Compositions and methods for characterizing and restoring gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota
a technology of applied in the field of compositions and methods for characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin and nasal microbiota, can solve the problems of insufficient explanation, insufficient explanation, and insufficient explanation of gerd and its related conditions, so as to facilitate calorie uptake, inhibit the growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and reduce weight gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Analysis of Gastrointestinal Microbiota of Mice Treated with Sub-Therapeutic Levels of Antibiotics and Associated Metabolic Effects
Animals
1. Mouse Species
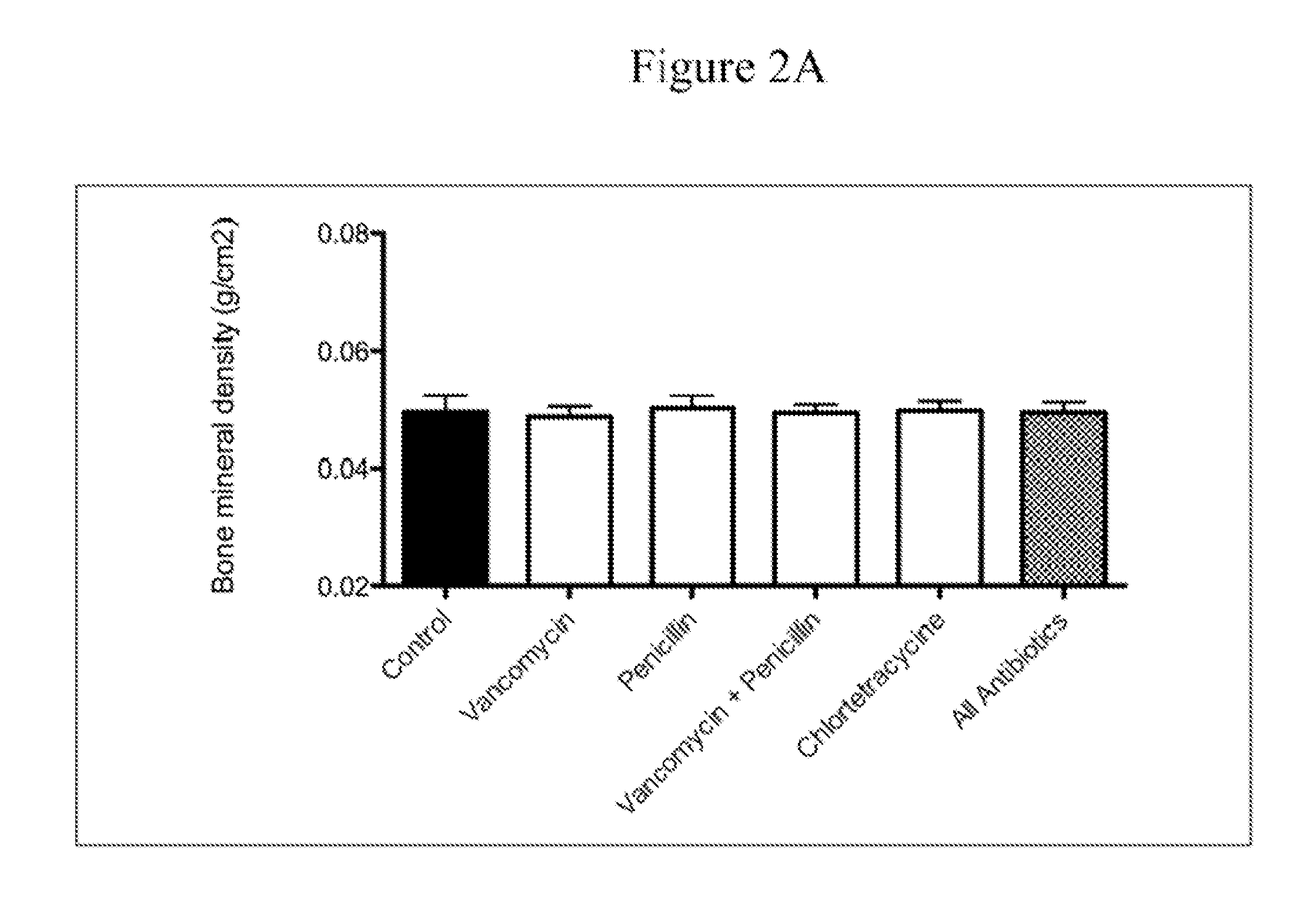
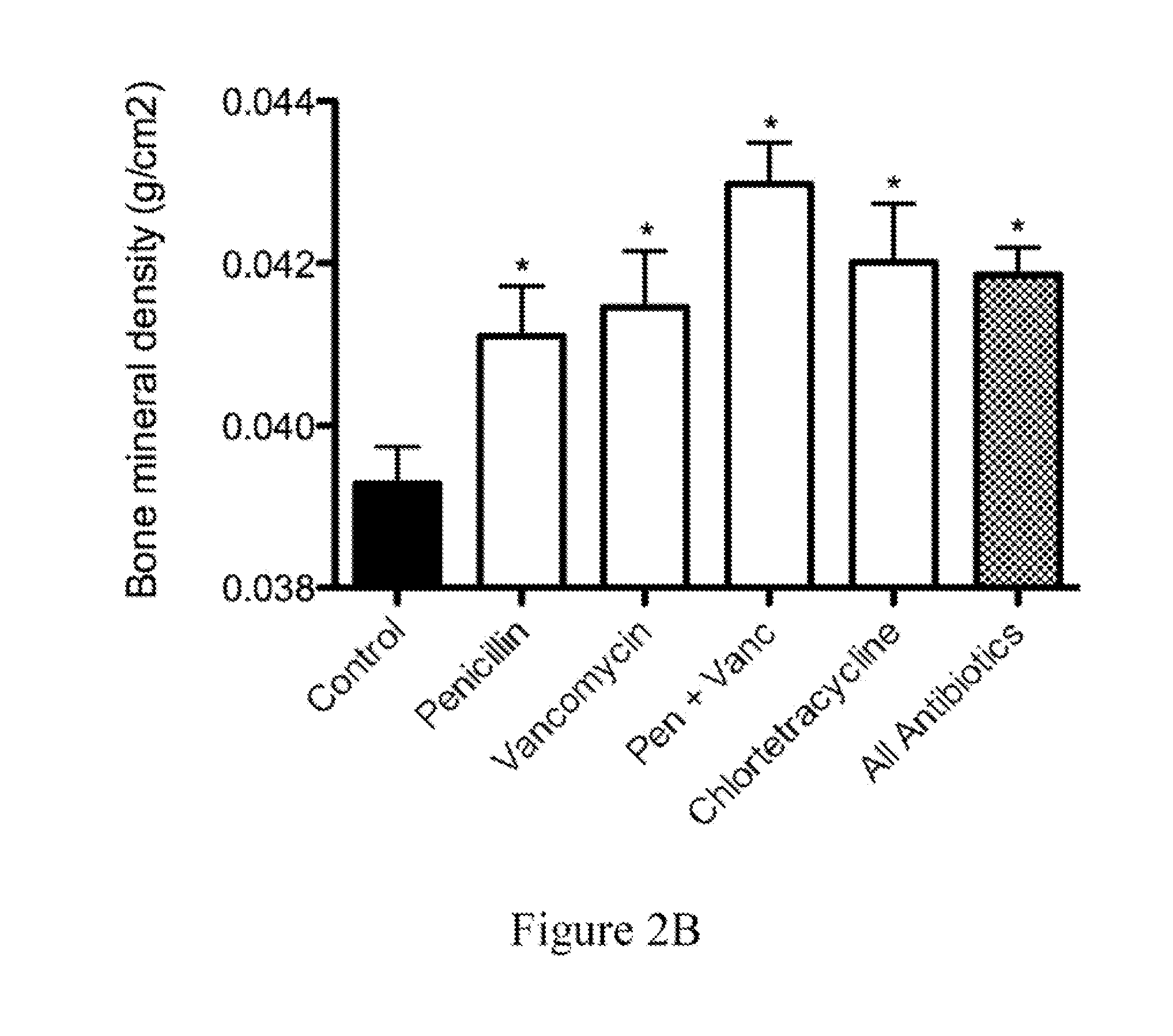
[0120]C57 / B6 mice were obtained at weaning (21 days) from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, Me.). They were weighed and then distributed in cages so that the mean weights of the mice in each cage were equal. The mice were then allowed to adjust to the NYU animal facility. At day 23 of life, the antibiotic-exposure experiment began. Animals were allowed ad libitum access to food and water and maintained with a 12-hour light / dark cycle. The mice were fed standard laboratory chow (Purina Mills International Diet # 5001). These conditions were continued until the time of sacrifice.
