Patents
Literature
38 results about "Interstitial tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
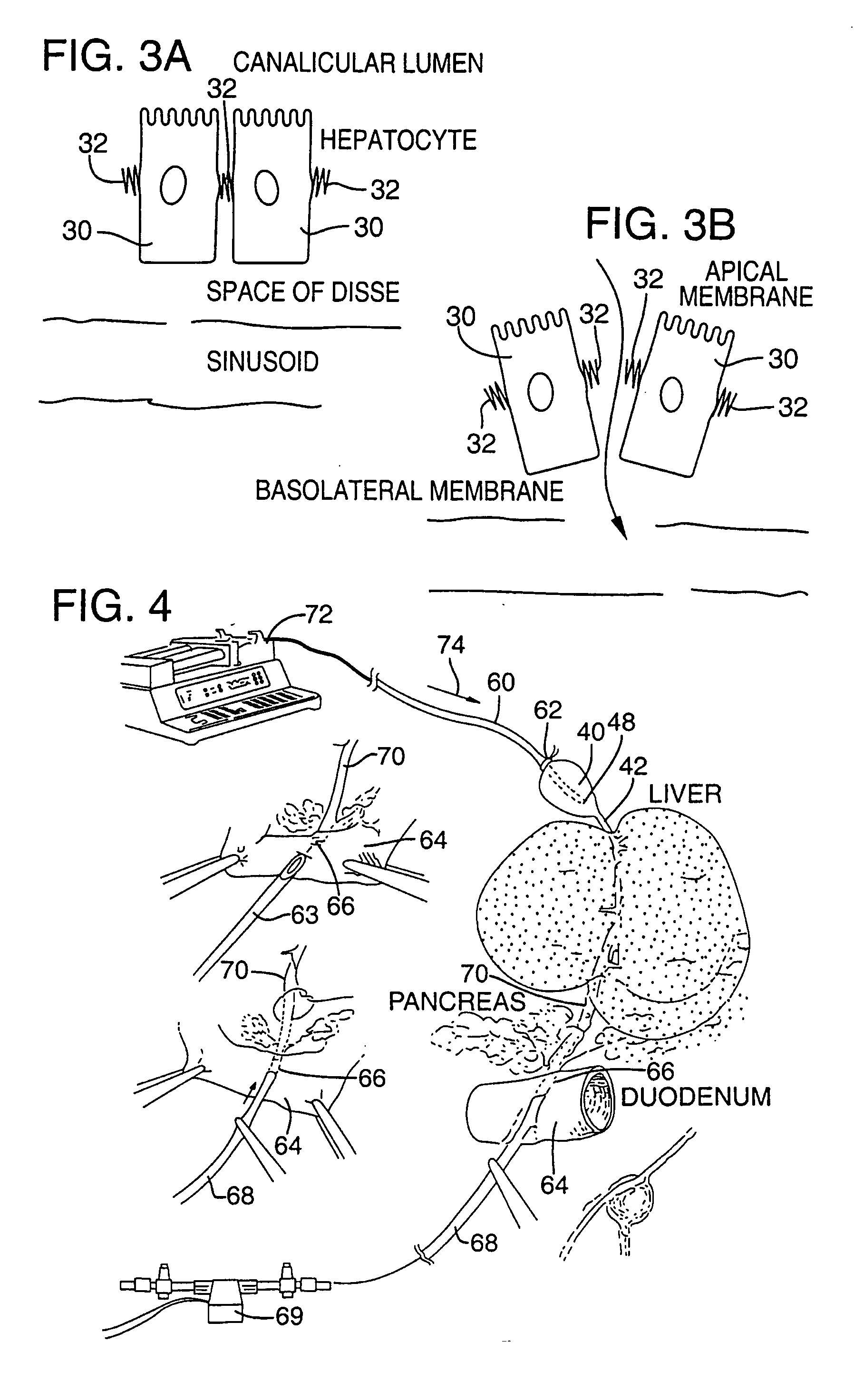
Radiofrequency Interstitial Tissue Ablation (RITA) is a minimally invasive procedure in which a thin needle electrode is inserted into an unresectable liver or bone lesion under ultrasound or CT guidance.
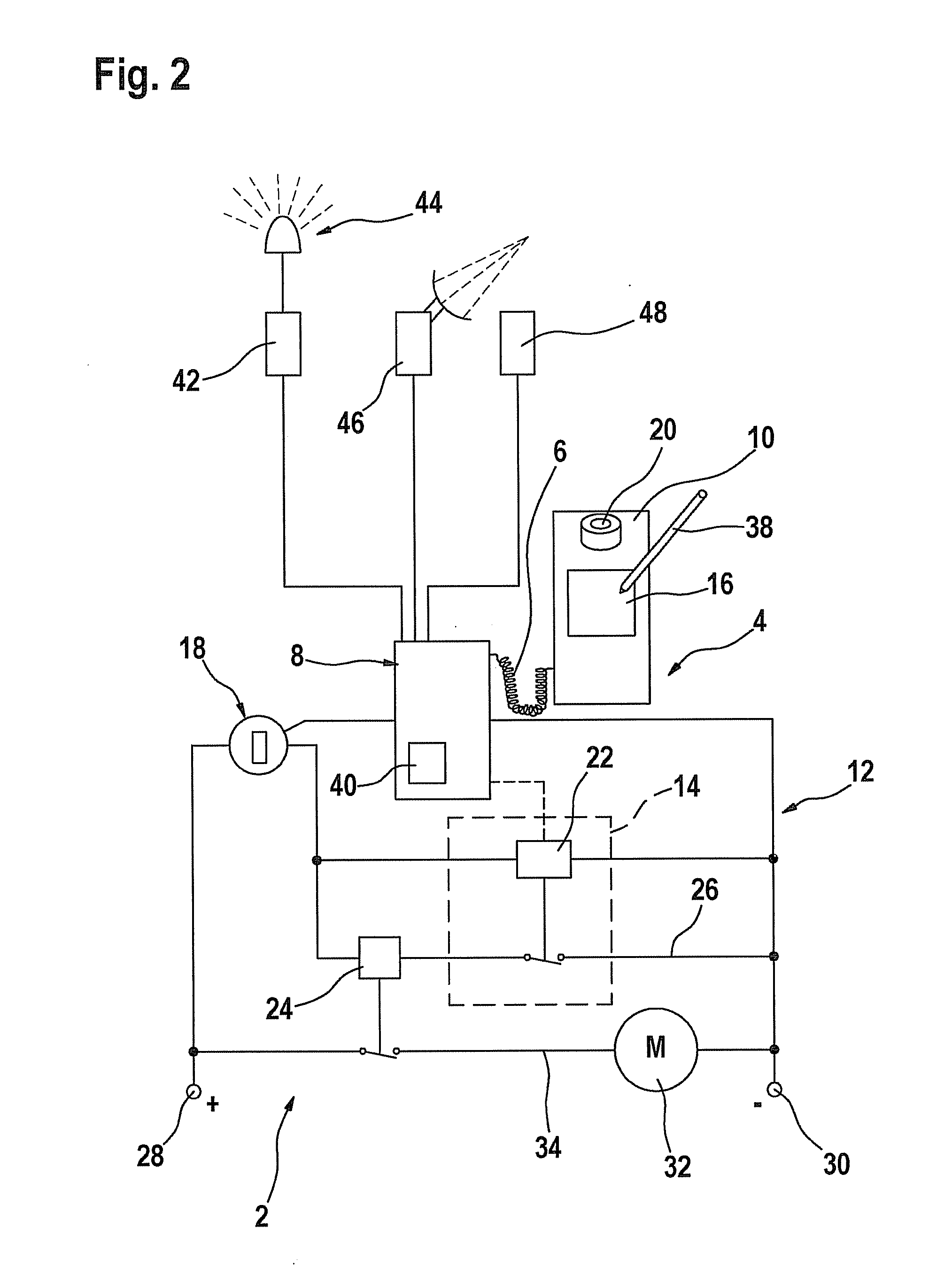
Process and device for selectively treating interstitial tissue
InactiveUS20080300571A1Minimize exposureIncreasing safety and effectivenessStentsUltrasound therapyBody organsCurative effect
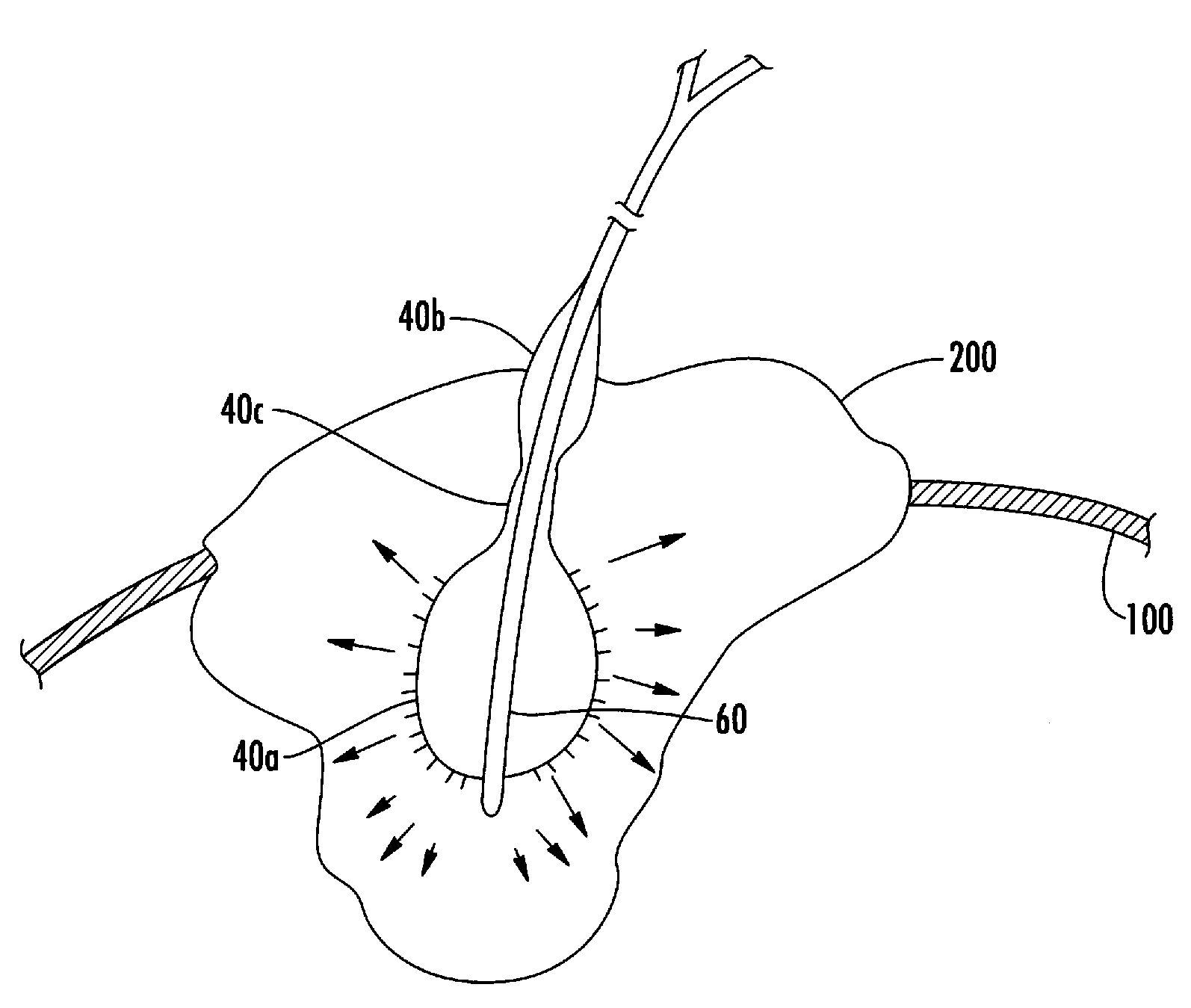
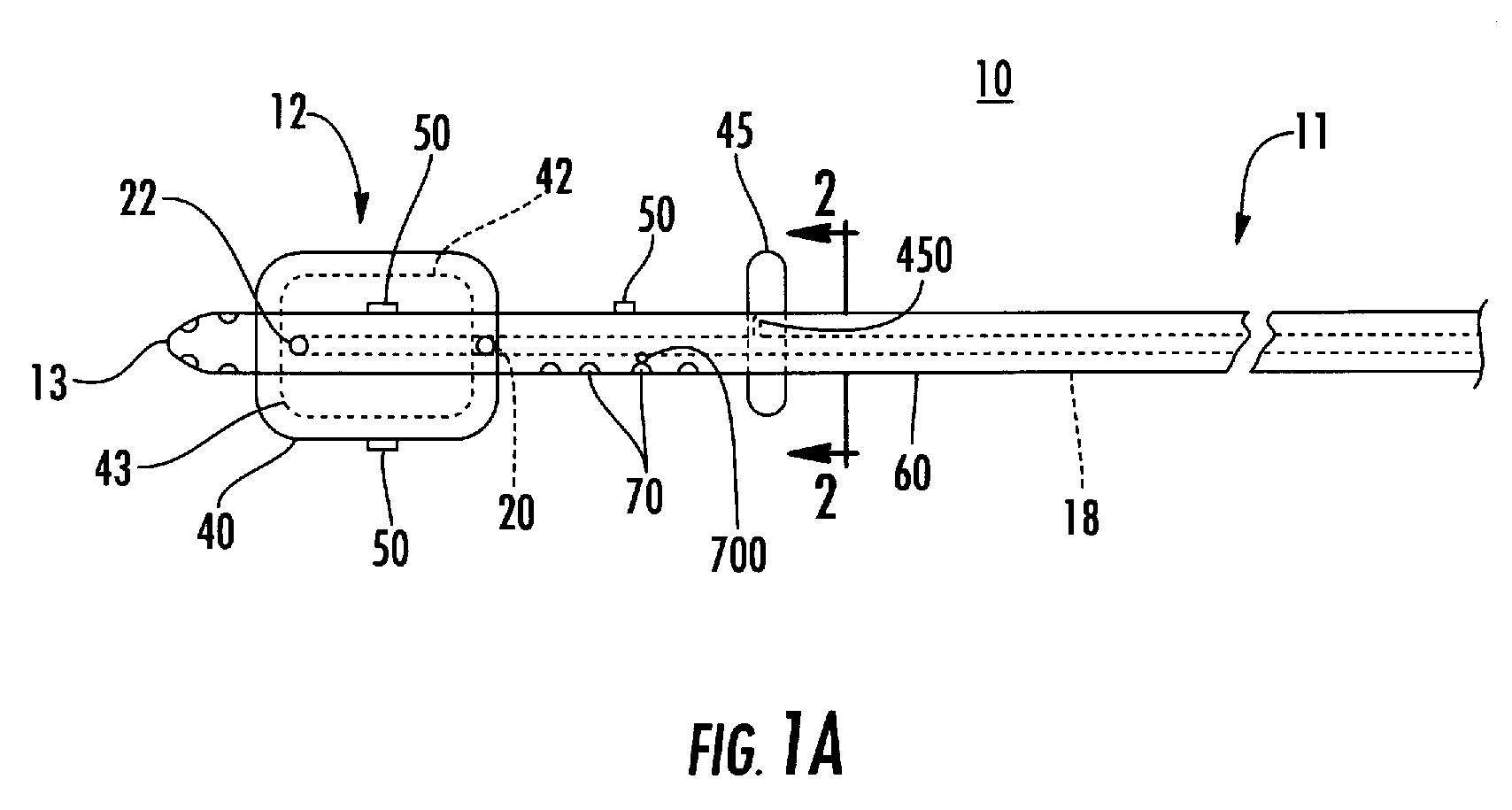
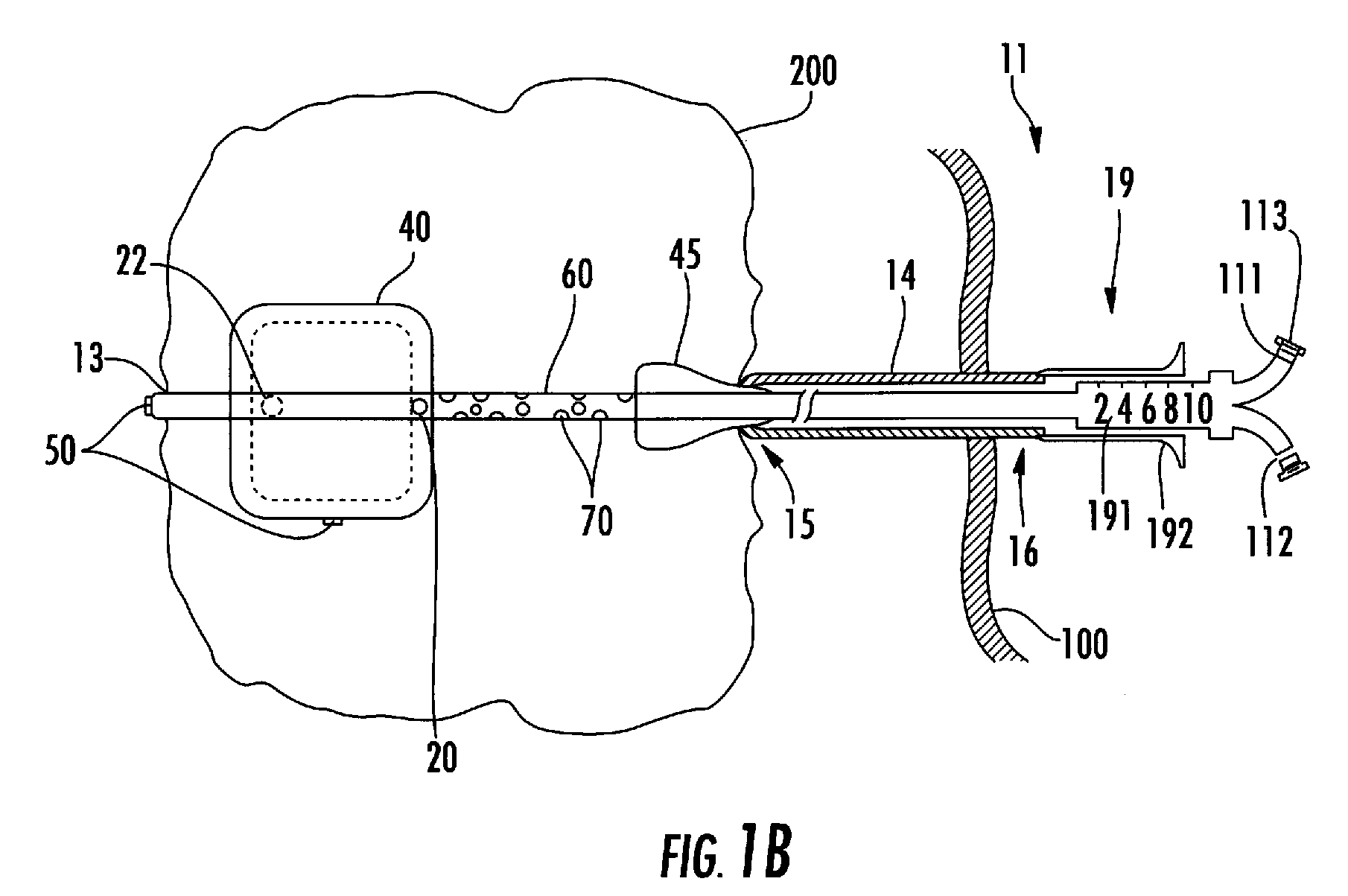
A method and apparatus for direct interstitial treatment of tissue, while preventing backflow and decreasing drainage of a flowable composition from an injected area, by using a catheter and / or a needle with single or multiple inflatable member(s) that stretches, dilates and compresses target tissue and allows for an improved interstitial deposition, distribution and retention of the flowable composition, drug(s), agent(s), or particle(s), into a body organ, fluid, tissue, or tumor, thereby increasing procedural safety and efficacy of direct interstitial therapies.
