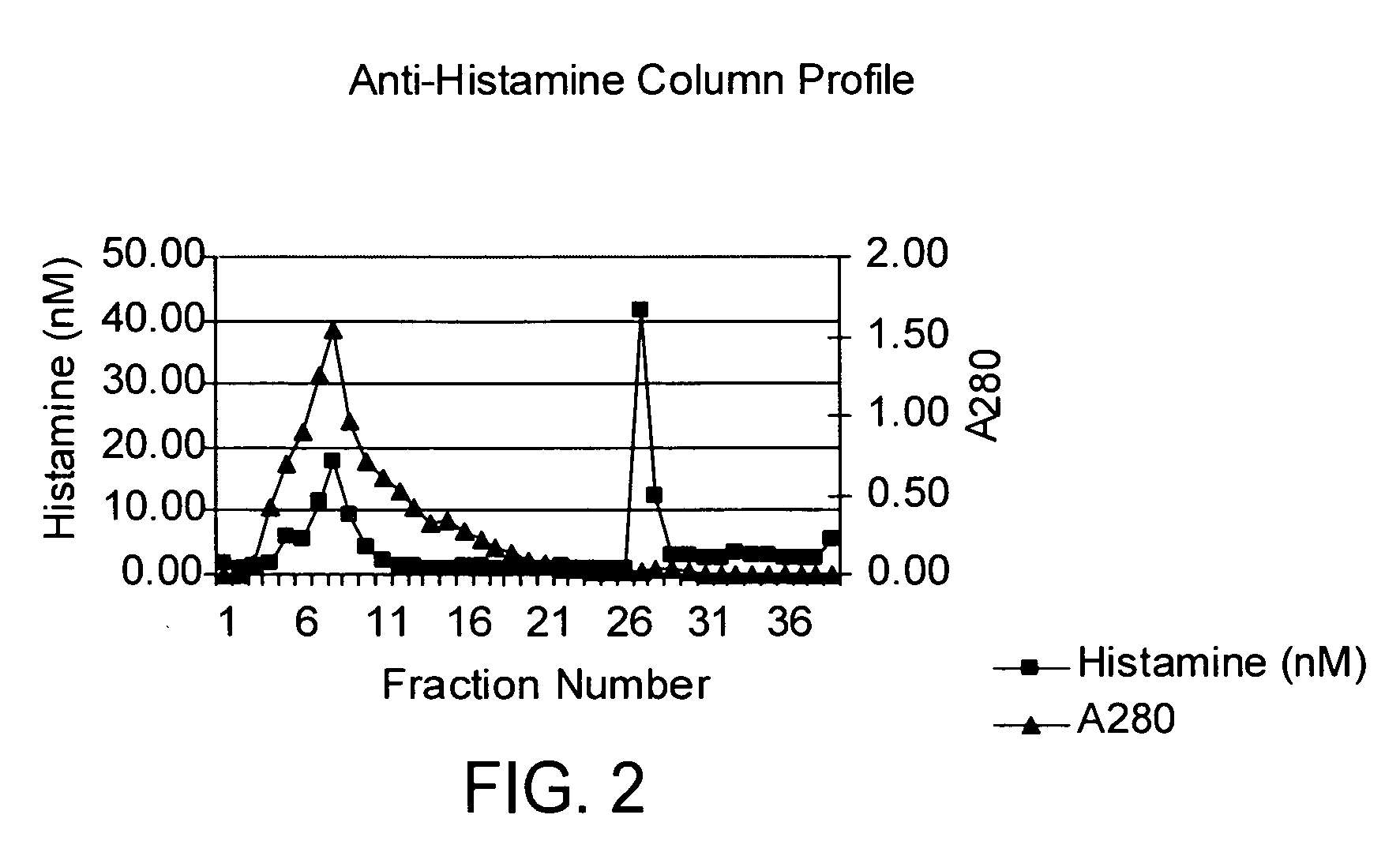
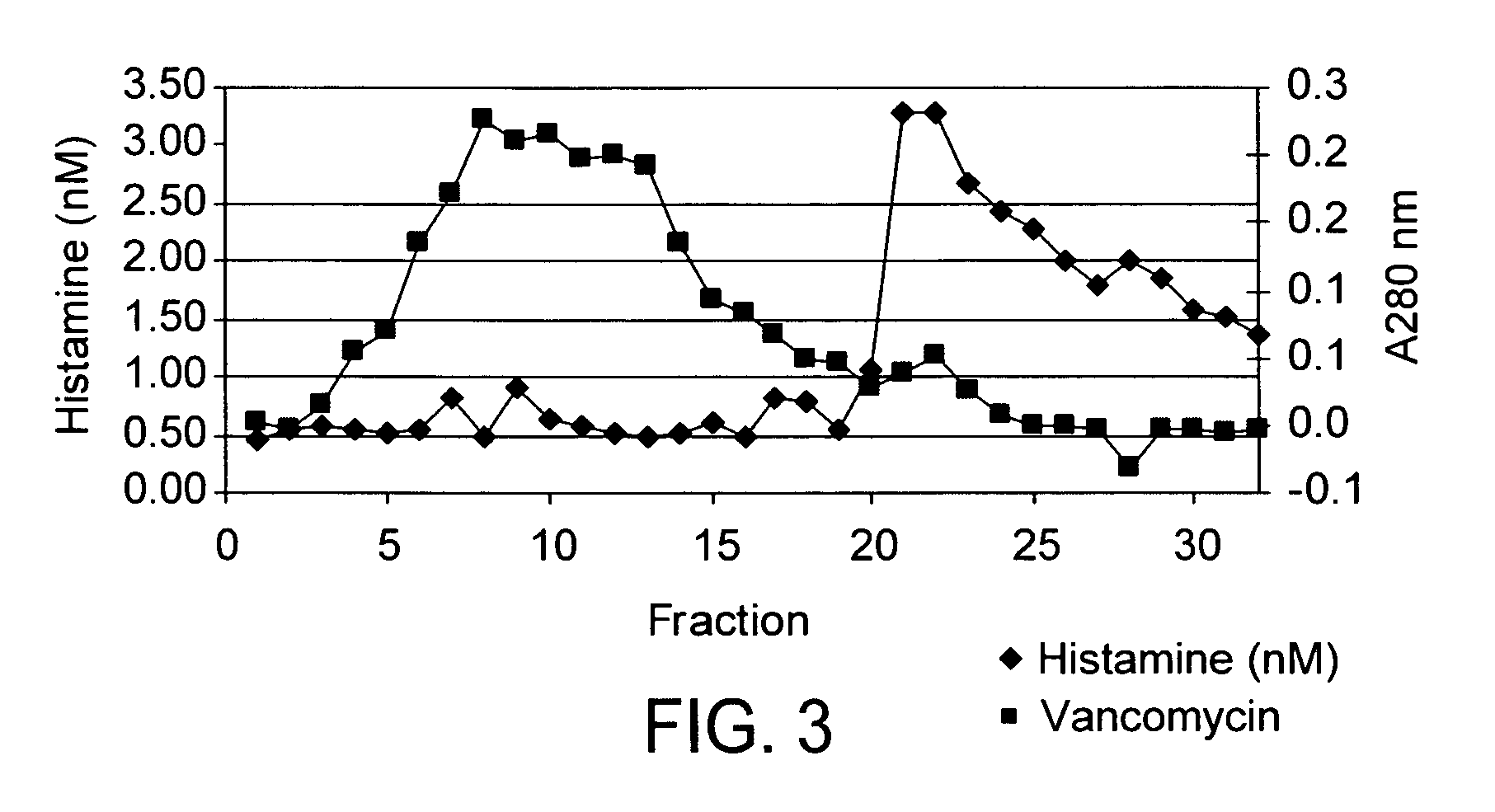
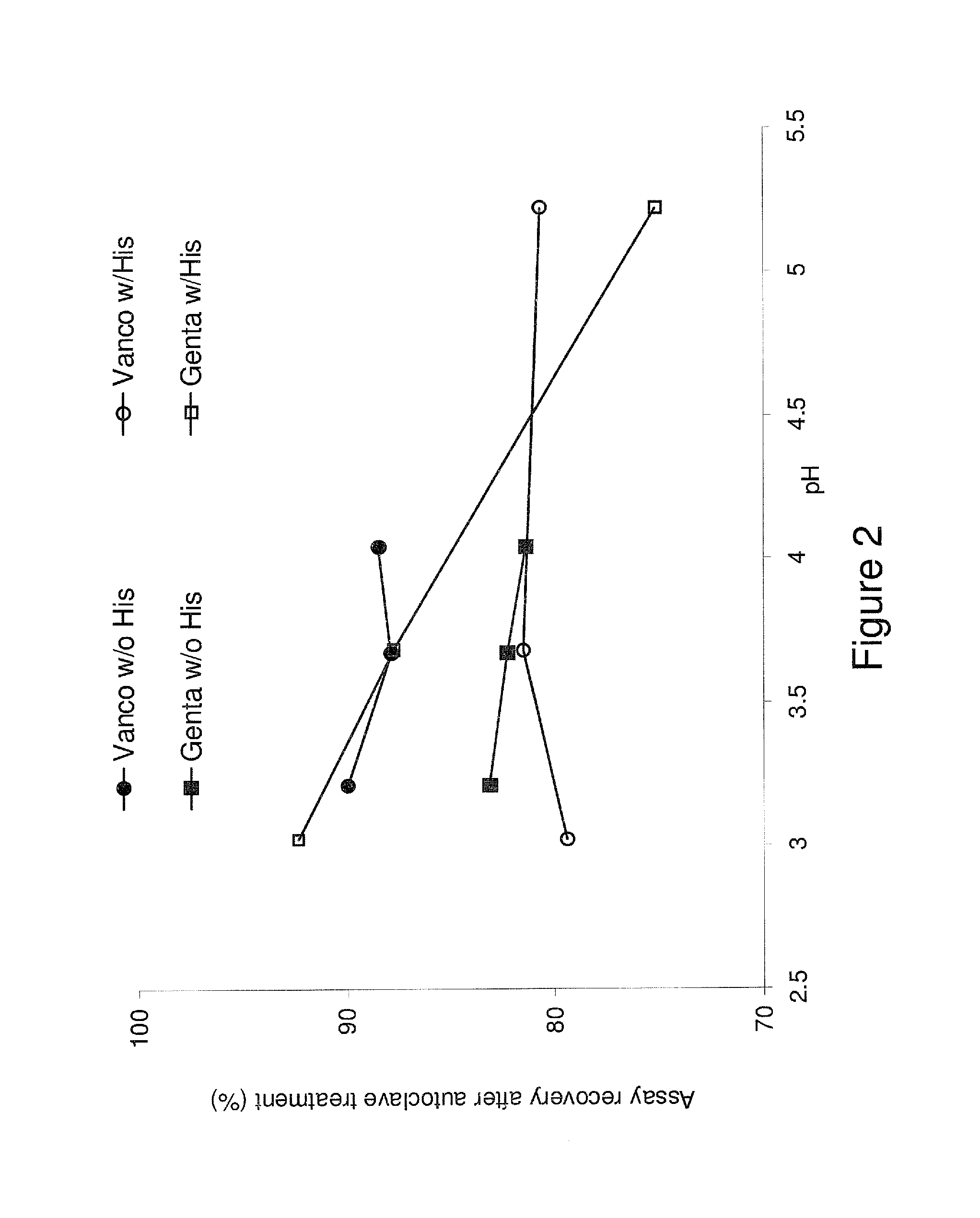
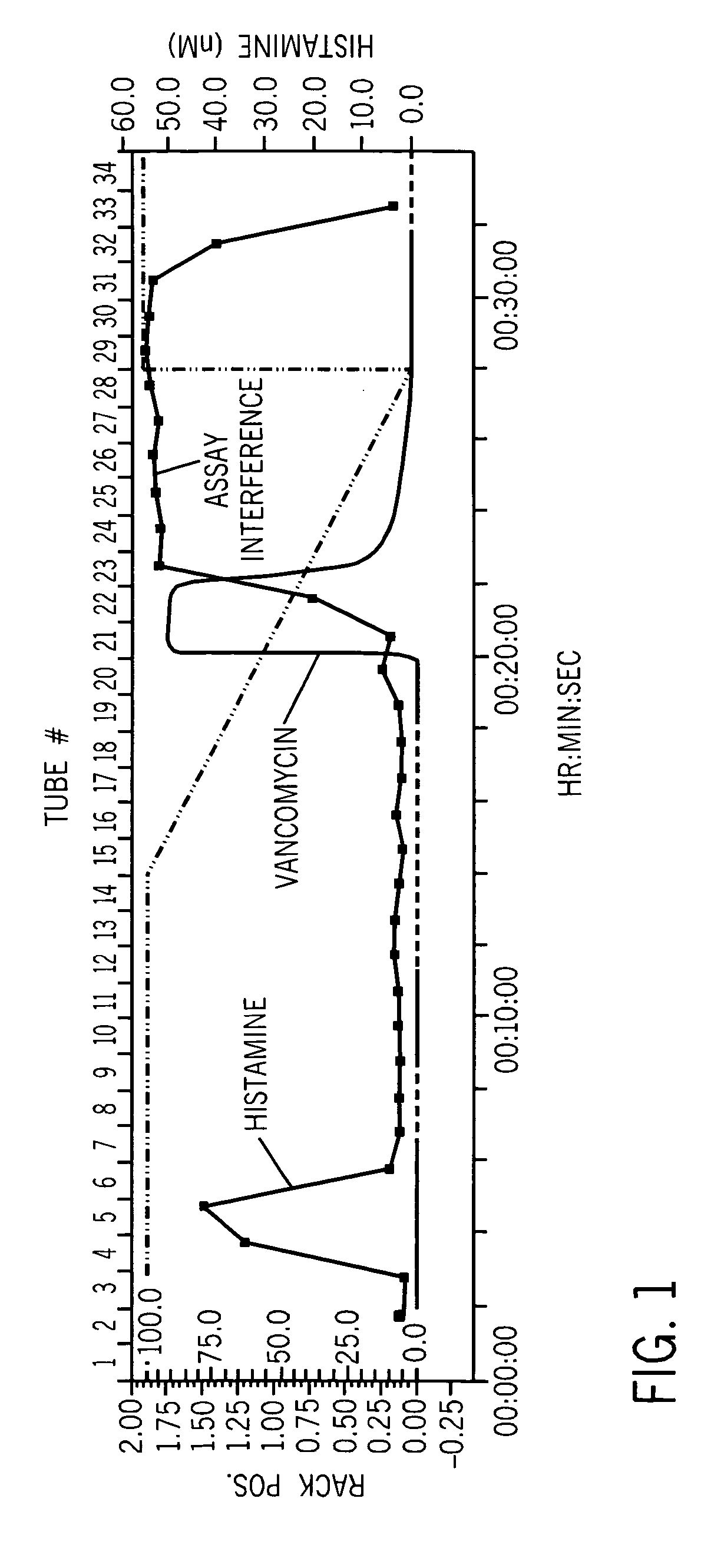
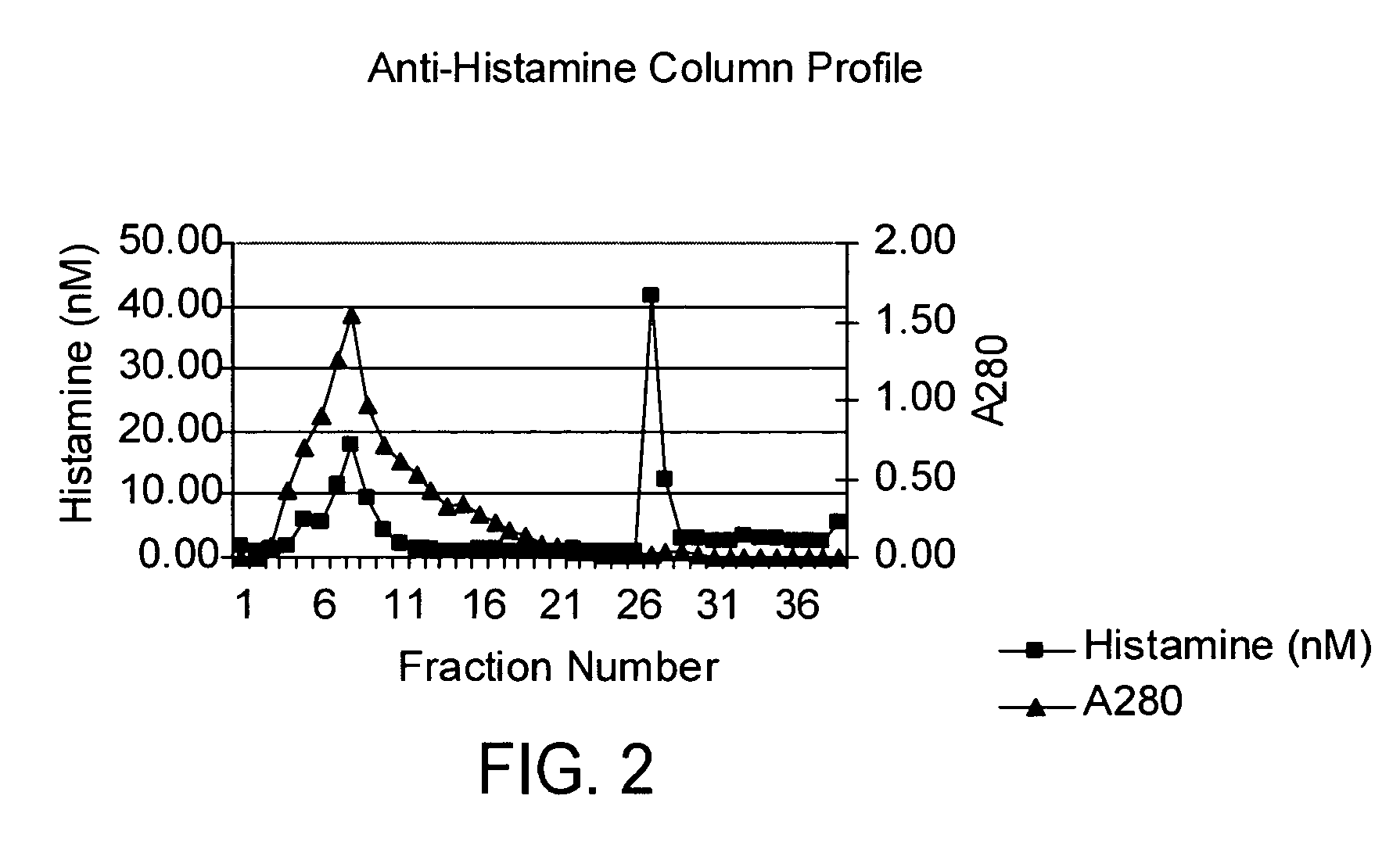
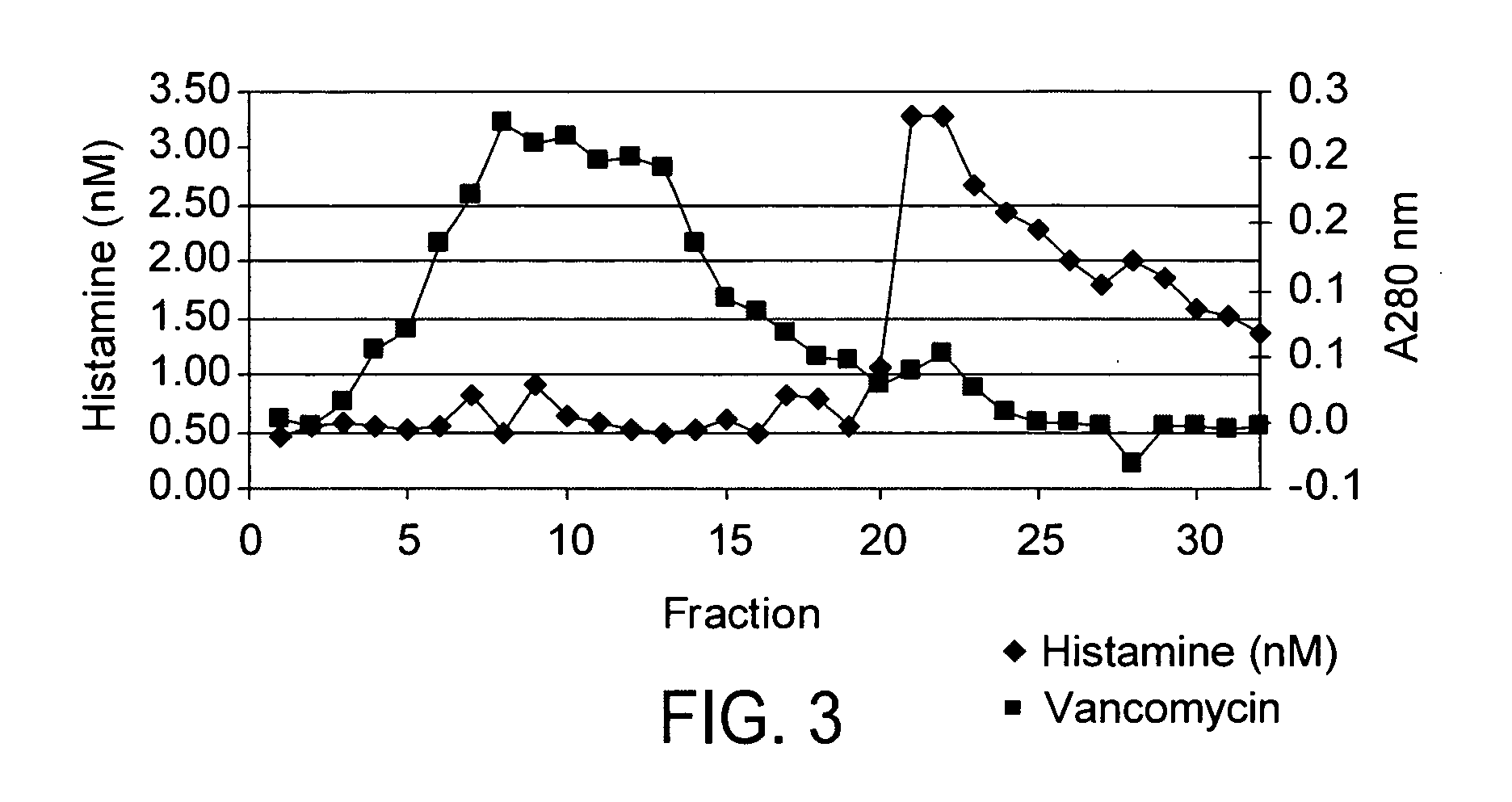
Vancomycin formulations having reduced amount of histamine
A time-released formulation of vancomycin. The invention also includes a vancomycin composition having a reduced level of histamine and a process for reducing the level of histamine in a vancomycin composition. The invention also includes a pharmaceutical composition containing vancomycin that reduces the incidence of Red Man Syndrome, phlebitis, and hypotension. The invention further includes a histamine-free growth media that supports growth of Amycolatopsis orientalis and the fermentation of vancomycin.
Owner:HOSPIRA
Composite degradable antibacterial artificial cerebral dura mater and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a composite degradable antibacterial artificial cerebral dura mater, comprising a vancomycin or ofloxacin hydrochloride injection, chitosan and sodium beta-glycerophosphate. The invention is characterized in that a spongy collagen biomembrane stent is prepared from a decellularized membrane-like derivative material, a chitosan solution with a concentration of 2% (w / v) and a sodium beta-glycerophosphate solution with a concentration of 56% (w / v) are used and mixed, and since a hydrogel formed by a compound of the chitosan solution and the sodium beta-glycerophosphate solution at a temperature of 37 DEG C has the characteristic of temperature sensitivity, the vancomycin or ofloxacin hydrochloride injection is added into the compound to form a solution which is used for soaking of the prepared spongy collagen biomembrane stent to prepare a suture-free cerebral dura mater, and the hydrogel compound uniformly infiltrates into the spongy collagen biomembrane stent after disposition in an incubator with a temperature of 37 DEG C for 10 min so as to form the absorbable artificial cerebral dura mater with antibacterial activity. The invention further provides a preparation method. The preparation method has the characteristics of convenience in preparation, easy film formation, low cost, convenient operation, etc.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
VEGF and vancomycin-supported multilayer slow release microsphere preparation, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104147594ABiologically activeHas antibacterial propertiesSkeletal disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsMicrosphereSide chain
The invention discloses a VEGF and vancomycin-supported multilayer local slow release microsphere preparation with sodium alginate and chitosan as a carrier, a preparation method of the microsphere preparation, and an application of the microsphere preparation in the preparation of medicines for treating bone defects, bone tissue regeneration and wound healing, and belongs to the technical field of medicine slow release microspheres. In the invention, a core