Antibacterial Macrolactin A that bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 produced in
A technology of macrolide and bacillus, applied in the field of antibiotics, can solve the problems of low yield, difficulty in identification, hindering industrial application, etc., and achieve the effect of broad-spectrum antibacterial activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1: the separation and identification of polyzyme bacillus KJS-2 and the generation of antibacterial substance
[0049] [Step 1: Isolation and Identification of Polyzyme Bacillus KJS-2]
[0050] During the antibacterial activity test of Polyzyme Bacillus isolated in 1933 by Dr. Terakado's research group in Japan, a strain was isolated that was morphologically different from other Bacillus strains. Microscopic observation showed that the strain had the characteristics of Bacillus and produced spores, and pedigree analysis based on the DNA sequence homology of 16s rRNA confirmed that it was a new strain belonging to the genus Bacillus. The present inventors confirmed that the base sequence of the 16s rRNA of the strain of the present invention is identical to that of the 16s rRNA of Bacillus PP19-H3 producing the previously known macrolide A (Korean Patent Application No. 10-2006096935: 2006.10.02) have 99% homology in their base sequences.
[0051] [Table 1] ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: purify antibacterial substance from the culture medium of polyzyme bacillus KJS-2
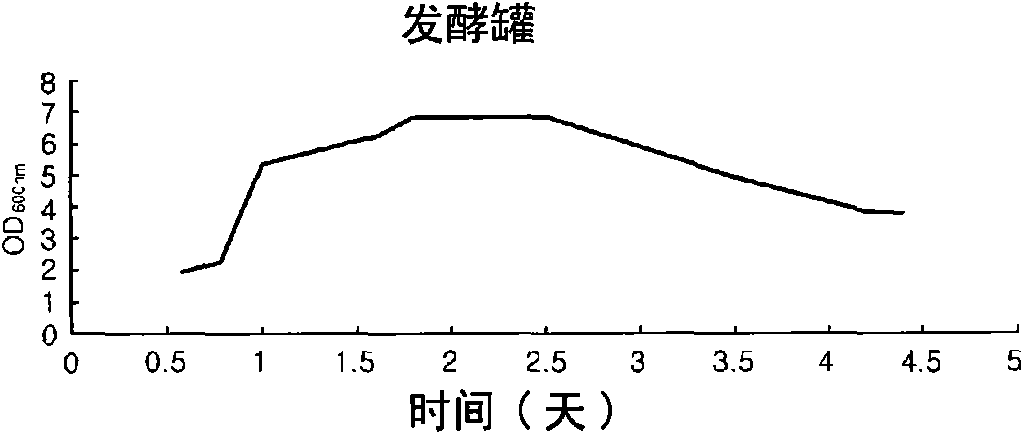
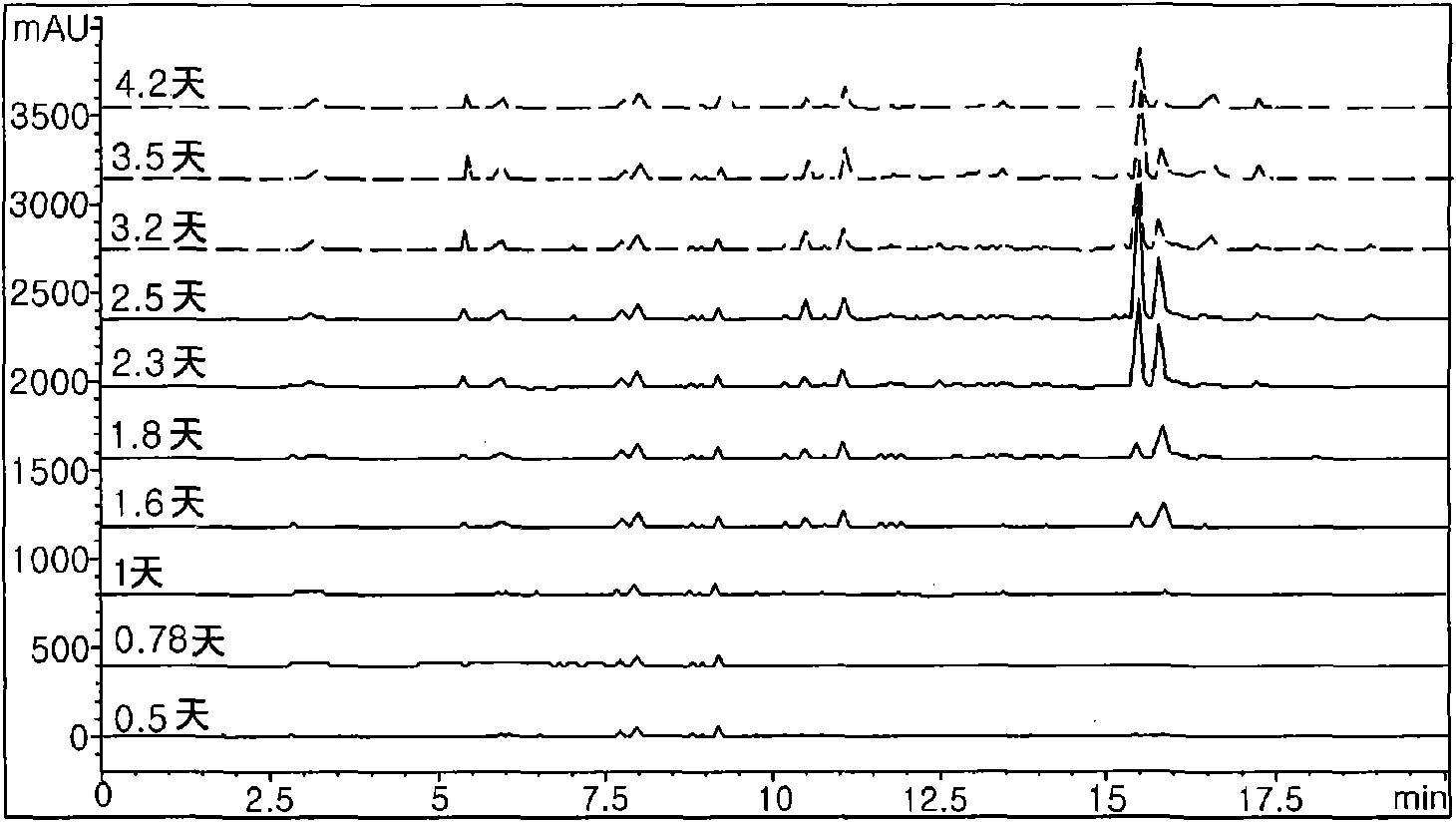
[0064] In order to purify the antibacterial substances produced by bacterial strain Bacillus polyzyme KJS-2, the seed culture of this bacterial strain was diluted in 3L of TSB medium (TSB agar: tryptone 17g, soytone 3g, glucose 2.5g, NaCl 5g, phosphoric acid dipotassium hydrogen 2.5g, pH6.8~7.2) to a final concentration of 4%, and cultivated for 2.5 days (30°C, 200rpm, 1vvm, pH6.8). The medium was extracted with ethyl acetate and analyzed by HPLC using the solvent of step 2 of Example 1 as Figure 4 Each peak was fractionated as shown in . Each fraction was tested for antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis 168 and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. The results showed that fractions 1, 4, 5 and 7 had antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli (see Figure 4 ), fractions 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 9 have antibacterial activity against Bacillus sub...