Owner:NUVUE THERAPEUTICS
Simulator for major surgical operations
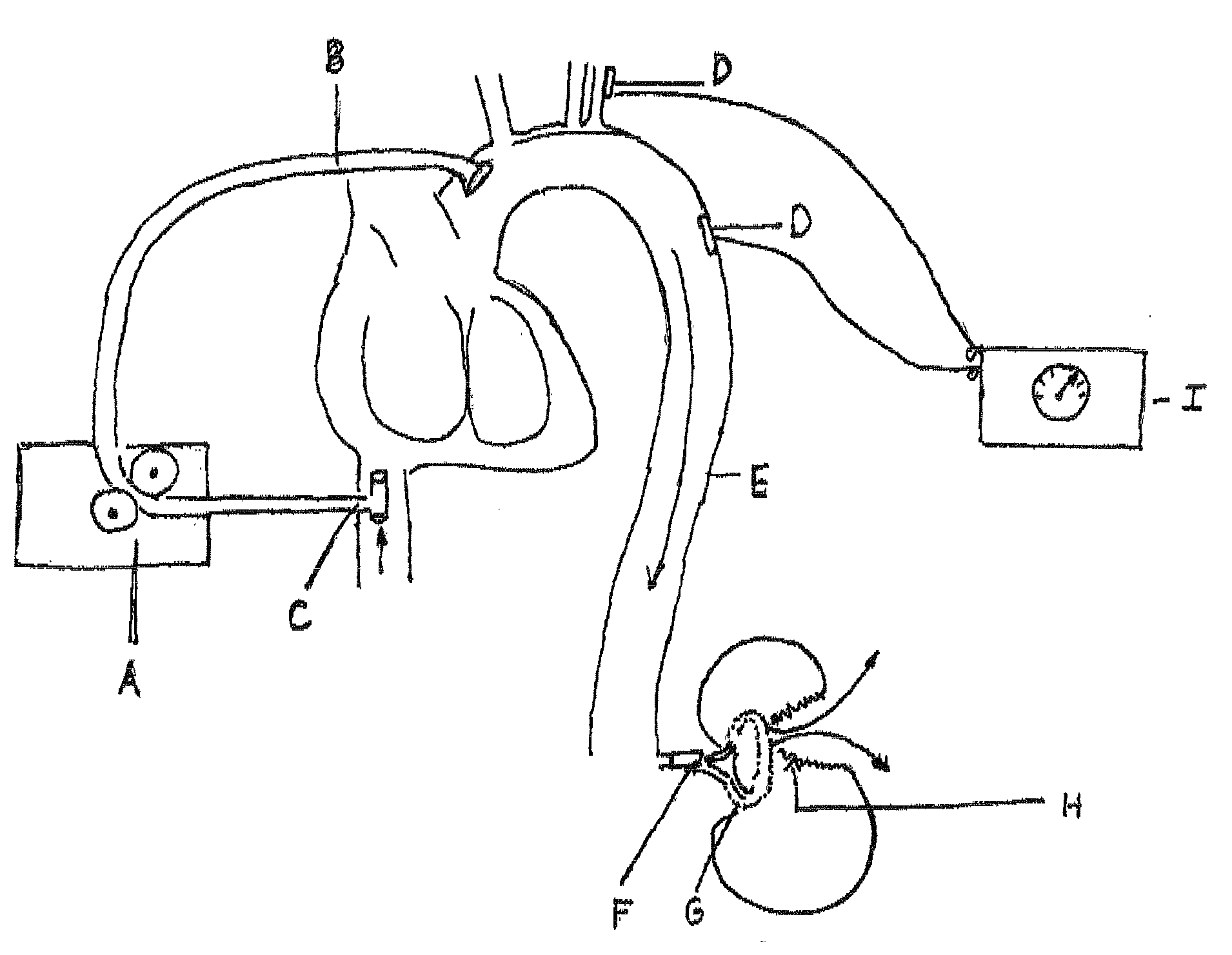
The invention consists of a hands-on, physically simulated human or animal body interior, containing physically simulated representations of all of the solid organs, hollow viscera, bladders, glands, major ducts, large and medium-sized blood vessels, muscle groups and interstitial tissues. The organs and vessels are life-sized and are composed of molded or sculpted open cell or closed cell foam rubber of varying density and load deformation, matching the physical properties of the specific biologic organs or tissues simulated. The organs, tissues and vessels may be treated with pigments, sealants and / or hardening agents to reflect the contours, appearances, densities, textures, elasticity, and deformability of normal or pathologically-altered internal organs and tissues. Organs contain molded vascular channels, reversibly attached to the larger blood vessels of the simulator. The model has a pressurized, watertight, simulated vascular system, monitored by electronic sensors.
Owner:OPERATIVE EXPERIENCE
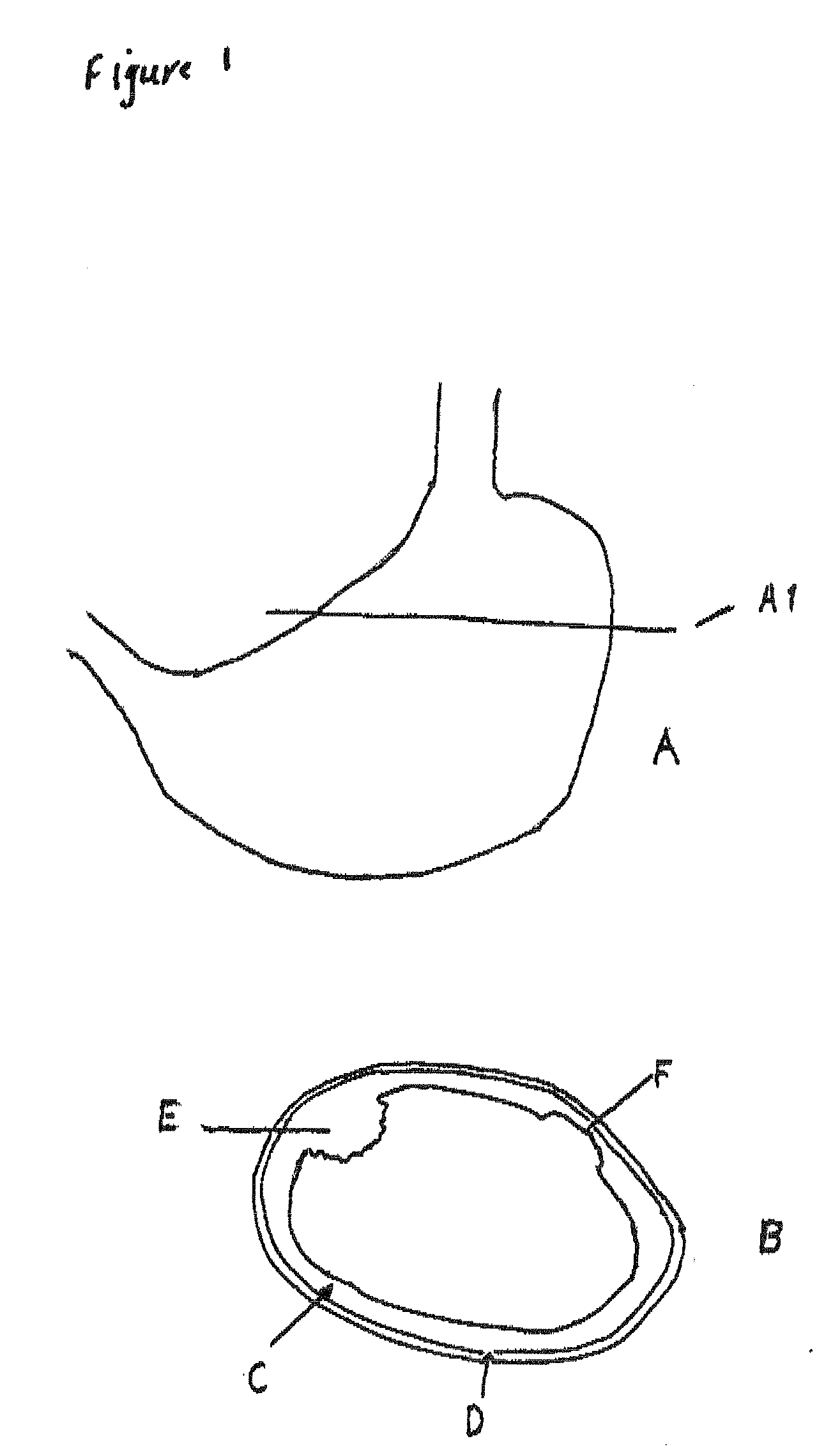
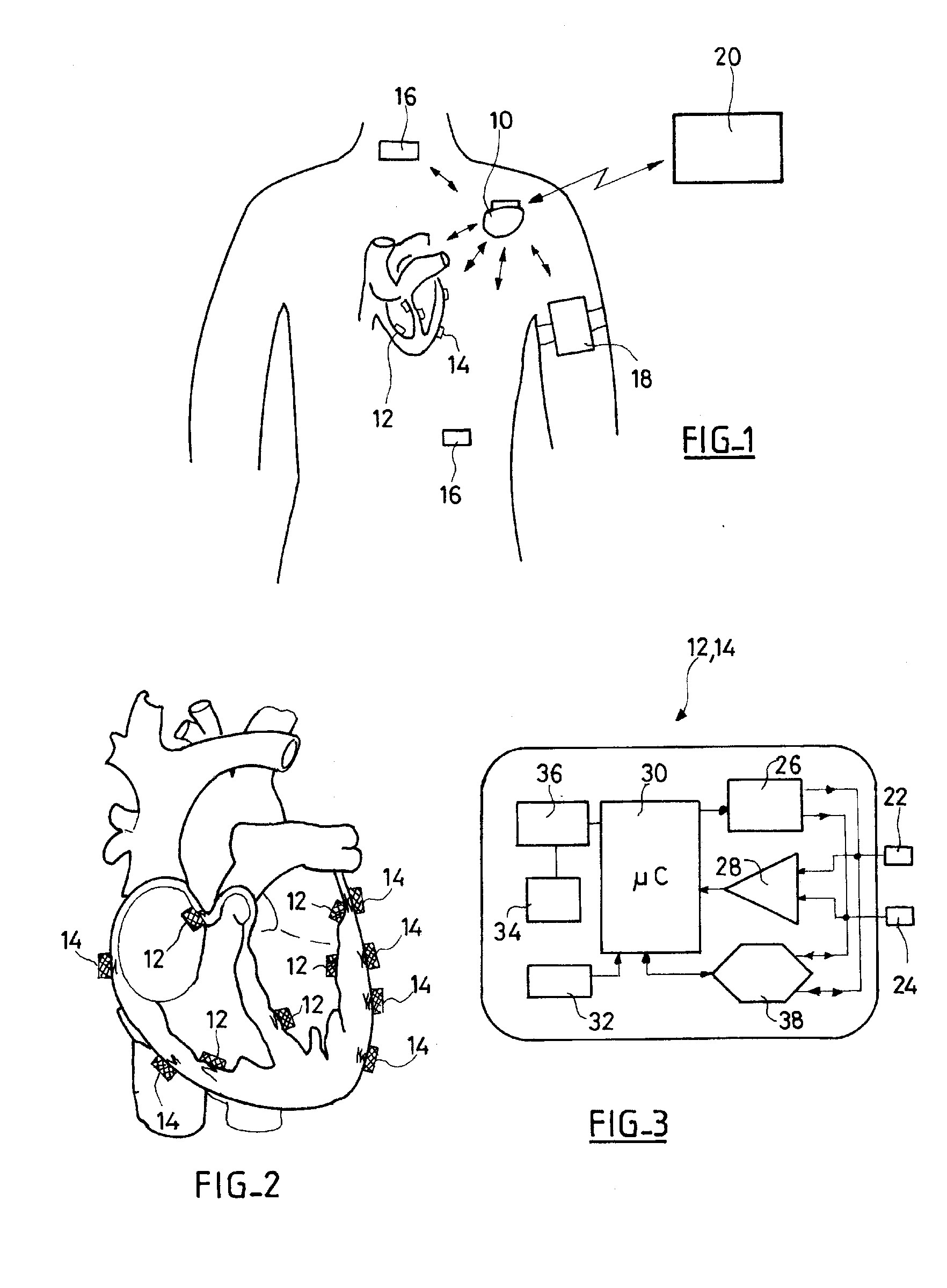
System, Methods And Apparatus For Waking An Autonomous Active Implantable Medical Device Communicating By Pulses Transmitted Through The Interstitial Tissues Of The Body
ActiveUS20120093245A1Minimum delayImprove responsivenessElectrotherapyModulated-carrier systemsSleep stateImplanted device
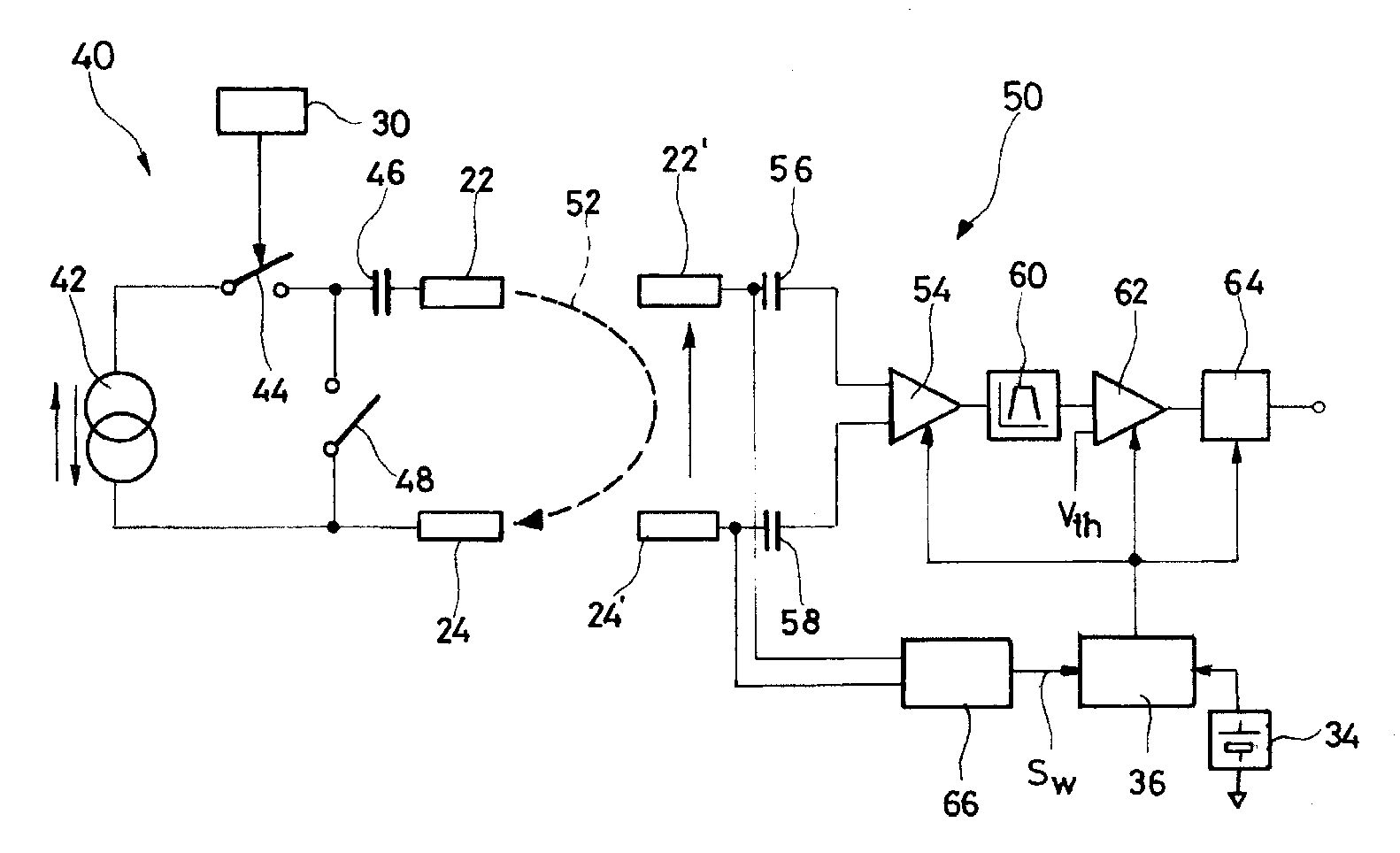
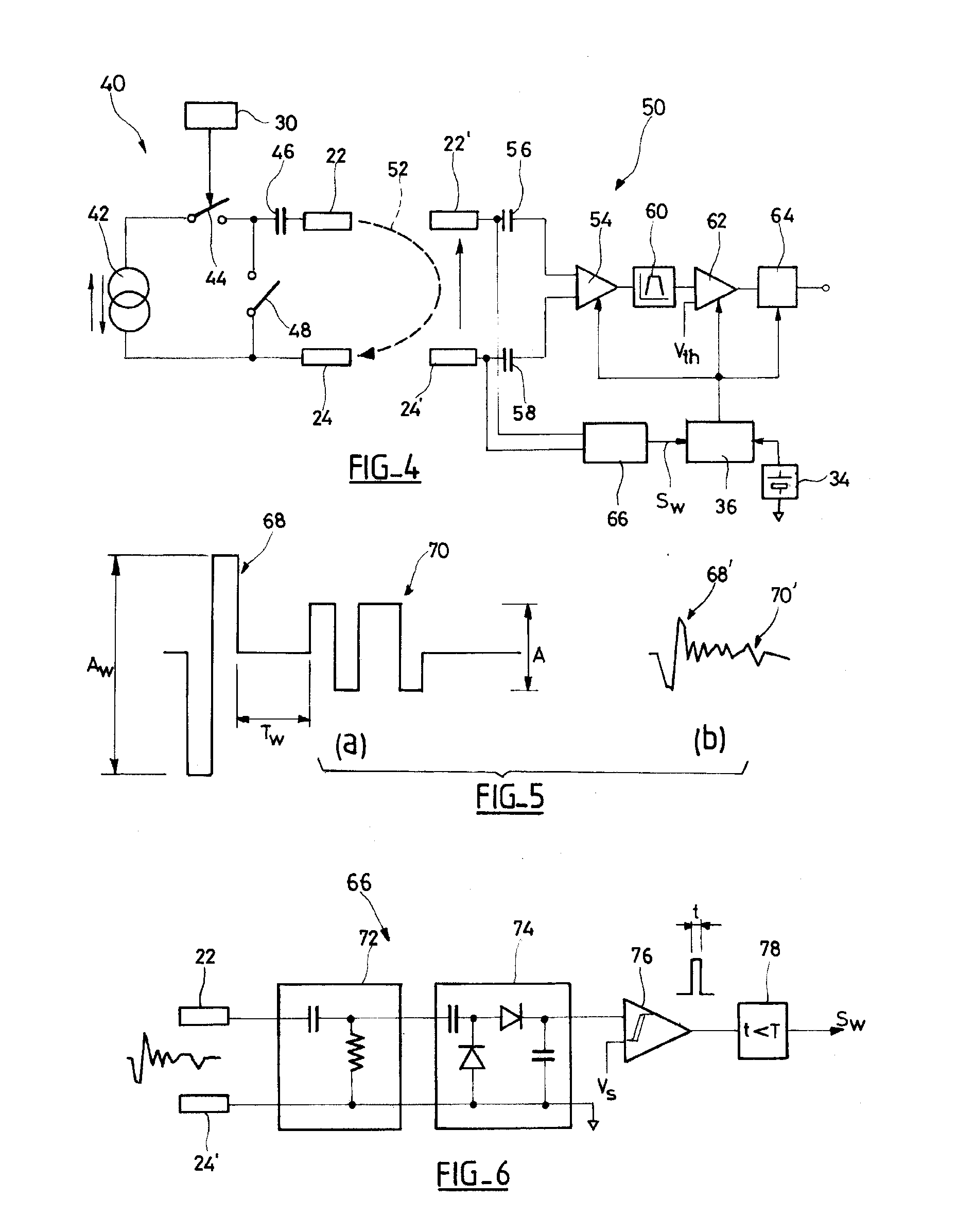
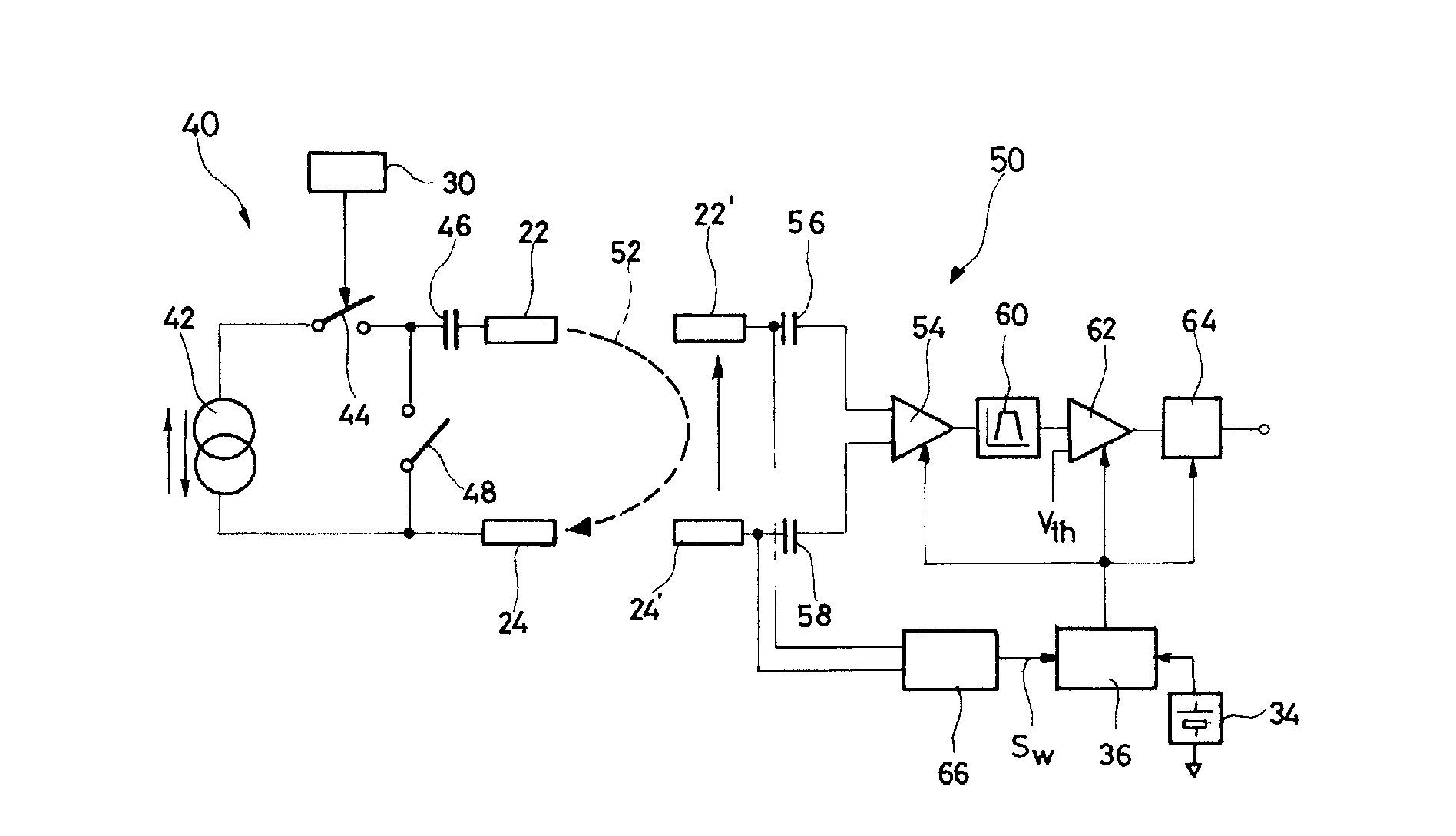
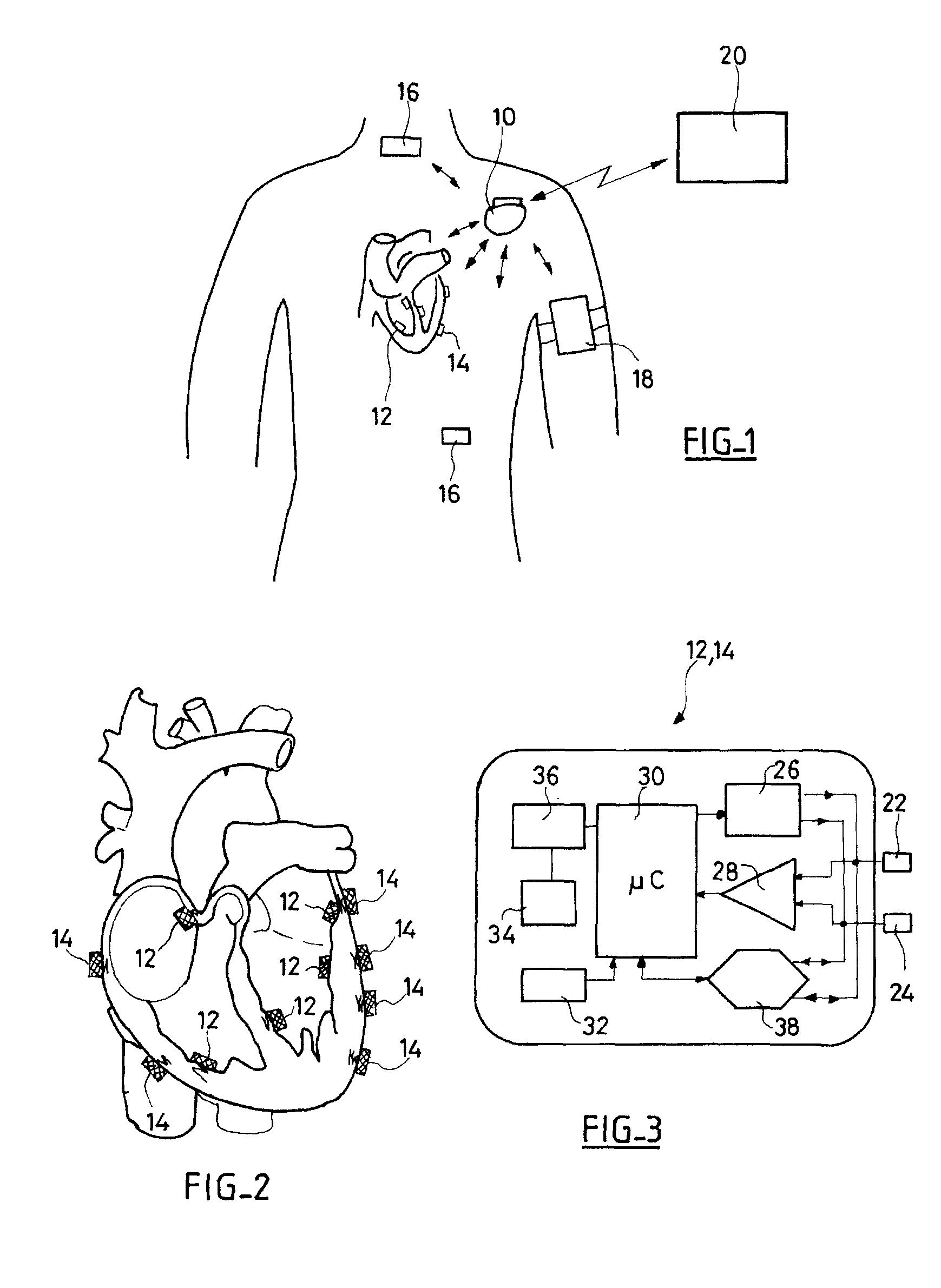
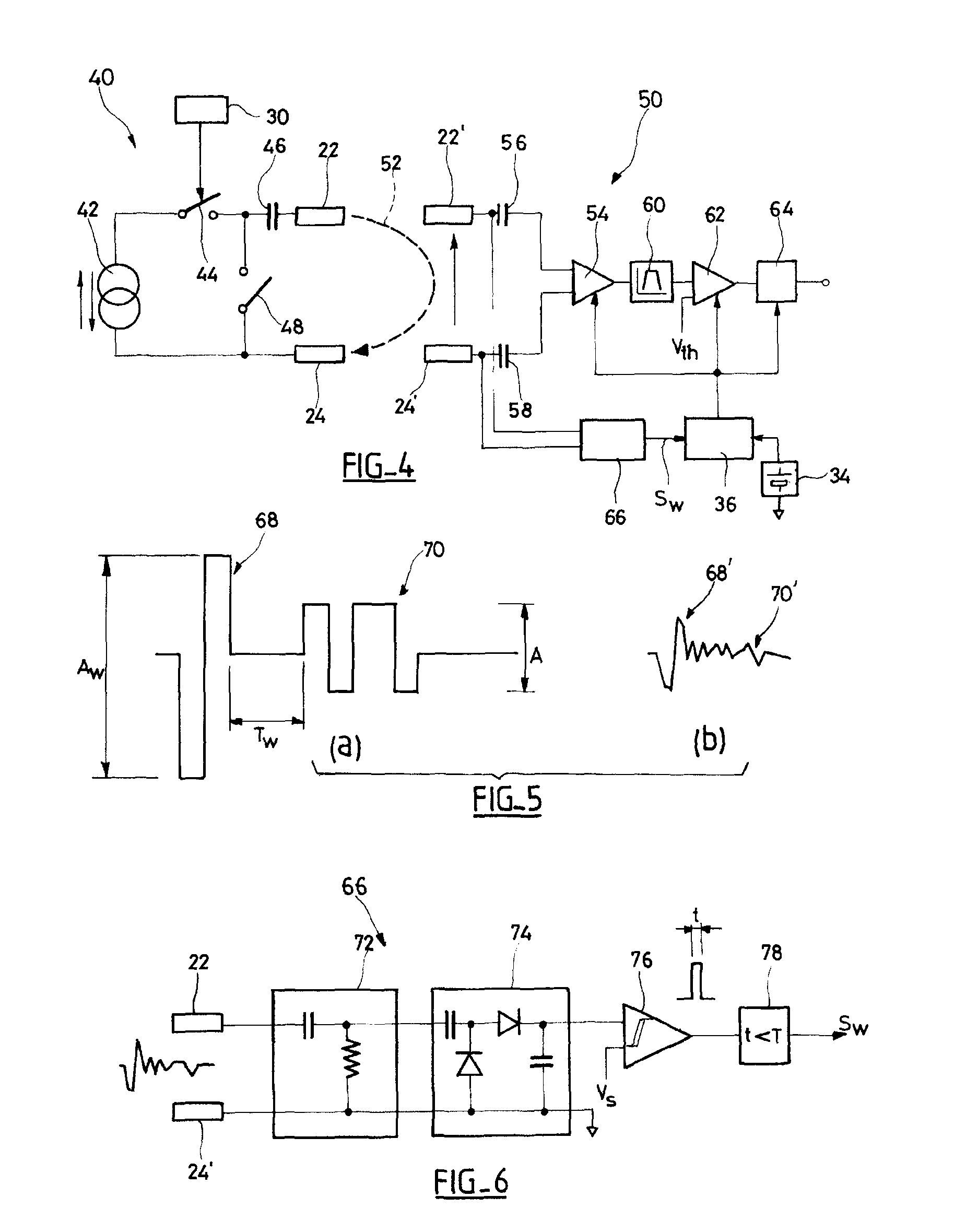
An autonomous active medical implantable device, with a power supply and a wake-up circuit that responds to receipt of specific pulses transmitted through the interstitial tissues of the body transmitter device (40) generates trains of modulated pulses applied to electrodes (22, 24), and a receiver (50) processes (e.g., filter, amplify and demodulate) pulses collected on electrodes (22′, 24′). The receiver circuits (50) are selectively activated from a dormant (sleep) state in which they are not powered by a power source (34), to an