sphere is prepared through an instillation process, and other multilayer microspheres are prepared according to a positive and negative charge attraction and layer-by-layer self assembling principle. Sodium alginate and chitosan are natural polymer polysaccharides, chitosan is a polycation polymer material, and the side chain structure of chitosan contains a large number of free amino groups; and sodium alginate is a polyanion material, the molecular side chain of sodium alginate contains a large number of carboxyl groups, sodium alginate and chitosan undergo a complexing reaction through attraction of positive and negative charges, and the core-shell multilayer slow release medicine multilayer sphere is formed by sequentially wrapping according to the layer-by-layer self assembling principle, so multilayer slow release microsphere preparation can promote local angiogenesis, improve blood circulation and control local infection.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
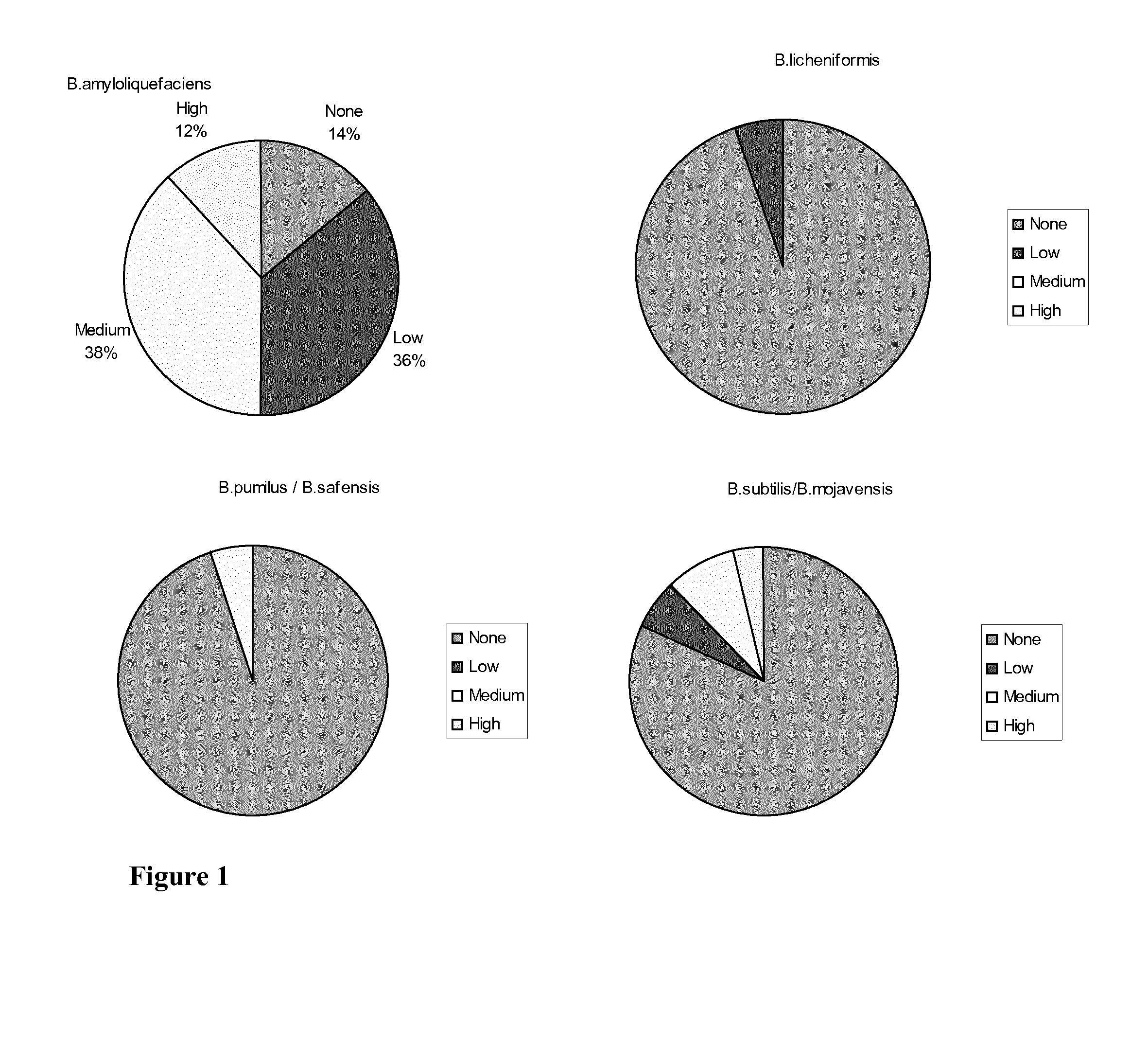
Antibiotic sensitive bacillus strains having antimicrobial effect against e. coli and clostridium perfringens and having high sporulation capacity
A Bacillus strain characterized by (i): sensitivity for ampicillin, vancomycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin, erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline and chloramphenicol; (ii) antimicrobial activity against E. coli and Clostridium perfringens; and (iii) a sporulation percentage of at least 80 when measured after 2 days of incubation. The invention further relates to a method for selecting such strains. Many of the identified strains according to the invention are of the species Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Some of the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens were further identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. amyloliquefaciens whereas others were identified as amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum. A Bacillus strain of the invention may be used as a feed additive to animal feed where it has a probiotic effect.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
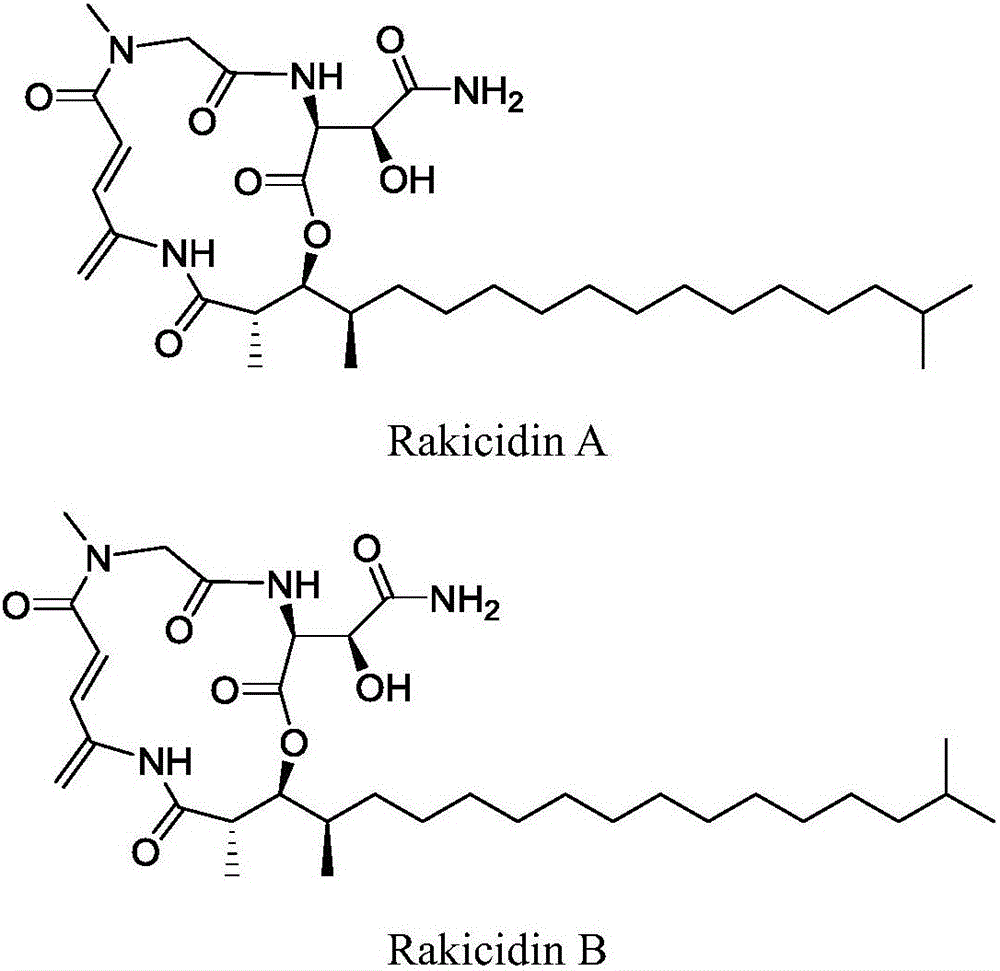
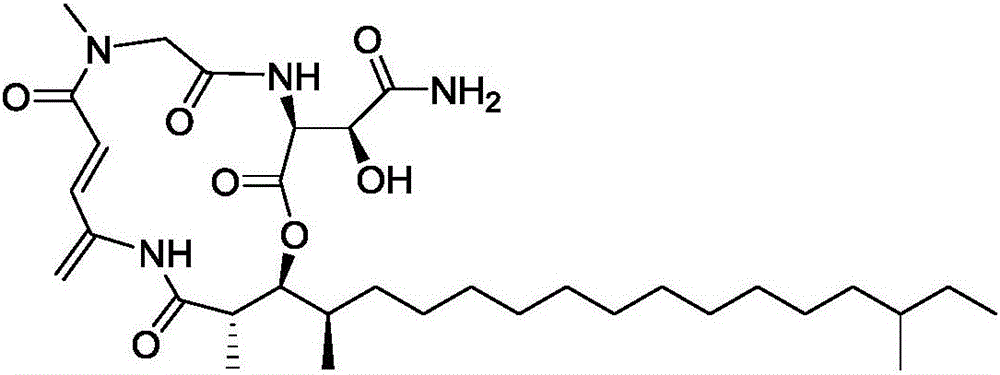
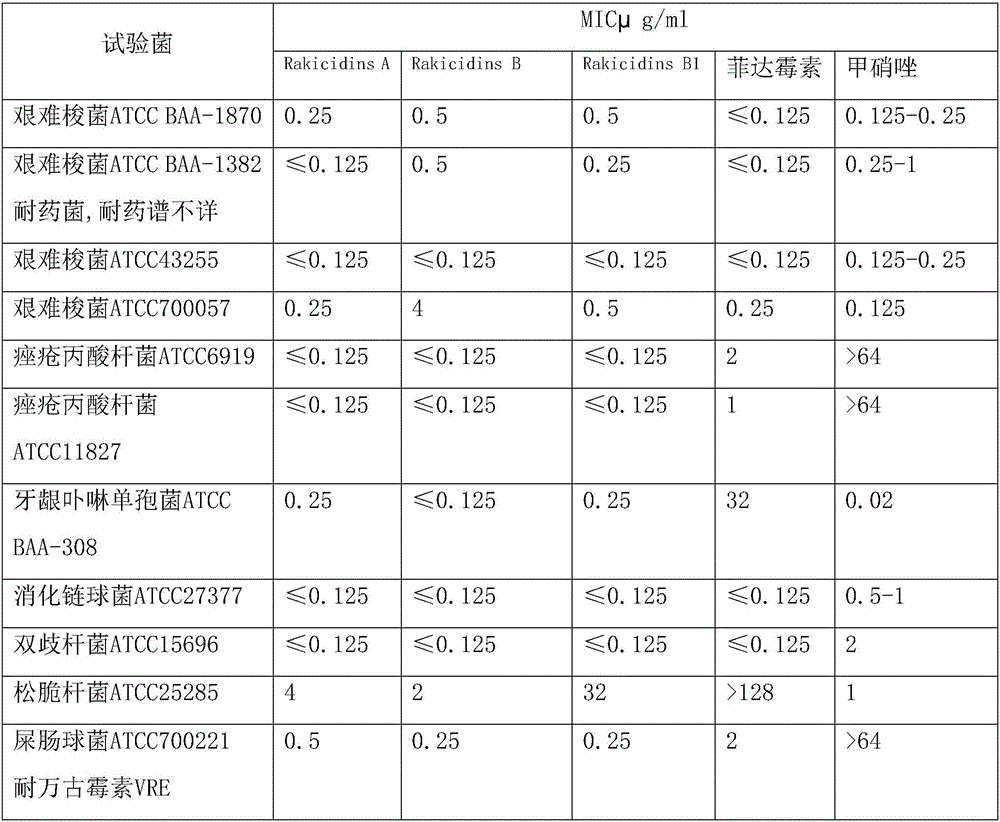
Application of Rakicidins compounds in resistance to clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria
ActiveCN105709205AQuite activeStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseUpper urinary tract infection
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to an application of Rakicidins compounds in resistance to clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria. Pharmacodynamic experiments indicate that the Rakicidins compounds have good resistant effect on the clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria and have the resistant effect on vancomycin enterococcus infection diseases. The Rakicidins compounds can be used for treating diarrhea, enteritis, alimentary infection, oral infection or skin acne caused by clostridium difficile as well as diseases such as urinary tract infection, or skin soft-tissue infection and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
