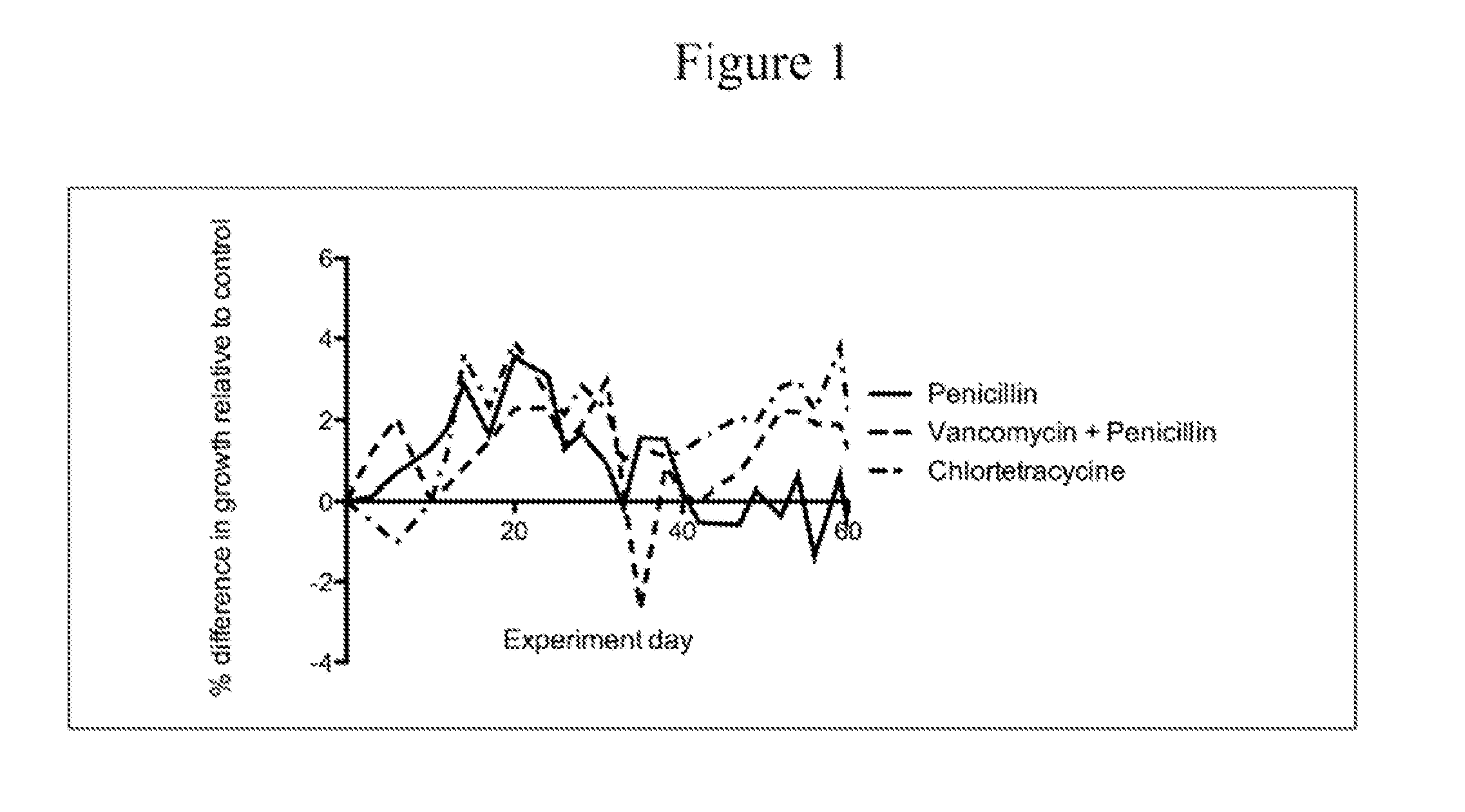
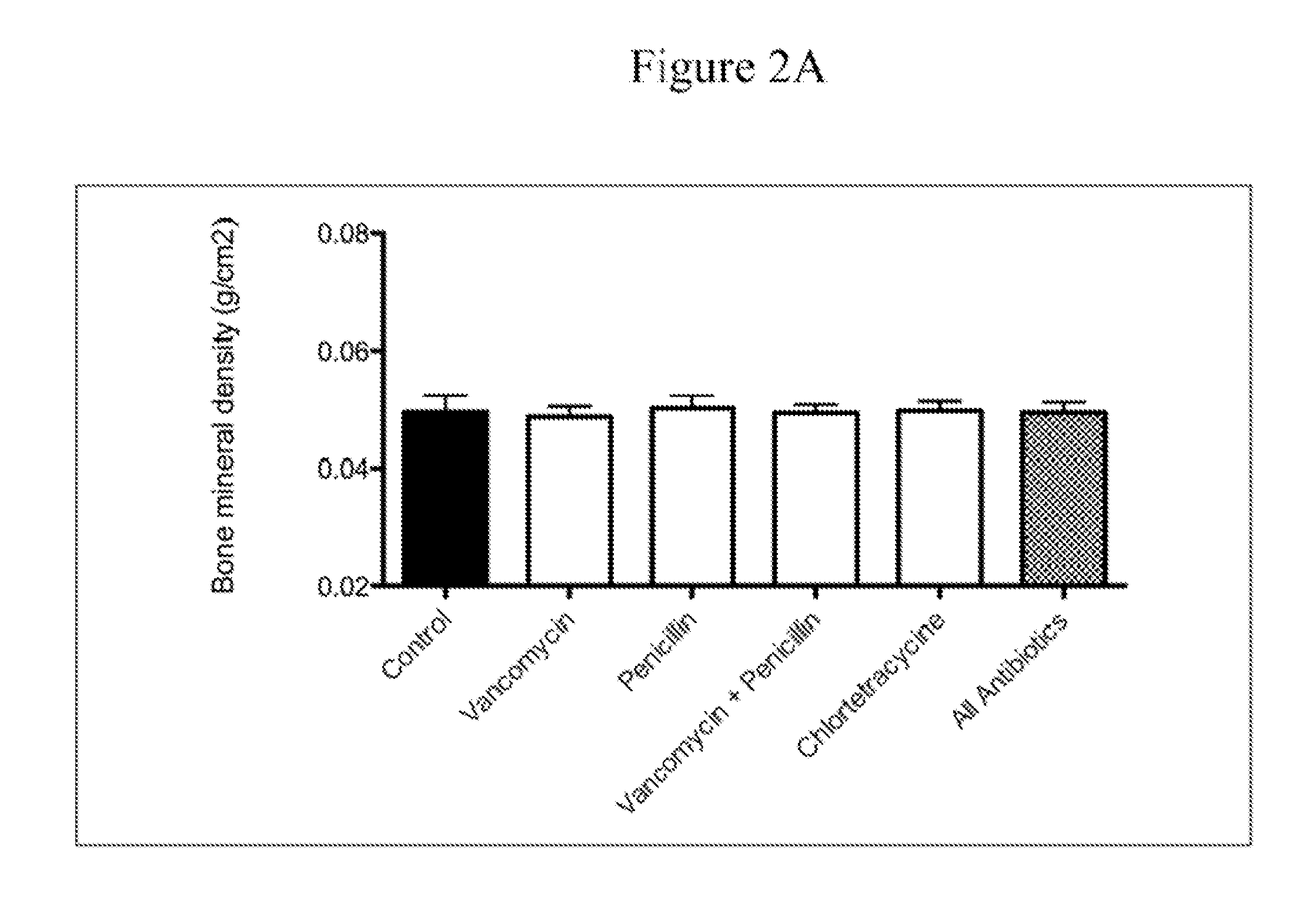
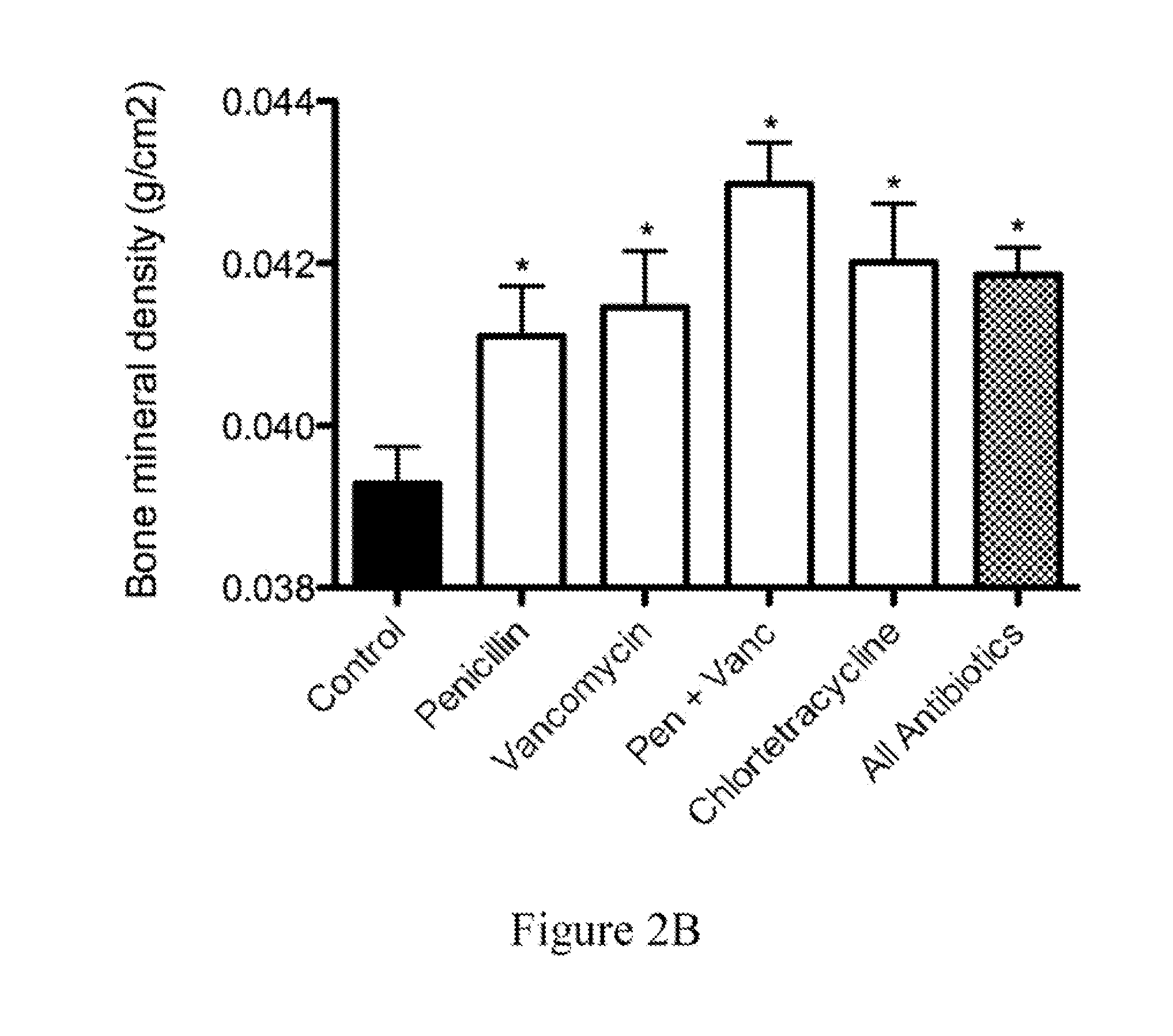
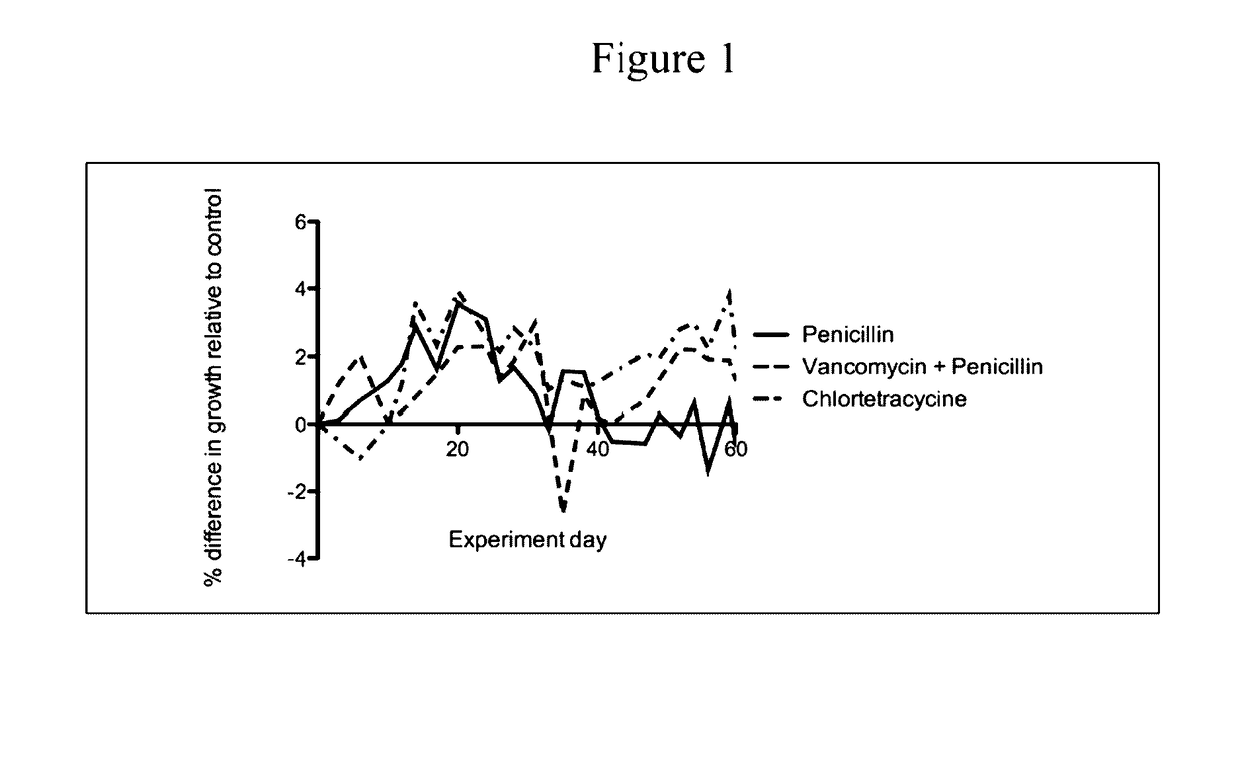
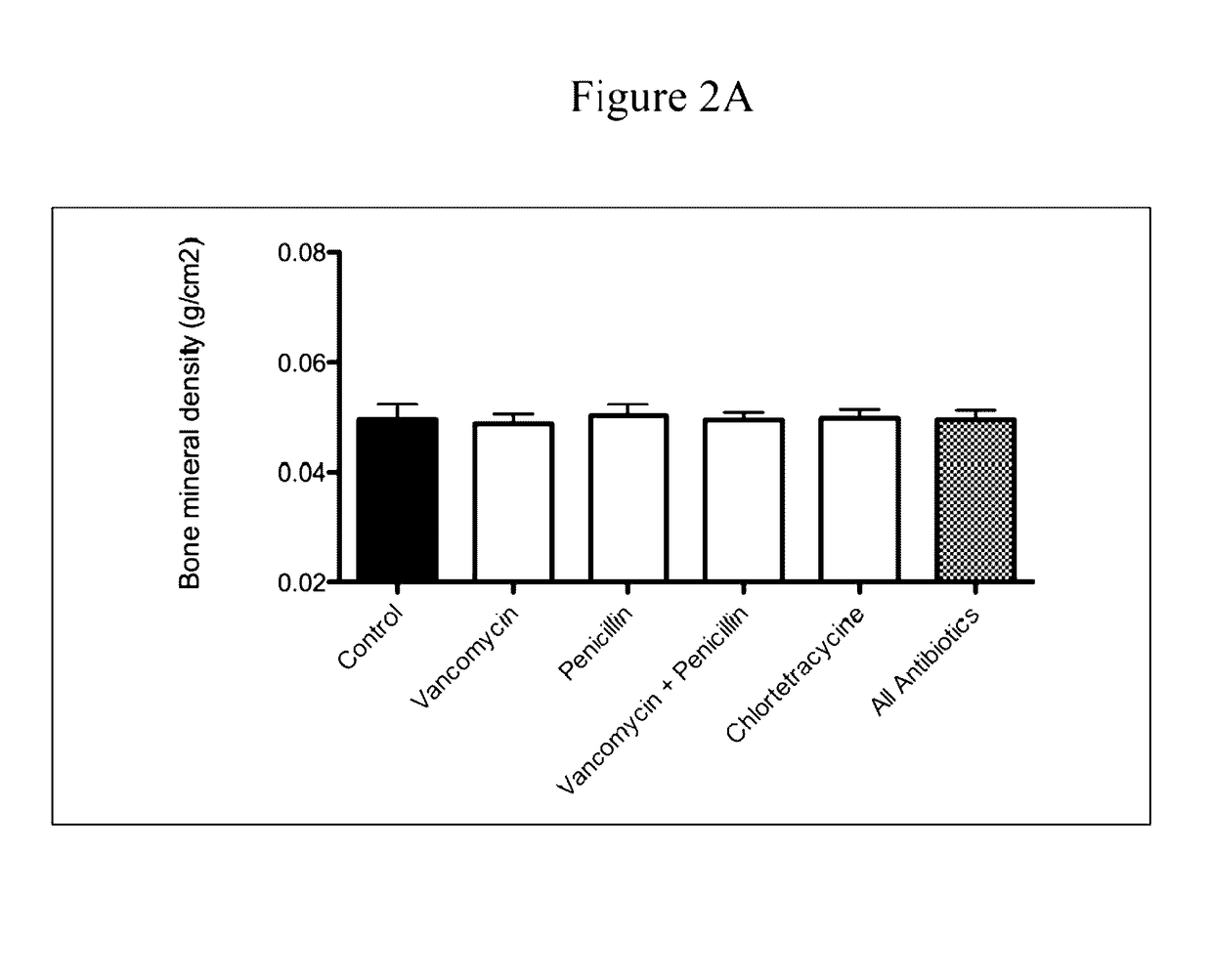
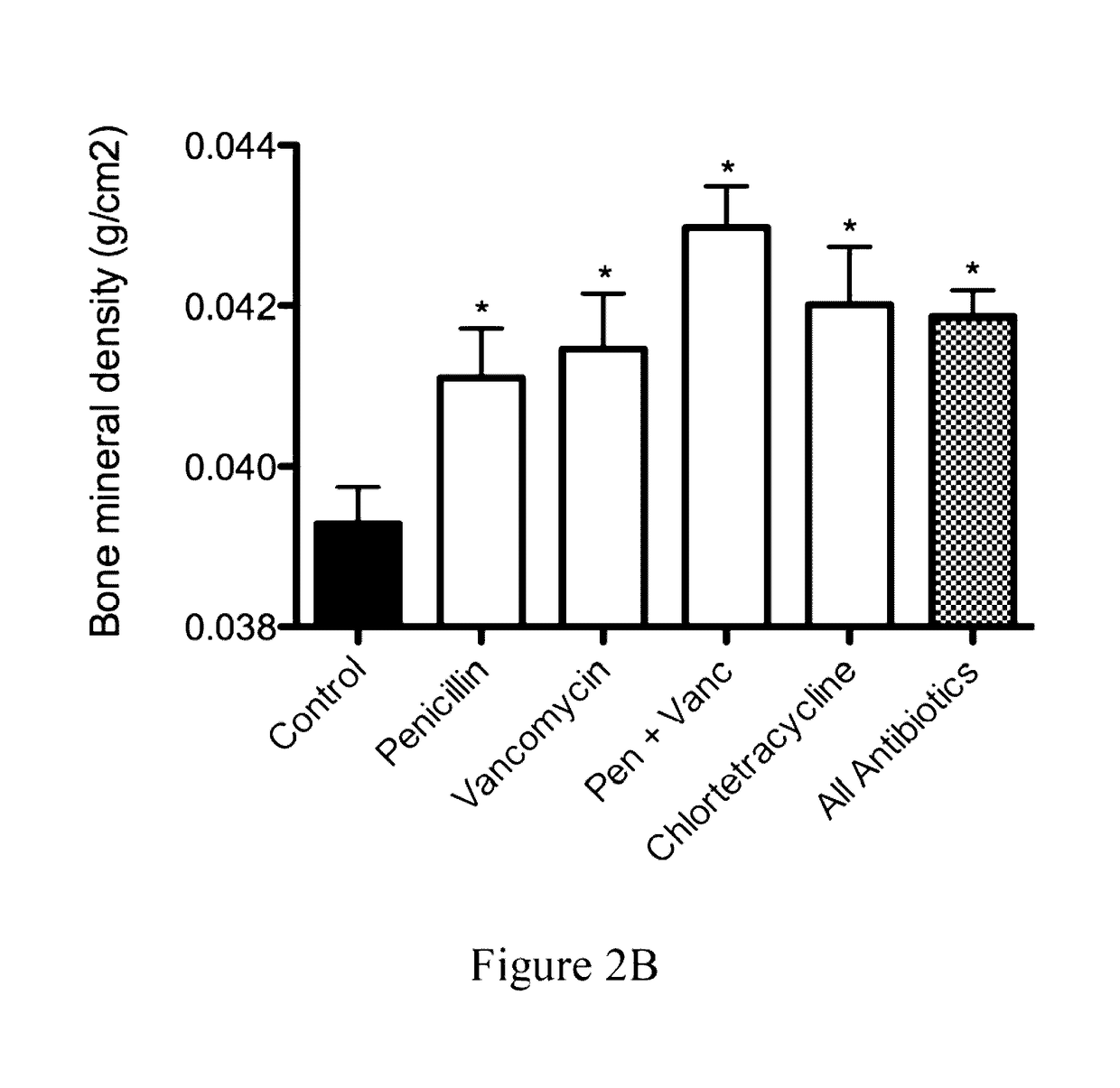
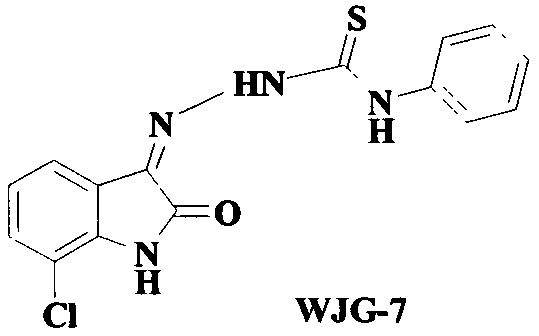
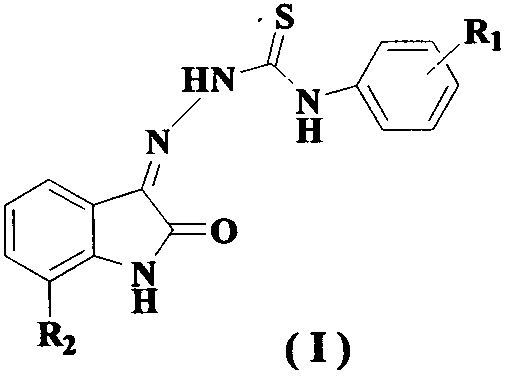
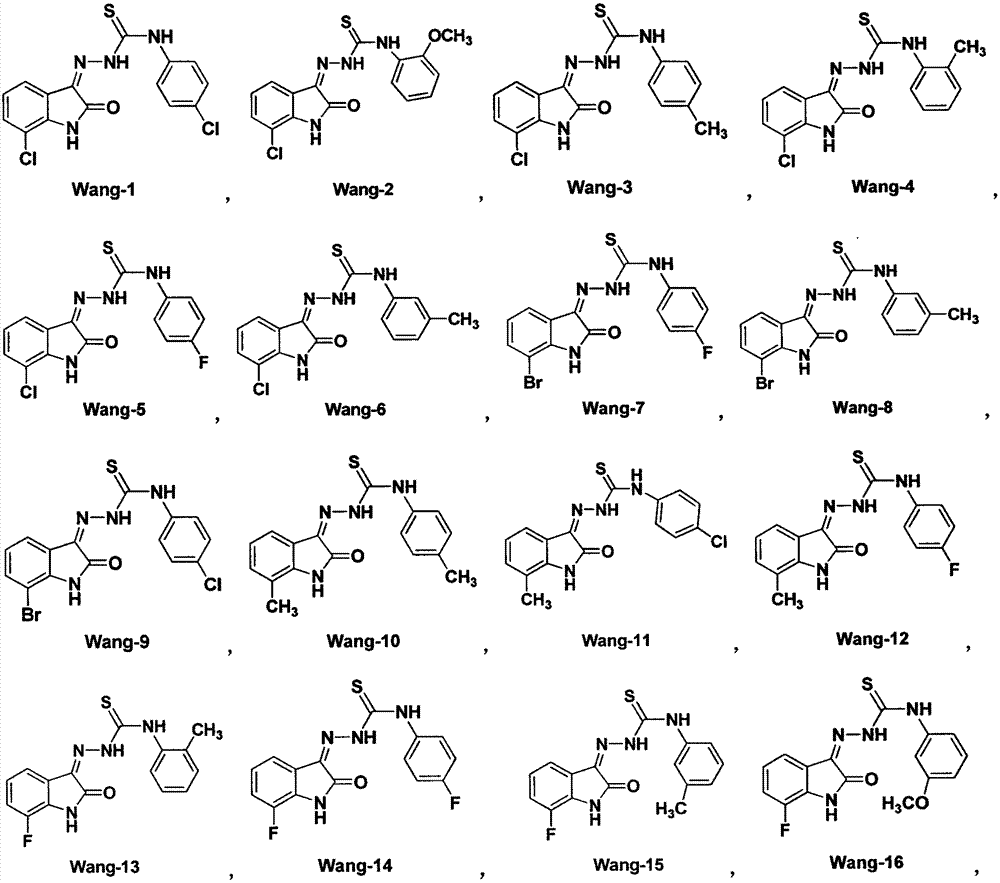
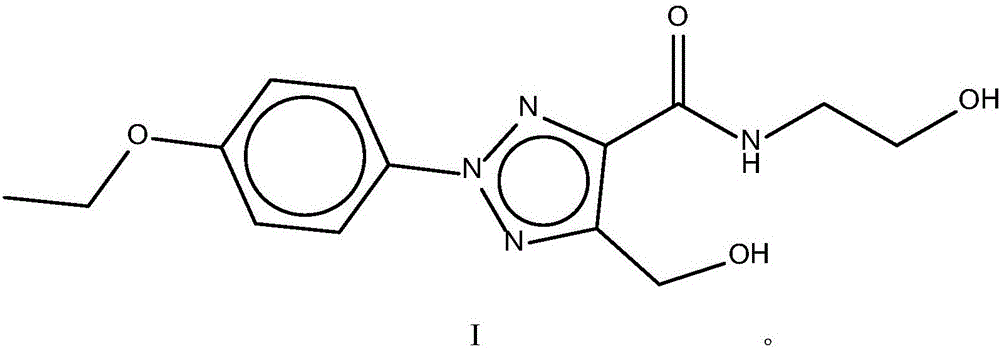
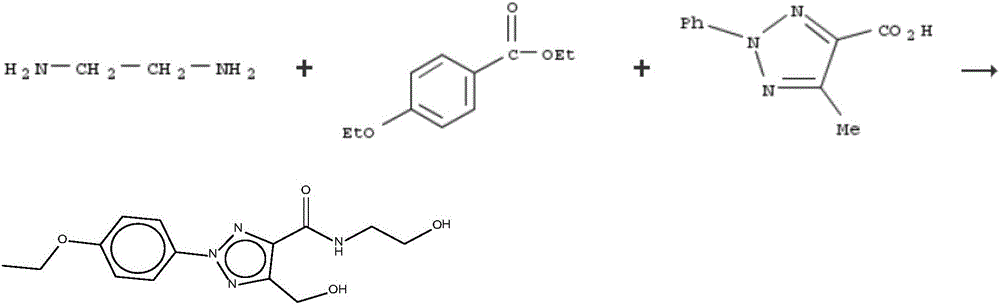
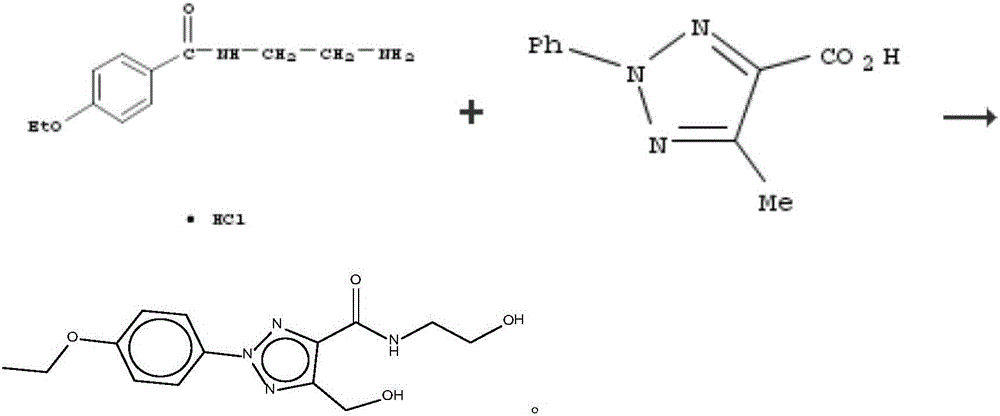
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods for characterizing and restoring gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota
ActiveUS20100074872A1Growth inhibitionFacilitate calorie uptakeBiocideMetabolism disorderBacteroidesDisease
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated with antibiotic treatment and various disease conditions (such as asthma, allergy, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), eosinophilic esophagitis, gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinomas (GEJAC), infections due to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, etc.) and related diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of live bacterial inoculants that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Compositions and methods for restoring gastrointestinal microbiota following antibiotic treatment