operational (active) state in which they are powered and able to process (e.g., filter, amplify and demodulate) the collected pulses specific wake-up pulse train, configured in a predetermined characteristic pulse pattern triggers passive wake-up circuits (66) in the receiver (50) to switch the receiver circuits from the sleep state to the operational state.
Owner:SORIN CRM
System, methods and apparatus for waking an autonomous active implantable medical device communicating by pulses transmitted through the interstitial tissues of the body
ActiveUS8577327B2Minimum delayImprove responsivenessElectrotherapyModulated-carrier systemsSleep statePulse sequence
An autonomous active medical implantable device, with a power supply and a wake-up circuit that responds to receipt of specific pulses transmitted through the interstitial tissues of the body. A transmitter device (40) generates trains of modulated pulses applied to electrodes (22, 24), and a receiver (50) processes (e.g., filter, amplify and demodulate) pulses collected on electrodes (22′, 24′). The receiver circuits (50) are selectively activated from a dormant (sleep) state in which they are not powered by a power source (34), to an operational (active) state in which they are powered and able to process (e.g., filter, amplify and demodulate) the collected pulses. A specific wake-up pulse train, configured in a predetermined characteristic pulse pattern, triggers passive wake-up circuits (66) in the receiver (50) to switch the receiver circuits from the sleep state to the operational state.
Owner:SORIN CRM
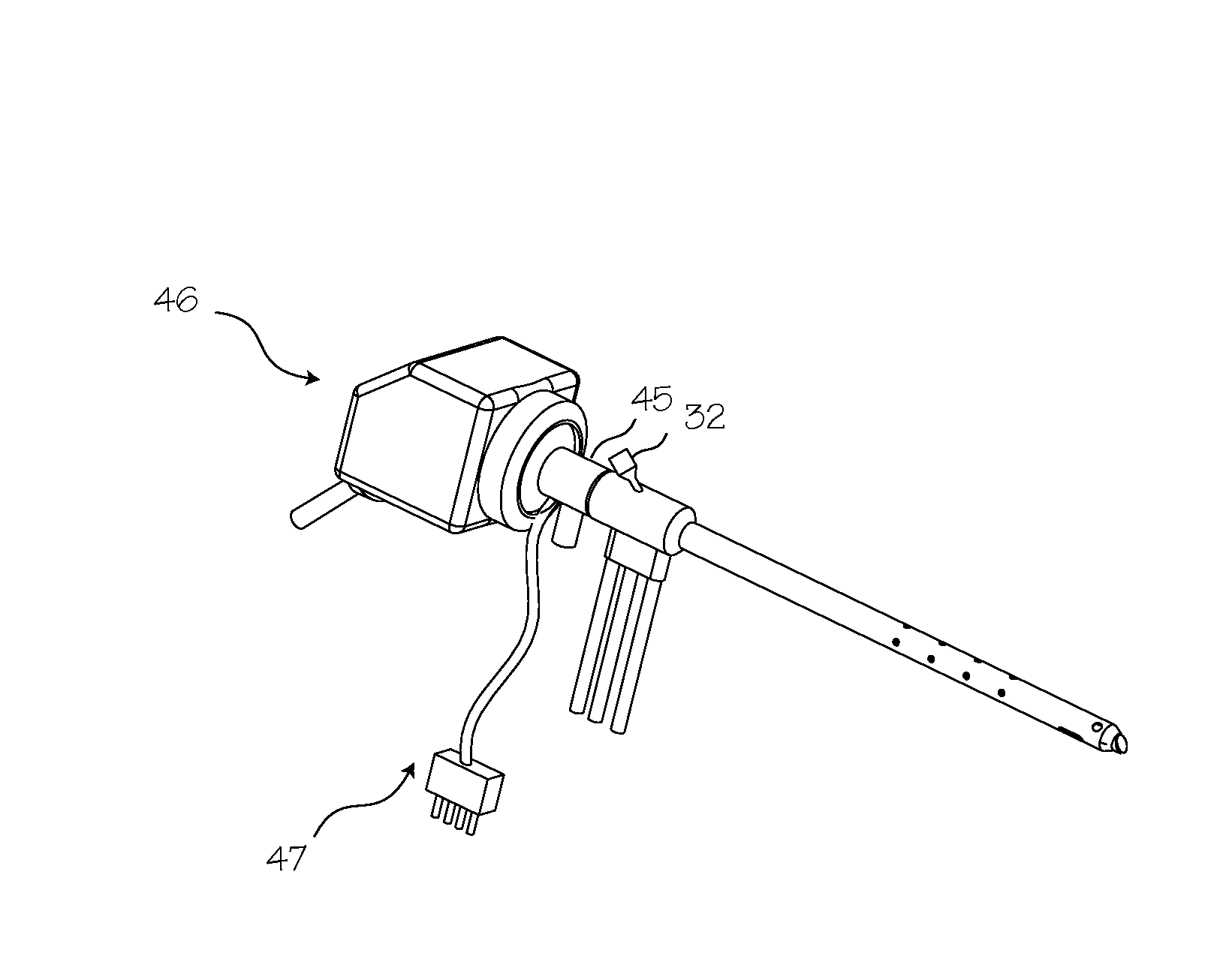
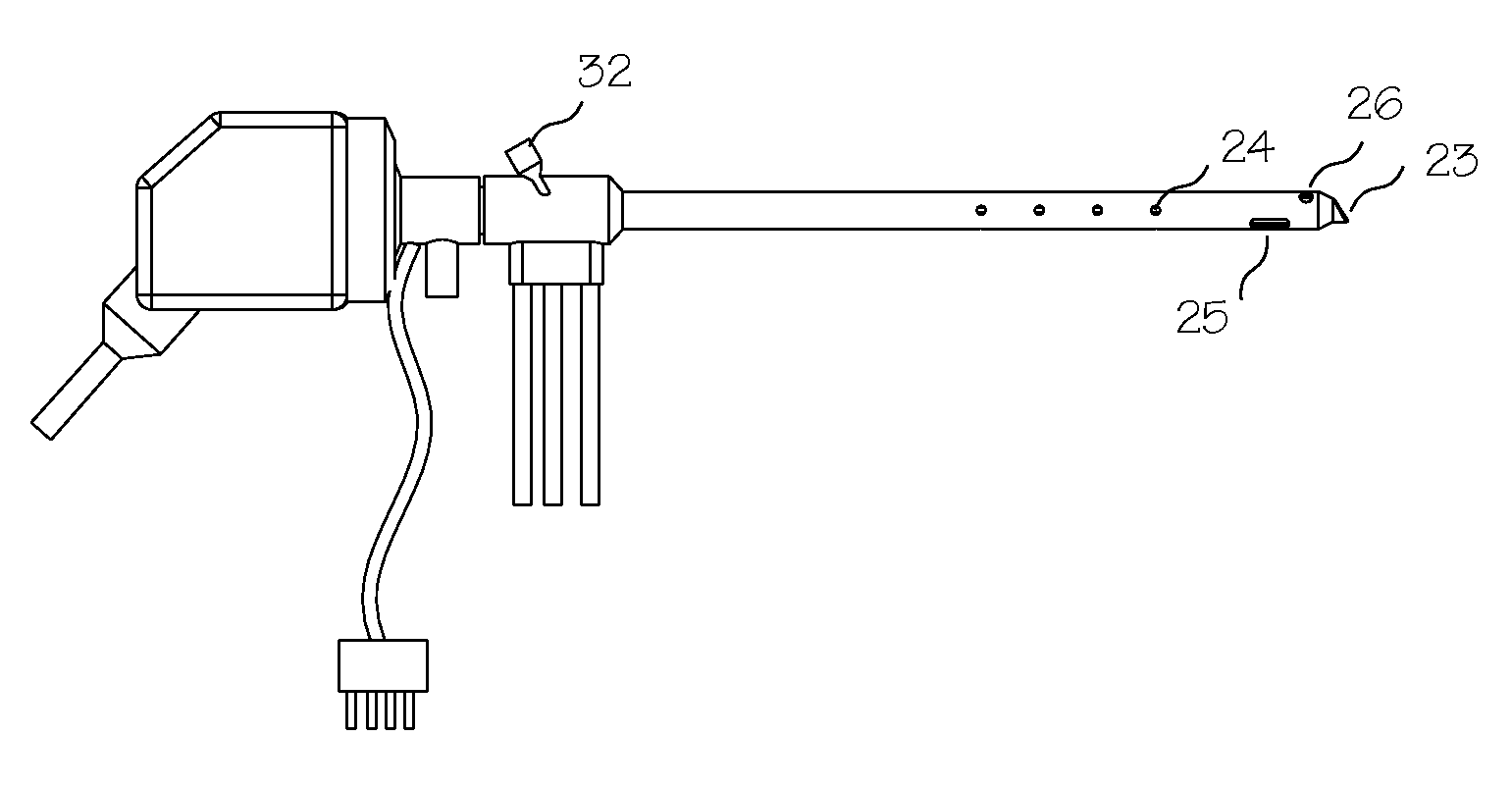
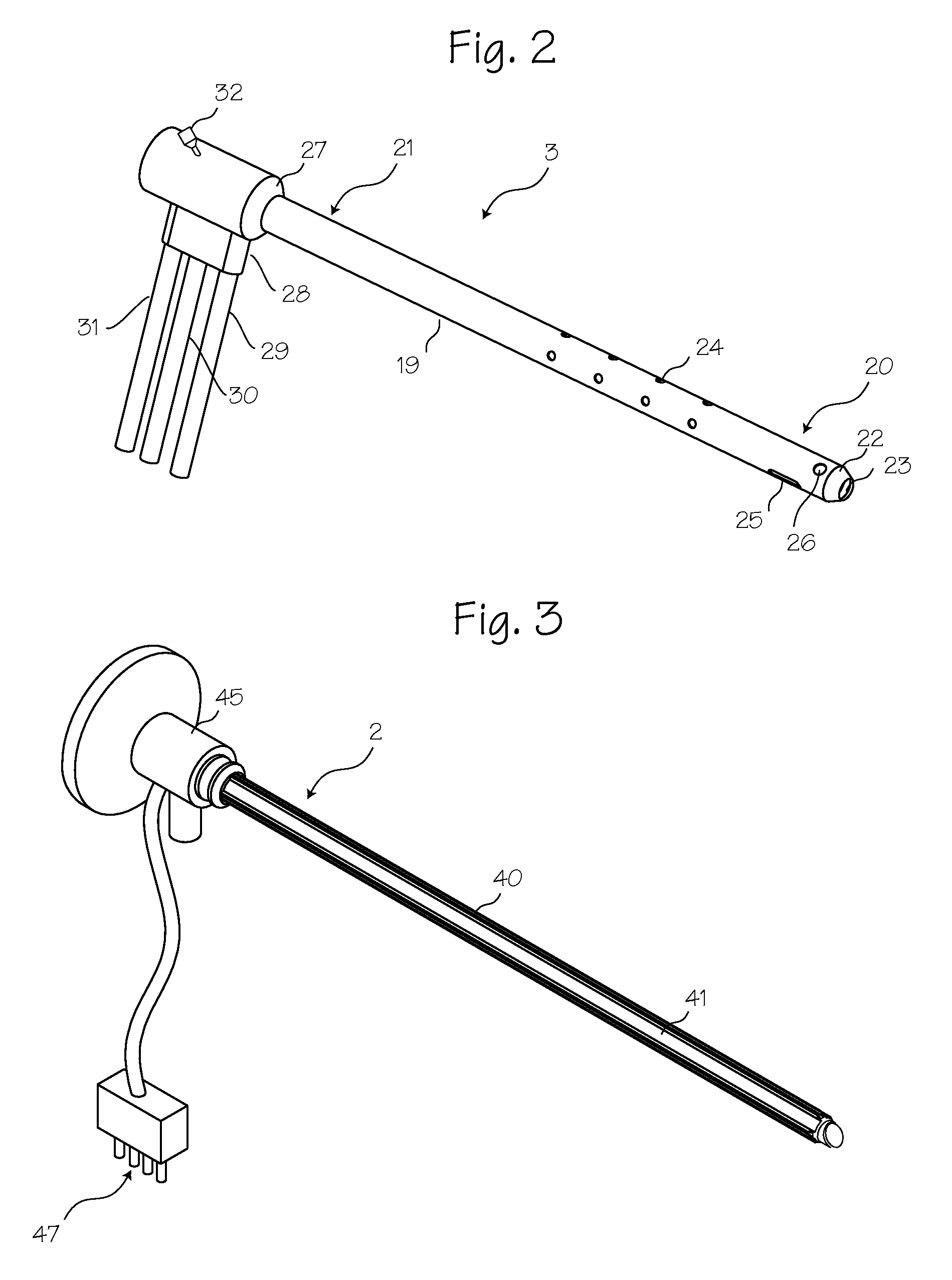
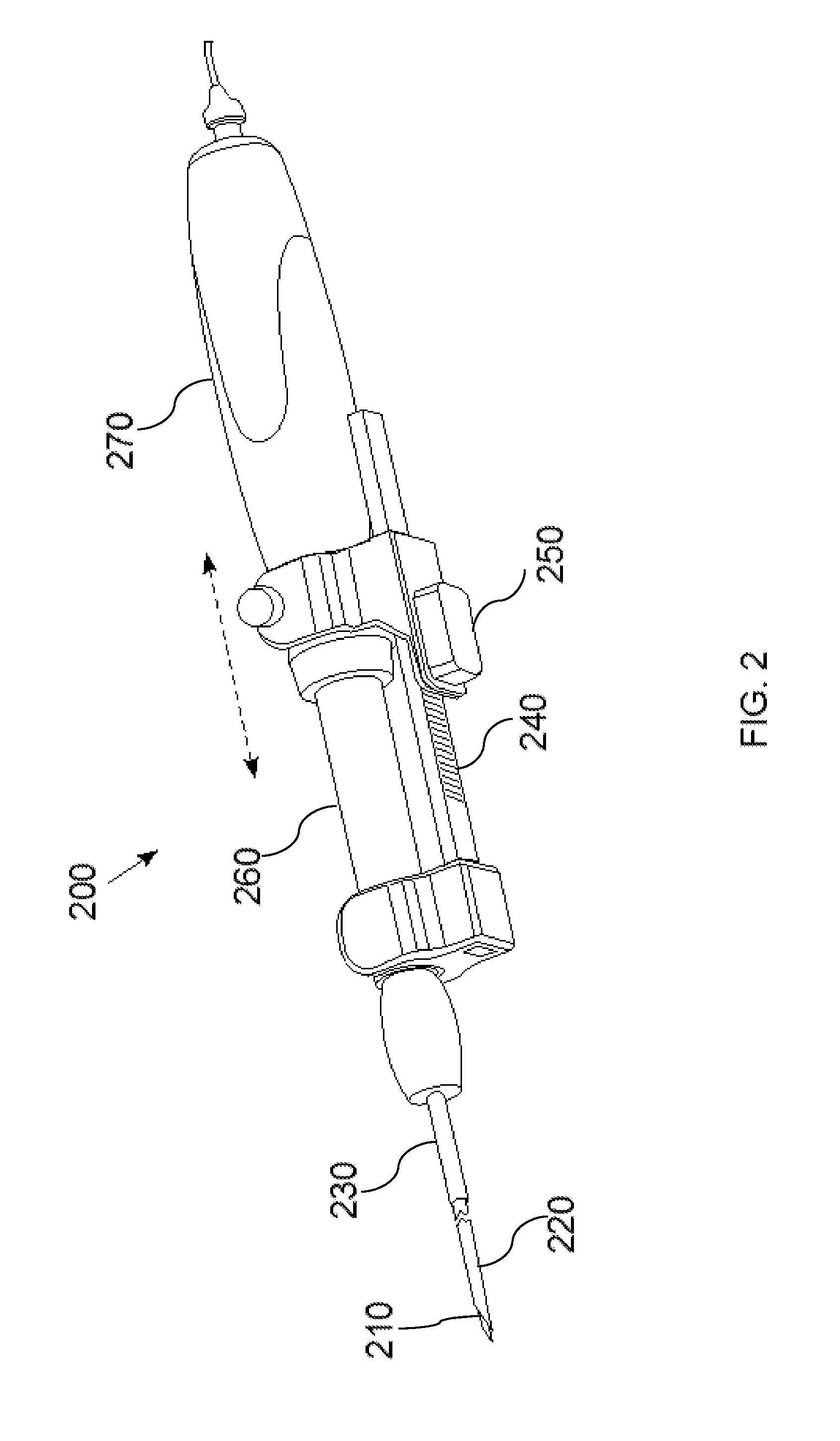
Rigid Arthroscope System
A reinforced arthroscope comprising external ribs to provide for a number of separate fluid channels, such as inflow, outflow and interstitial tissue drainage, when the arthroscope is slipped into a disposable external sheath. The arthroscope is constructed to be sufficiently rigid so as to penetrate and move within a joint without damaging the rod optics inside. The externality of the arthroscope channels allow for cleaning and sterilizing the scope between uses.