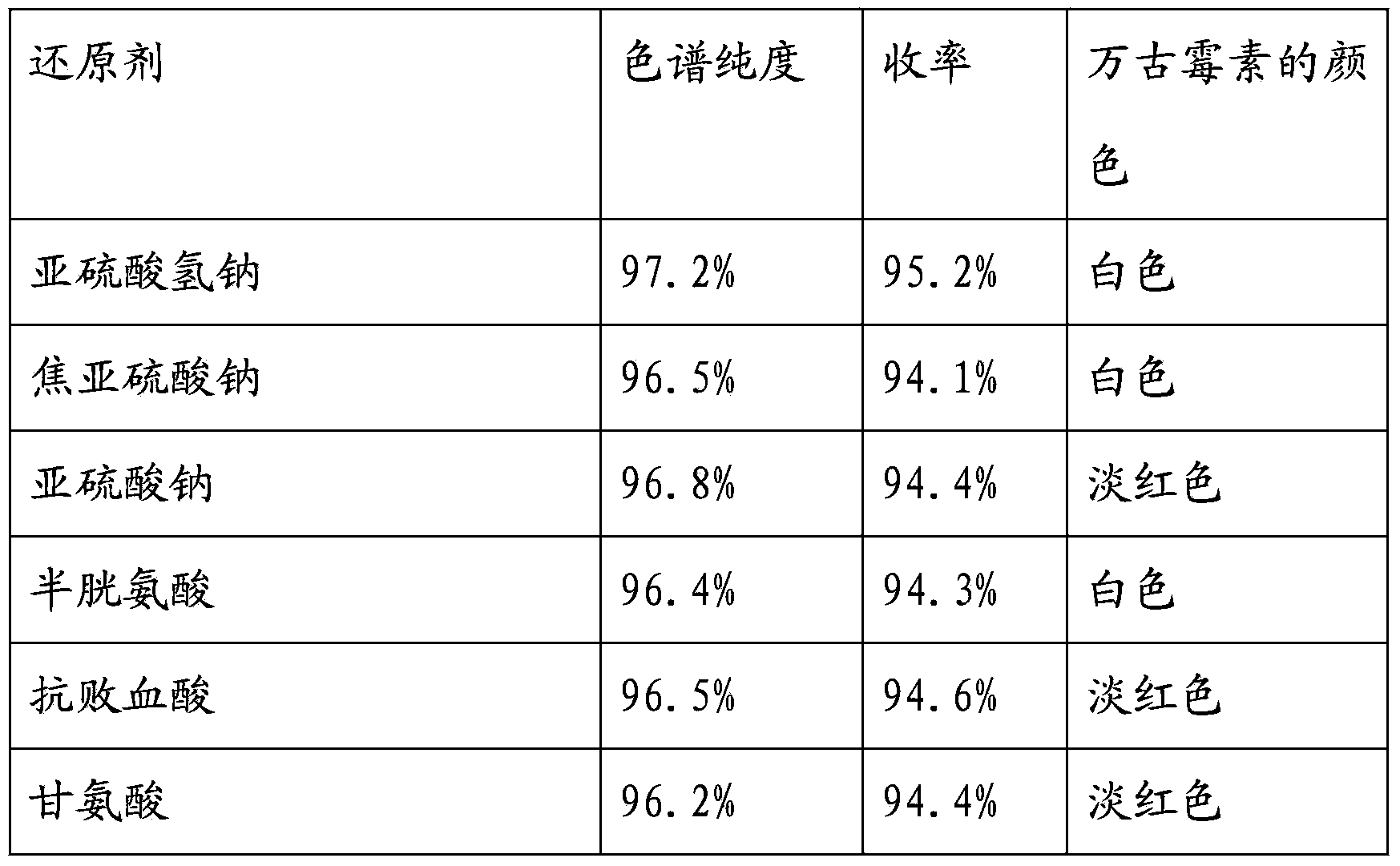
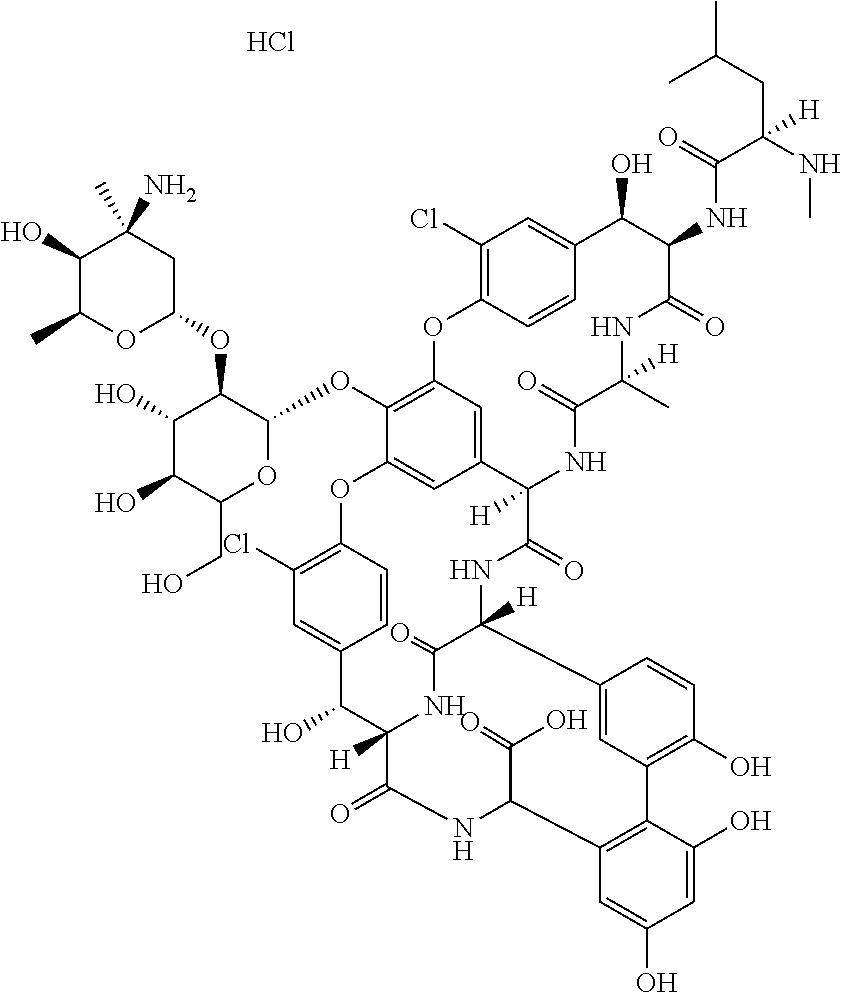
Vancomycin hydrochloride for injection and its preparing method
InactiveCN1857716AThe composition of the prescription is simpleThe method is reliable and practicalAntibacterial agentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismVancomycin HydrochlorideGlycine
The vancomycin hydrochloride injection consists of medicine vancomycin hydrochloride in 90%-99% and supplementary material in 1%-10%, and is prepared into powder for injection with supplementary material of stabilizer and / or antioxidant. The medicine powder has potency higher than 900 IU / mg, and is dissolved in water to form 50 mg / ml solution with absorbance at 465 nm lower than 0.065 and pH 2.0-4.0. It is prepared through freeze drying process. The vancomycin hydrochloride injection of the present invention has simple preparation process, common medicinal supplementary material citric acid, glycine, L-cysteine etc, and high normal temperature storage stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Glycosylated glycopeptide antibiotic derivative
InactiveCN101959900AGood water solubilityGood body dynamicsAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsVancomycinumSimple aromatic ring
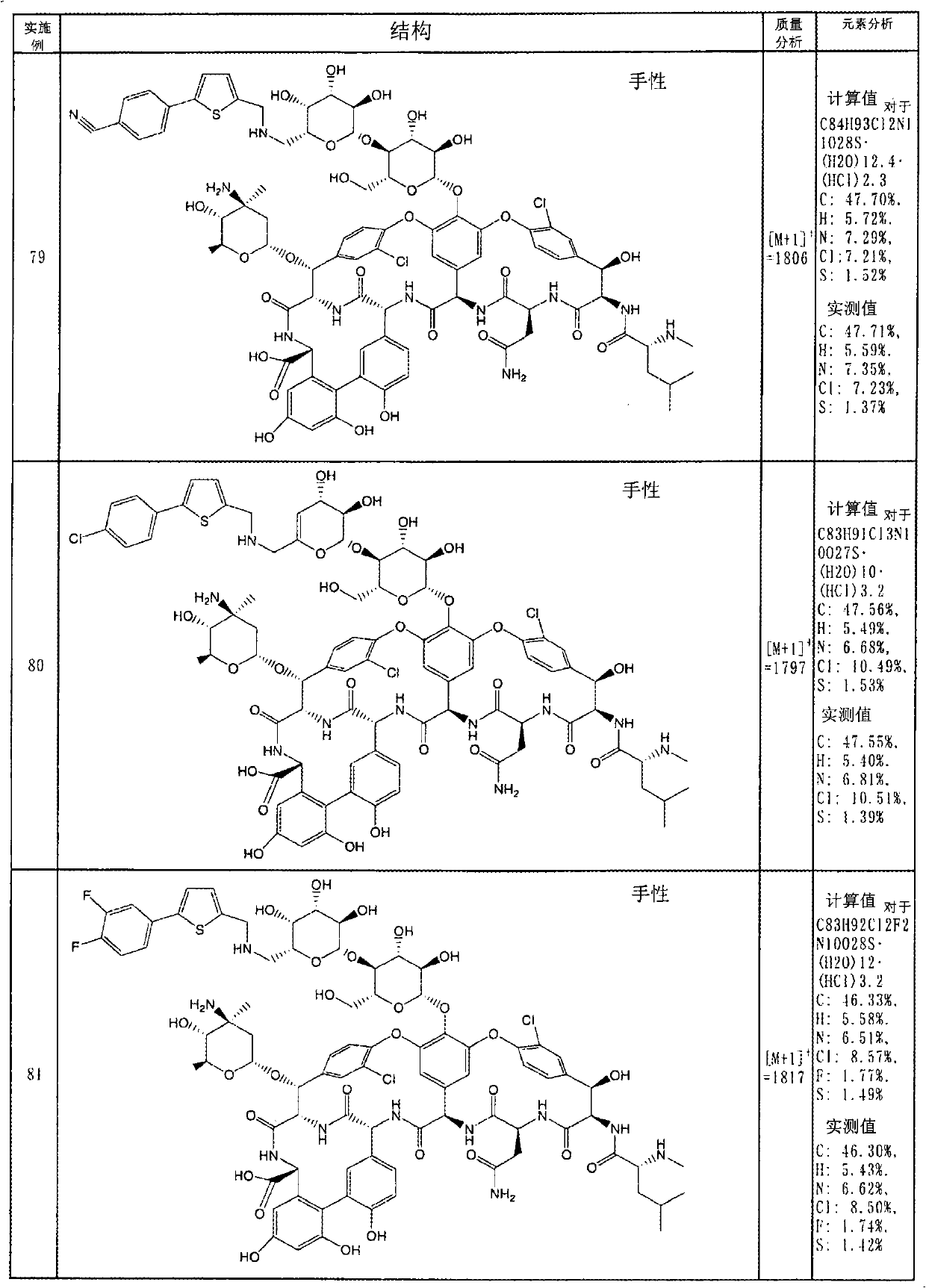
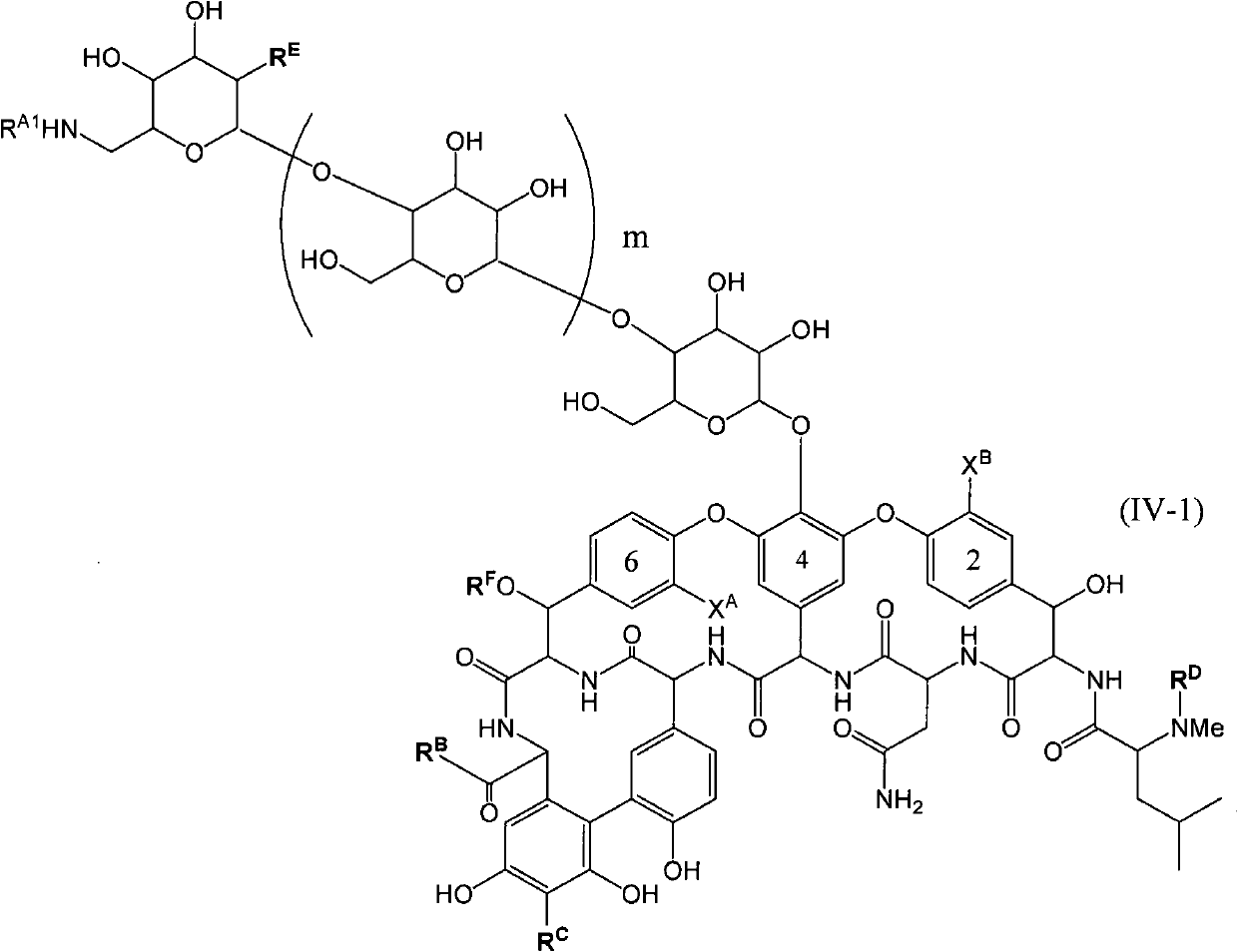
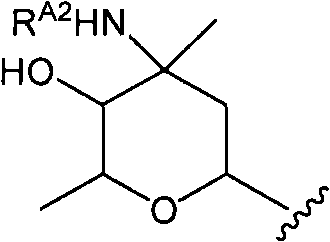
Disclosed is a novel glycopeptide antibiotic derivative. The glycopeptide antibiotic derivative is characterized by having a sugar residue (I) represented by formula (I) [wherein n represents an integer of 1 to 5; Sug's independently represent a monosaccharide, and (Sug)n represents a bivalent sugar residue formed by binding 1 to 5 monosaccharides which are the same as or different from each other; RA1 represents a lower alkyl which may be substituted, a lower alkenyl which may be substituted, or a cycloalkyl which may be substituted; and RE represents OH or NHAc (wherein Ac represents an acetyl)] bound to an aromatic ring in the 4th amino acid residue located in a glycopeptide skeleton. The derivative has an antibacterial activity against a vancomycin-resistant bacterium.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Drug-loading sustained-release support composite body for treating infectious bone defect
InactiveCN108671269AAchieve the purpose of infection controlFor the purpose of infection controlTissue regenerationProsthesisMicrosphereBone formation