2. Treatment Groups
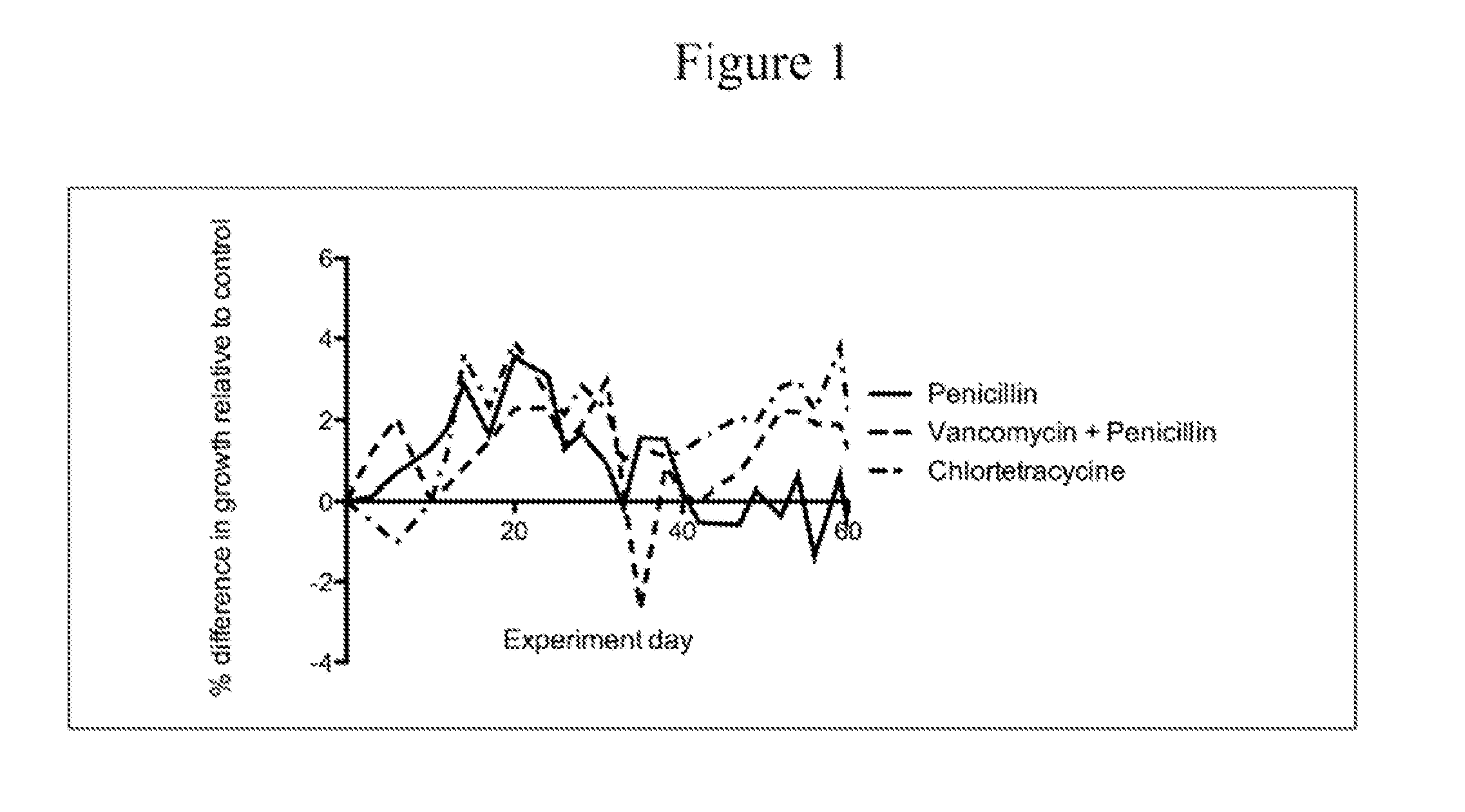
[0121]Mice were given standard water (pH 6.8) or water containing the following antimicrobial agents (at sub-therapeutic levels) in groups of 5-10 mice per experimental condition.
TABLE 2ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS STUDIEDDosageAntimicrobialAntimic...
example 2
Adjusting Cutaneous Microbiota to Treat MRSA Infection
[0147]This Example pertains to adjusting cutaneous microbiota. Adjusting cutaneous (i.e., skin) microbiota is helpful to prevent or treat such conditions as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. Opportunistic bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), are not only affecting patients who have been hospitalized, and / or recently received antibiotics, but also are causing infections in individuals who are perfectly healthy and who have not had any of the high-risk exposures. It is proposed that opportunistic bacteria, such as MRSA, can colonize and cause infections in such hosts due to the loss of indigenous microbiota due to prior antibiotic use, that could have been remote in time. An approach to this problem is to determine the nature of the missing bacteria and restore their populations by providing the bacteria, bacterial analogues, or prebiotics.
[0148]To determine the missing (...
example 3
Adjusting Gastrointestinal Microbiota to Treat C. difficile Infection
[0151]Another opportunistic pathogen is Clostridium difficile, which has been spreading greatly in hospitalized patients, especially those receiving antibiotics (McDonald et al., N. Engl. J. Med. 2005). Therapeutic and prophylactic approaches already are in use with specific Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species (Fuller, J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1989, 66: 365-378). However, it is not clear that these populations have really been lost, are native to the adult human colon, and not surprisingly they have only minimal and not reproducible efficacy. Improved approaches are necessary.
[0152]An approach that parallels Example 2, as applied to fecal samples is proposed. The relevant comparison is between the fecal samples of patients with C. difficile infection and fecal samples of age- and gender-matched healthy controls. The above-described approach would be used (Example 2) to identify the consistently missing organisms i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com