Owner:PSIP2 LLC
Pluripotent stem cells originating in skeletal muscle intestinal tissue
InactiveUS20050079606A1Efficient removalEasily discriminatedGenetically modified cellsDrug screeningNerve degenerationOsteoblast
The present invention relates to multipotent stem cells derived from the interstitial tissues of skeletal muscle. The multipotent stem cell of the present invention is capable of differentiating into skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, blood cells, vascular endothelial cells, adipocytes, osteoblasts, nervous cells, hepatocytes and pancreatic cells, and is useful for regeneration of tissues and cells and treatment for cardiac failure, hepatic insufficiency, renal insufficiency, leukemia, nerve degeneration disease, arthritis, diabetes, arteriosclerosis, and the like.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD +2
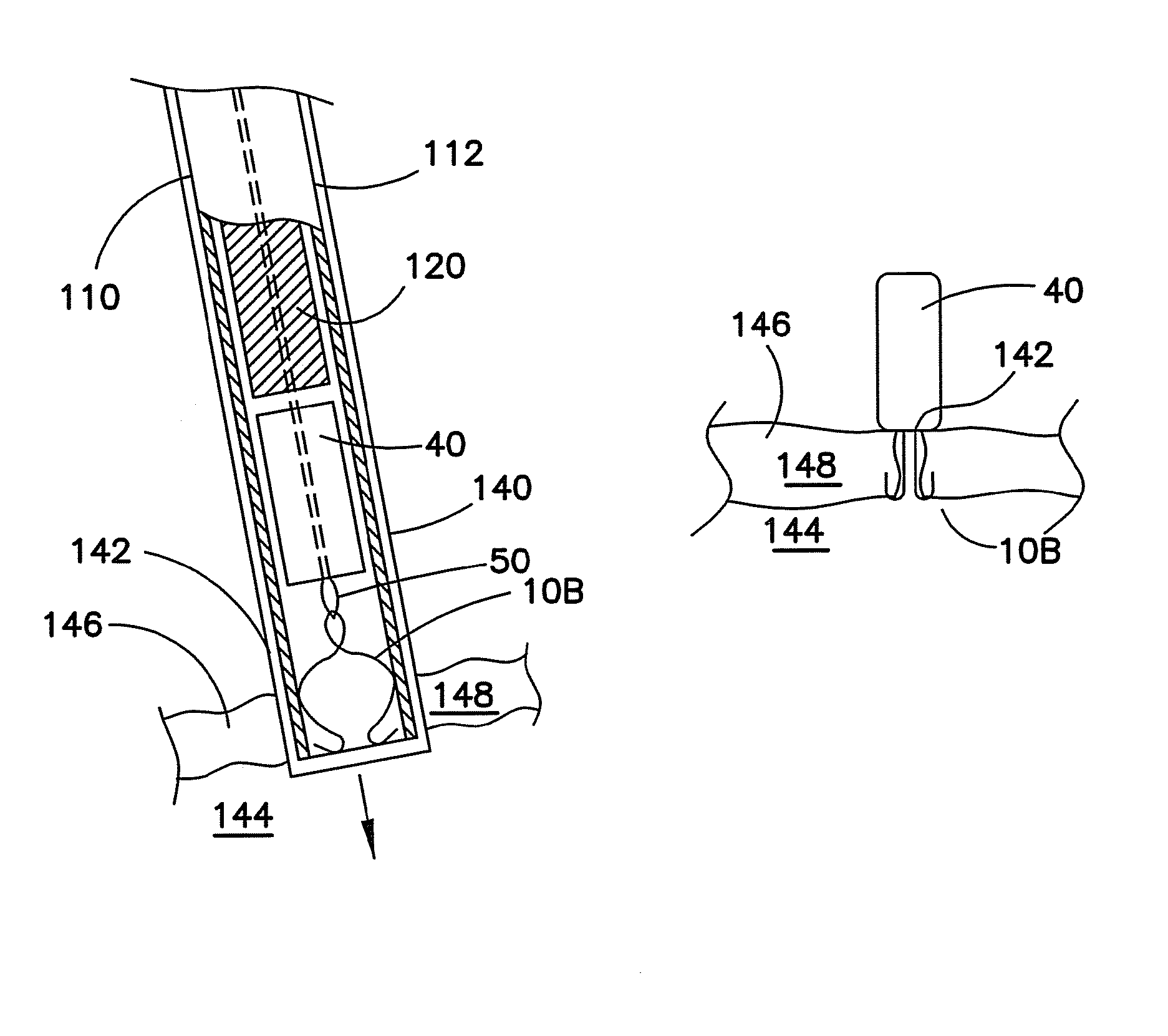
Vascular closure device
ActiveUS20100198254A1Promote faster healingPrevent movementSurgical veterinaryWound clampsVascular closure deviceVascular device
A device for closure of an opening formed through a wall of a body vessel of a patient is provided, as well as an introducer system for delivery of the closure device. Various embodiments include the closure device having hook members configured to engage the tissue interior of the body vessel wall, hook members configured to engage interstitial tissue adjacent to the body vessel, a plug member to contact sealably the opening from inside the body vessel, and combinations thereof. A retraction member is removably attached to the each of the embodiments to permit manipulation of the device. Remodelable material may be included with each of the embodiments to promote quicker healing. The introducer includes a sheath that is insertable through the opening and a pusher disposed within the lumen of the sheath and movable within the sheath lumen to deploy the device.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
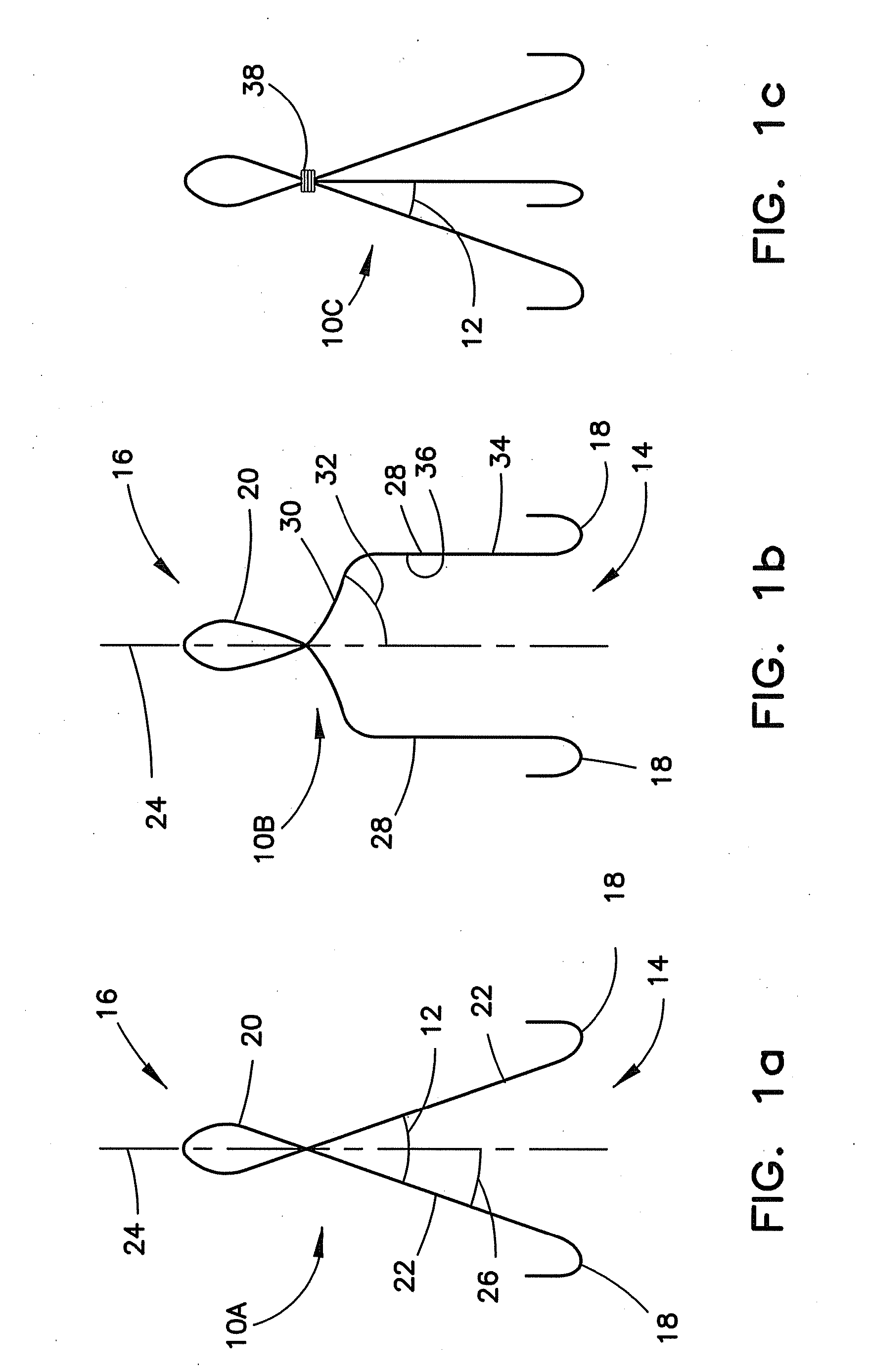
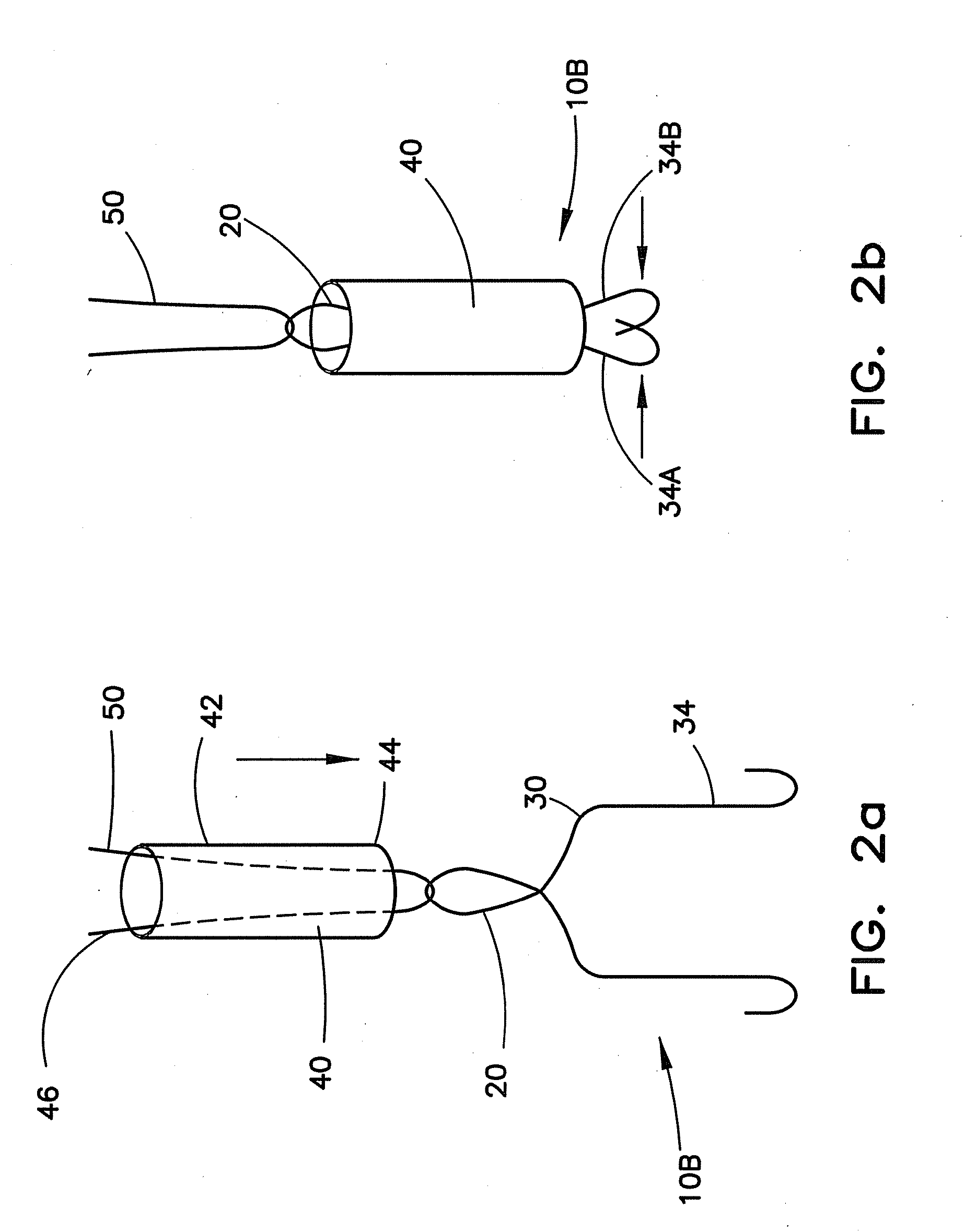
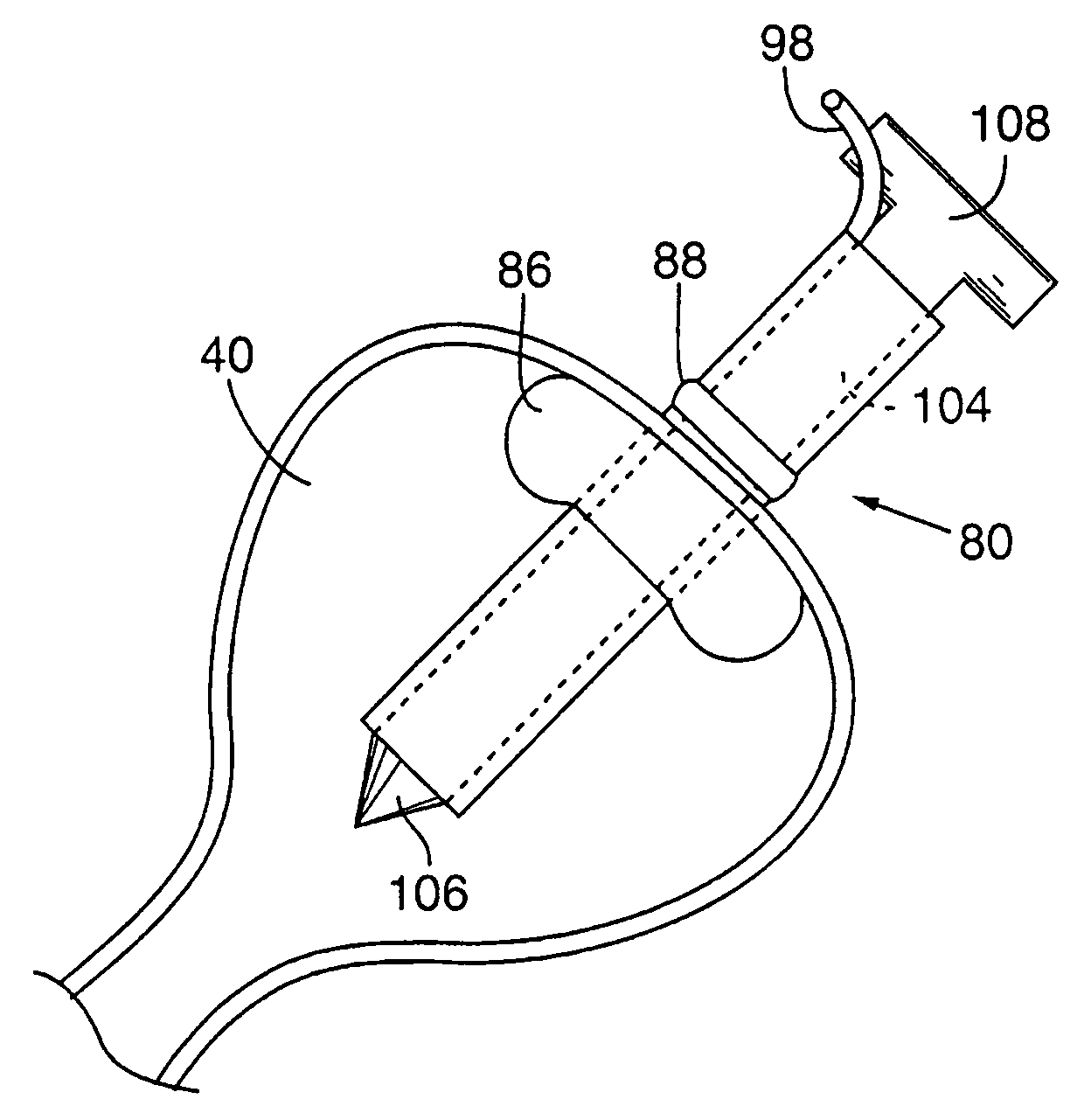
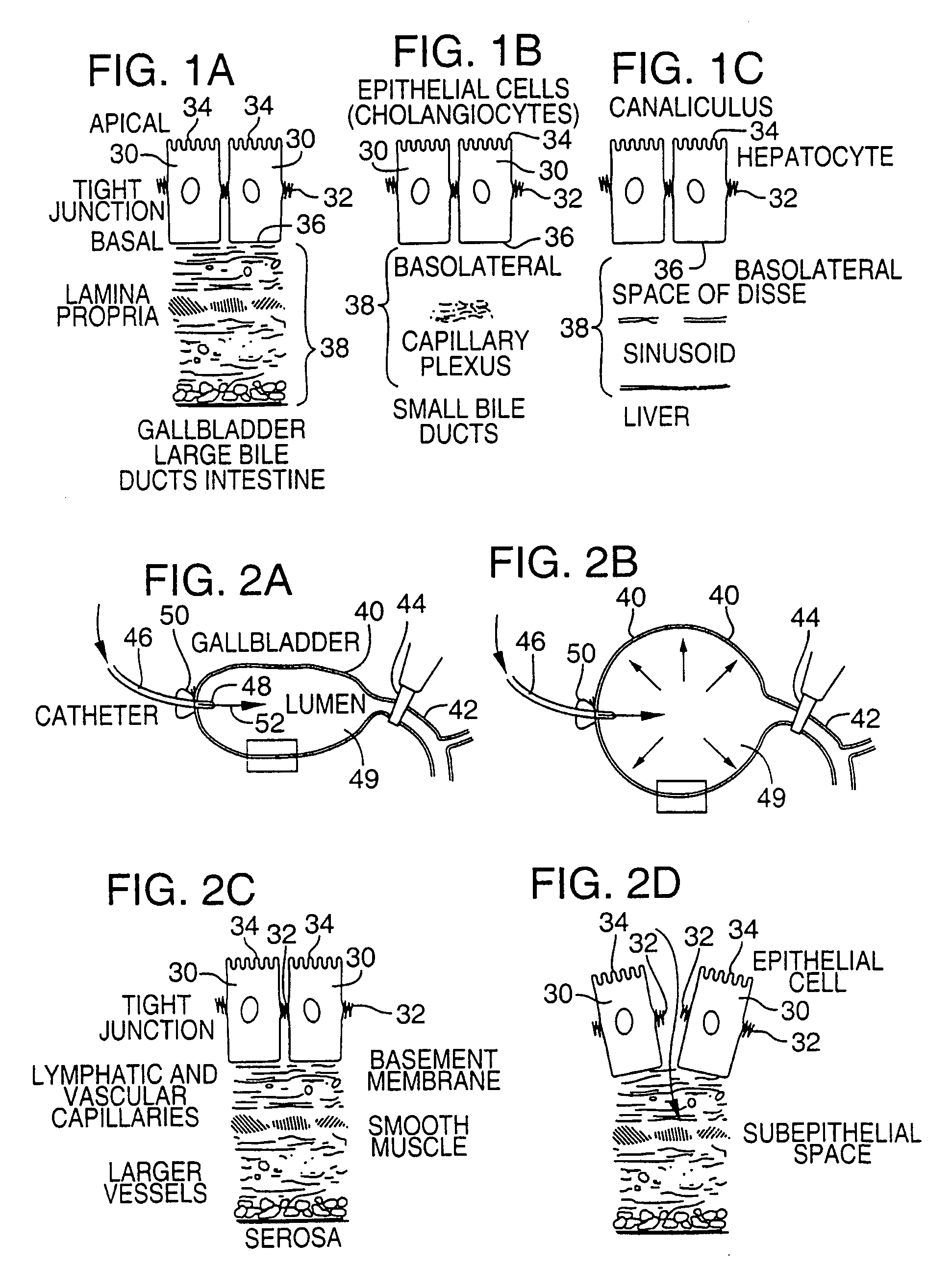
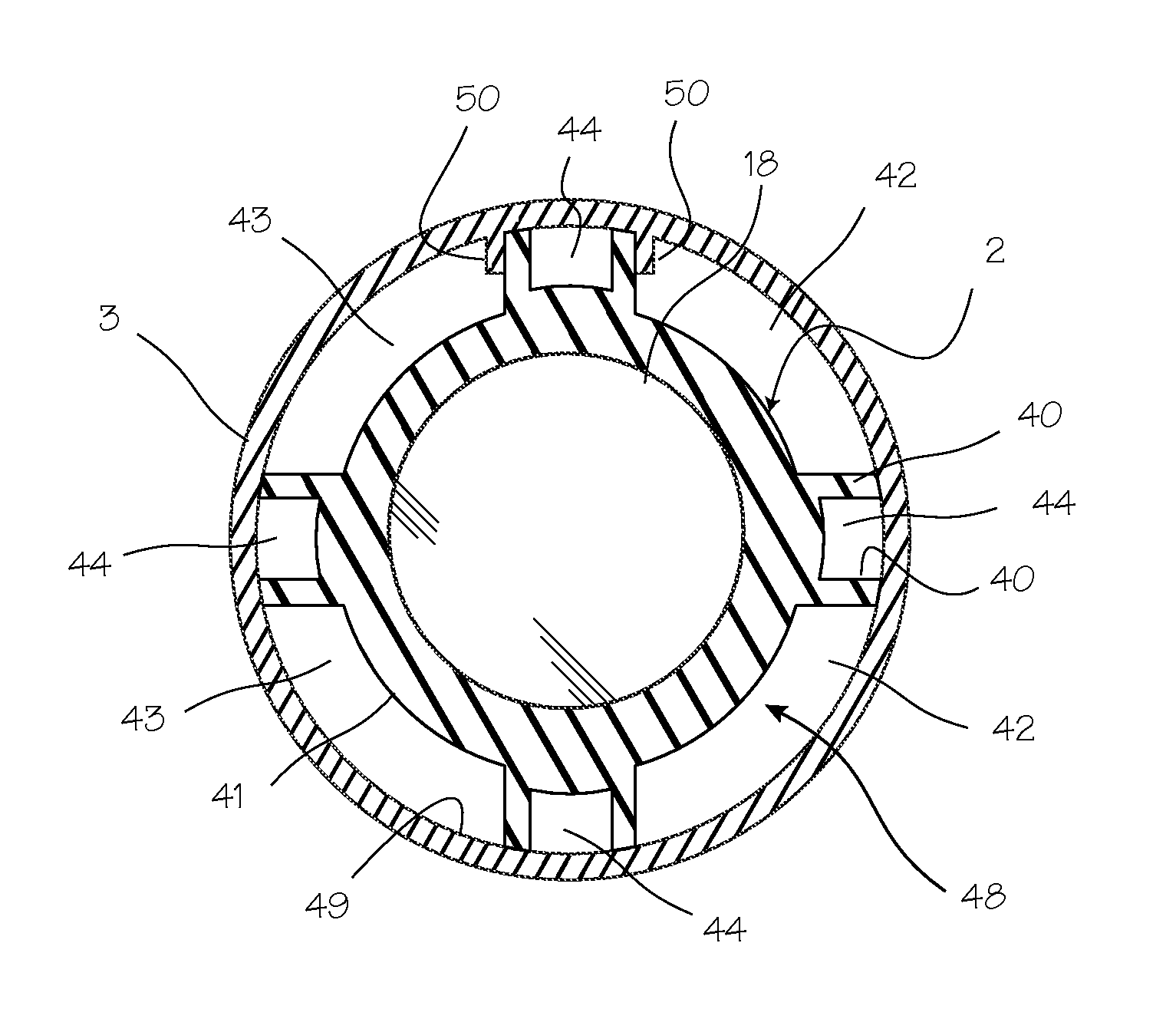
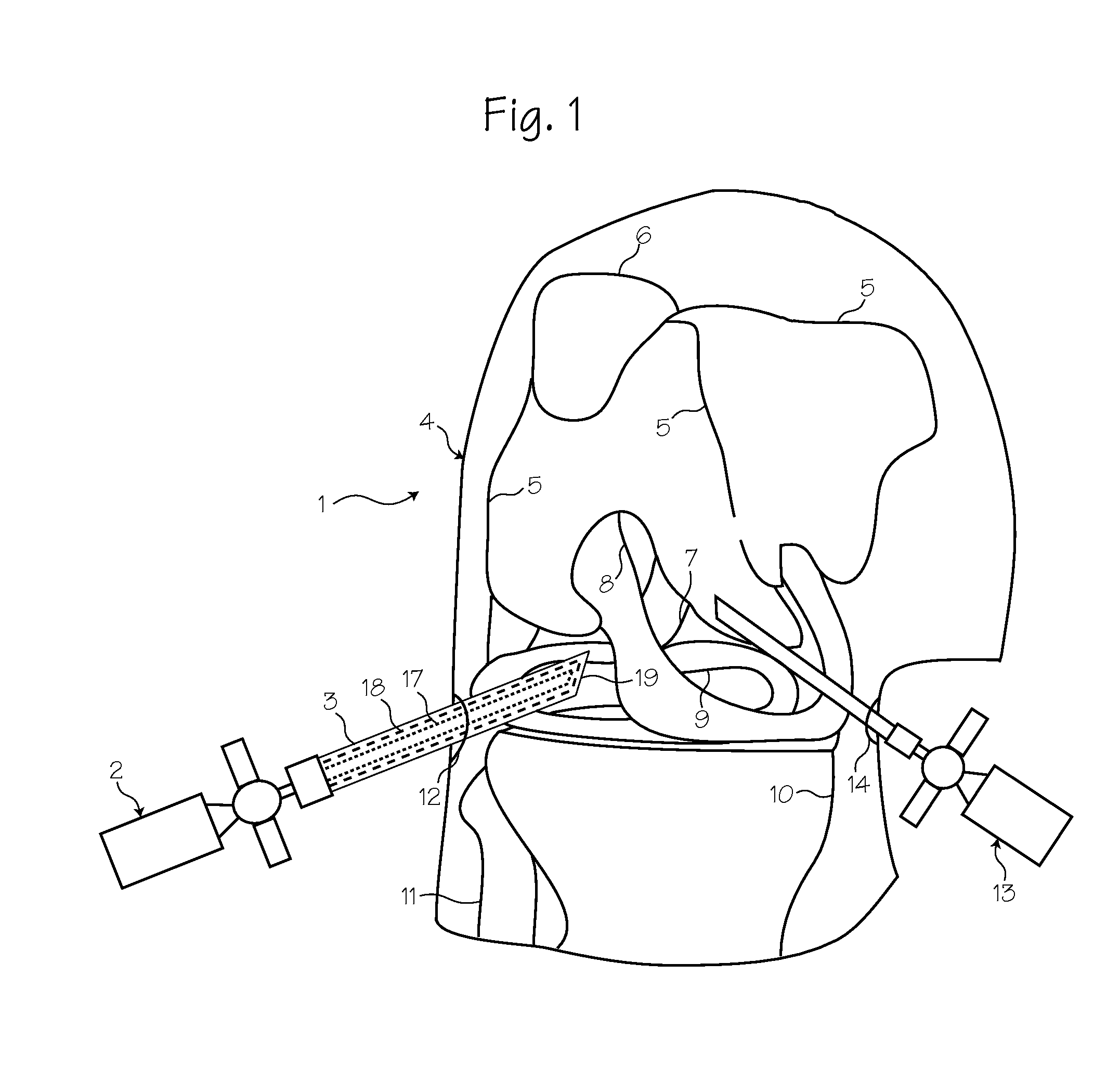
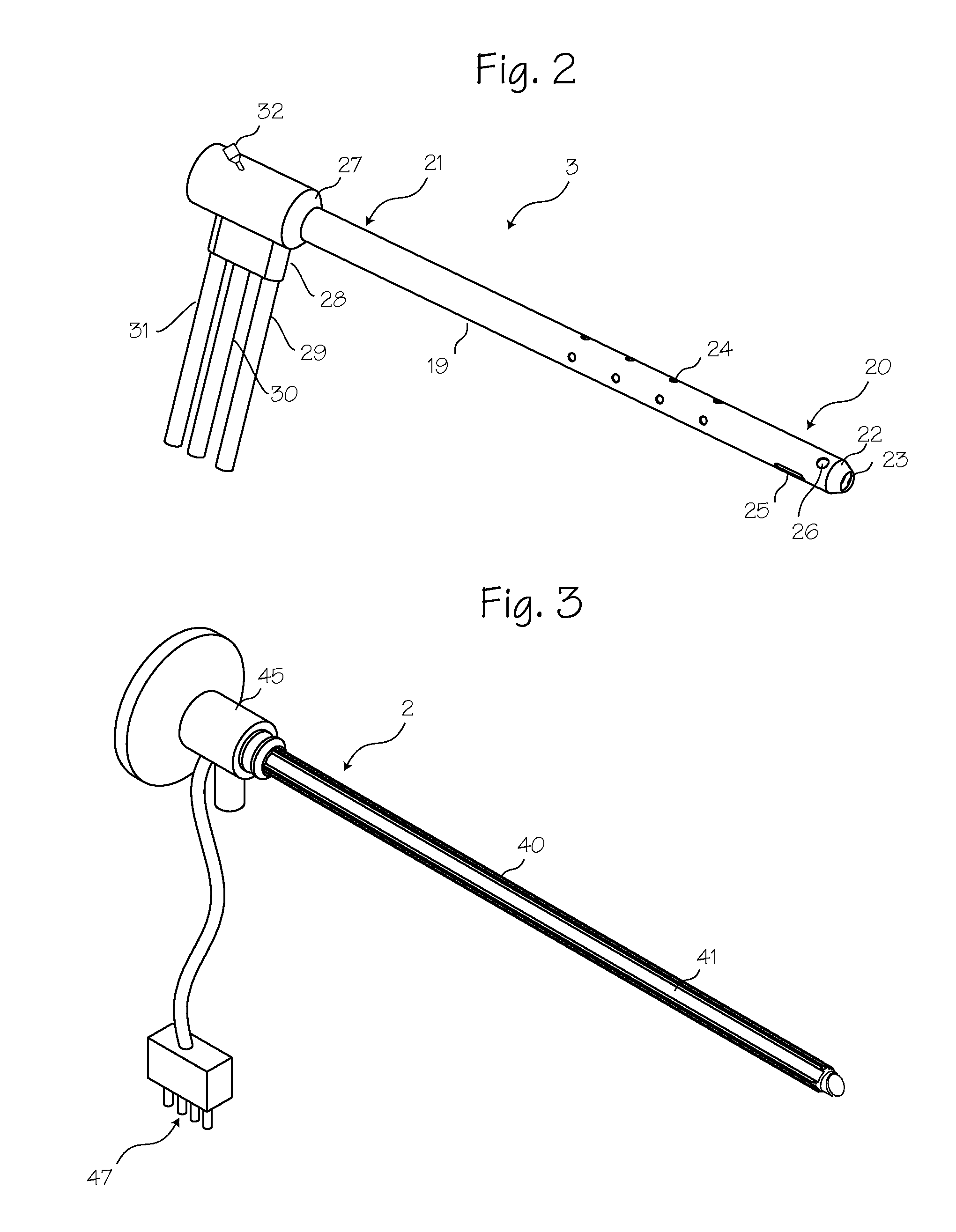
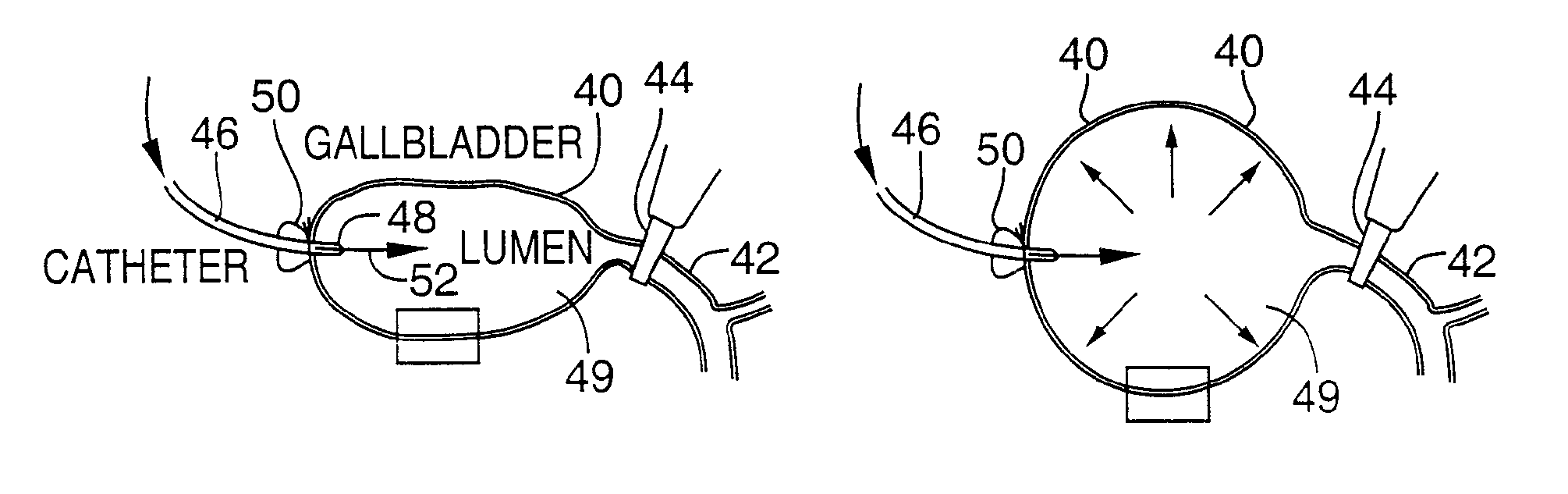
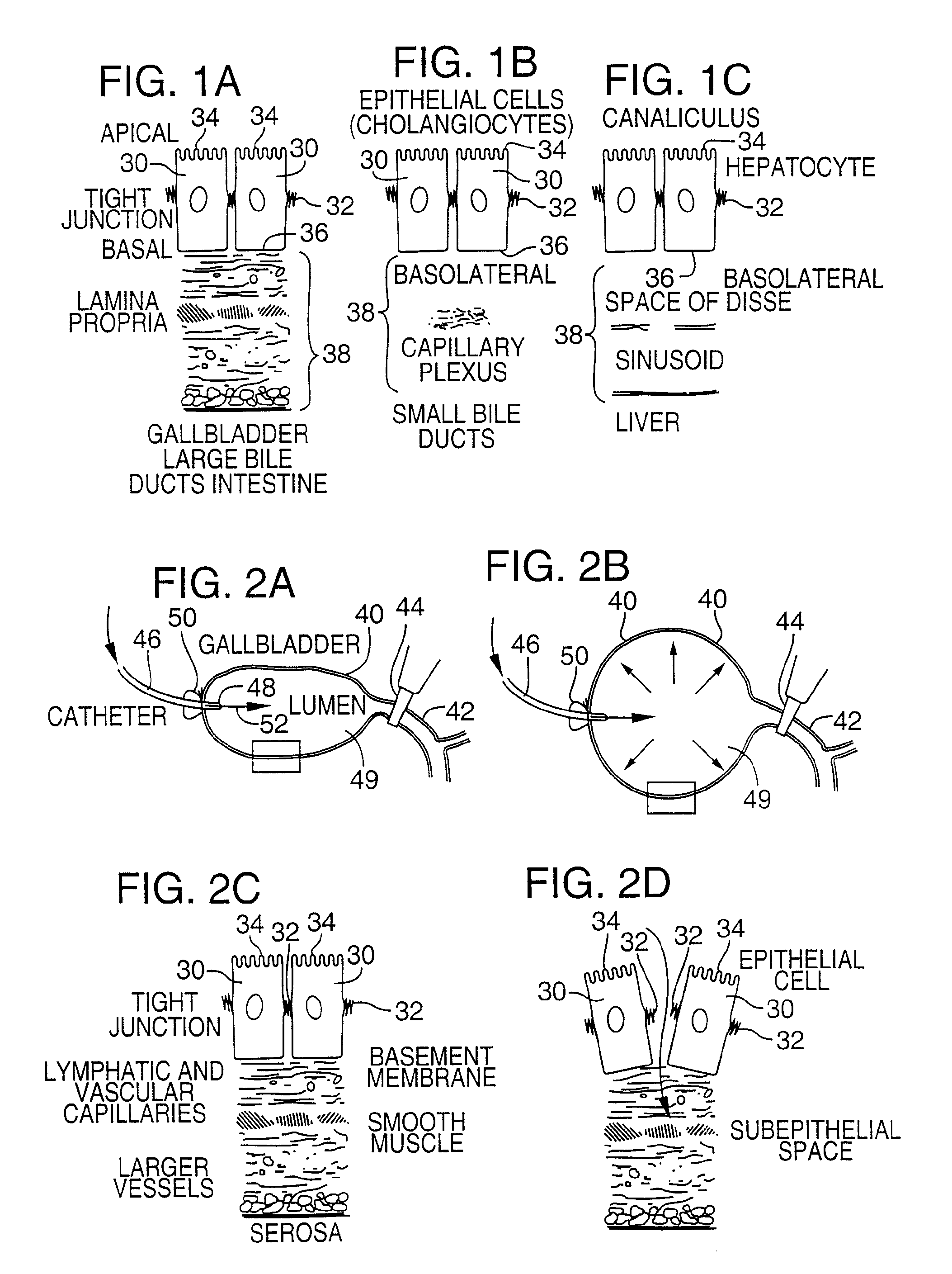
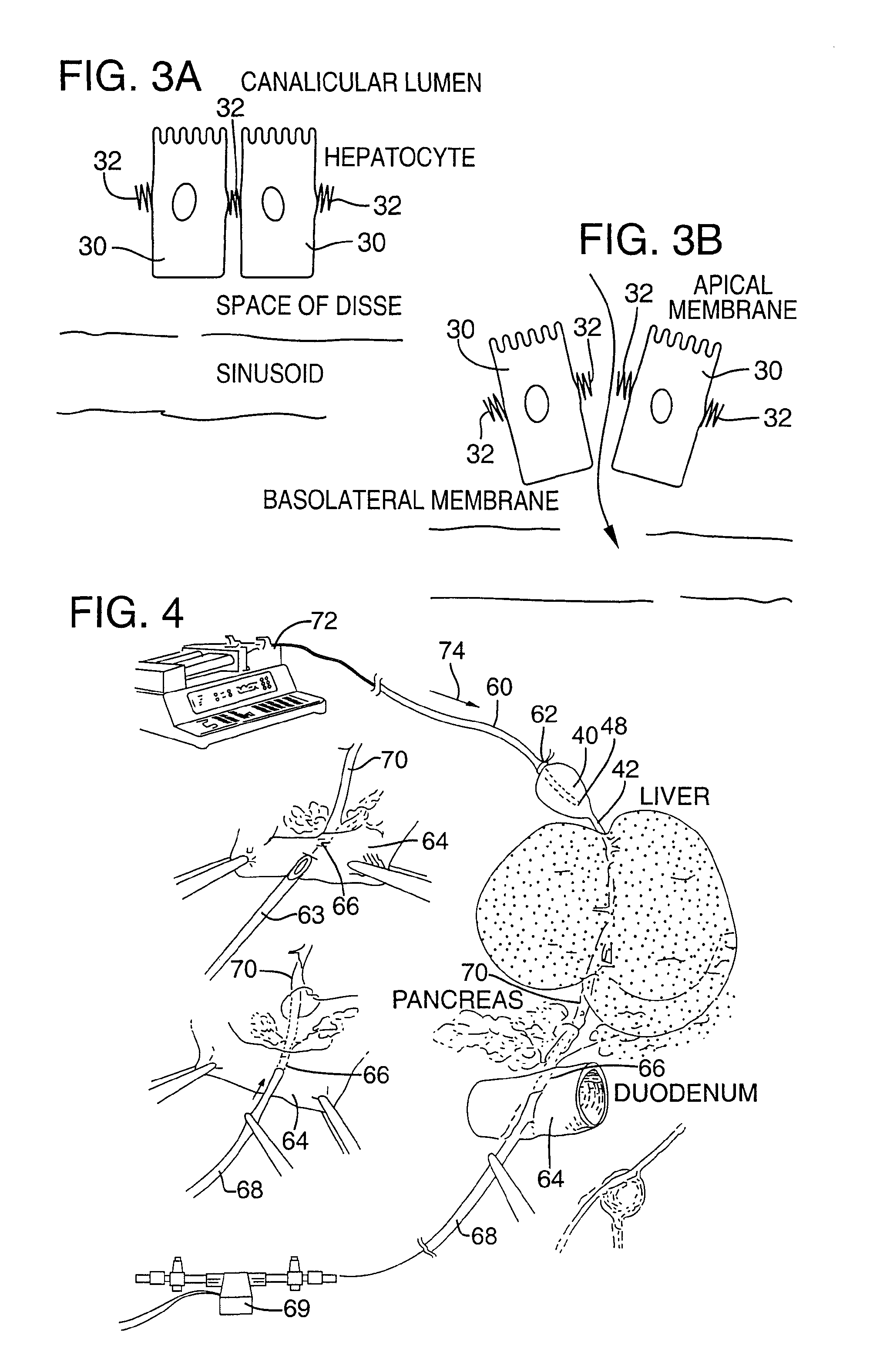
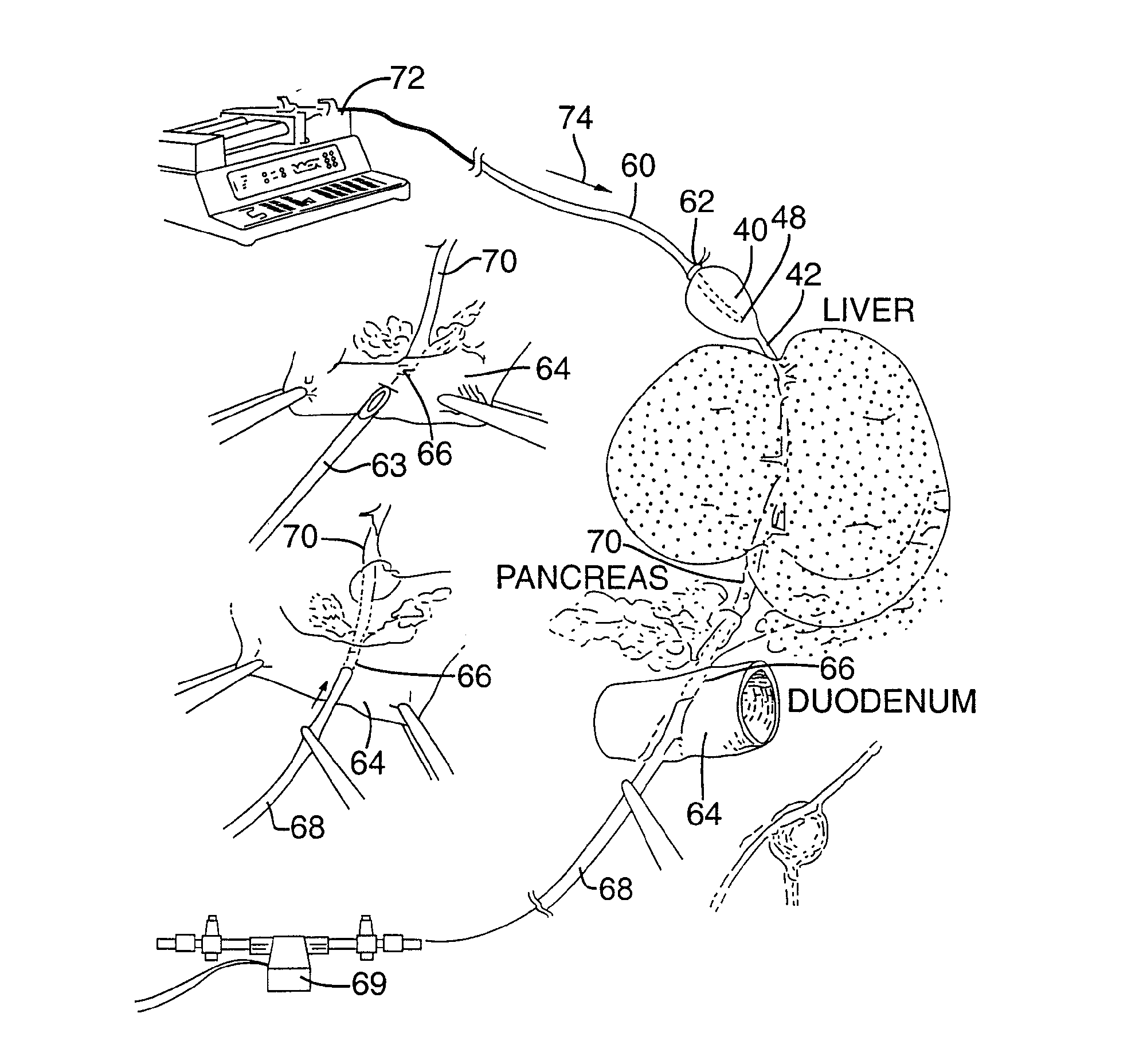
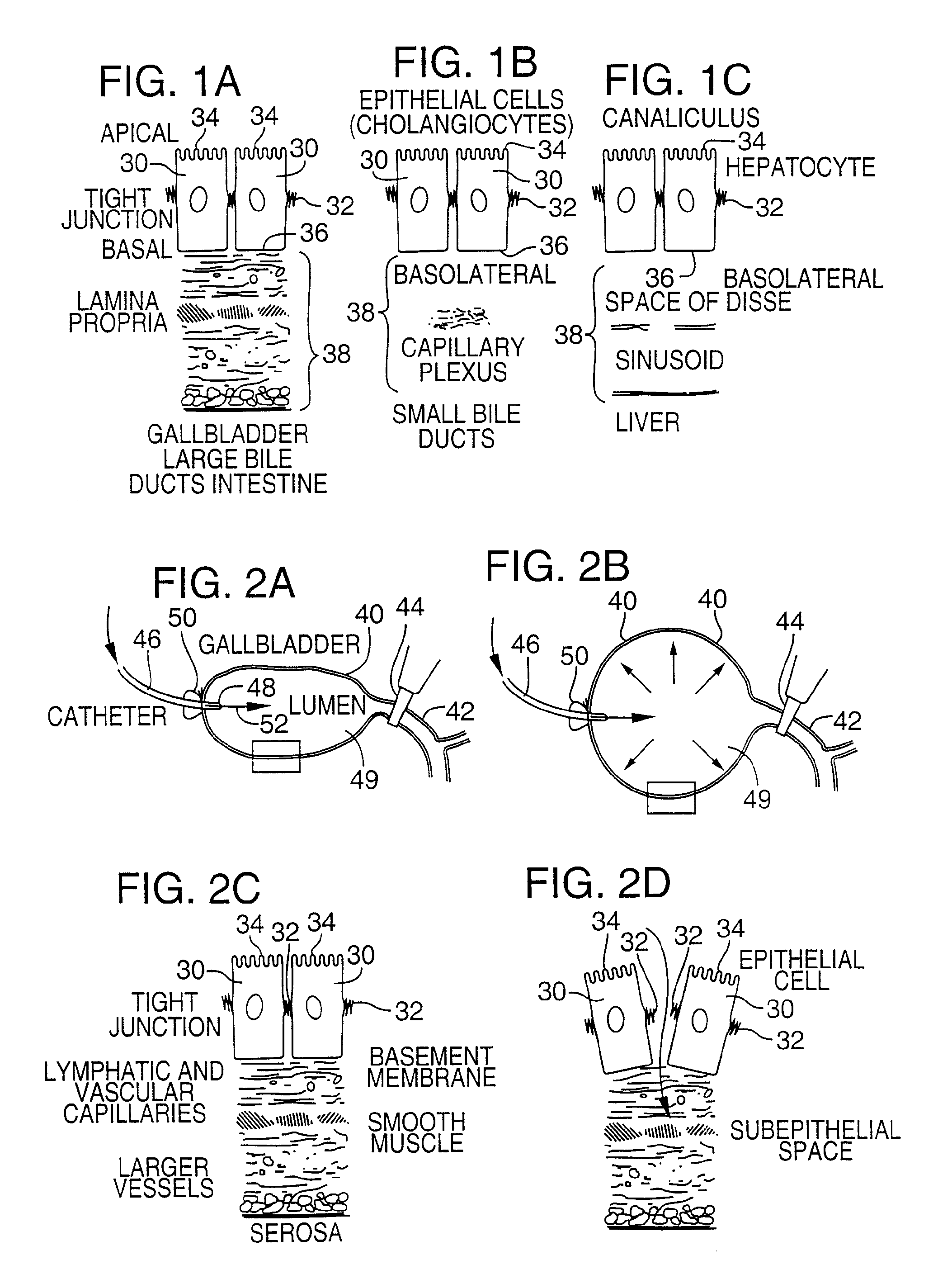
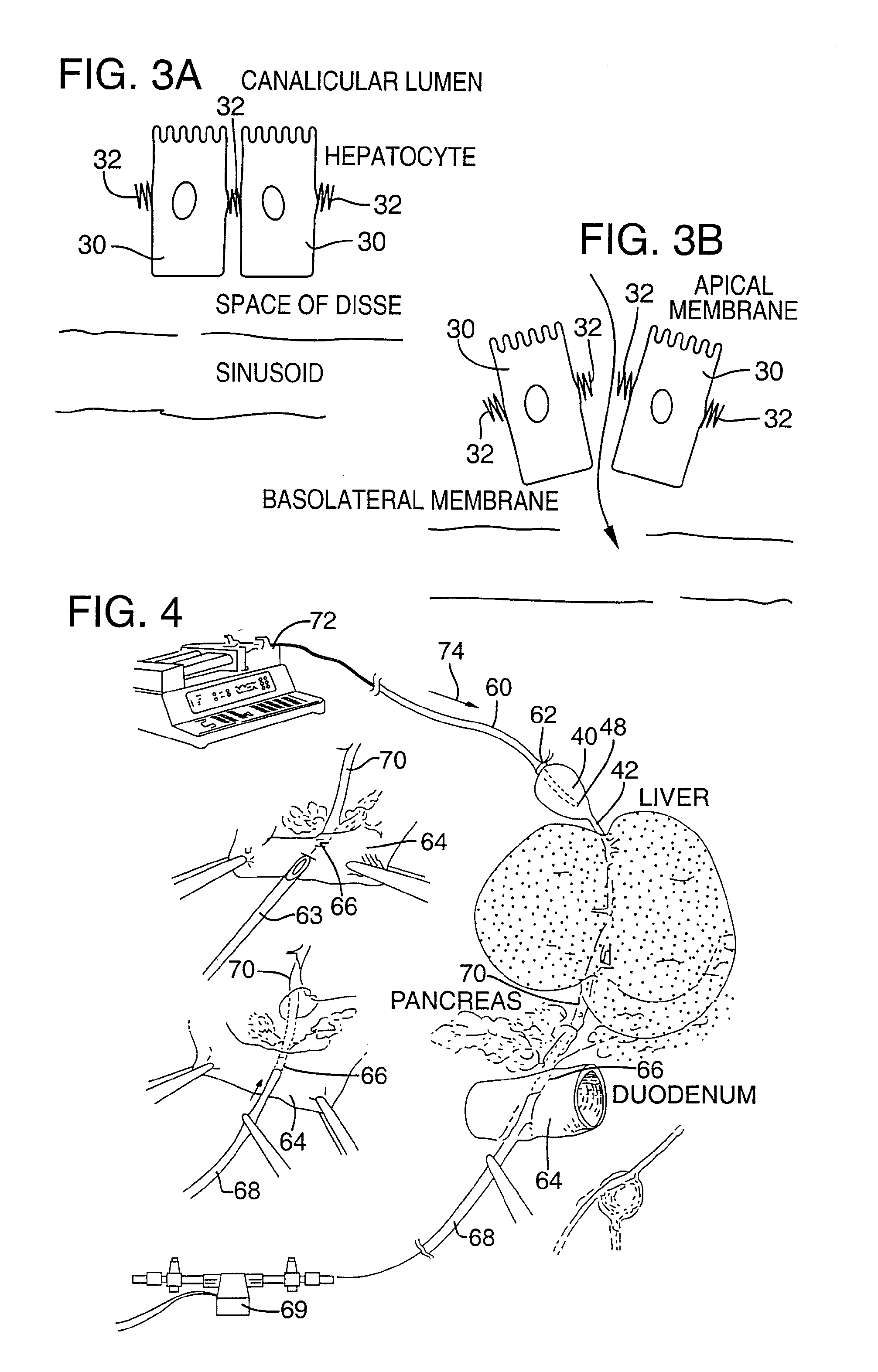
Method for pressure mediated selective delivery of therapeutic substances and cannula