The invention relates to a drug-loading sustained-release support composite body for treating infectious bone defect. The drug-loading sustained-release support composite body is prepared by the stepthat vancomycin is encapsulated by polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer to prepare sustained release microspheres and loaded to a beta-tricalcium phosphate support. The vancomycin, with broad-spectrum antibacterial capacity, is encapsulated by the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer to prepare into sustained microspheres, and loaded to the beta-tricalcium phosphate support to prepare a novel drug-loading sustained-release anti-infection bone substitute material which can slowly release the vancomycin at a part of the infectious bone defect. When being applied to treating the infectiousbone defect, the material can release the encapsulated vancomycin in an all-dimensional mode for a long time in a partial three-dimensional space of the infectious bone defect after being embedded; thus, the purpose of controlling infection within the focus of infection is achieved; meanwhile, the effects of filling bone defect, promoting bone formation and quickening bone reconstruction are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH +1
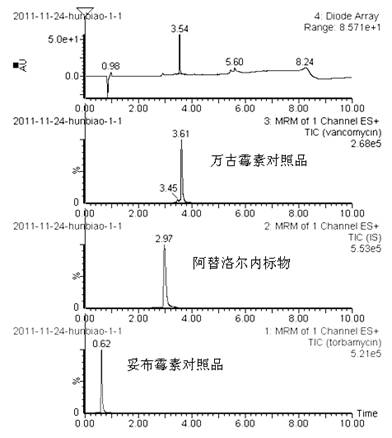
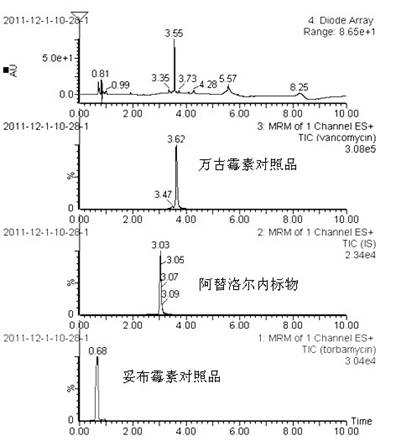
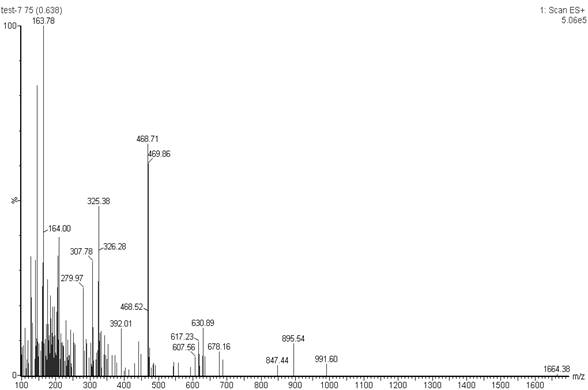
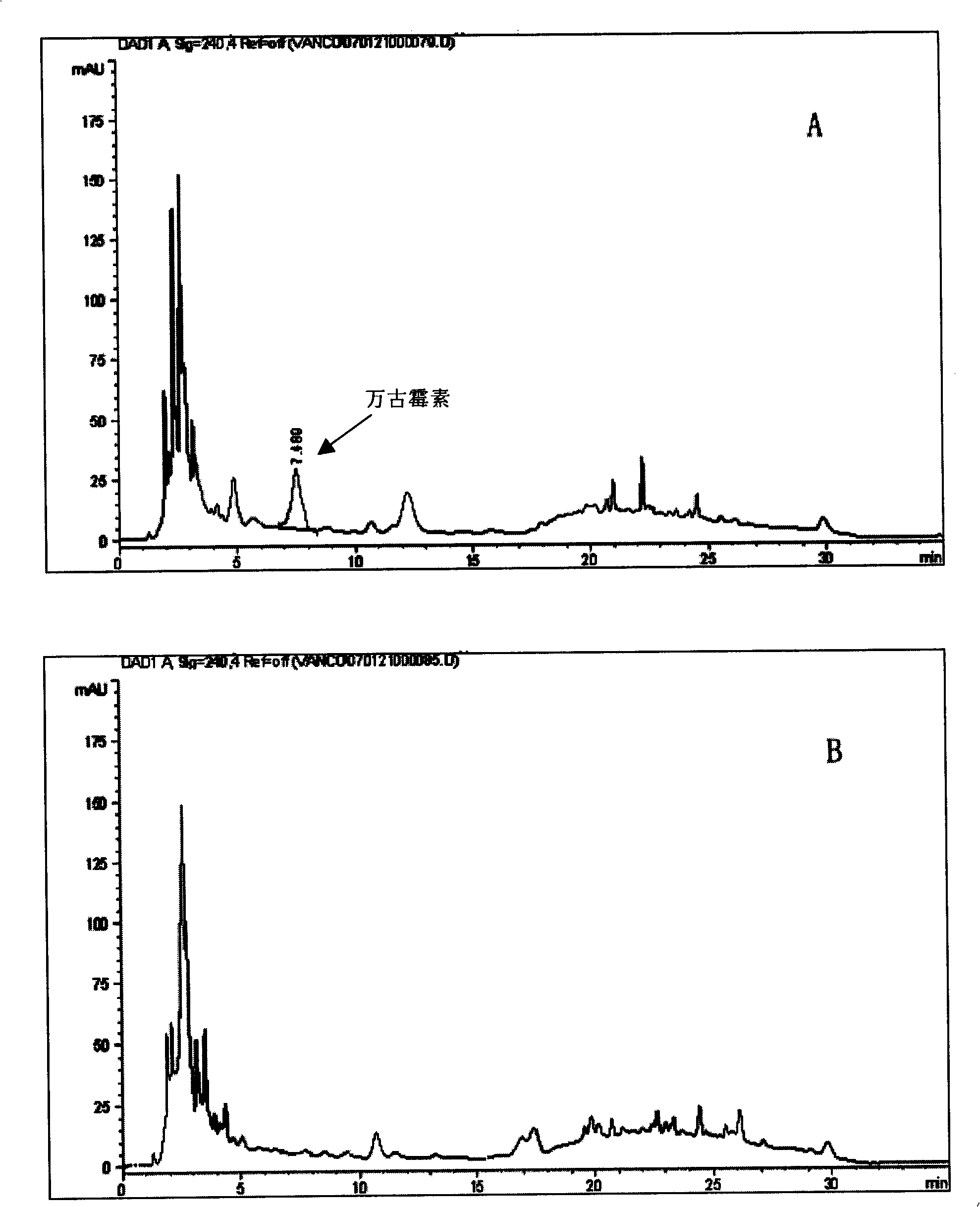
Method for simultaneously determining content of vancomycin and tobramycin in tissue drainage liquid through ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC-TQD) coupling technique
The invention relates to the field of drugs, in particular to a detection method for simultaneously determining content of vancomycin and tobramycin in tissue drainage liquid. A method for simultaneously determining content of vancomycin and tobramycin in tissue drainage liquid through an ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC-TQD) coupling techniquecomprises the following steps of: 1) preparing reference samples; 2) preparing internal standard solution; 3) preparing sample solution; 4) preparing mobile-phase solution; 5) setting chromatographicconditions; 6) optimizing mass spectrometric conditions; 7) determining the samples; 8) preparing gradient-concentration reference sample solution; 9) preparing a standard curve; and 10) analyzing and computing data. The method has the characteristics that: 1) the method is advanced; 2) the method is rapid and high-efficiency the loss is low; and 3) the clinical application prospect and the effect are good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Phospholipid depot
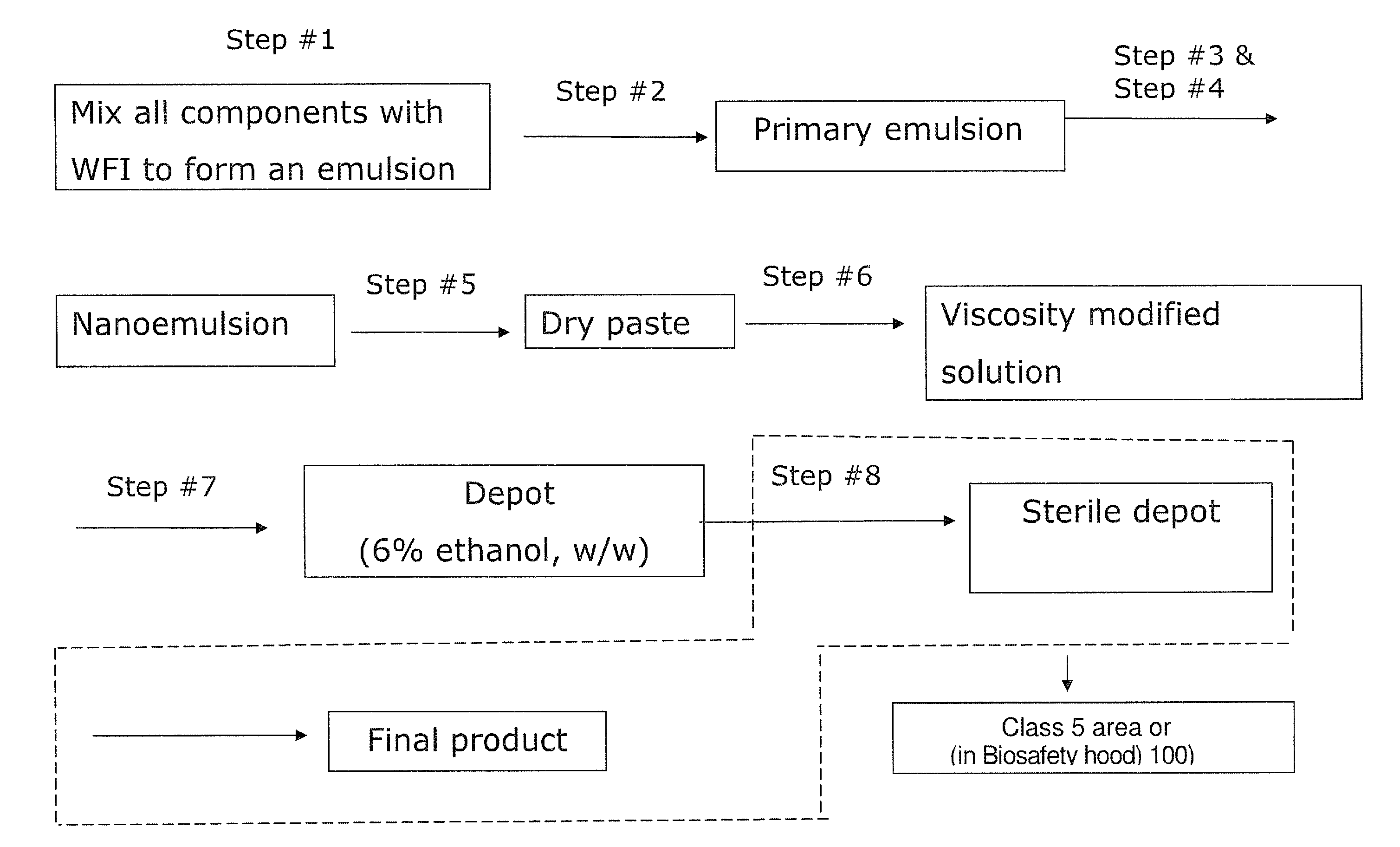
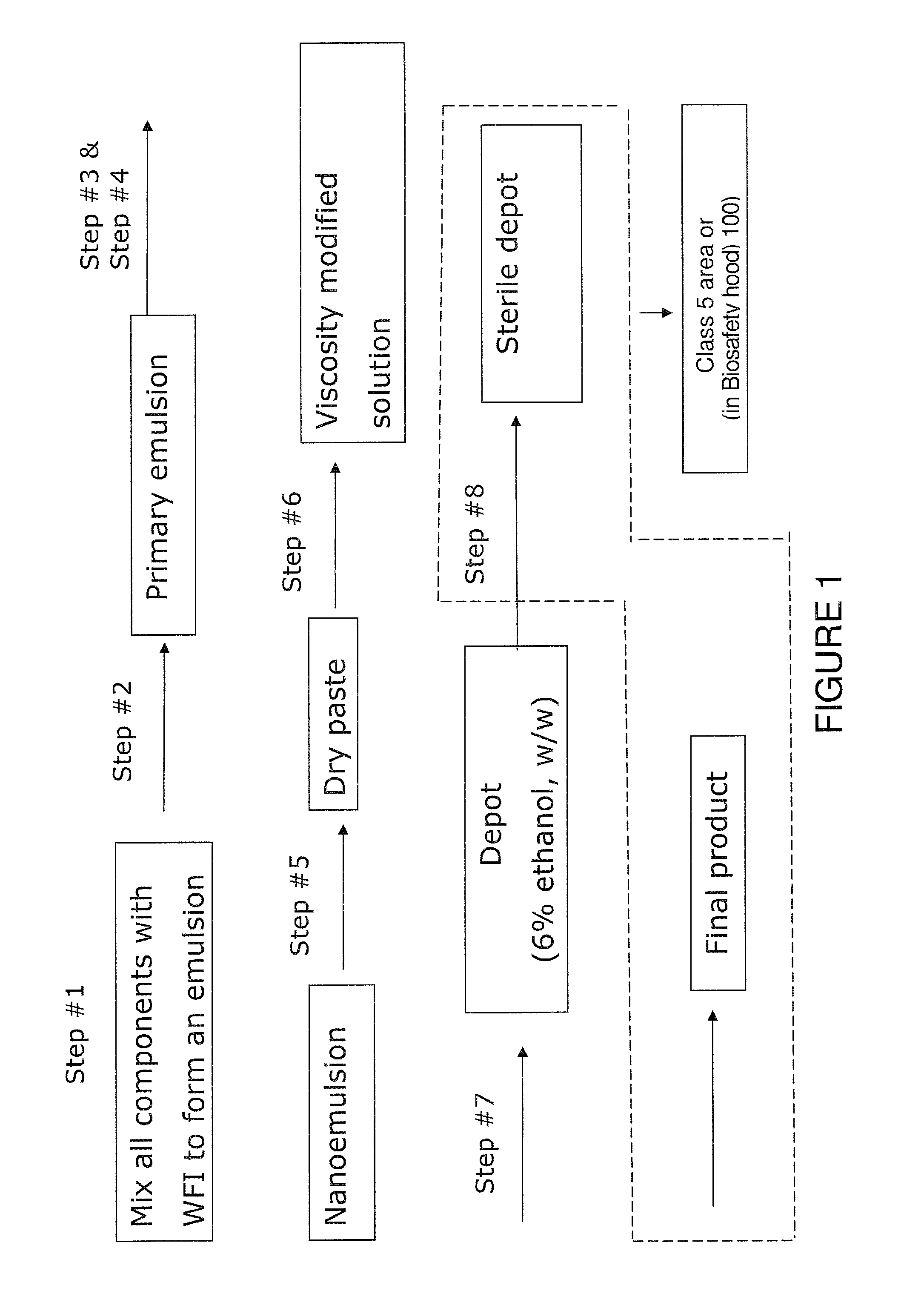
ActiveUS20120046220A1Low viscosityPrevent unintended introductionAntibacterial agentsBiocideActive agentVancomycin
The present invention provides a clear depot comprising at least one hydrophilic water-soluble pharmaceutically active agent selected from the group consisting of vancomycin, gentamicin, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a mixture thereof, water, a phospholipid, an oil, optionally a pH adjusting agent, and a viscosity modifying agent selected from the group consisting of ethanol, isopropanol, and a mixture thereof, wherein the water present in the depot is no more than about 4 wt % relative to the total weight of the depot and the depot has a pH of between about 3 and about 6, method of making and administering same.