ActiveUS9603876B2Increase the number ofGrowth inhibitionBiocideMetabolism disorderDiseaseIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated with antibiotic treatment and various disease conditions (such as asthma, allergy, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), eosinophilic esophagitis, gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinomas (GEJAC), infections due to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, etc.) and related diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of live bacterial inoculants that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
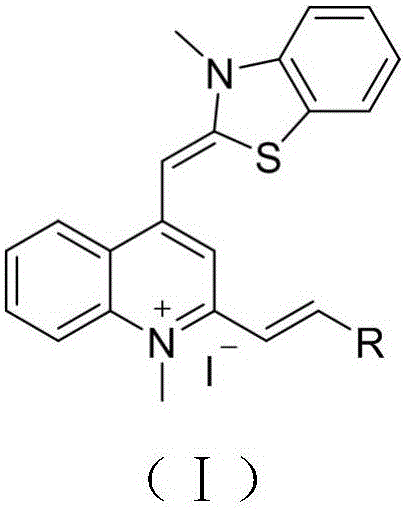
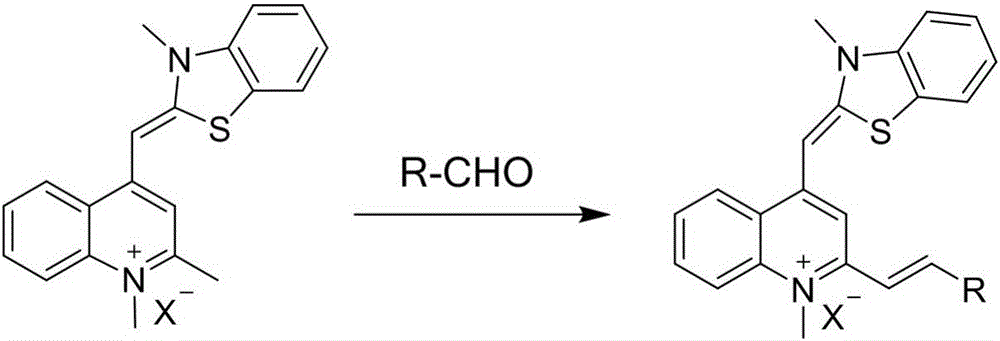
Thiazole orange styrene derivative, method for preparing same and application of thiazole orange styrene derivative to preparing medicines capable of resisting medicine-resistant bacteria
ActiveCN106188031AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaSide effect
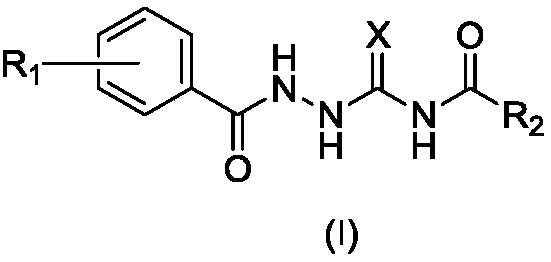
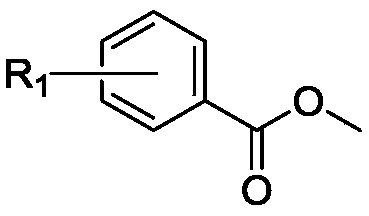
The invention belongs to the field of novel medicines and compounds, and discloses a thiazole orange styrene derivative, a method for preparing the same and application of the thiazole orange styrene derivative to preparing medicines capable of resisting medicine-resistant bacteria. The thiazole orange styrene derivative is of a structure shown as a formula (I). An R in the formula is defined as an instruction book. The method includes carrying out condensation reaction on thiazole orange analogues and different types of aromatic aldehyde to obtain the thiazole orange styrene derivative. The thiazole orange styrene derivative, the method and the application have the advantages that the method is simple, and raw materials for the thiazole orange styrene derivative are easily available; excellent interaction between the thiazole orange styrene derivative and bacterium division proteins FtsZ can be realized, and accordingly reproduction of diversified medicine-resistant bacteria such as vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus can be inhibited; the thiazole orange styrene derivative is little in toxic and side effect and has a prospect of being developed to obtain novel antibiotic medicines.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Macrocyclic polymorphs, compositions comprising such polymorphs and methods of use and manufacture thereof
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Oligonucleotides, methods and kits for detecting and identifying vancomycin-resistant enterococcus
InactiveUS20120171681A1Quick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersVancomycin-Resistant Enterococci
The present invention relates to methods for detecting the presence or absence of vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE) in a sample using a multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mtx-PCR) assay. Furthermore, the present invention relates to oligonucleotide primers and kits for the detection of VRE.