Methods and devices are disclosed for selective delivery of therapeutic substances to specific histologic or microanatomic areas of organs. Introduction of the therapeutic substance into a hollow organ space (such as an hepatobiliary duct or the gallbladder lumen) at a controlled pressure, volume or rate allows the substance to reach a predetermined cellular layer (such as the ephithelium or sub-epithelial space). The volume or flow rate of the substance can be controlled so that the intralumenal pressure reaches a predetermined threshold level beyond which subsequent subepithelial delivery of the substance occurs. Alternatively, a lower pressure is selected that does not exceed the threshold level, so that delivery occurs substantially only to the epithelial layer. Such site specific delivery of therapeutic agents permits localized delivery of substances (for example to the interstitial tissue of an organ) in concentrations that may otherwise produce systemic toxicity. Occlusion of venous or lymphatic drainage from the organ can also help prevent systemic administration of therapeutic substances, and increase selective delivery to superficial epithelial cellular layers. Delivery of genetic vectors can also be better targeted to cells where gene expression is desired. The access device comprises a cannula with a wall piercing tracar within the lumen. Two axially spaced inflatable balloons engage the wall securing the cannula and sealing the puncture site. A catheter equipped with an occlusion balloon is guided through the cannula to the location where the therapeutic substance is to be delivered.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICE THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC
Vascular closure device
ActiveUS8821532B2Promote faster healingPrevent movementSurgical veterinaryWound clampsVascular deviceBlood vessel
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Rigid arthroscope system
A reinforced arthroscope comprising external ribs to provide for a number of separate fluid channels, such as inflow, outflow and interstitial tissue drainage, when the arthroscope is slipped into a disposable external sheath. The arthroscope is constructed to be sufficiently rigid so as to penetrate and move within a joint without damaging the rod optics inside. The externality of the arthroscope channels allow for cleaning and sterilizing the scope between uses.
Owner:PRISTINE SURGICAL LLC
Method for pressure mediated selective delivery of therapeutic substances and cannula