Owner:DR REDDYS LAB SA
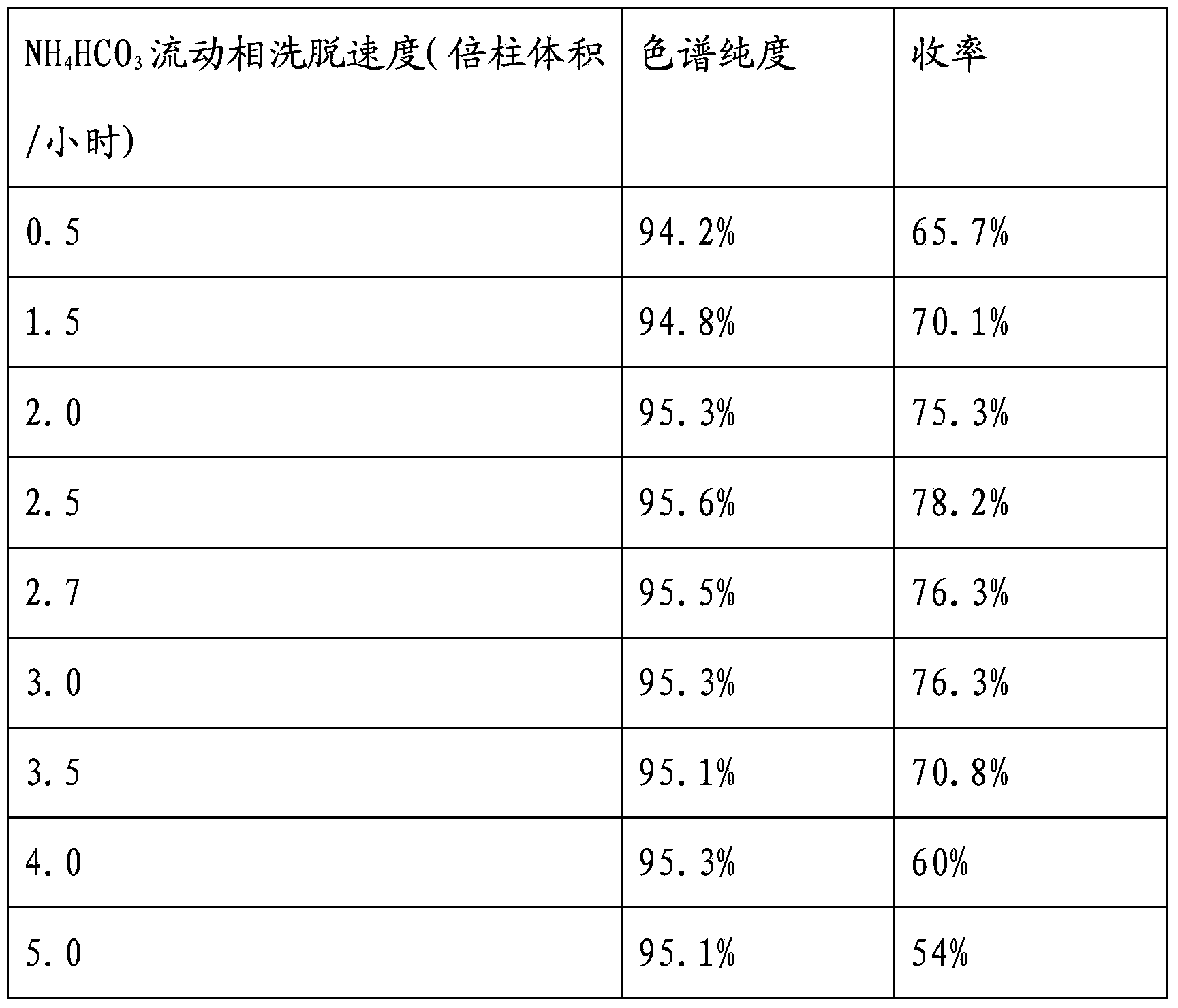
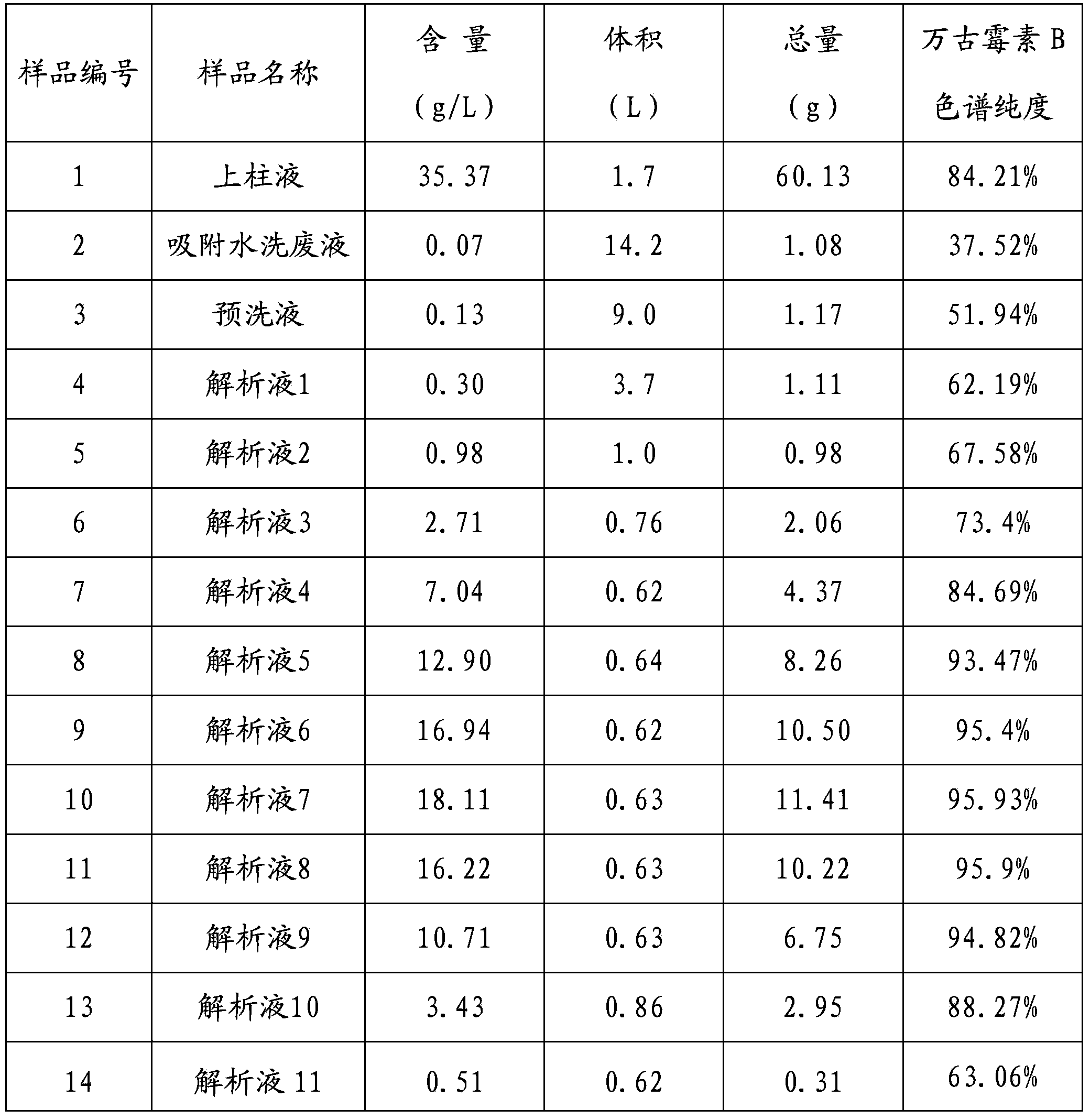
Preparation method of vancomycin with high purity
ActiveCN103408639ASmall granularityLow swelling ratePeptide preparation methodsChromatography liquidVancomycin
The invention belongs to the field of antibiotic preparation technologies, and more specifically relates to a preparation method of vancomycin with high purity. The preparation method comprises following steps: a destaining solution of vancomycin is subjected to column chromatography in a chromatography media, wherein the chromatography media is UniPMM50CAR, the NH4HCO3 mass concentration of a mobile phase of column chromatography is 0.2 to 0.7%; when absorbance rises to 40 at a detection wavelength of 280nm, chromatography liquids are collected segment by segment, the pH value of the chromatography liquids is adjusted to 3.0 to 3.5, the chromatography liquids are preserved under 4 DEG C, and the collected chromatography liquids are mixed. Bubbles in the chromatographic column caused by degradation of carbonate are not likely to generate by using the preparation method. The preparation method is capable of increasing stage number and separation efficiency. The appearance of the obtained vancomycin is improved significantly, purity is as high as 99%, and the vancomycin can be taken orally or by injection.
Owner:LIVZON GROUP FUZHOU FUXING PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Method for producing vancomycin hydrochloride by utilizing vancomycin fermentation broth
ActiveCN103641895ASimple extraction processShorten the production cyclePeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyVancomycinum
A method for producing vancomycin hydrochloride by utilizing a vancomycin fermentation broth comprises pretreatment of the vancomycin fermentation broth, inorganic ceramic membrane filtration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, crystal water-washing, acid-base neutralization and vacuum freeze drying. The method helps to realize the stable efficient production of vancomycin hydrochloride. Also the method helps to improve the extraction yield, shorten the production period, reduce the cost and improve the yield of vancomycin hydrochloride.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
Method for processing vancomycin fermentation waste slag with solid-state fermentation
The invention provides a processing method of vancomycin fermentation residue. The invention makes use of vancomycin fermentation residue as a sole culture medium, and the solid state culture method is adopted under the proper conditions for culturing yeast. The obtained yeast culture dry powder does not contain vancomycin residue after the culture and proper drying and smashing. Thus, the method not only solves the vancomycin residue problem in vancomycin fermentation residue and realizes the harm-free processing, but also can effectively cultures yeast and obtains a great deal of yeast protein with application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Antimicrobial methacrylate cements
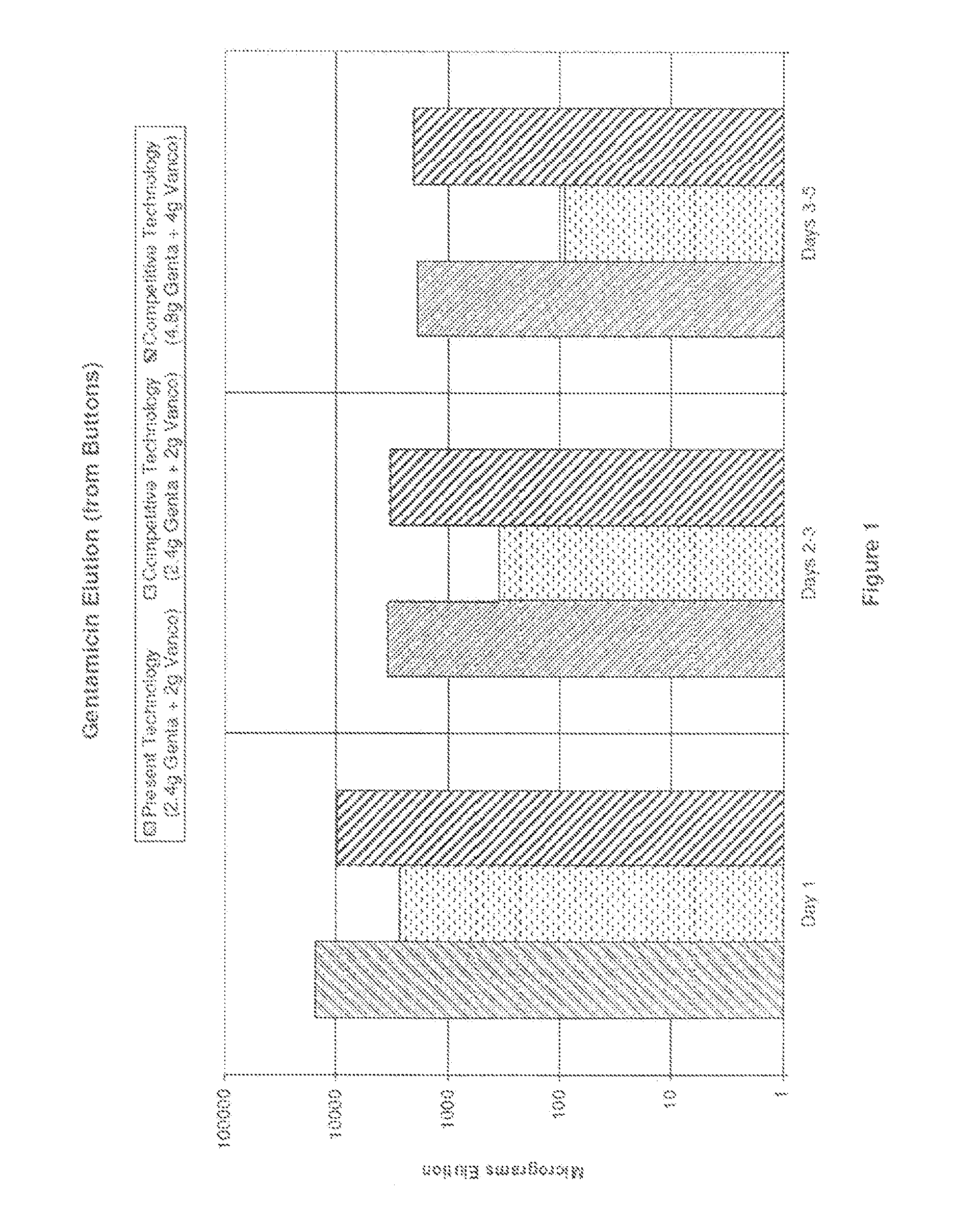
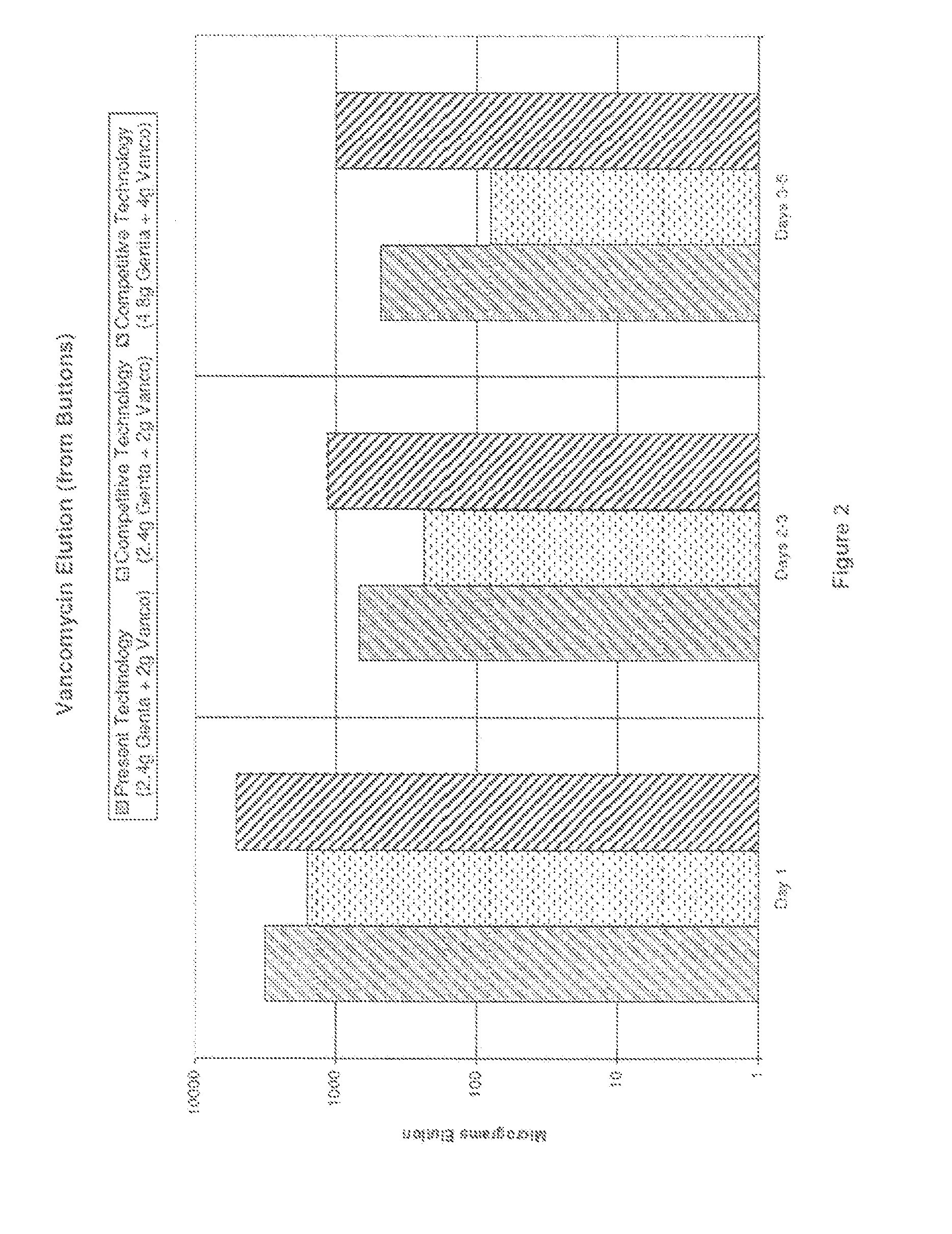
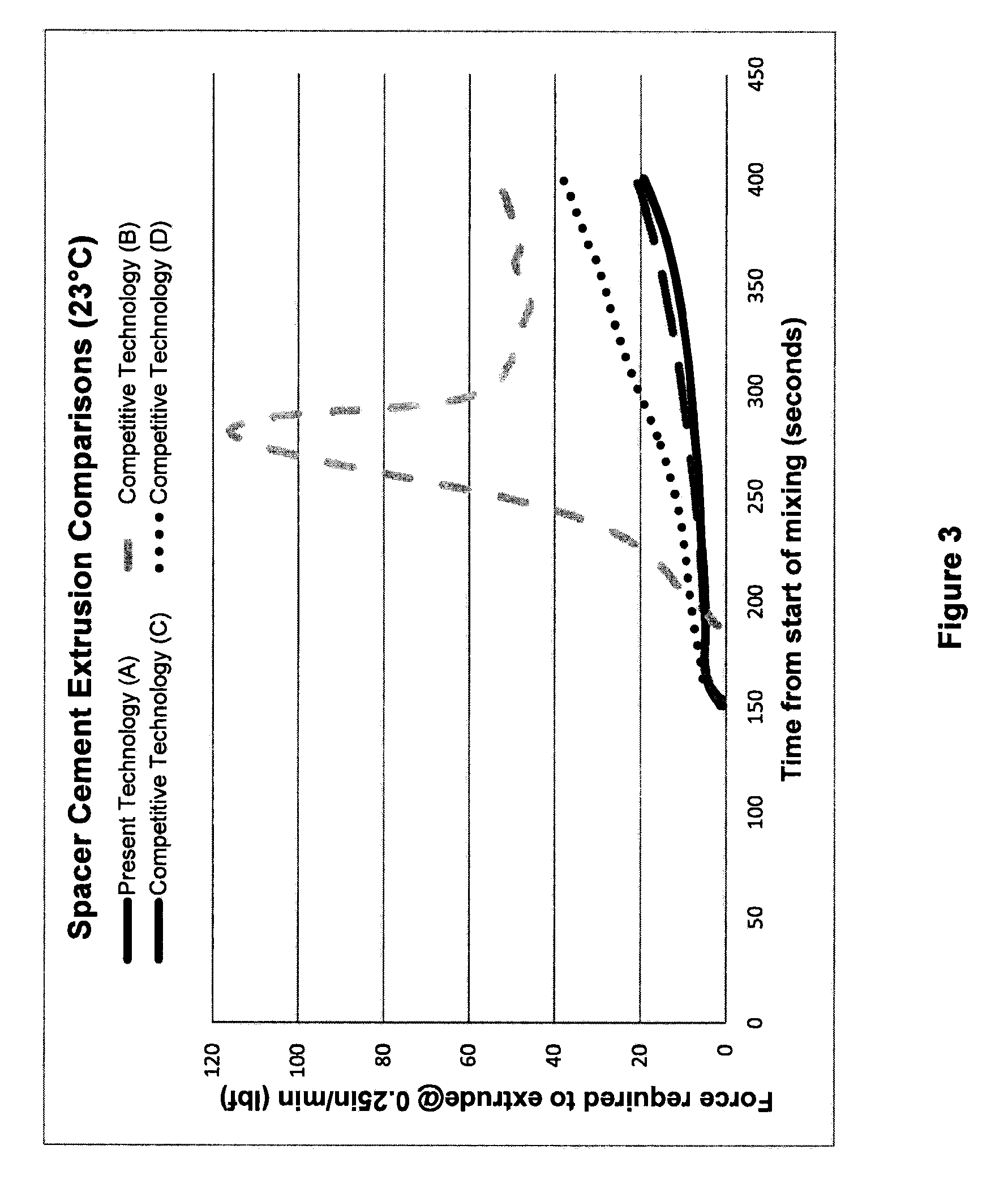