Owner:TAAG GENETICS
Method for detecting the presence or absence of pathogenic Staphylococci in a test sample, including test mixture with micro particles
InactiveUS8546103B2Favorable source of coagulase substrateImprove performance consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiFirst generation
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
Antibacterial Macrolactin A that bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 produced in
InactiveCN101636501AShow broad-spectrum antimicrobial activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryMicroorganismAntibiotic Y
The present invention relates to uses of Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 (KCCM 10769P), which is a new bacillus strain, as an antibiotic. Macrolactin A of the present invention, which is produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, shows a broad spectrum of antibiotic activity against a variety of microorganisms and fungi, and is proved to be very efficient for the inhibition of particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) that are multidrug-resistant bacteria. The antibiotic Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, can be used as an excellent antibiotic against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), and thus the present invention is a very useful invention for medical industry.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
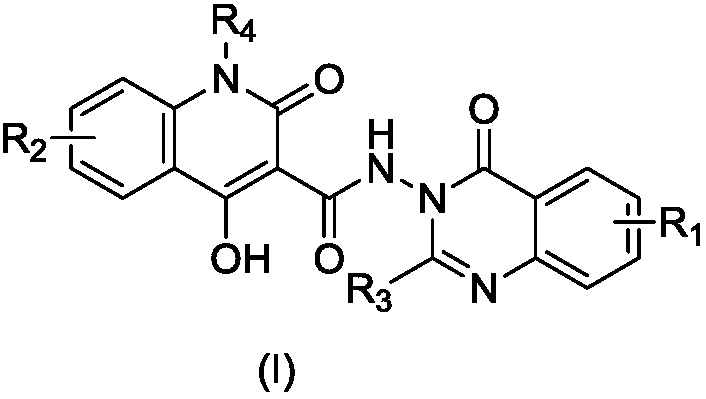
4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-nitrogen-(4-quinazolinone)-3-formamide derivatives
ActiveCN110041306AAddressing drug resistanceEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidisQuinazolinone
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibacterial drugs and relates to 4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-nitrogen-(4-quinazolinone)-3-formamide derivatives as well as a preparation method and an application thereof as an antibacterial drug. The compounds are shown in a formula (I), wherein R1 is selected from hydrogen, trifluoromethyl, C1-C8 alkyl, C1-C8 alkoxy and halogen; R2 is selected from hydrogen, nitryl, C1-C8 alkyl, C1-C8 alkoxy and halogen; R3 is selected from C1-C8 alkyl and aryl methyl; R4 is selected from C1-C8 alkyl. The 4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-nitrogen-(4-quinazolinone)-3-formamidederivatives are first discovered antibacterial compounds of novel structures, the compounds have higher inhibition functions on gram-positive bacteria including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcusepidermidis, enterococcus and the like, particularly, drug-resistant gram-positive bacteria (MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus), MRSE (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis)and VRE (vancomycin-resistant enterococci)) and can be used for following further modification and development.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
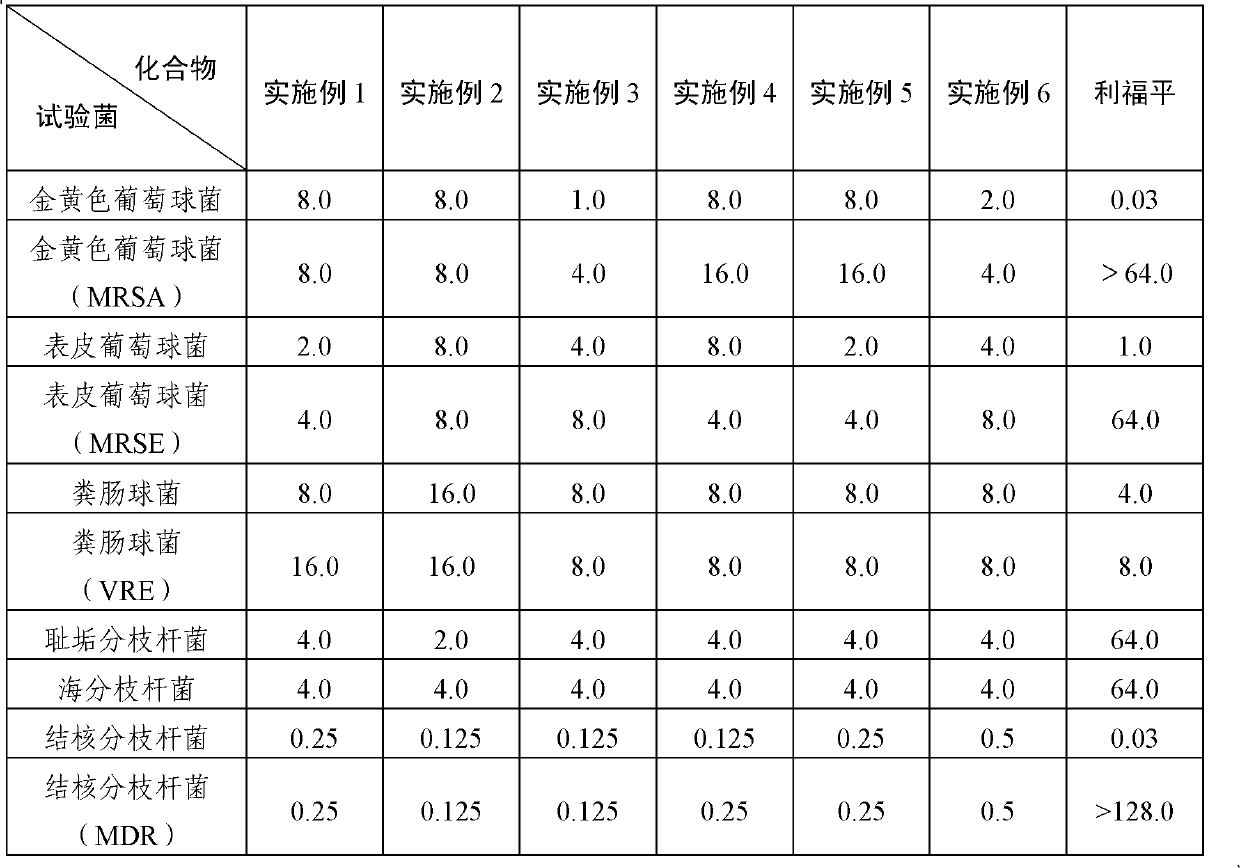
Mediucm for detecting vana and vanb vancomycin-resistant enterocci and method of using the same
Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci detection media as well as a method of selectively detecting Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci clinically important in vancomycin resistant enterococci from testing microorganisms or specimens using the media. The media for selectively detecting Van A and Van B VRE from testing microorganisms and specimens are media where enterococci can grow where vancomycin, D-cycloserine and D-lactate are added. Preferably 32-256 mug / ml of vancomycin, 1-64 mug / ml of D-cycloserine, and 0.025-0.8 mol / l of sodium lactate are added to culture medium where enterococci can grow.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Antimicrobial peptide
ActiveCN106518974AAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsAntimicrobial peptidesVancomycin-Resistant Enterococci