Methods and devices are disclosed for selective delivery of therapeutic substances to specific histologic or microanatomic areas of organs. Introduction of the therapeutic substance into a hollow organ space (such as an hepatobiliary duct or the gallbladder lumen) at a controlled pressure, volume or rate allows the substance to reach a predetermined cellular layer (such as the ephithelium or sub-epithelial space). The volume or flow rate of the substance can be controlled so that the intralumenal pressure reaches a predetermined threshold level beyond which subsequent subepithelial delivery of the substance occurs. Alternatively, a lower pressure is selected that does not exceed the threshold level, so that delivery occurs substantially only to the epithelial layer. Such site specific delivery of therapeutic agents permits localized delivery of substances (for example to the interstitial tissue of an organ) in concentrations that may otherwise produce systemic toxicity. Occlusion of venous or lymphatic drainage from the organ can also help prevent systemic administration of therapeutic substances, and increase selective delivery to superficial epithelial cellular layers. Delivery of genetic vectors can also be better targeted to cells where gene expression is desired. The access device comprises a cannula with a wall piercing tracar within the lumen. Two axially spaced inflatable balloons engage the wall securing the cannula and sealing the puncture site. A catheter equipped with an occlusion balloon is guided through the cannula to the location where the therapeutic substance is to be delivered.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Alcohol immobilizer having an emergency drive option
InactiveUS20100312431A1Improper useVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMobile vehicleAlcohol content
A device for preventing the start-up or initial operation of a vehicle, in particular of a motor vehicle, by a vehicle driver who is under the influence of alcohol, as well as a vehicle equipped with such a device. The device includes a device for determining the alcohol content in the breath, blood, tissue, sweat of the skin, or in the interstitial tissue fluid of the vehicle driver, as well as an immobilizer which prevents the start-up or the initial operation of the vehicle when the alcohol content in the vehicle driver's breath, blood, tissue, sweat of the skin, or interstitial tissue fluid, that is ascertained by the device, exceeds a specified threshold value. Means are provided for bypassing or disabling the immobilizer.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Rigid Arthroscope System
A reinforced arthroscope comprising external ribs to provide for a number of separate fluid channels, such as inflow, outflow and interstitial tissue drainage, when the arthroscope is slipped into a disposable external sheath. The arthroscope is constructed to be sufficiently rigid so as to penetrate and move within a joint without damaging the rod optics inside. The externality of the arthroscope channels allow for cleaning and sterilizing the scope between uses.