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Structural analysis of fractions showing excellent antibacterial activity against VRE
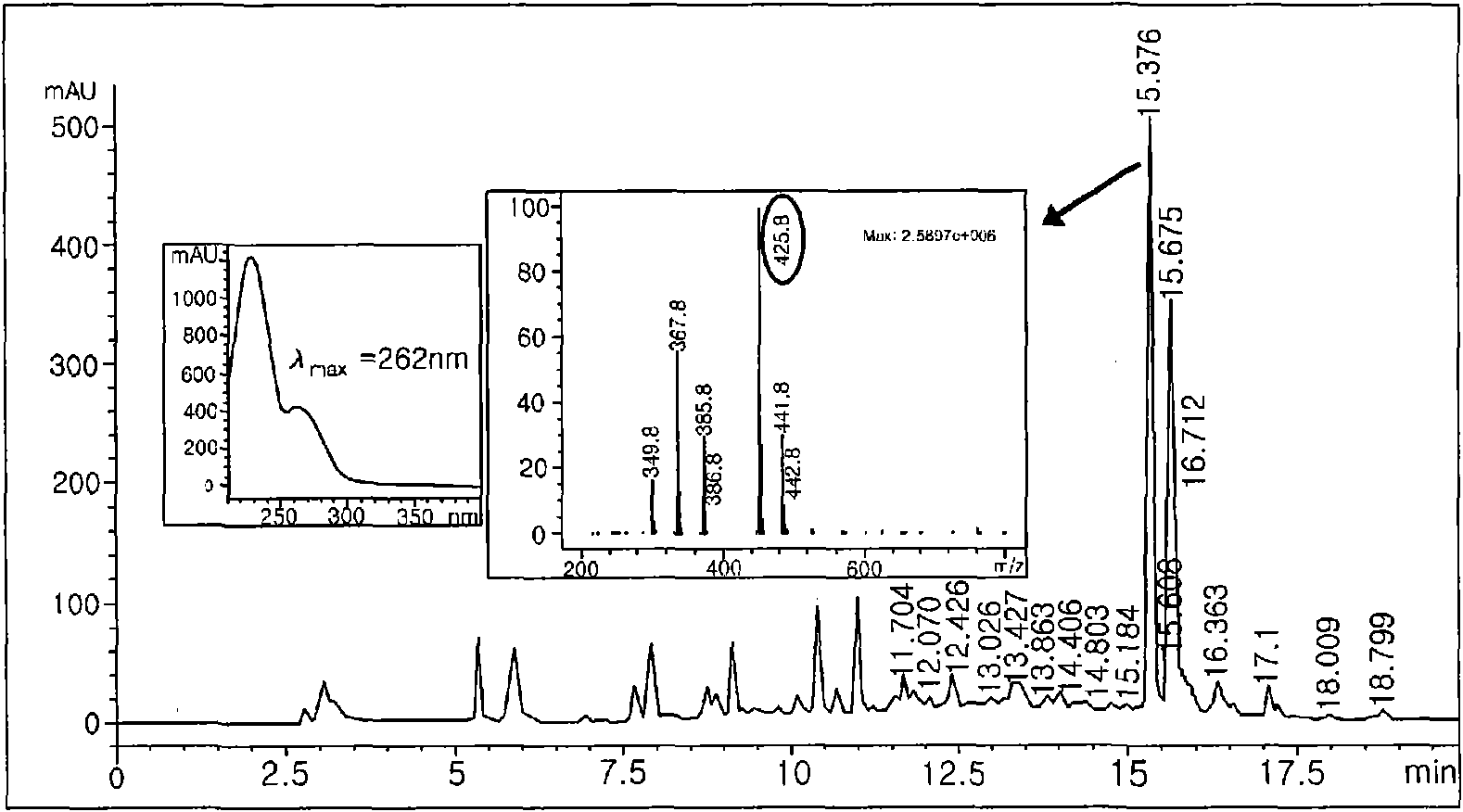
[0066] In order to analyze the structure of the substance that inhibits the growth of Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis 168 and vancomycin-resistant enterococcus of the final purification, a large number of fractions were prepared under the same conditions as the preparative LC of step 2 of Example 1 (see Figure 6 ). Fractions were analyzed under the same conditions as the LC / Mass of Step 2 of Example 1, and Fraction 1 of Example 2 was purified with a purity of 97.72% (see Figure 7 ). 30 mg of material purified by preparative LC was dissolved in 700 μl of solvent DMSO-d6 and tested for first and second NMR ( 1 H-NMR, 13 C-NMR, 90-DEPT, 135-DEPT, H-H COZY, HMQC, HMBC). The results of the NMR analysis are shown in Table 2 below. Figure 8 , Figure 9 , Figure 10 , Figure 11 , Figure 12 , Figure 13 and Figure 14 middle. Based on the results of NMR analysi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com