The invention discloses an antimicrobial peptide, which has the sequence as follow: Tyr-Gly-Arg-Lys-Lys-Arg-Arg-Gln-Arg-Arg-Arg-X1-X2-Arg-Arg-Leu-Trp-Gly-Ala, wherein the X1 is selected from Lys, Arg, Trp, Leu, Phe and Tyr; and the X2 is selected from Trp, Arg, Lys, Phe, Ser and His. The antimicrobial peptide has an obvious inhibiting effect on methicillin-resistant s. aureus, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, carbapenem-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa and carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae, and has lower hemolytic activity, good stability, high antimicrobial activity, and an efficient broad-spectrum bacteriostatic action.
Owner:BEIJING PEPMAGIC BIOTECH CORPORATION LTD
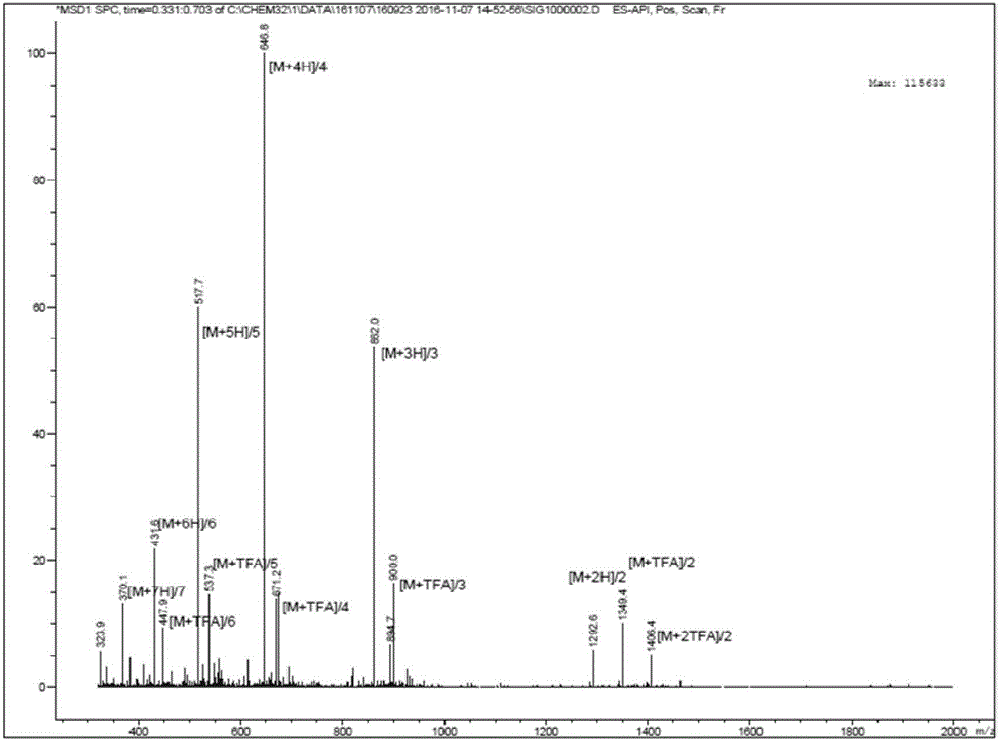
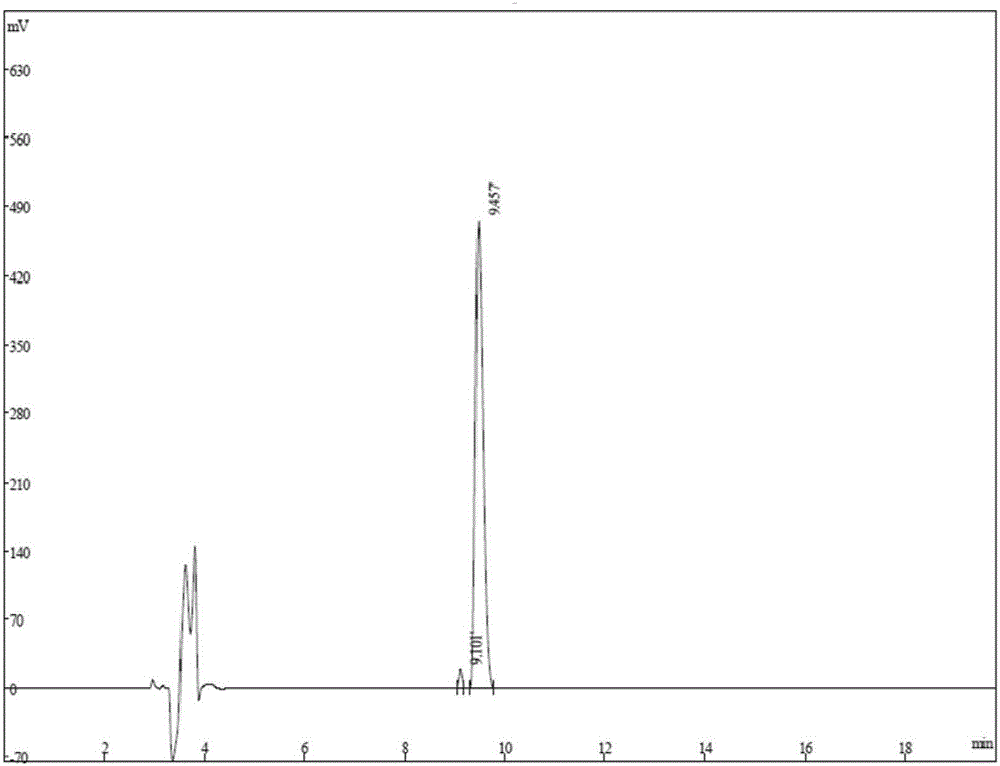
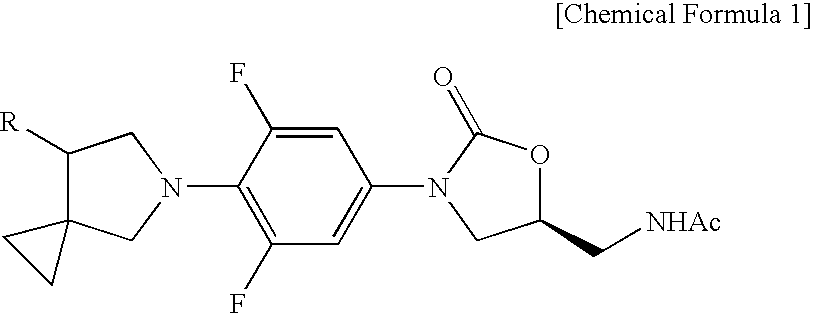
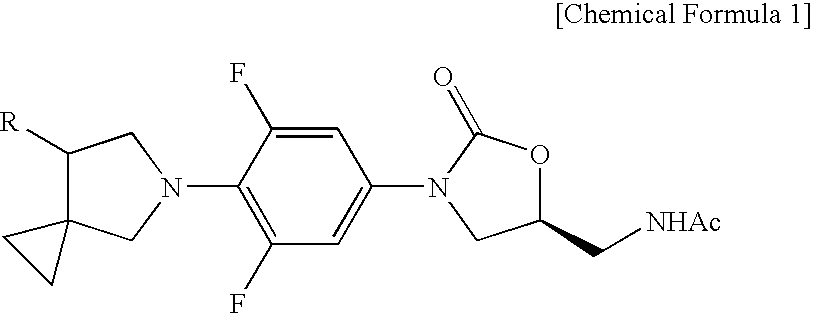
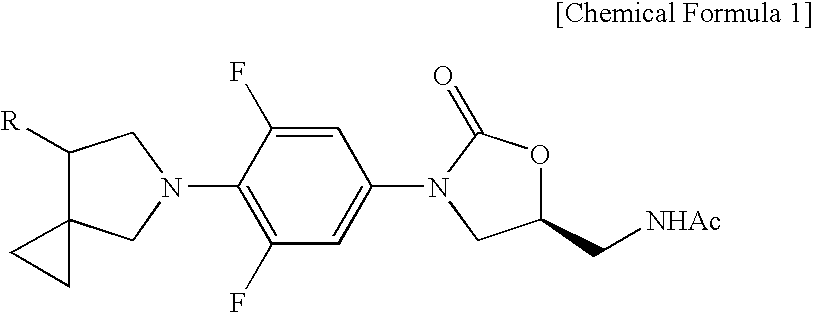
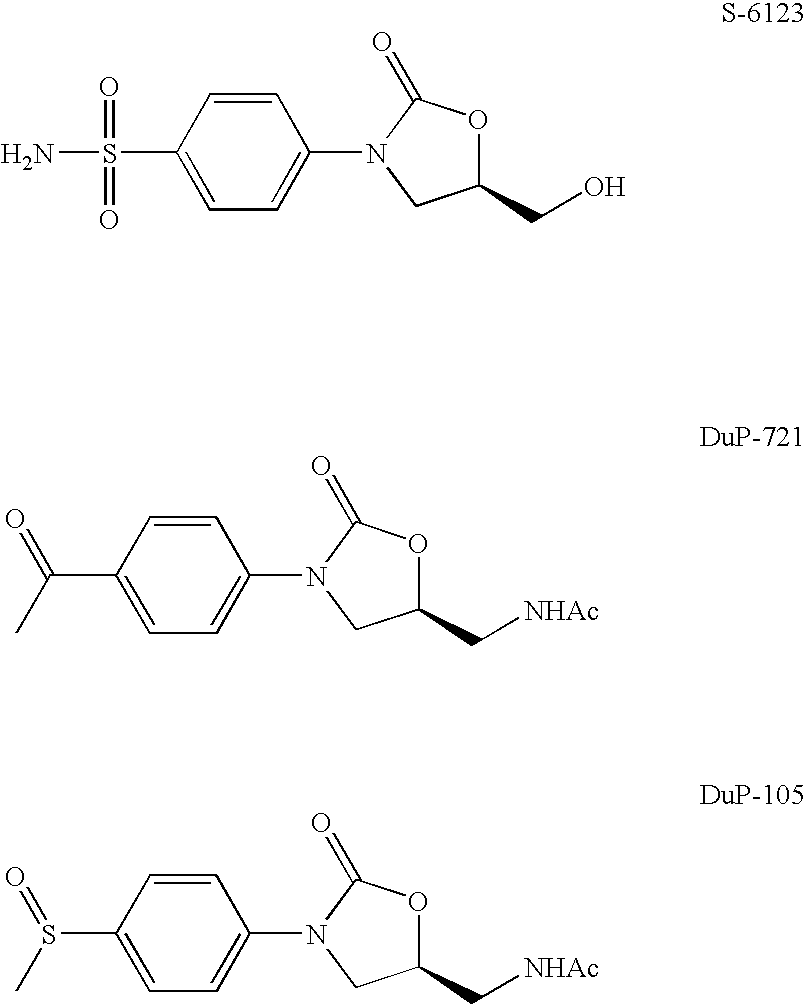
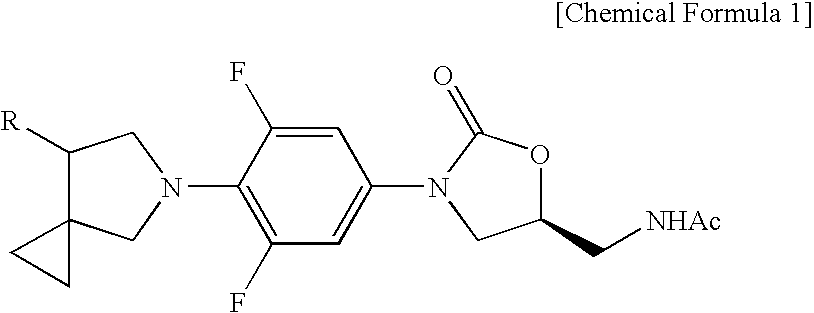
Novel oxazolidinone derivative with difluorophenyl moiety, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, preparation method thereof and antibiotic composition containing the same as an active ingredient
Novel oxazolidinone derivatives with a difluorophenyl moiety, represented by Chemical Formula 1, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient are provided. Exhibiting potent inhibitory activity against Gram-positive bacteria including Haemophilus influenza and Coagulase negative staphylococci and resistant bacteria including vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), the pharmaceutical composition is useful as an antibiotic.(wherein, R is as defined in the specification)
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
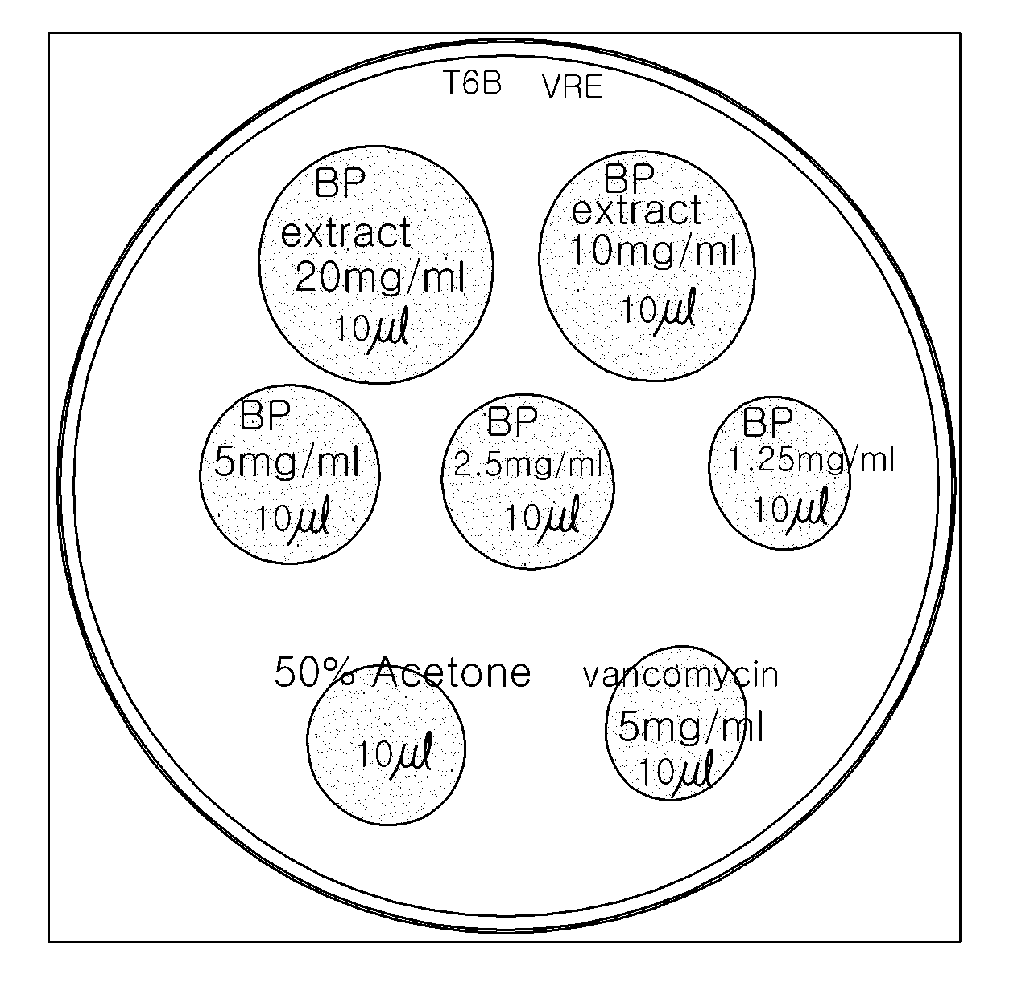
Use of fermented soy extract in inhibiting vancomycin-resistant enterococci
The present invention relates to a new use of a fermented soy extracts in preventing VRE infections.
Owner:MICROBIO CO LTD
Method and reagents for detecting the presence or absence of staphylococcus aureus in a test sample
InactiveUS20110027823A1Small amountFavorable source of coagulase substrateMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
A presence / absence test for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) involves placing a first generation test sample in a solution that will clot in the presence of S. aureus. The solution contains components that will selectively grow S. aureus and also contains clotting factors that will react with S. aureus, if S. aureus is present in the sample, to clot the solution. Examples of specimen samples that can be tested include nasal swabs and lesion swabs, among others. The test can also be modified to detect the presence or absence of methicillin resistant S. Aureus (MRSA). The addition of micro particles having a size in the range of about 0.1 micron to about 1.0 mm provides localities where the bacteria agglomerate, thereby significantly decreasing the clotting time, and providing a significantly stronger clot. The micro particles can be used in other bacteria tests to accelerate the production of an end result. Such other tests can include a vancomycin-resistant enterococcus test; a Group B Streptococcus test; a test for hemolytic E. coli; and a test for Listeria monocytogenes, to name a few. These tests are all performed in a liquid broth-type reagent mixture and do not necessarily involve clotting of the broth.
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
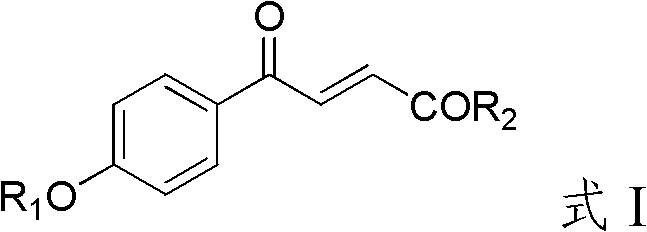
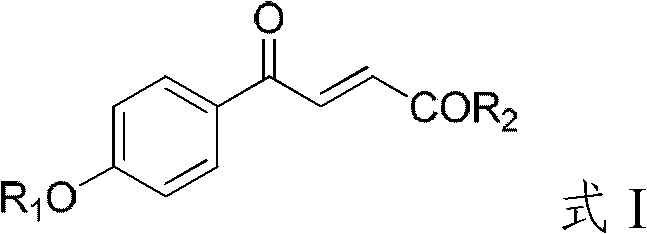
4-hydroxybenzoylacrylic acid derivative, preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN102816067AEasy to prepareSimple and fast operationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidisCross-resistance
The invention provides a 4-hydroxybenzoylacrylic acid derivative. The 4-hydroxybenzoylacrylic acid derivative is a compound which is represented as formula I, wherein R1 is C1-C8 alkyl, C1-C8 alkyl which is substituted by halogen or hydroxyl, C6-C8 aryl, C1-C9 alkanoyl or C6-C9 aroyl; and R2 is C1-C8 alkyl, C6-C8 aryl, C1-C8 alkylamino or C6-C8 arylamino. The 4-hydroxybenzoylacrylic acid derivative has inhibitory activity for mycobacterium tuberculosis protein kinase PknB can inhibit mycobacterium tuberculosis, multidrug resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis and several drug resistant Gram-positive bacterium such as methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis and vancomycin-resistant enterococci, no cross resistance exists in the 4-hydroxybenzoylacrylic acid derivative and existing antibiotics and the 4-hydroxybenzoylacrylic acid derivative has good antibacterial effect.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