Owner:PRISTINE SURGICAL LLC
Separation, storage culture and amplification method of pouch fat interstitial cell
InactiveCN102586180APromote wound healingPromote healingDead animal preservationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLiver functionDiabetic ulcer
The invention relates to a separation and storage method of a pouch fat interstitial cell, which comprises the following steps of: cutting to obtain a pouch fat tissue by adopting a surgical knife, extracting an interstitial tissue of the pouch fat tissue and separating the cell by using an adherent method. The culture and amplification method of the pouch fat interstitial cell comprises the following steps of: carrying out large-scale tissue culture by adopting a paper carrier technology, freezing and storing by using a definite and non-specific genetic component and preserving the cell for a long time. Through the separation and storage method, the pouch interstitial cell can be extracted, massively cultured and preserved for a long time; and the cultured interstitial cell can be used for promoting the healing of skin wound, the healing of diabetic ulcer, the repair of myocardial injury and the repair of hepatic injury.
Owner:EASTERN UNION STEM CELL & GENE ENG
Apparatus for assessing muscle quality
ActiveUS20150045690A1Increase the differenceImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMuscle tissueBiological body
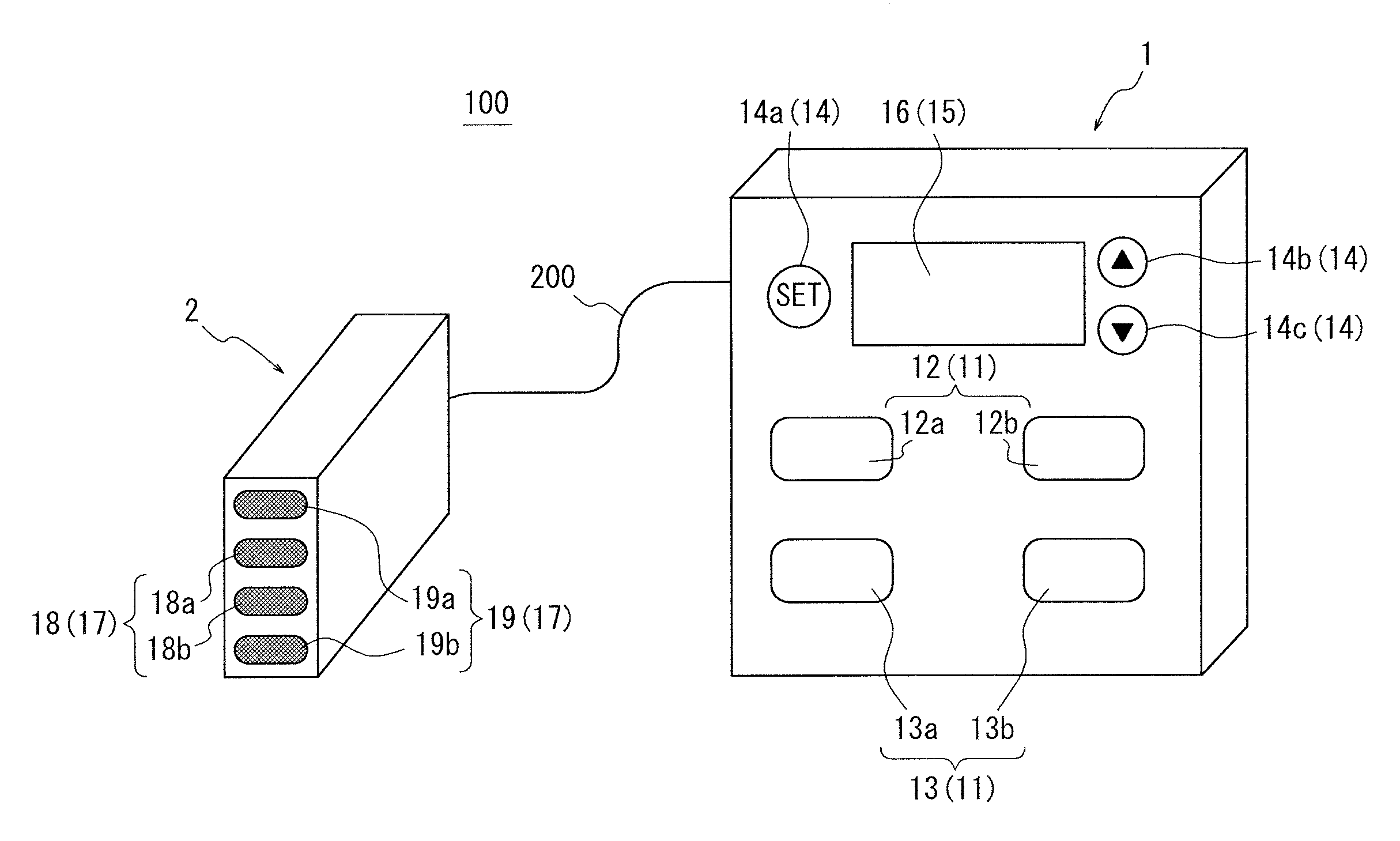
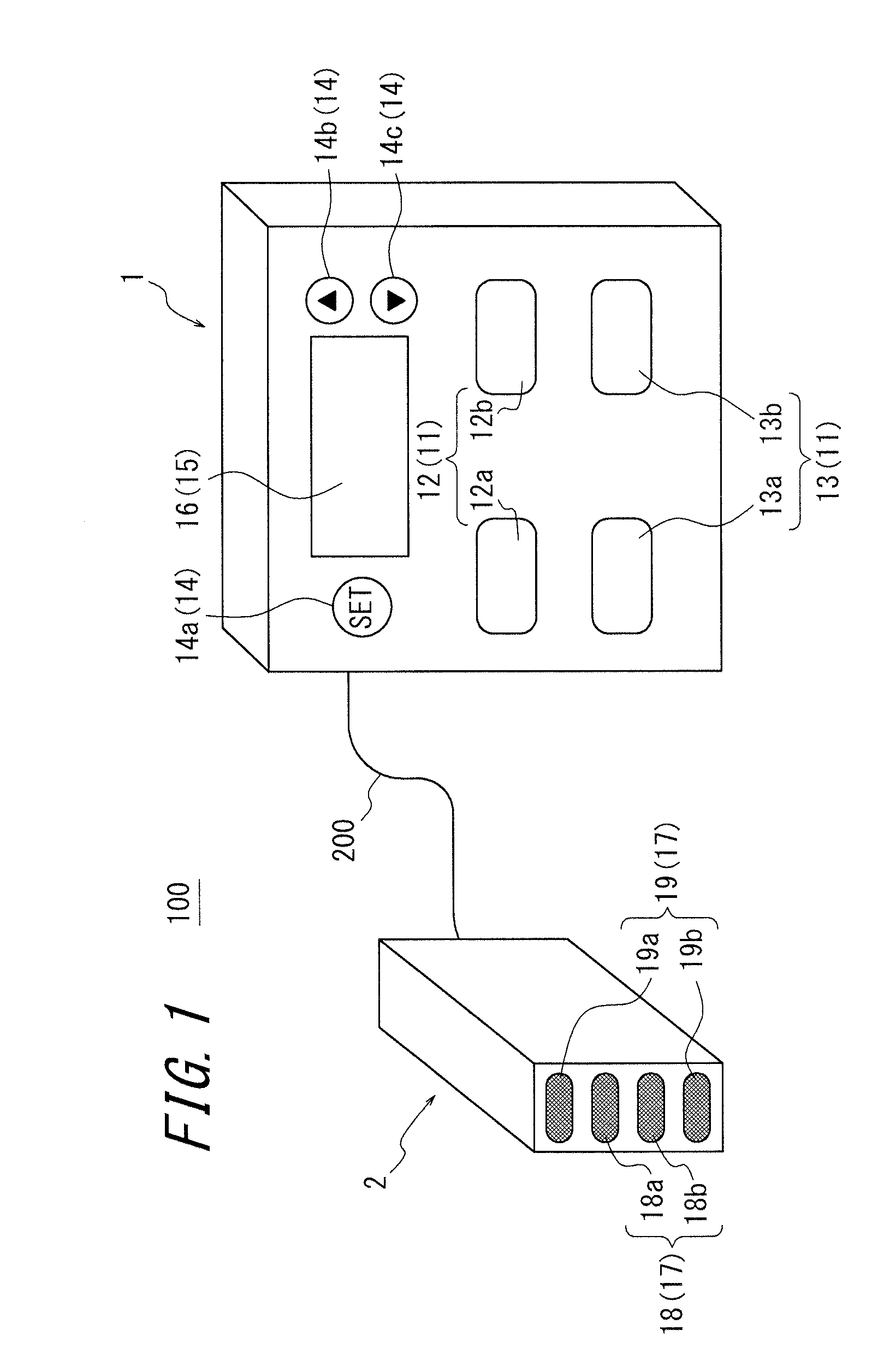
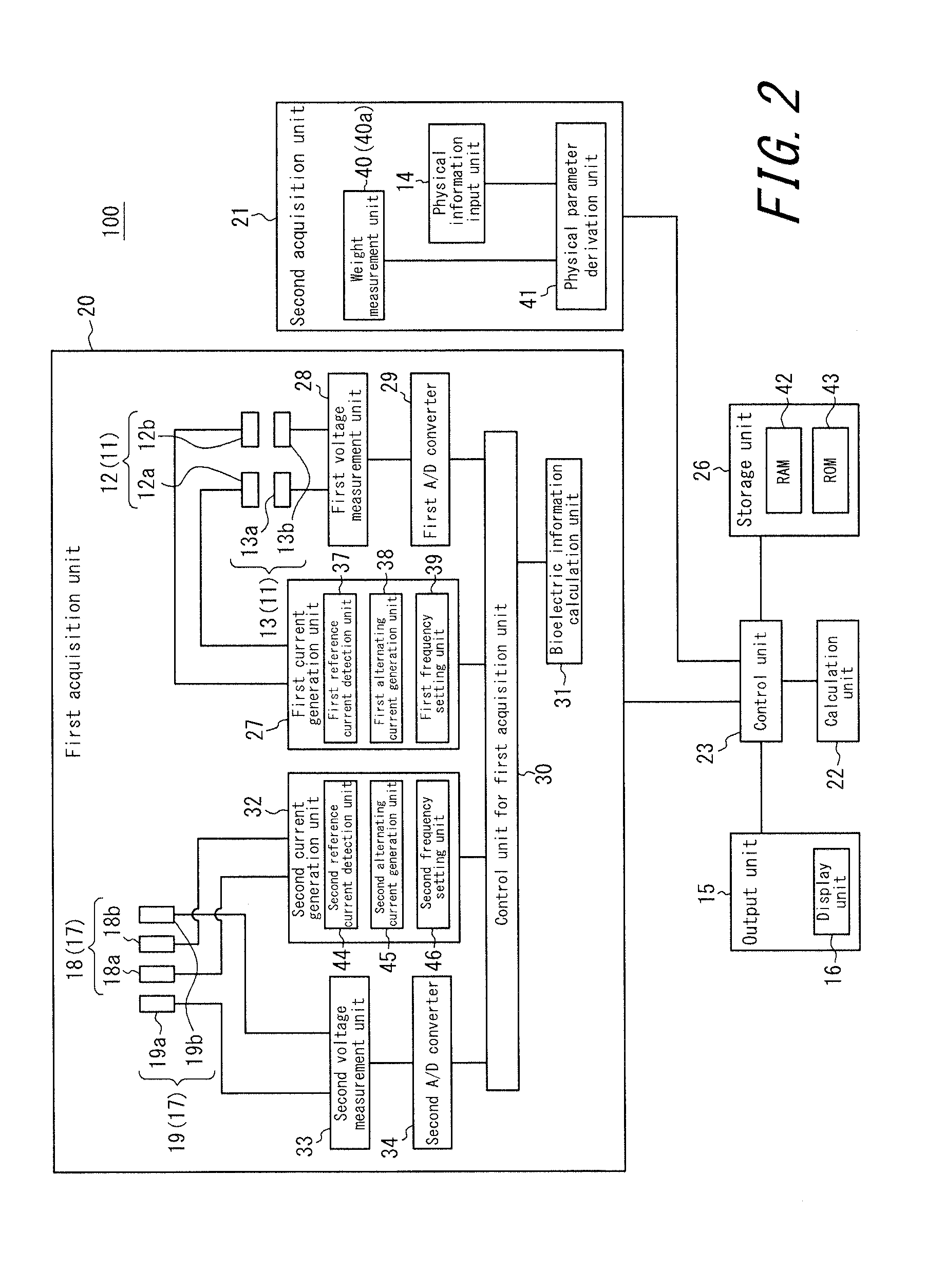
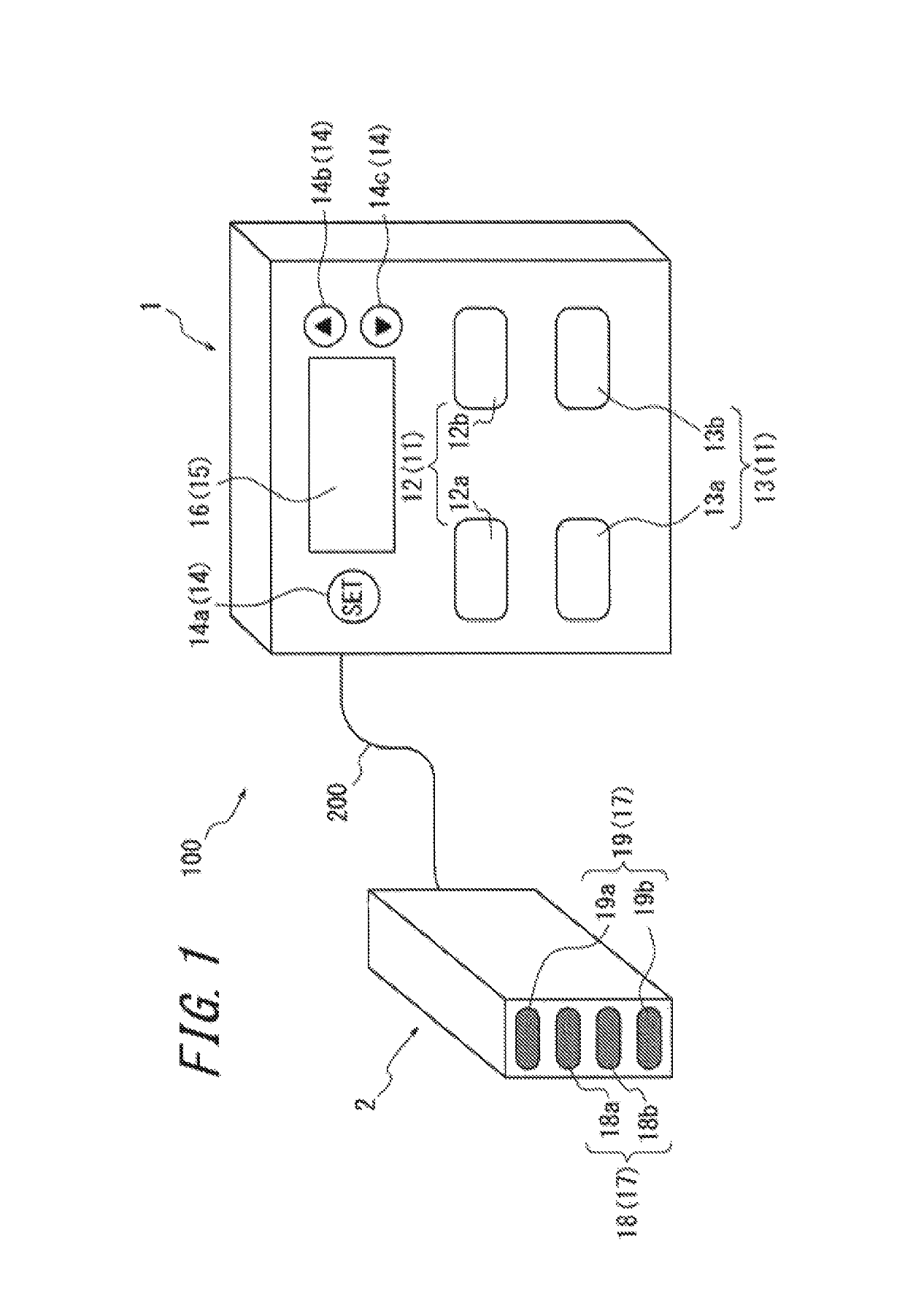
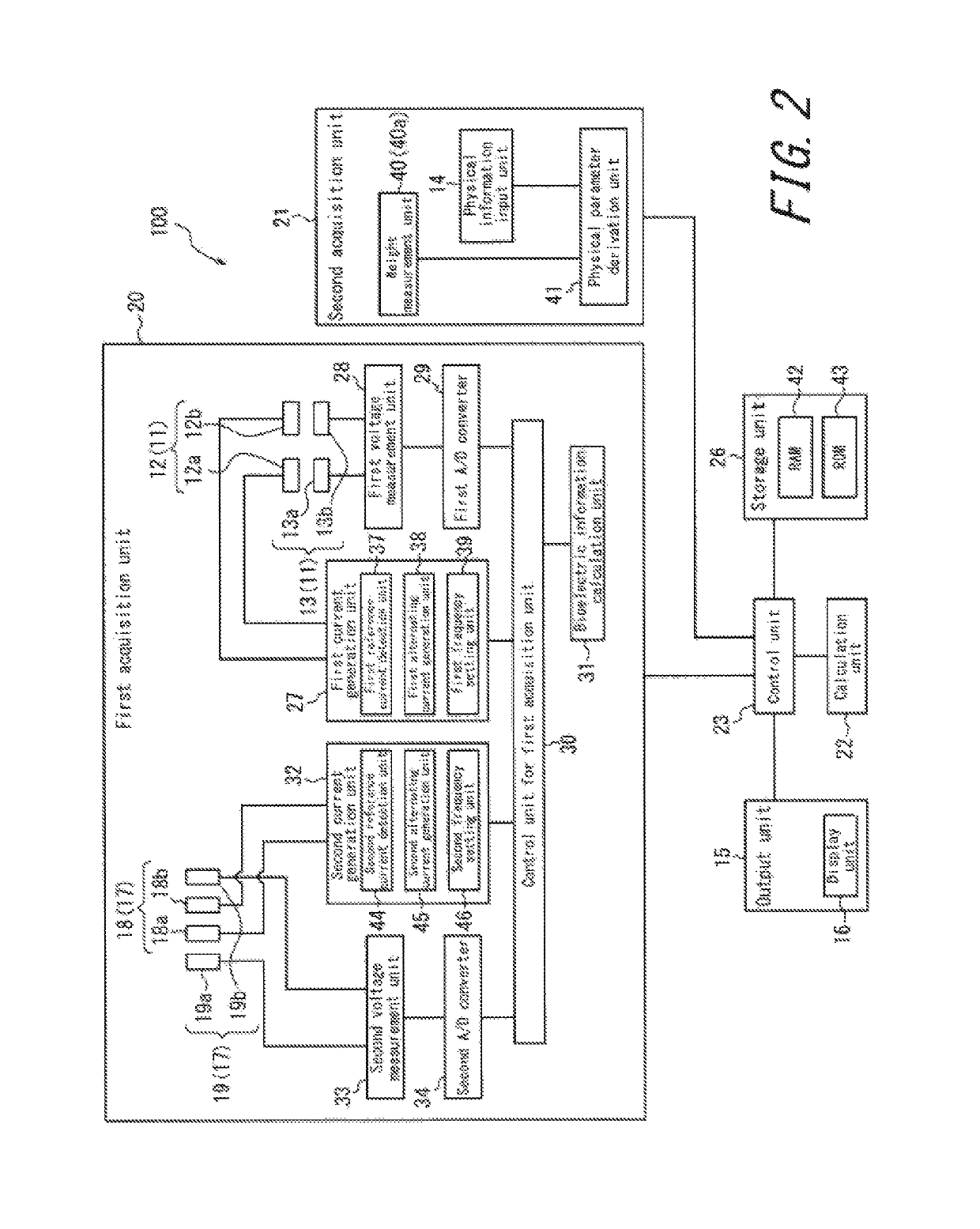
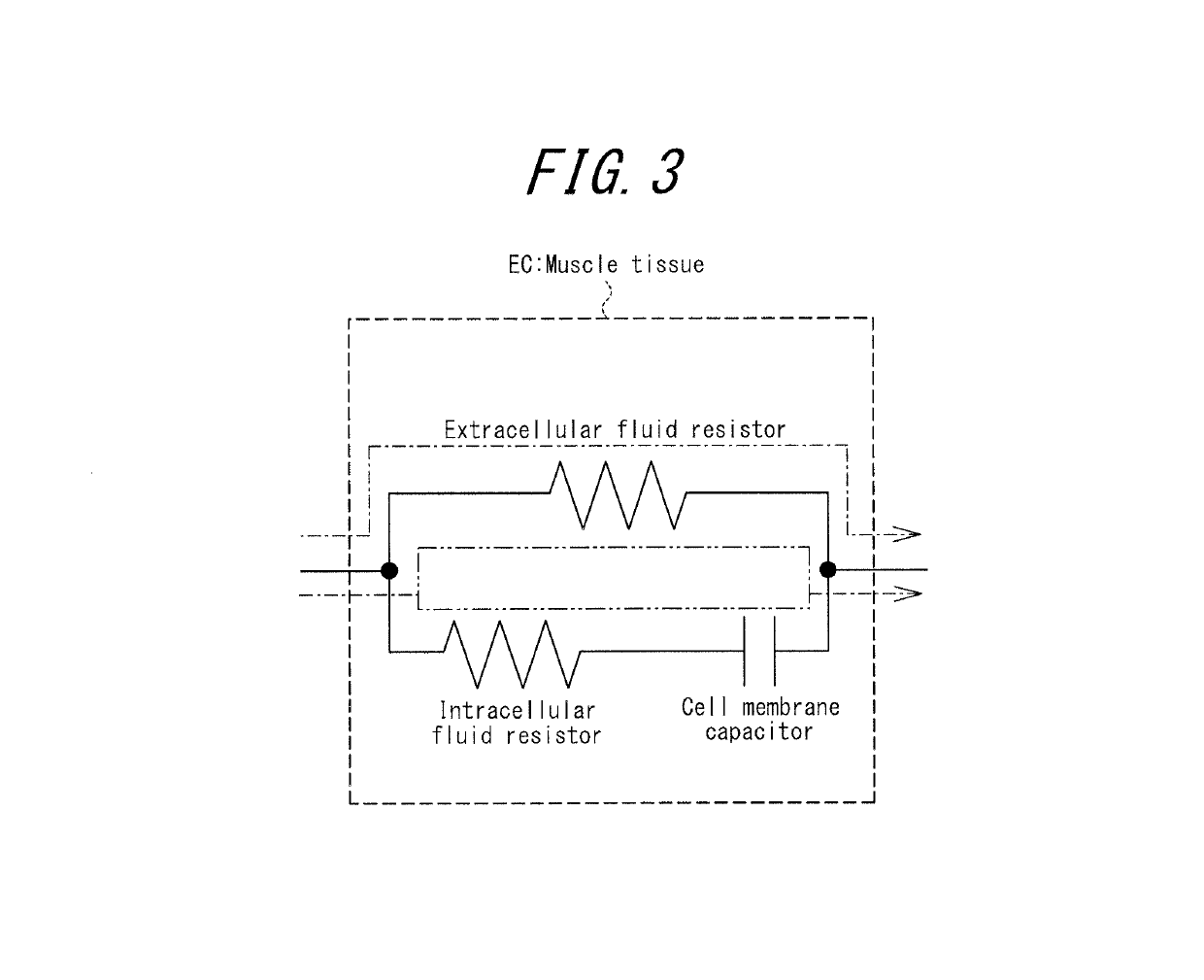
An apparatus for assessing muscle quality includes a first acquisition unit that acquires bioelectric information including at least one of (i) a resistance component and a reactance component of bioelectrical impedance and (ii) first impedance measured by supplying alternating current at a predetermined low frequency to a living organism and second impedance measured by supplying alternating current at a predetermined high frequency to the living organism; a second acquisition unit that acquires a physical parameter related to physique of the living organism; and a calculation unit that calculates an index in accordance with a proportion, in muscle tissue, of muscle fiber to interstitial tissue based on the physical parameter and on at least one of a first parameter represented as a ratio between the resistance component and the reactance component and a second parameter represented as a ratio between the first impedance and the second impedance.