Bone cement compositions and methods of making two-part bone cements. The methods comprise transferring premixed powder and a liquid component into a receptacle, and mixing the powder component and the liquid component to form a cement composition. The premixed powder component comprises an acrylic polymer and a radical initiator. The bone cement is loaded with from about 5% to about 6% gentamicin by weight of the powder component, and from about 4% to about 5% vancomycin by weight of the powder component. The methods include filling a mold cavity with the bone cement composition to form a temporary spacer implant. The bone cement compositions provide a viscosity profile sufficient for the bone cement composition to flow within the mold cavity for an elapsed working time period of greater than about 6 minutes from the start of mixing at approximately 23° C.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Myrtucommulone R and application thereof in preparing antibacterial drug
ActiveCN106986852AStrong antibacterial activityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsANTU toxicityAntibacterial agent
The invention discloses Myrtucommulone R and application thereof in preparing antibacterial drug. Structure of phloroglucinol tripolymer Myrtucommulone R is shown as a formula I, and Myrtucommulone R is a new natural product. The compound even at low concentration has remarkable antibacterial activity to staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-intermediate-resistant staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococcus faecium and has quite low toxicity to eukaryocytes, indicating that the compound has good medicinal prospect and can be applied to preparing an antibacterial drug preparation. The antibacterial drug preparation contains Myrtucommulone R and the balance of medicinal auxiliary materials or other compatible drugs. The antibacterial drug preparation includes various clinical drug dosage forms.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
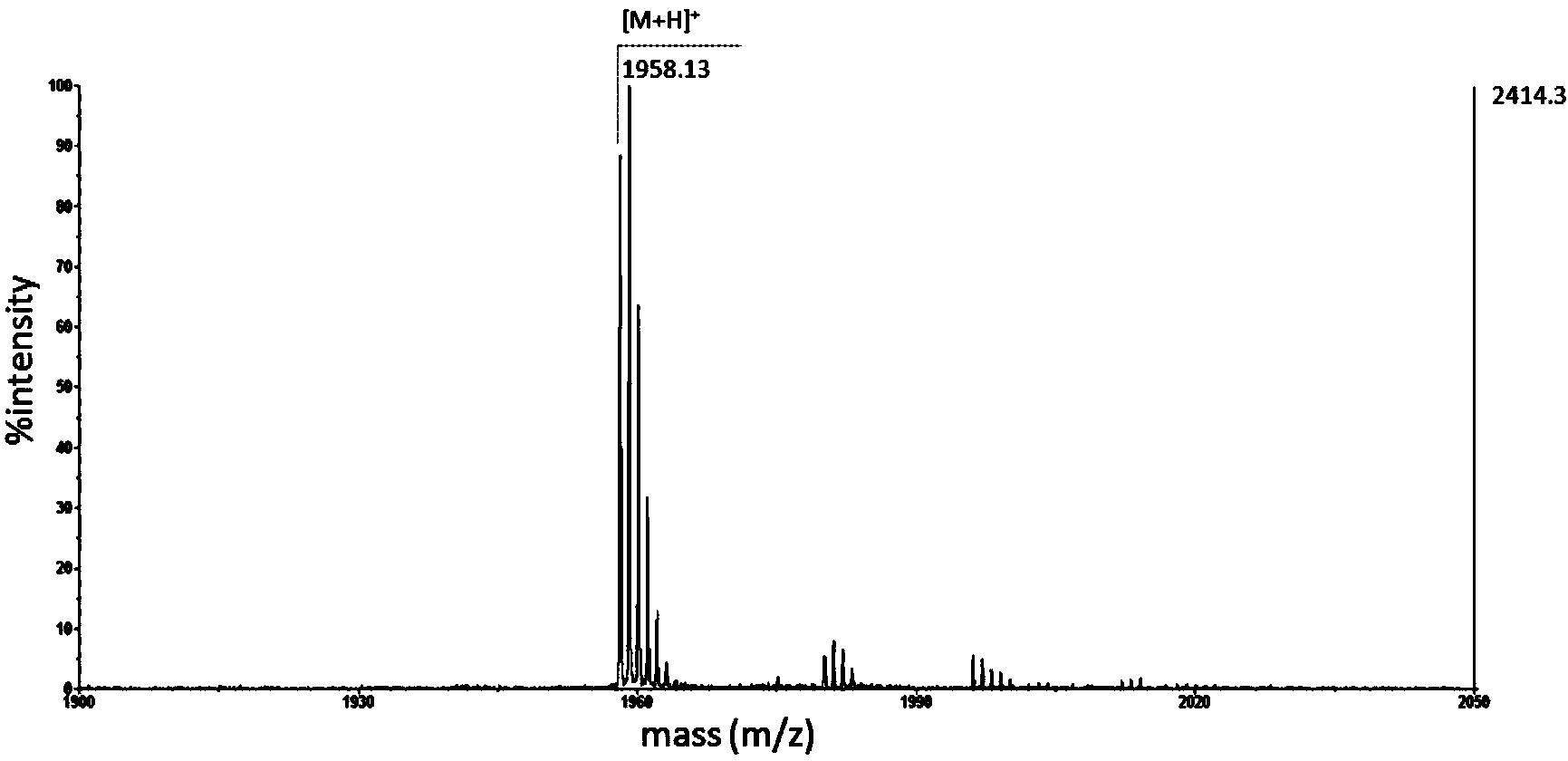
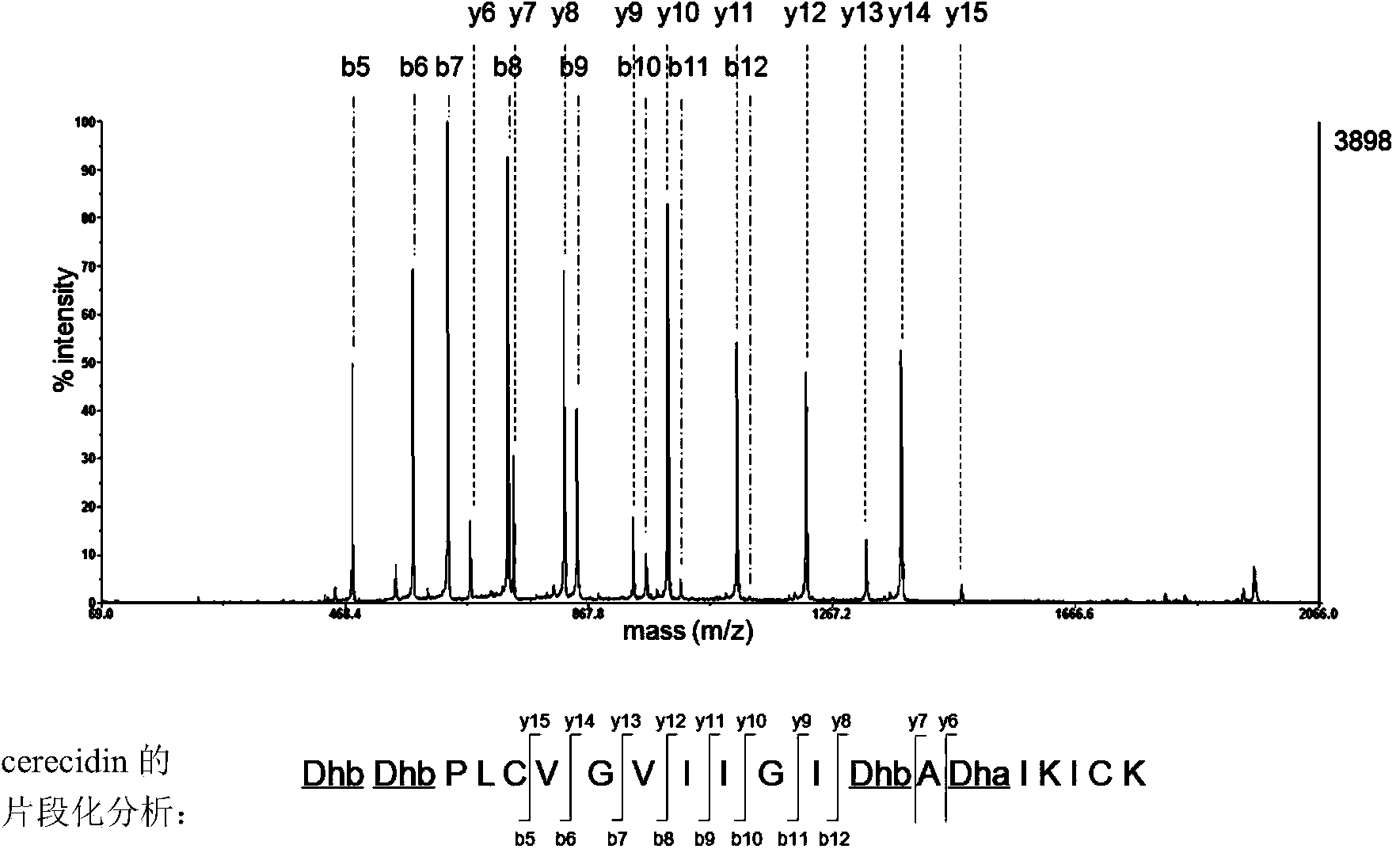
Novel effective cerecidin and application thereof
ActiveCN103483433AIncrease productionThe synthesis method is simpleAntibacterial agentsFungiAntibacterial activityVancomycin
The invention discloses novel effective cerecidin and an application thereof. The cerecidin disclosed by the invention is a modified polypeptide. A synthetic method of the cerecidin disclosed by the invention is simpler compared with the conventional method. Meanwhile, the synthesized cerecidin has relatively high antibacterial activity, the antibacterial effect of the cerecidin for resisting vancomycin enterococcus faecalis V583(VRE) is better than that of nisin, and under a relatively wide pH condition and a high temperature, the cerecidin is relatively stable.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
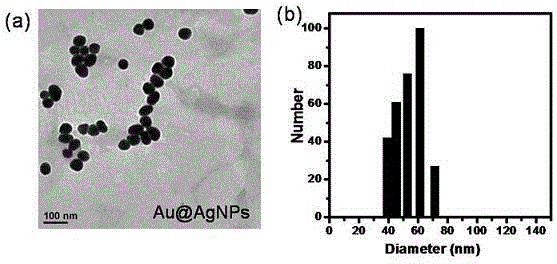
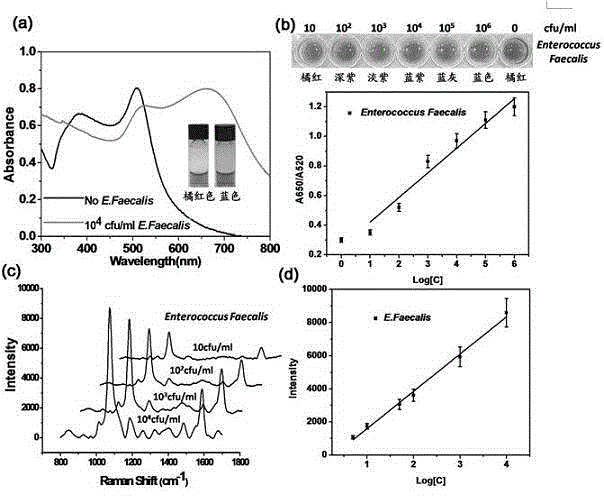
Universal type multi-signal output biosensor, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104807760AReduce the impactStrong specificityRaman scatteringColor/spectral properties measurementsDisulfide bondingComposite nanoparticles
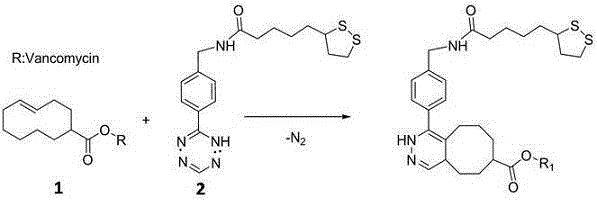
The invention discloses a universal type multi-signal output biosensor, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The universal type multi-signal output biosensor comprises two parts: a transcyclooctene modified vancomycin derivative used as a recognition molecule and functionalized gold and silver compound nanoparticles used as a signal conversion element, wherein the amino activated locus of the vancomycin molecule is covalently coupled with transcyclooctene; the gold and silver compound nanoparticles adopt silver shell-gold core compound nanoparticles; the surfaces of the gold and silver compound nanoparticles are simultaneously modified with a disulfide bond-containing tetrazine compound and a Raman microprobe molecule. The universal type multi-signal output biosensor can be applied to detection of Gram-positive pathogens, has the advantages of being high in efficiency, low in external environment influence, wide-spectral in targets and the like, and can meet the requirement of actual production and living.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