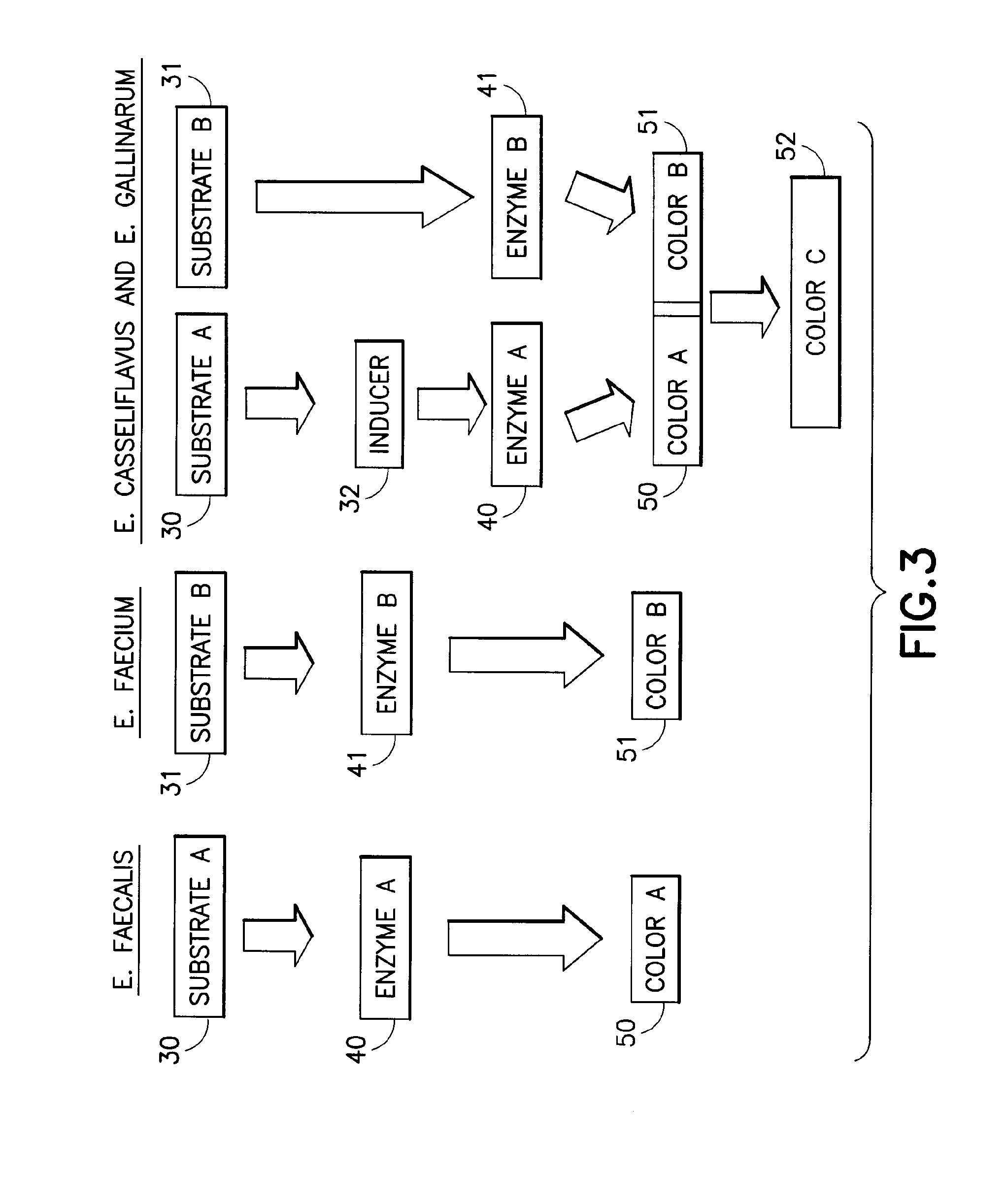
Chromogenic medium for the detection and identification of vancomycin resistant enterococci and method therefor
ActiveUS20080145881A1Facilitates direct identification and differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismChromogenic Substrates
A microbe-specific medium, containing specific chromogenic substrates, for the detection of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in a biological sample, whereby both the detection and identification of vancomycin-resistant enterococci at the species level is achieved utilizing one sample and one test.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
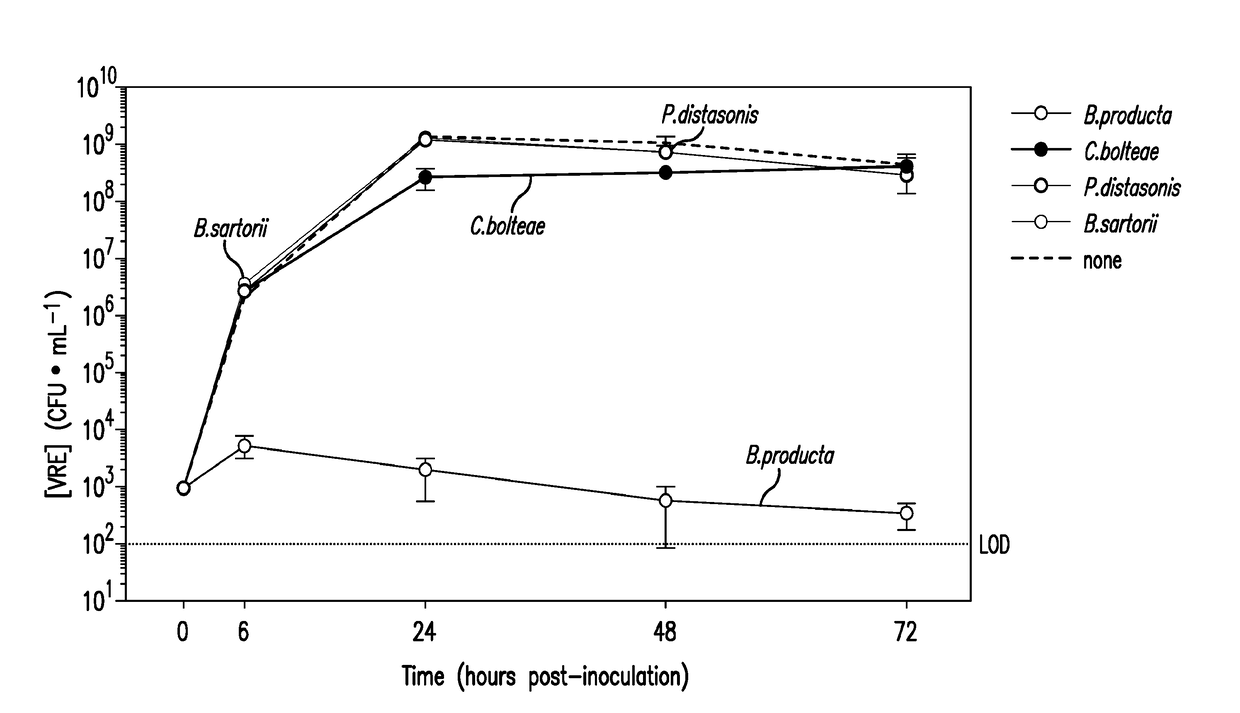
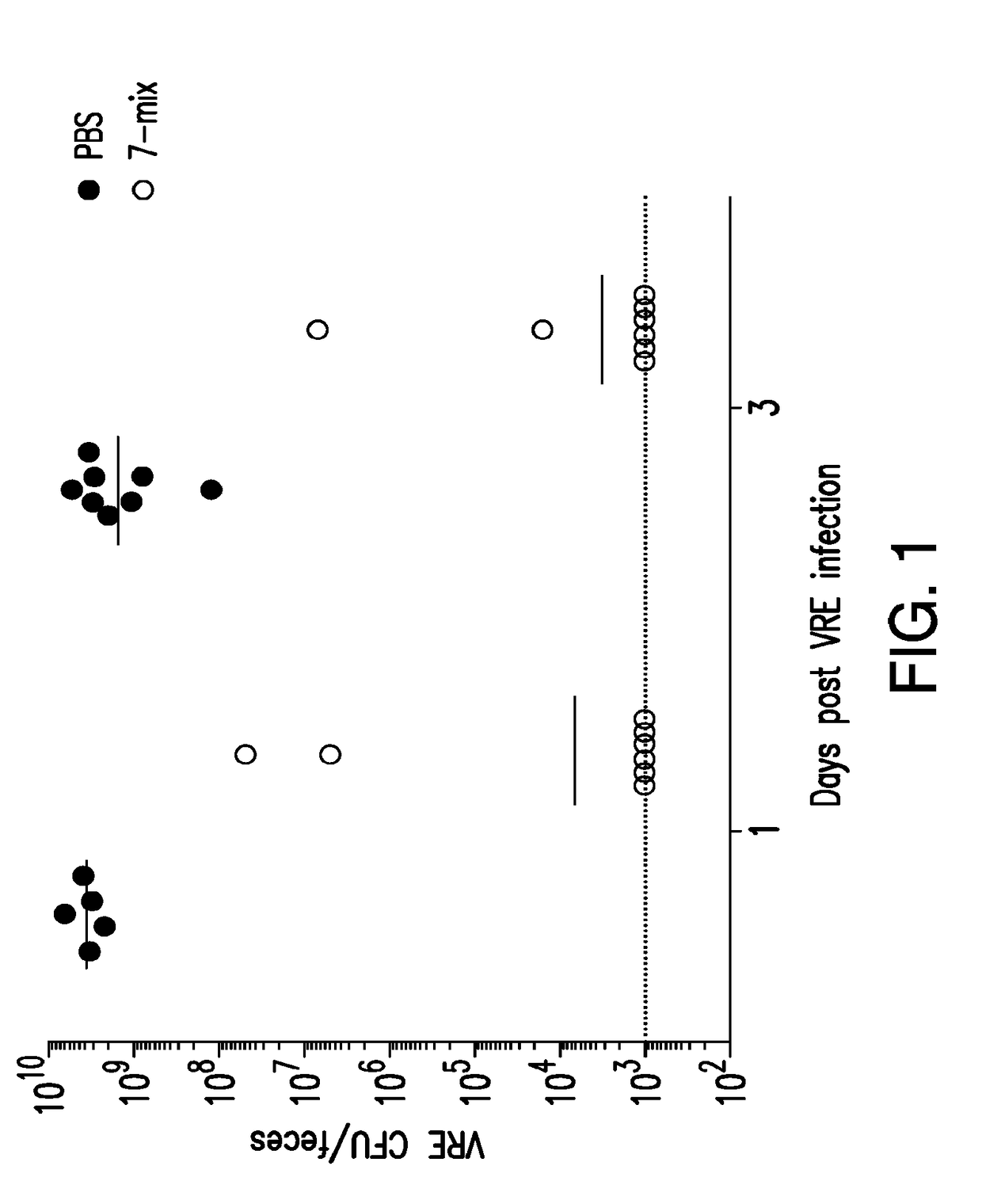
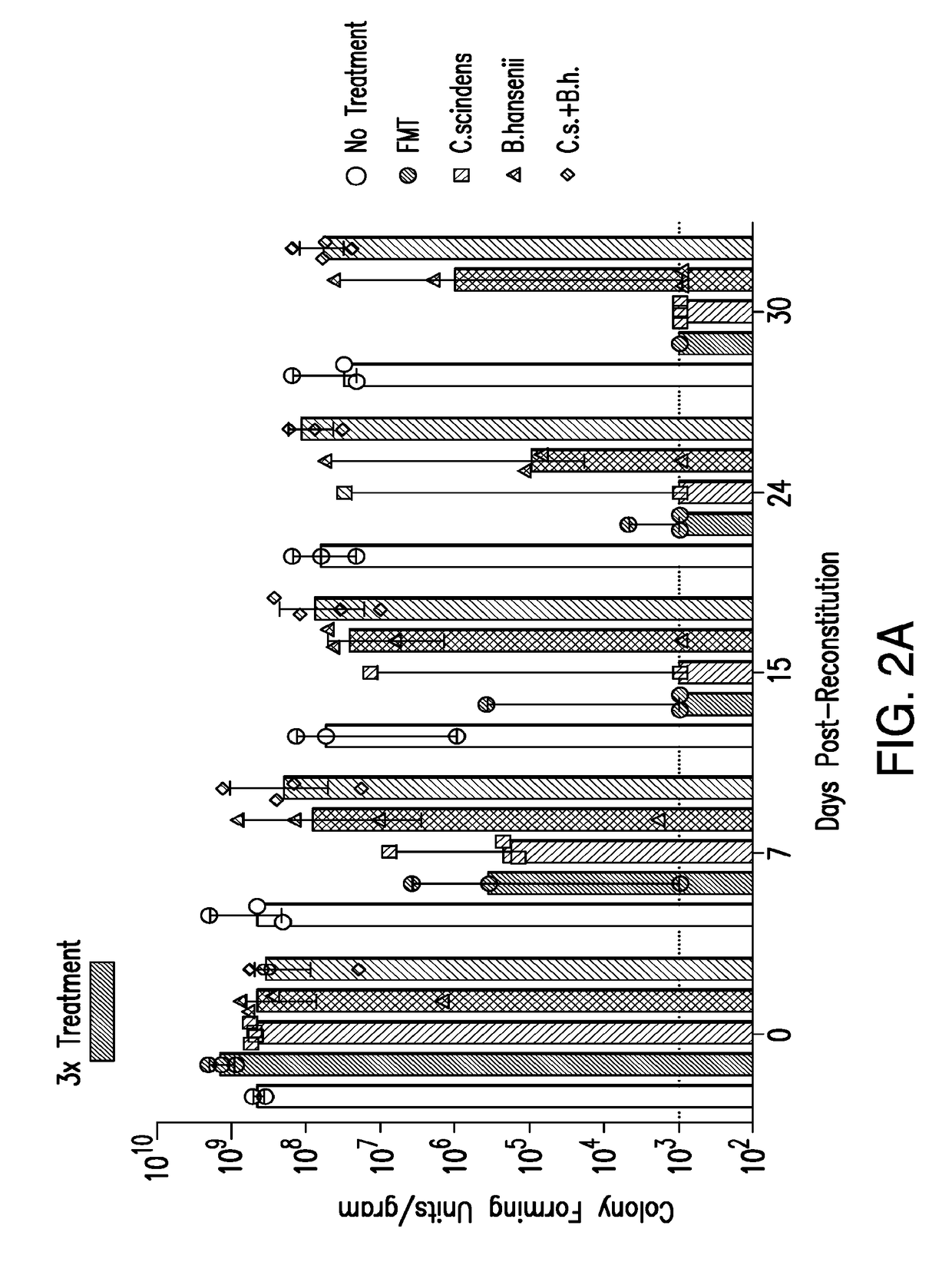
Methods and compositions for reducing vancomycin-resistant enterococci infection or colonization
ActiveUS20180256653A1Reduce riskImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing the risk and severity of vancomycin-resistant Enterococci infection or colonization. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that a restricted fraction of the gut microbiota, including the bacteria Clostridium scindens and / or the bacteria Blautia producta contribute substantially to resistance against vancomycin-resistant Enterococci infection or colonization. Without being bound by any particular theory, it is believed that this is achieved through the biosynthesis of secondary bile acids in the case of Clostridium scindens.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Indole full dione thiosemicarbazone type compound and use thereof in resisting medicament-resistant bacteria
InactiveCN103483239AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaMethicillin resistant Staphylococcus
The invention relates to an indole full dione thiosemicarbazone type compound and a use thereof in preparation of anti-medicament-resistant bacteria medicaments. The indole full dione thiosemicarbazone type compound provided by the invention has a very strong effect on inhibiting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aurei (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and can be used for preparing the novel and effective anti-medicament-resistant bacteria medicaments. The medicaments can be prepared into injections, tablets, pills, capsules, suspensions or emulsions for use. A medicament delivery way can adopt oral medication and transdermal, intravenous or intramuscular injection. The chemical structural formula of the indole full dione derivative provided by the invention is as shown in formula (I), and in the formula, R1 is o-CH3, o-OCH3, o-F, m-CH3, m-OCH3, m-F, m-Cl, p-CH3, p-OCH3, p-F, p-Cl, p-Br or H; and R2 is CH3, F, Cl, Br, I or H.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Novel apparatus and methods to improve infection control in facilities
InactiveUS20140339076A1Risk minimizationEfficiently and effectively clean and sanitize and disinfectCellsMachining electric circuitsIndividual animalChemistry
An Apparatus that generates onsite three antimicrobial solutions by electrolyzing a dilute brine solution. At least one of the generated solutions can be used to dissolve protein, emulsify oils and fats making it an effective general purpose cleaner. A second solution can be used as a non-corrosive, fast active general purpose sanitizer and a third solution can be used as a high level disinfectant, capable of killing all microorganism, including MRSA (methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureaus), C. diff (clostridium difficle), VRE (vancomycin resistant enterococci) and acinetobactor baumannii. The onsite generated antimicrobial solutions reduce the occurrence of infectious diseases in hospitals, other human or animal health care settings, cruise-ships, hotels and other facilities whereas there is a higher risk of spreading infectious diseases.
Owner:AQUAOX
1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acylsemicarbazide derivative, preparation method thereof, and use thereof as antibacterial medicine
InactiveCN110272364AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidisOxygen
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibacterial medicines, and relates to a 1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acylsemicarbazide derivative, a preparation method thereof, and a use thereof as an antibacterial medicine. The compound is represented by formula (I); and in the formula (I), R1 is selected from hydrogen, a hydroxyl group, a C1-C8 alkyl group, a C1-C8 alkoxy group, an arylmethoxy group and a halogenated arylmethoxy group, R2 is selected from hydrogen, a C1-C8 alkyl group and a halogenated C1-C8 alkyl group, and X is selected from sulfur and oxygen. The 1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acylsemicarbazide derivative of the present invention has a strong inhibition effect on Gram-positive bacteria, especially methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and can be used for preparing novel drug-resistant bacteria medicines.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Antibacterial macrolactin a that bacillus polyfermenticus kjs-2 produced in
InactiveUS20100087516A1Broad spectrum of antibiotic activityExcessive activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismEnterococcus avium
The present invention relates to uses of Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 (KCCM 10769P), which is a new bacillus strain, as an antibiotic. Macrolactin A of the present invention, which is produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, shows a broad spectrum of antibiotic activity against a variety of microorganisms and fungi, and is proved to be very efficient for the inhibition of particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) that are multidrug-resistant bacteria. The antibiotic Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, can be used as an excellent antibiotic against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), and thus the present invention is a very useful invention for medical industry.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Novel oxazolidinone derivative with difluorophenyl moiety, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, preparation method thereof and antibiotic composition containing the same as an active ingredient
Novel oxazolidinone derivatives with a difluorophenyl moiety, represented by Chemical Formula 1, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient are provided. Exhibiting potent inhibitory activity against Gram-positive bacteria including Haemophilus influenza and Coagulase negative staphylococci and resistant bacteria including vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), the pharmaceutical composition is useful as an antibiotic.(wherein, R is as defined in the specification)
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Broad spectrum root canal filing composition for endodontric usage
InactiveUS20140234442A1Fight infectionBiocideImpression capsVancomycin-Resistant EnterococciRoot canal
Disclosed is dental root canal filling (intracanal medicament) compositions that are effective against resistant root canal infections caused by Enterococcus faecalis and Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci.
Owner:PAVASKAR RAJDEEP S
Antibacterially active linezolid alkali cation amphiphilic compounds and synthesis method thereof
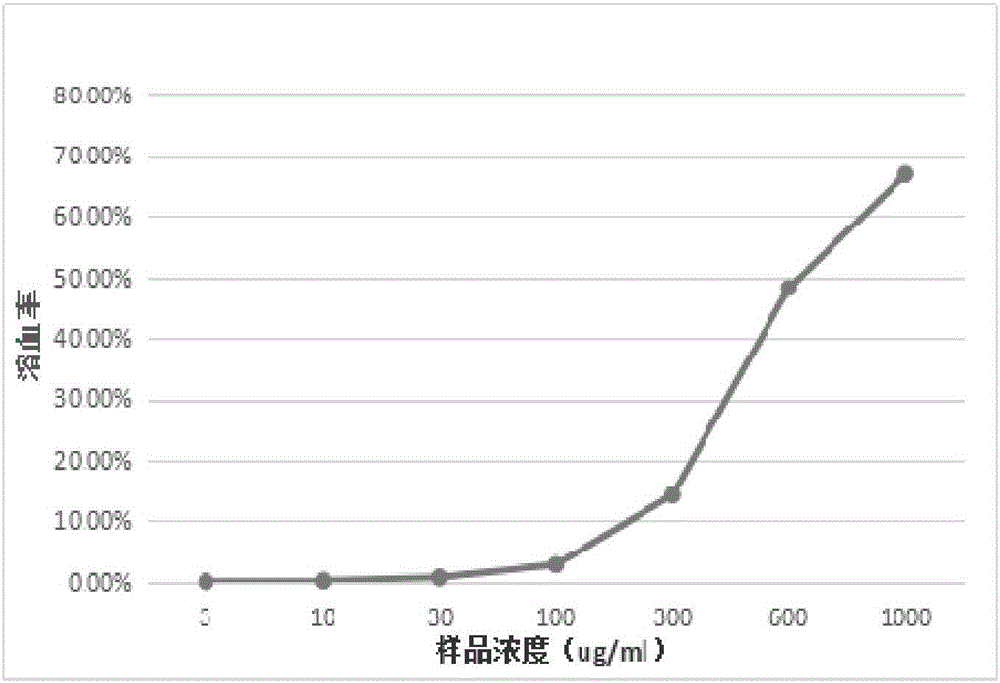
ActiveCN107382893AHigh activityGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryEscherichia coliSalmonella enterica
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and discloses antibacterially active linezolid alkali cation amphiphilic compounds and a synthesis method thereof. Three target products are obtained simply and quickly through a two-step or three-step reaction. The main structure is as follows: in-vitro antibacterial activity experiments show that the series of compounds show good antibacterial effects on sensitive strains such as staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteric, and some of the compounds show excellent antibacterial effects on super bacteria including methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and carbapenemases-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). In-vitro erythrocytotoxicity experiments show that the series of compounds have less erythrocytotoxicity, and the series of compounds are expected to be used as new antibacterial drug candidates.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Treatment of disease associated with the use of antibiotics
InactiveUS20130274175A1Prevent relapseEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseAntibiotic Y
This invention relates to the treatment or prevention of diseases associated with the use of antibiotics or cancer chemotherapies or antiviral therapies, such as colitis, pseudomembranous colitis, antibiotic associated diarrhea and infections due to C. difficile, C. perfringens, Staphylococcus species including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or Enterococcus including vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) with Compound I.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
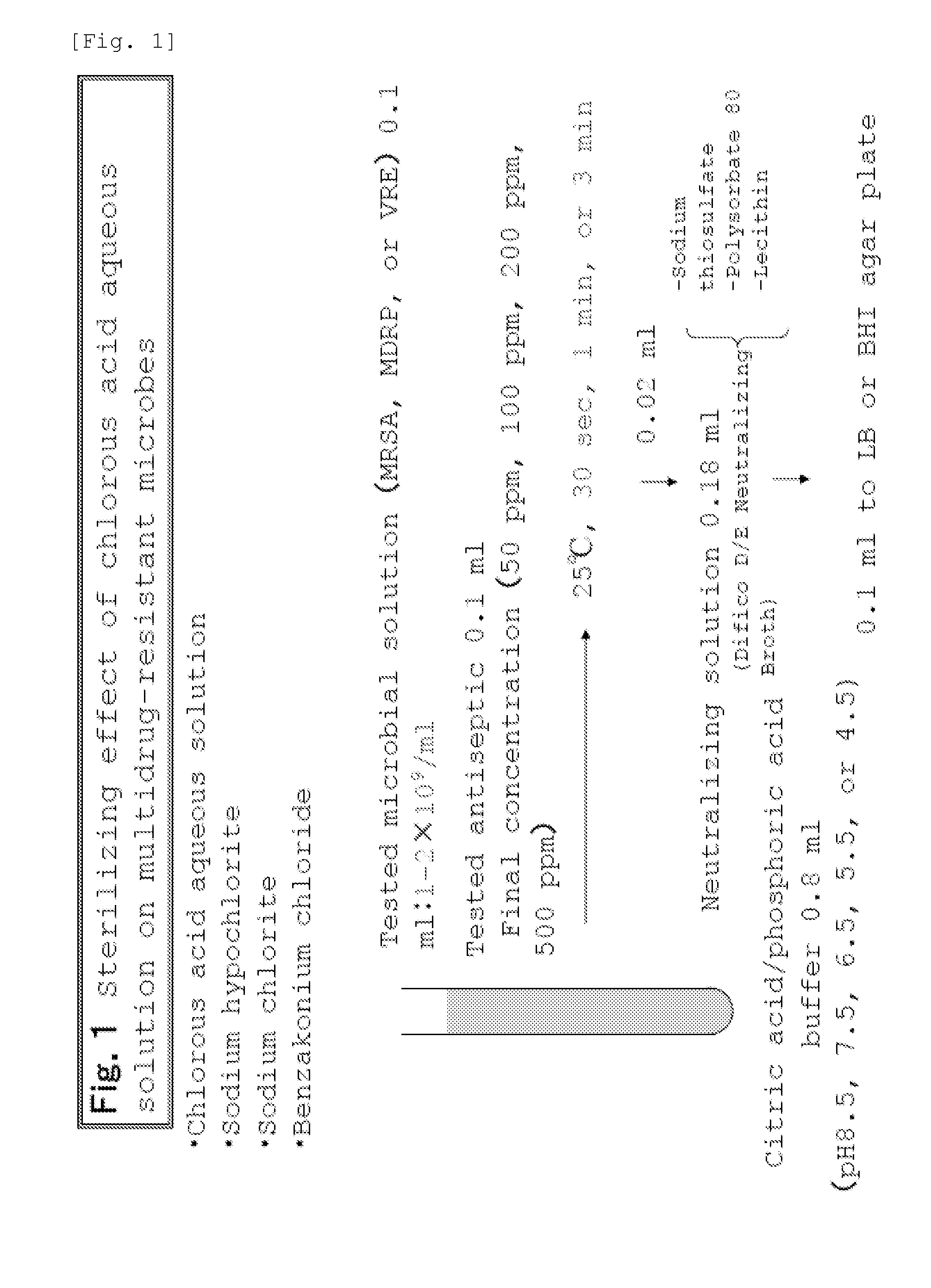
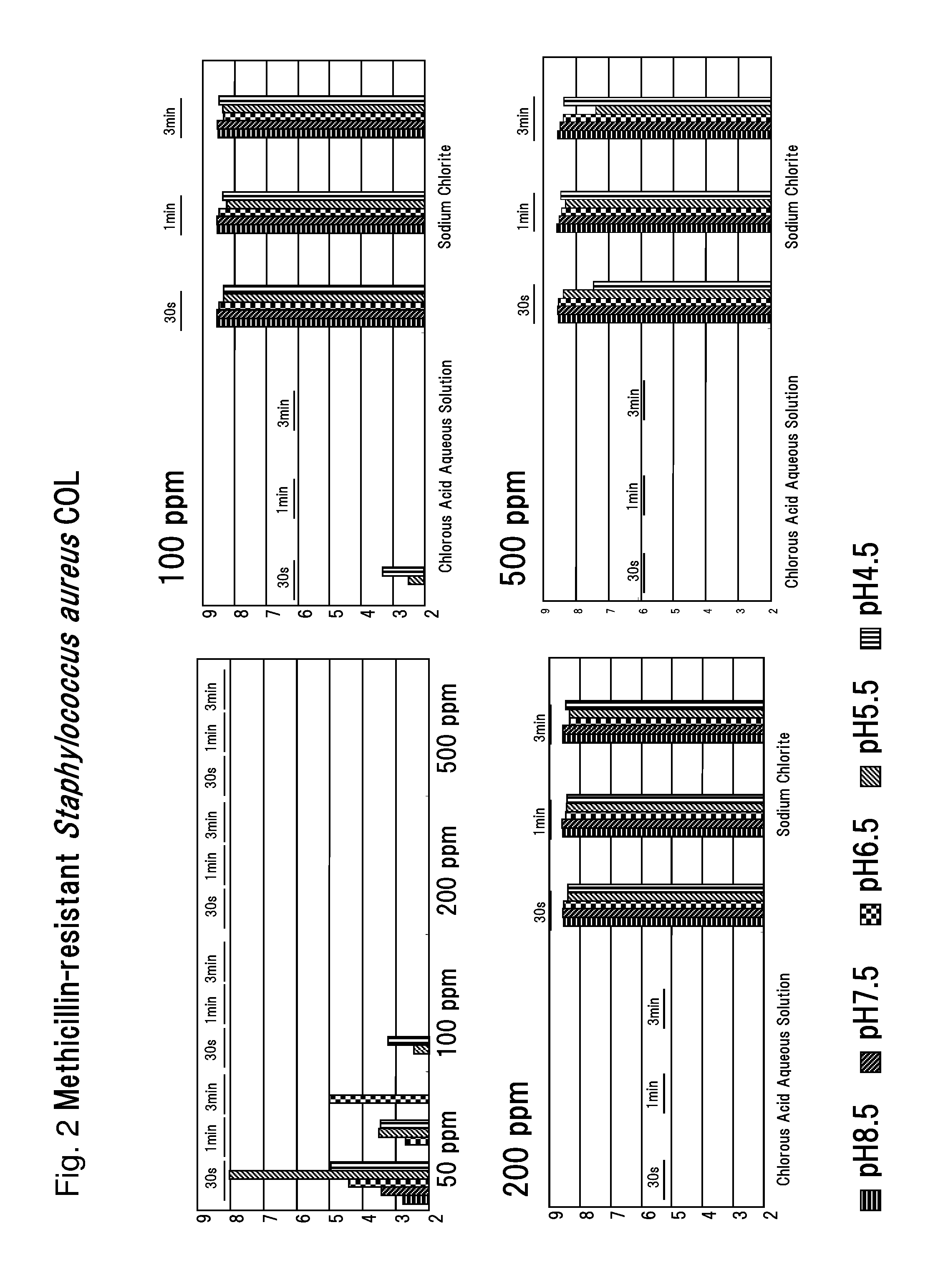
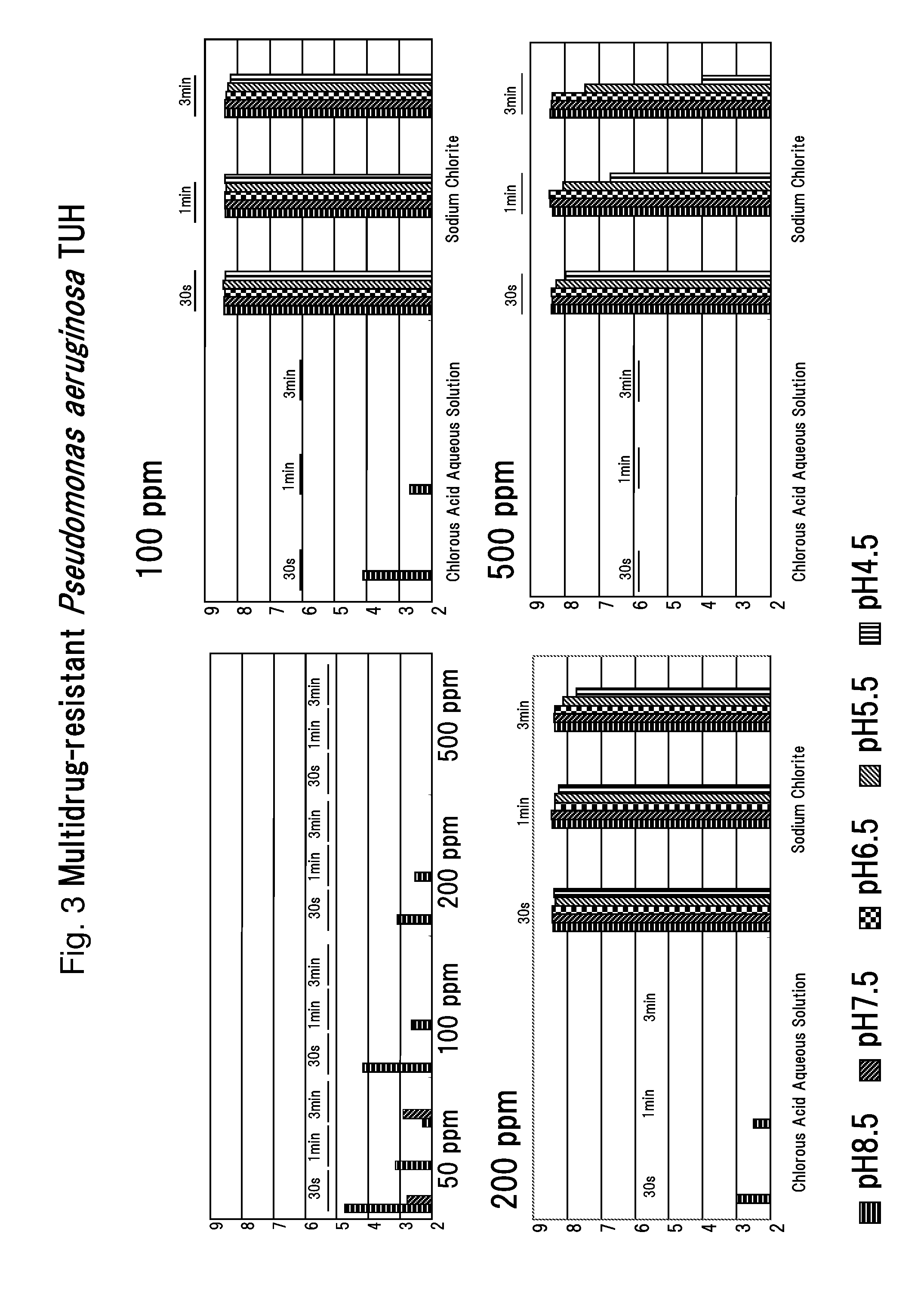
Drug-resistant microbe and variant microbe disinfectant containing chlorous acid aqueous solution
InactiveUS20160106106A1Easy to useSuppress generationBiocideCosmetic preparationsSalmonella entericaFood additive