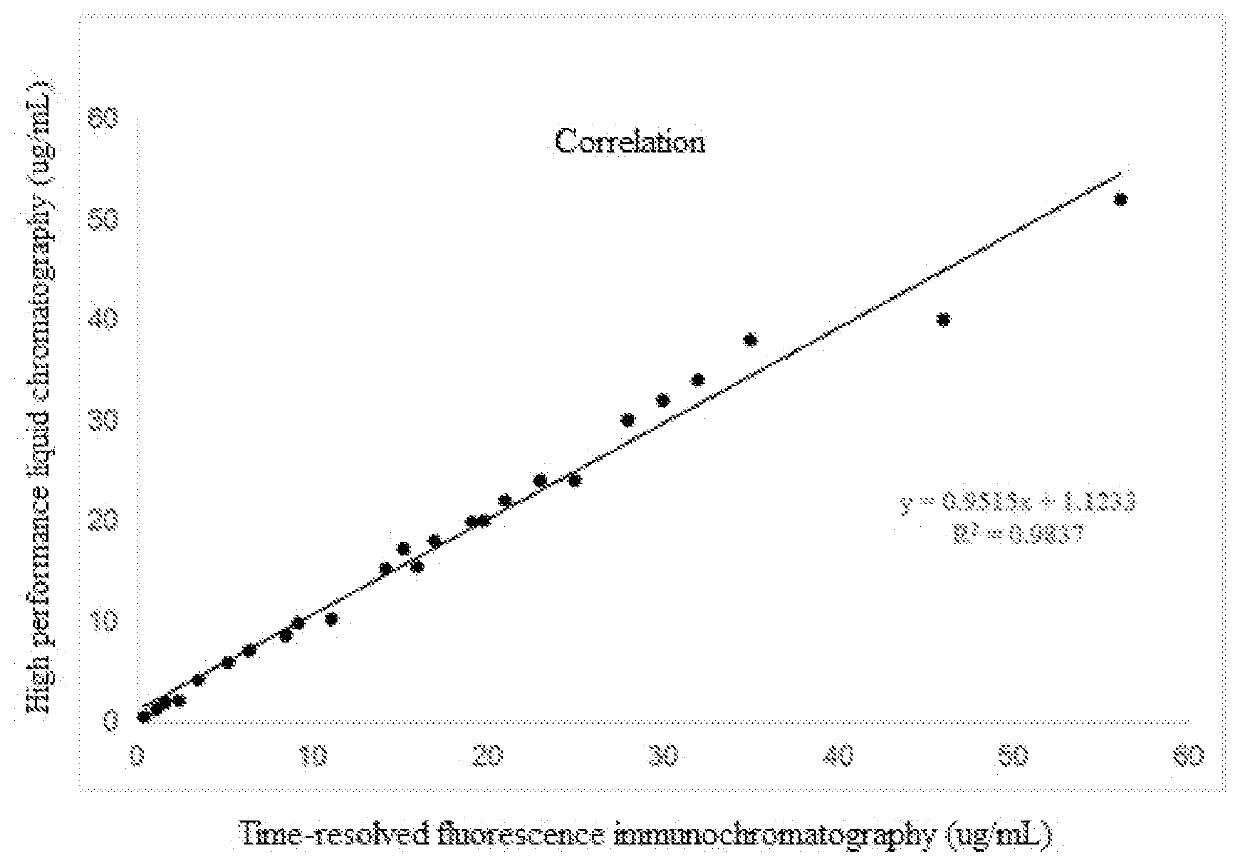
Time-resolved fluorescent immunochromatographic test strip for detecting vancomycin as well as preparation method and application thereof
Some embodiments of the disclosure provide a time-resolved fluorescent immunochromato-graphic test strip for detecting vancomycin as well as a preparation method and application thereof. In some embodiments, the test strip includes a bottom plate and a sample absorption pad. A fluorescent microsphere pad, a nitrocellulose membrane coated with a vancomycin-carrier protein conjugate, and an absorbent pad are sequentially overlapped and pasted on the bottom plate. The fluorescent microsphere pad is sprayed with a fluorescent microsphere-labeled vancomycin monoclonal antibody, and the vancomycin monoclonal antibody is prepared by using a vancomycin-bovine serum albumin conjugate as an immunogen.
Owner:BEIJING DIAGREAT BIOTECH CO LTD
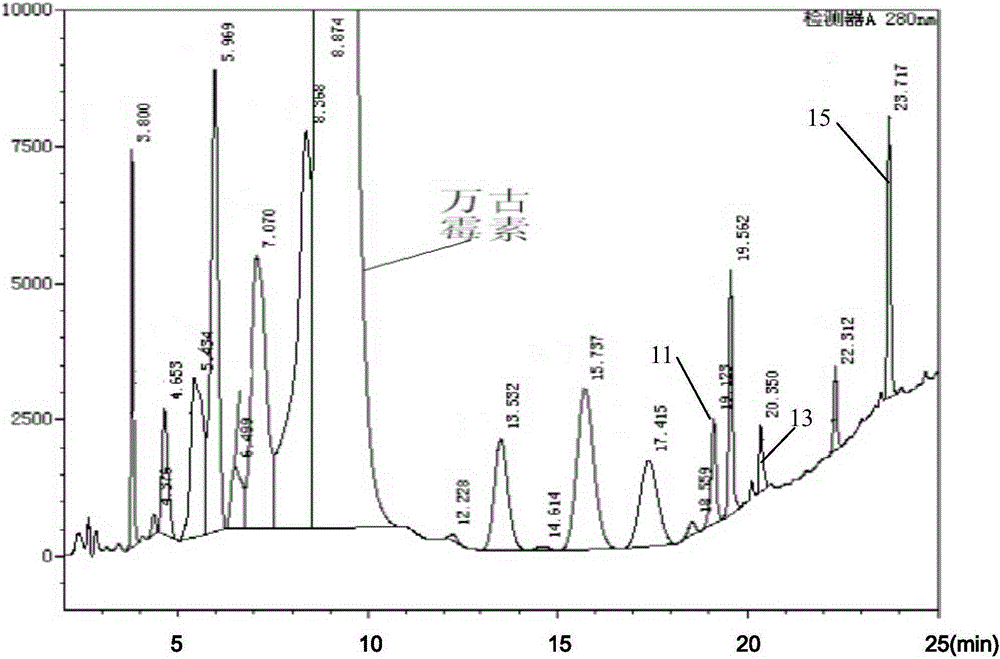
Preparation method of high purity samples of vancomycin hydrochloride impurities 11, 13, and 15
The invention discloses a preparation method of high purity samples of vancomycin hydrochloride impurities 11, 13, and 15. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a vancomycin hydrochloride water solution with a concentration of 60 to 70 g / L from vancomycin hydrochloride crystallized powder, adjusting the pH to 4-6, maintaining a constant temperature of 40 to 42 DEG C for 8 to 9 hours in water bath, adjusting the pH to 6-7, carrying out macroporous resin chromatographic enrichment, collecting the coarse product liquids (with impurities from 40 to 60%) of impurities 11, 13, and 15, subjecting the coarse product liquids to ultrafiltration and nano filtration in sequence, and desalinating the nano filtrate by a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) column to obtain the high purity samples of vancomycin hydrochloride impurities 11, 13, and 15. The technology is simple, and the preparation cost is largely reduced.
Owner:新方正控股发展有限责任公司 +2
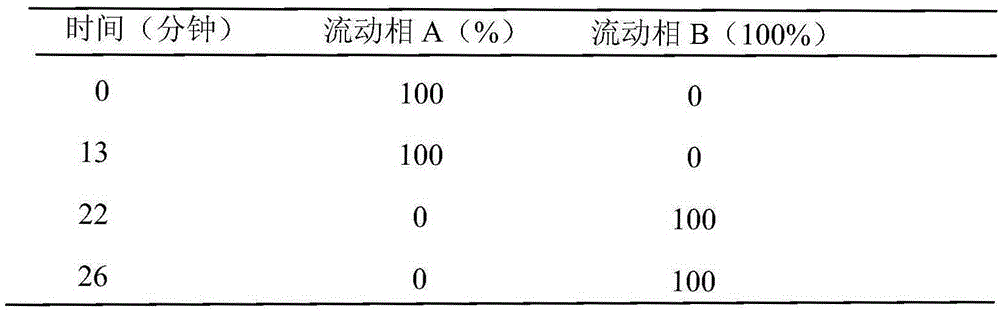
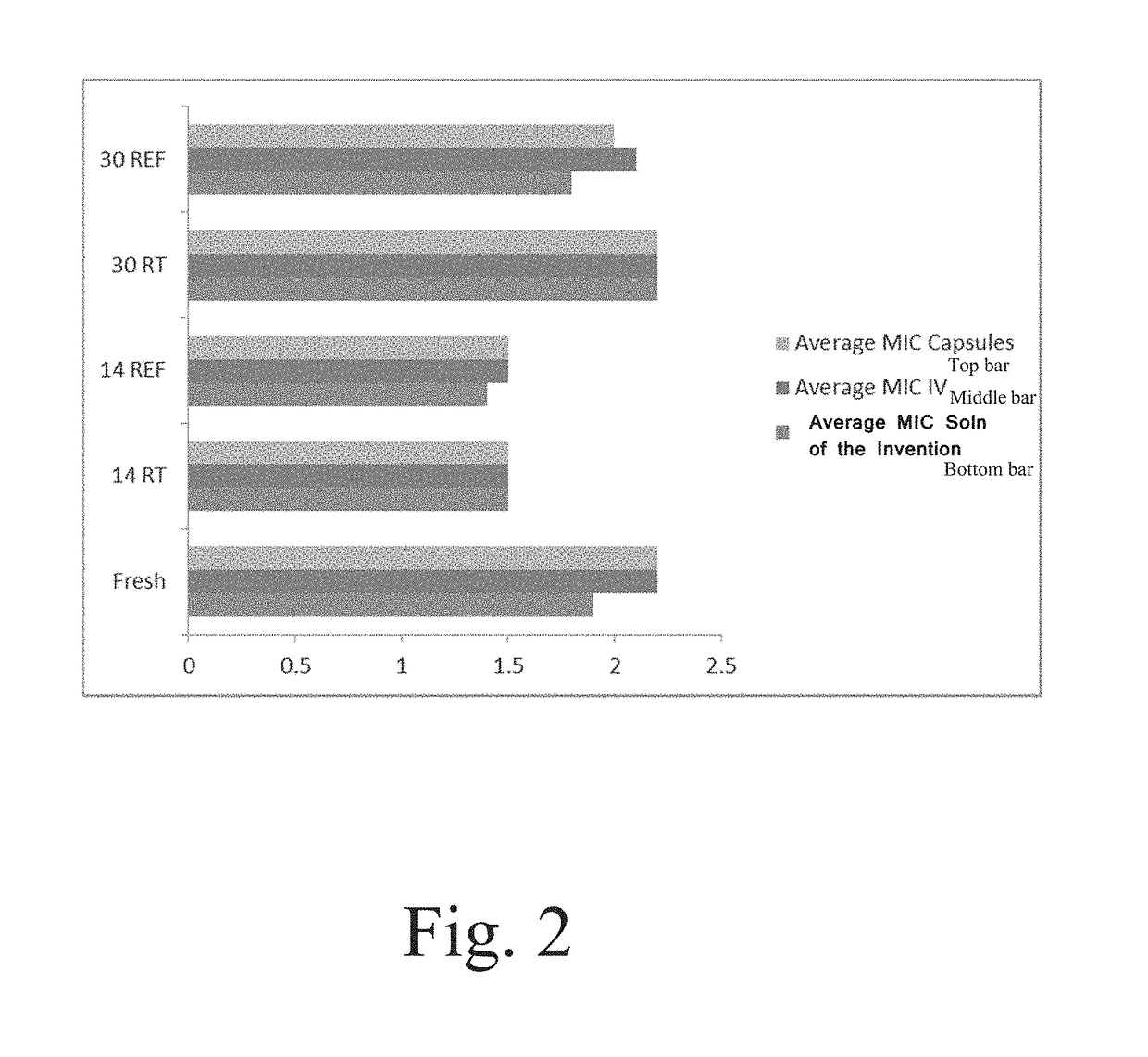
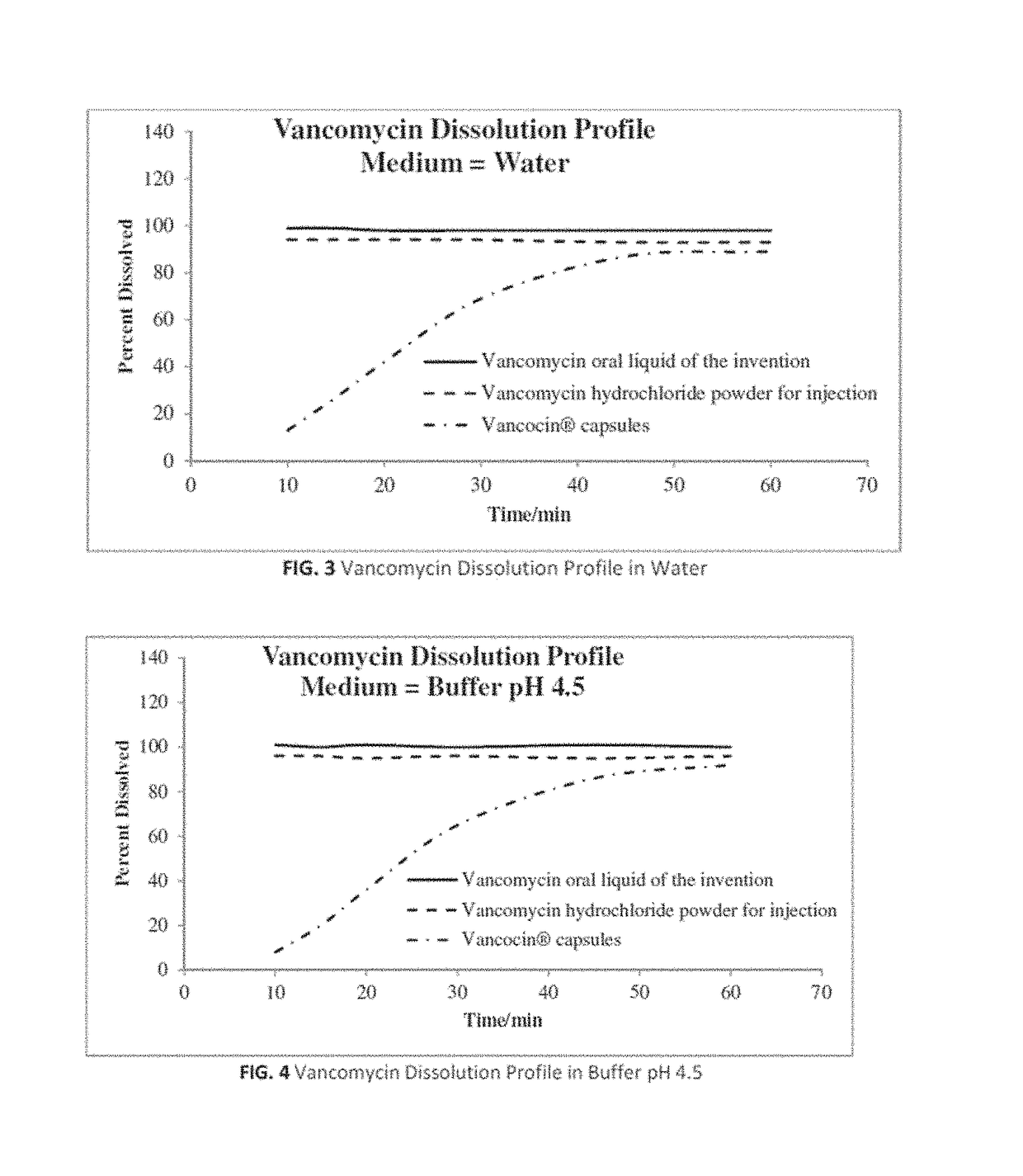
Composition and method for vancomycin oral liquid
Owner:AZURITY PHARMA INC
Mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis and process for preparing vancomycin hydrochloride
The present invention provides a process for preparing vancomycin hydrochloride using a mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P) comprising the steps of i) mutating and isolating a strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P) for producing vancomycin from mother strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. ATCC-19795) using NTG(N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine) in the selection medium; ii) seed culturing the isolated mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P); iii) cultivating and fermenting said mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis in the fermentation medium consisting of 12˜18 (w / v) % of dextrin, 2.2˜3.8 (w / v) % of bean powder, 1.9˜2.9 (w / v) % of potato protein, 0.10˜0.14 (w / v) % of sodium chloride and a small amount of minerals; iv) filtering vancomycin using microfilter in the cultivation broth by removing mycelia; v) purifying obtained vancomycin using column system compacted with cation exchange resin, anion exchange resin and absorbent resin; and vi) crystallizing the purified vancomycin with hydrochloric acid.