The present invention provides microbe disinfectants, providing: Drug-resistant microbe disinfectants comprising a chlorous acid aqueous solution for inactivating microbes selected from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus; and microbe disinfectants, which are made with acidity when applied to gram-negative microbes and with alkalinity when applied to gram-positive microbes. The microbes comprise at least one species of microbes selected from the group consisting of E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, microbes of genus Bacillus, microbes of genus Paenibacillus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus, Salmonella enterica, and periodontal disease microbes. The present invention is usable as a microbe disinfectant that is safe to human body and easy to handle as a microbe disinfectant for pretreatment in food processing and produces chlorous acid that generates little chlorine dioxide. The microbe disinfectant comprising a chlorous acid aqueous solution of the present invention can be utilized as a sterilizing agent, food additive, antiseptic, quasi-drug, medicine, etc.
Owner:HONBU SANKEI
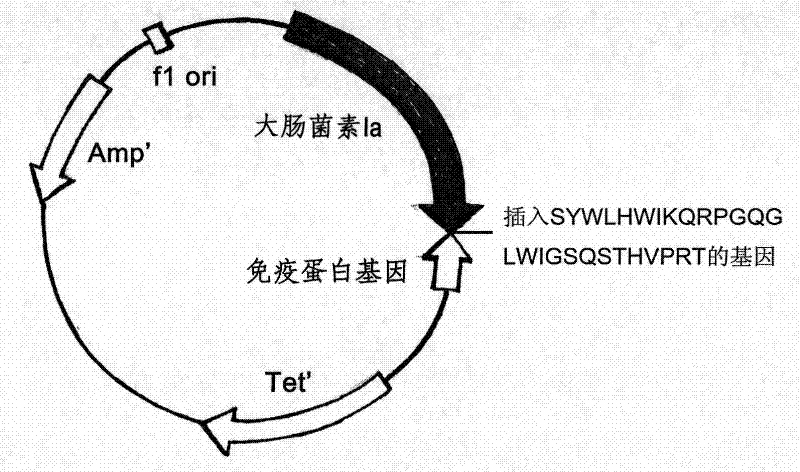
A kind of novel antibiotic containing antibody mimetic and its preparation method and application
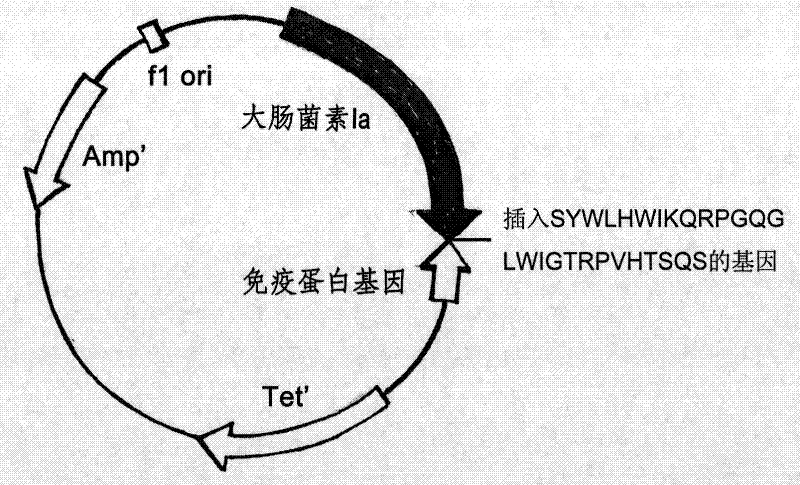
ActiveCN101633699BImprove permeabilityLow immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsComplementarity determining regionAntibiotic Y
The present invention belongs to field of biology and medicine, and especially relates to a novel antibiotic comprising a mimetic antibody, its preparation methods and uses thereof. The novel antibiotic comprising comprising an antibody mimetic and a colicin,or comprising an antibody mimetic and a channel-forming domain of a colicin, the antibody mimetic covalently bonded to the carboxyl end of the polypeptide of the colicin or the channel-forming domain of the colicin, wherein the colicin is selected from a group consisting of colicin E1, Ia, Ib, A, B, N; wherein said antibody mimetic being yielded by fusing two complementarity determining regions (CDRs), V H CDR 1 ) and V L CDR through a cognate framework region (V H FR 2 ) of an immunoglobulin; wherein the immunoglobulin specifically recognizes bacterium porins. Its antibacterial ability is a thousandfold powerful than normal antibiotics. Due to its unique action mechanism, drug resistance resulted in mutation can hardly be acquired by pathogenic bacteria. And the antibiotic will not hurt normal human cells when it kills pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, it can be used for manufacturing antibacterial medicament of killing Diplococcus intracellularis, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:PHEROMONICIN BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Colon-targeted pellets containing vancomycin and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a colon-targeting pellet with vancomycin as an active ingredient and a preparation method thereof. The targeted pellet preparation is composed of a blank core, a drug coating layer and a colonic enteric coating layer, wherein the blank core is a commercially available product, and the drug layer is composed of vancomycin, anti-adhesive agent and methyl acrylate copolymer , the colonic enteric coating layer is composed of anti-adhesive agent, plasticizer and methyl acrylate, and the colon-targeted micropills of vancomycin are prepared by adopting a fluidized bed micropellet coating method. The colon-targeted pellet preparation is used for the treatment of pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile caused by long-term administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics. The targeted drug release can not only improve the curative effect, but more importantly, avoid vancomycin Exposure to non-acting sites effectively reduces the incidence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE).
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY
Pharmaceutical composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106632104AGive full play to medicinal valueGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition and application thereof. The pharmaceutical composition is a compound shown as a chemical formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers thereof: (the formula is shown in the description). The compound can be used for preparing an antibacterial drug, in particular preparing a medicine for preventing or treating vancomycin-resistant bacteria infectious diseases. Experimental data show that the compound is combined with glycopeptide antibacterial drugs, so that the growth of vancomycin-resistant enterococci can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:XIANGTAN ZHILIAN TECH MATASTASIS PROMOTE CO LTD
Chromogenic medium for the detection and identification of Vancomycin resistant enterococci and method therefor
ActiveUS10782291B2Facilitates direct identification and differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisVancomycinumChromogenic Substrates
A microbe-specific medium, containing specific chromogenic substrates, for the detection of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in a biological sample, whereby both the detection and identification of vancomycin-resistant enterococci at the species level is achieved utilizing one sample and one test.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Site-selective functionalization of glycopeptide antibiotics
Site-selective functionalized glycopeptide antibiotics, methods of making and using are described herein. The compounds exhibit improved activity against methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-sensitive S. aureus (VSE), vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), or combinations thereof. The compounds can be administered as the neutral free acid or free base or can be administered as a pharmaceutically acceptable acid-addition or base-addition salt. The compounds can be formulated with one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients to prepare pharmaceutical compositions. The compounds can be administered by a variety of routes of administration including enteral, parenteral, topical, or transmucosal.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com