Owner:BIONGENE
Reagents and methods for the detection and quantification of vancomycin in biological fluids
InactiveUS20080206788A1Interference be notImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHybrid cell preparationFluoresceinTest sample
Immunoassay reagents, methods and test kits for the specific quantification of vancomycin in a test sample are disclosed. The reagent comprises antibodies prepared with immunogens of FIG. 6 wherein P is an immunogenic carrier material and X is a linking moiety.Also described is the synthesis of labeled reagents of FIG. 8 wherein Q is a detectable moiety, preferably fluorescein or a fluorescein derivative, and X is a linking moiety.
Owner:ADAMCZYK MACIEJ +3
Pre-mixed, ready to use vancomycin compositions
InactiveUS20200188478A1Inorganic non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismVancomycinumMedical waste
Pre-mixed, ready-to-use injectable compositions possess certain advantages such as convenience and ease of use as compared to an ampule formulation, improved safety for patients due to elimination of dosage errors and solution contamination, reduction of medical waste, and ease of administration in emergency situations. Pre-mixed, ready-to-use Vancomycin injectable preparations though marketed have numbers of disadvantages which makes its handling and use difficult. The present invention therefore provides pre-mixed, ready-to-use injectable formulations of Vancomycin which eliminates disadvantages and difficulties of the marketed product and at the same time maintains desired stability for prolonged time.
Owner:FTF PHARMA
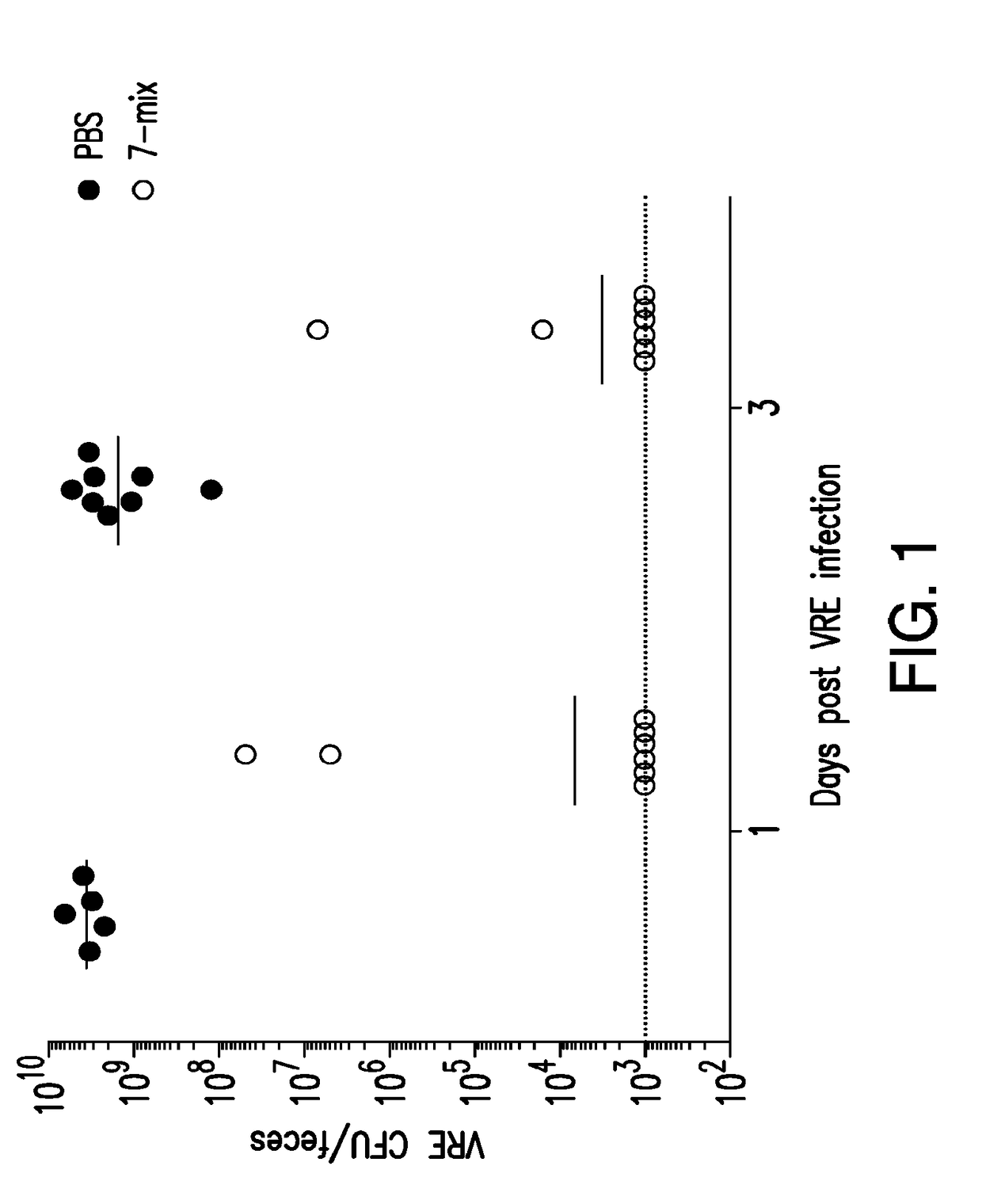
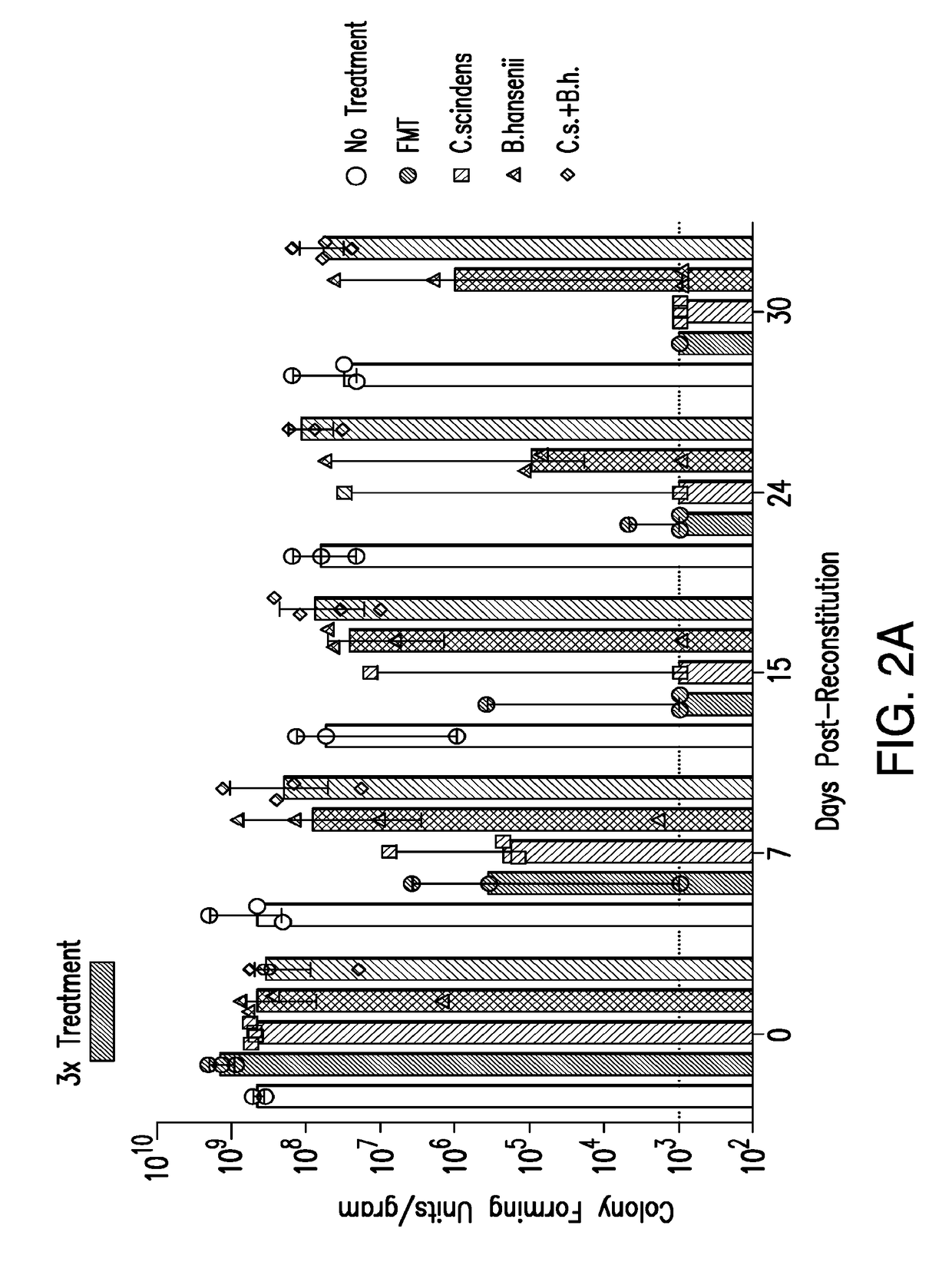
Methods and compositions for reducing vancomycin-resistant enterococci infection or colonization
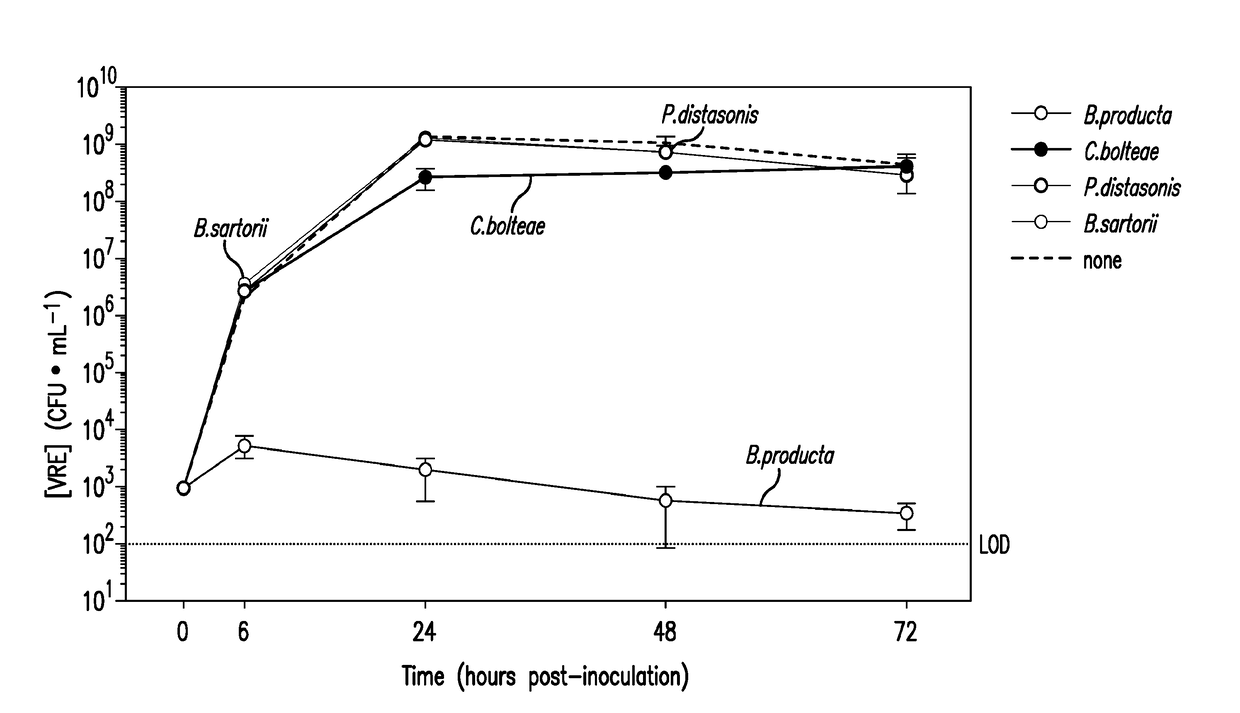
ActiveUS20180256653A1Reduce riskImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing the risk and severity of vancomycin-resistant Enterococci infection or colonization. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that a restricted fraction of the gut microbiota, including the bacteria Clostridium scindens and / or the bacteria Blautia producta contribute substantially to resistance against vancomycin-resistant Enterococci infection or colonization. Without being bound by any particular theory, it is believed that this is achieved through the biosynthesis of secondary bile acids in the case of Clostridium scindens.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Vancomycin formulations having reduced amount of histamine
InactiveUS20070105757A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRed Man SyndromeHistidine decarboxylase
Vancomycin composition treated to remove histamine and a method of removing histamine from vancomycin. The invention also includes an isolated polynucleotide sequence including an isolated polynucleotide sequence of histidine decarboxylase from Amycolatopsis orientalis. The vancomycin composition of the present invention is used to redue the incidence of Red Man Syndrome, phlebitis, and hypotension.
Owner:HOSPIRA
Porous Ti-based nano-composite material for hard tissue material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108404222AGood dispersionImprove bindingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingTissue regenerationDispersityRelease time
The invention provides a porous Ti-based nano-composite material. The porous Ti-based nano-composite material comprises a porous Ti-based material, a hydroxyapatite layer composited on the porous Ti-based material, and chitosan-vancomycin composited on the hydroxyapatite layer. The porous Ti-based nano-composite material is capable of, through the porous Ti-based material, reducing or eliminatinga 'stress shielding' effect, and has a stronger binding force. The provided porous Ti-based nano-composite material is further provided with the chitosan-vancomycin composited on the outer surface, the porous Ti-based nano-composite material and the chitosan-vancomycin are combined for greatly solving problems that infection is easy suffered after an osteogenesis transplantation operation at the present stage, inflammation or function degeneration of a transplant are caused so that the transplantation is failure, a binding force problem is existent and drug controlled-release time is short. The provided porous Ti-based nano-composite material is capable of using a porous structure to combine a HAp, a chitosan-functionality drug, and a combined composite coating better, and better in dispersity, and stronger in binding force. The controlled-release time is apparently improved, and the long-term anti-bacterial effect is achieved.
Owner:湖南早晨纳米机器人有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com