Owner:TANITA CORP
Method for pressure mediated selective delivery of therapeutic substances and cannula
Methods and devices are disclosed for selective delivery of therapeutic substances to specific histologic or microanatomic areas of organs. Introduction of the therapeutic substance into a hollow organ space (such as an hepatobiliary duct or the gallbladder lumen) at a controlled pressure, volume or rate allows the substance to reach a predetermined cellular layer (such as the ephithelium or sub-epithelial space). The volume or flow rate of the substance can be controlled so that the intralumenal pressure reaches a predetermined threshold level beyond which subsequent subepithelial delivery of the substance occurs. Alternatively, a lower pressure is selected that does not exceed the threshold level, so that delivery occurs substantially only to the epithelial layer. Such site specific delivery of therapeutic agents permits localized delivery of substances (for example to the interstitial tissue of an organ) in concentrations that may otherwise produce systemic toxicity. Occlusion of venous or lymphatic drainage from the organ can also help prevent systemic administration of therapeutic substances, and increase selective delivery to superficial epithelial cellular layers. Delivery of genetic vectors can also be better targeted to cells where gene expression is desired. The access device comprises a cannula with a wall piercing tracar within the lumen. Two axially spaced inflatable balloons engage the wall securing the cannula and sealing the puncture site. A catheter equipped with an occlusion balloon is guided through the cannula to the location where the therapeutic substance is to be delivered.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
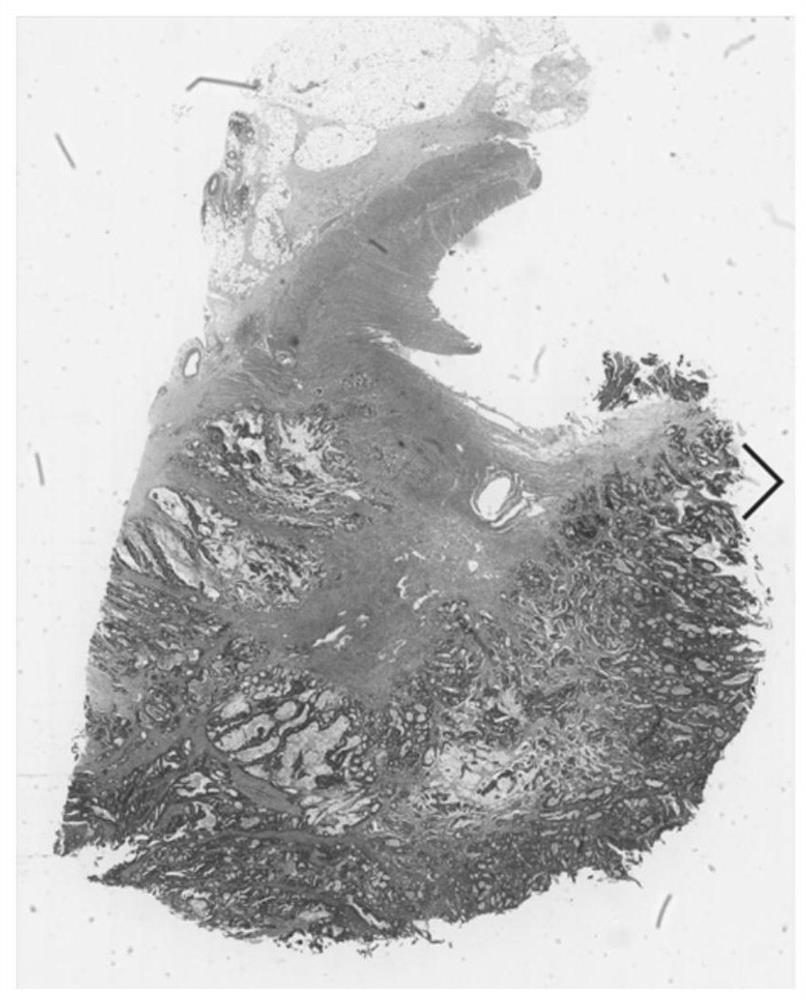
Esophageal cancer pathological image labeling method
PendingCN110826560AReduce labor costsSave time and costImage enhancementImage analysisStainingEdge model
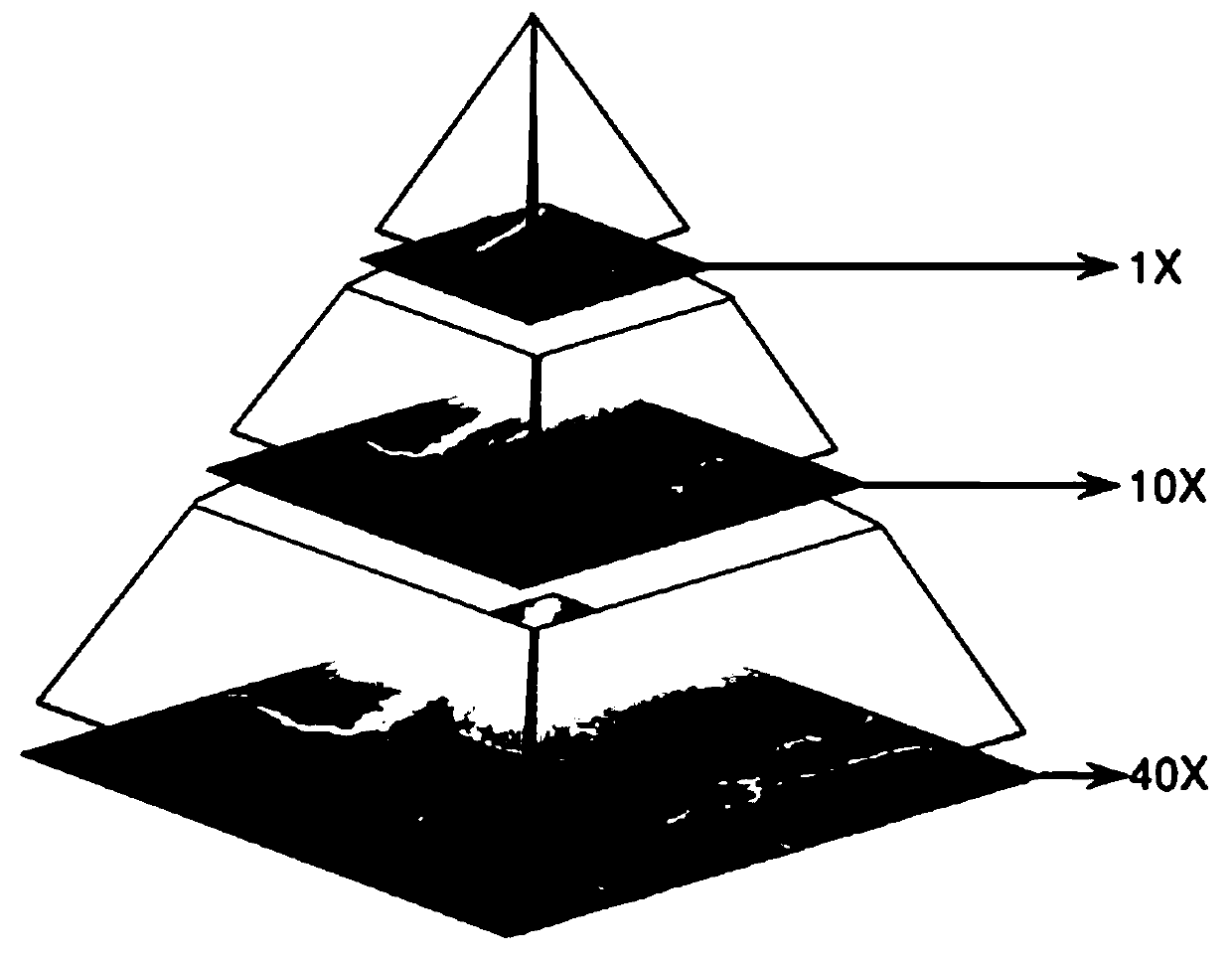
The esophageal cancer pathological image labeling method comprises the following steps: a) performing dyeing correction processing on an esophageal pathological image subjected to H & E dyeing; b) labeling expert canceration areas; c) mapping the canceration area outline marked by the expert into a pathological image of 40X; d) constructing an epithelial tissue contour detection model; d-1) marking whether pixel points belong to an epithelial region, an interstitial tissue or an irrelevant blank region; (d-2) constructing an end-to-end convolutional neural network model; and e) fusing the labeling areas. According to the method, the epithelial tissue contour is automatically drawn in the labeling process according to the characteristic that the esophageal cancer morbidity area occurs in the epithelial tissue basal layer area, so that the time cost of expert labeling is greatly saved. The method only aims at esophageal pathological section image modeling; only the edge of the epithelialtissue is detected, the model is relatively simple, operation is rapid, epithelial boundary detection has obvious advantages in detection precision, meanwhile, the method automatically learns effective features and expressions, the complex manual feature selection process is avoided, and the actual application requirements can be met.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
Atherosclerosis imaging agents and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20180055953A1Avoid excessive accumulationReduce leakageDiagnostics using lightLuminescence/biological staining preparationImaging agentAtheroma
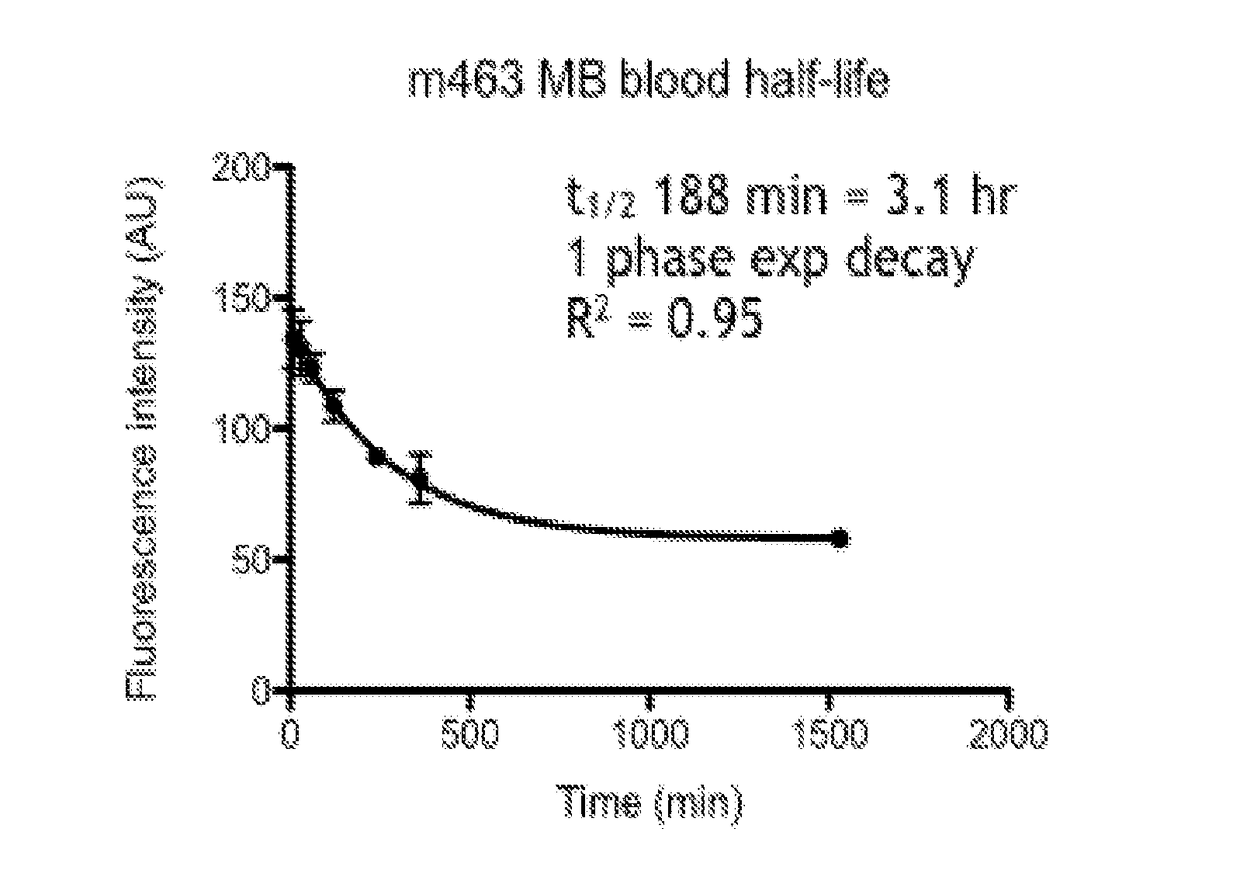
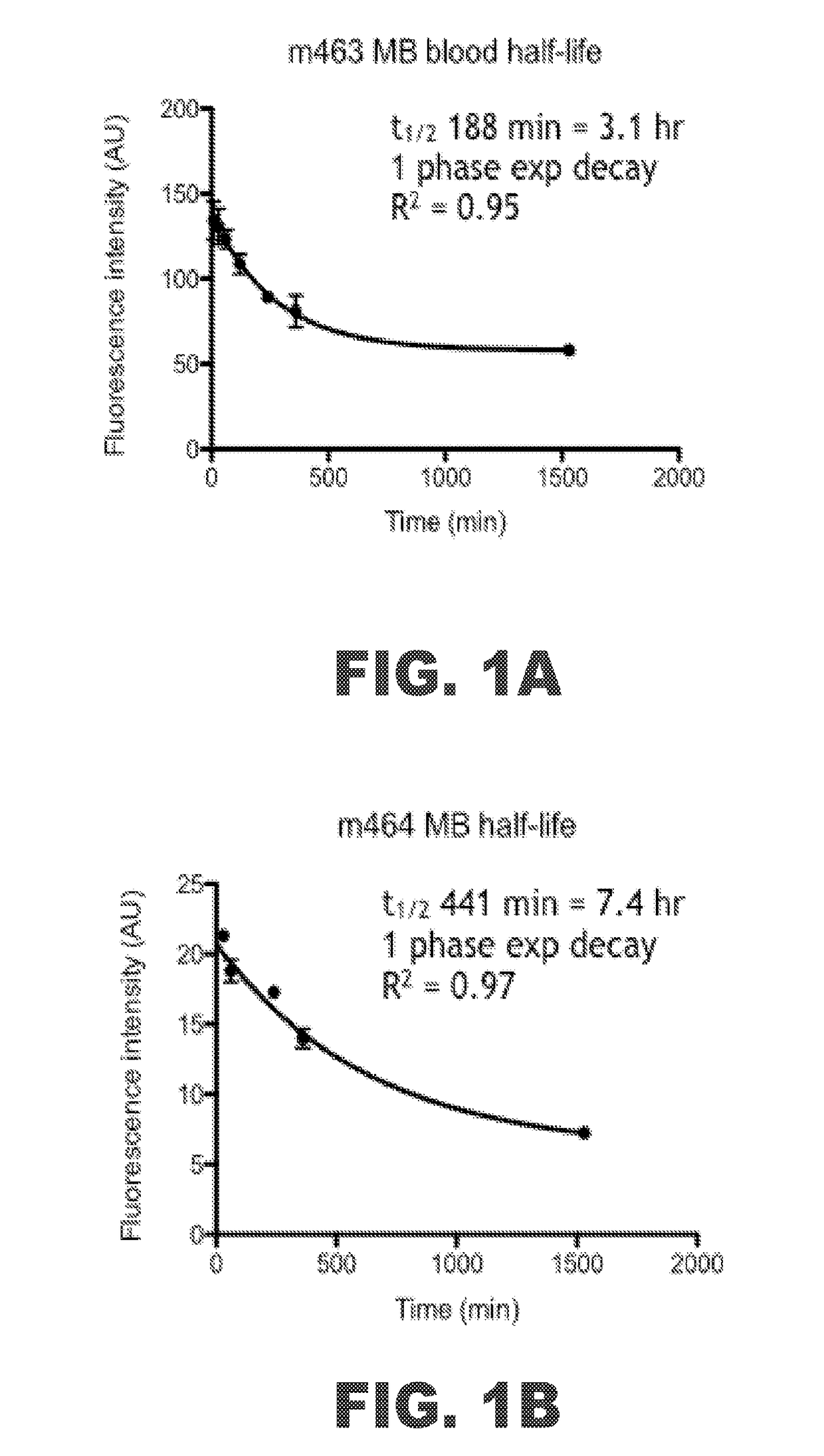
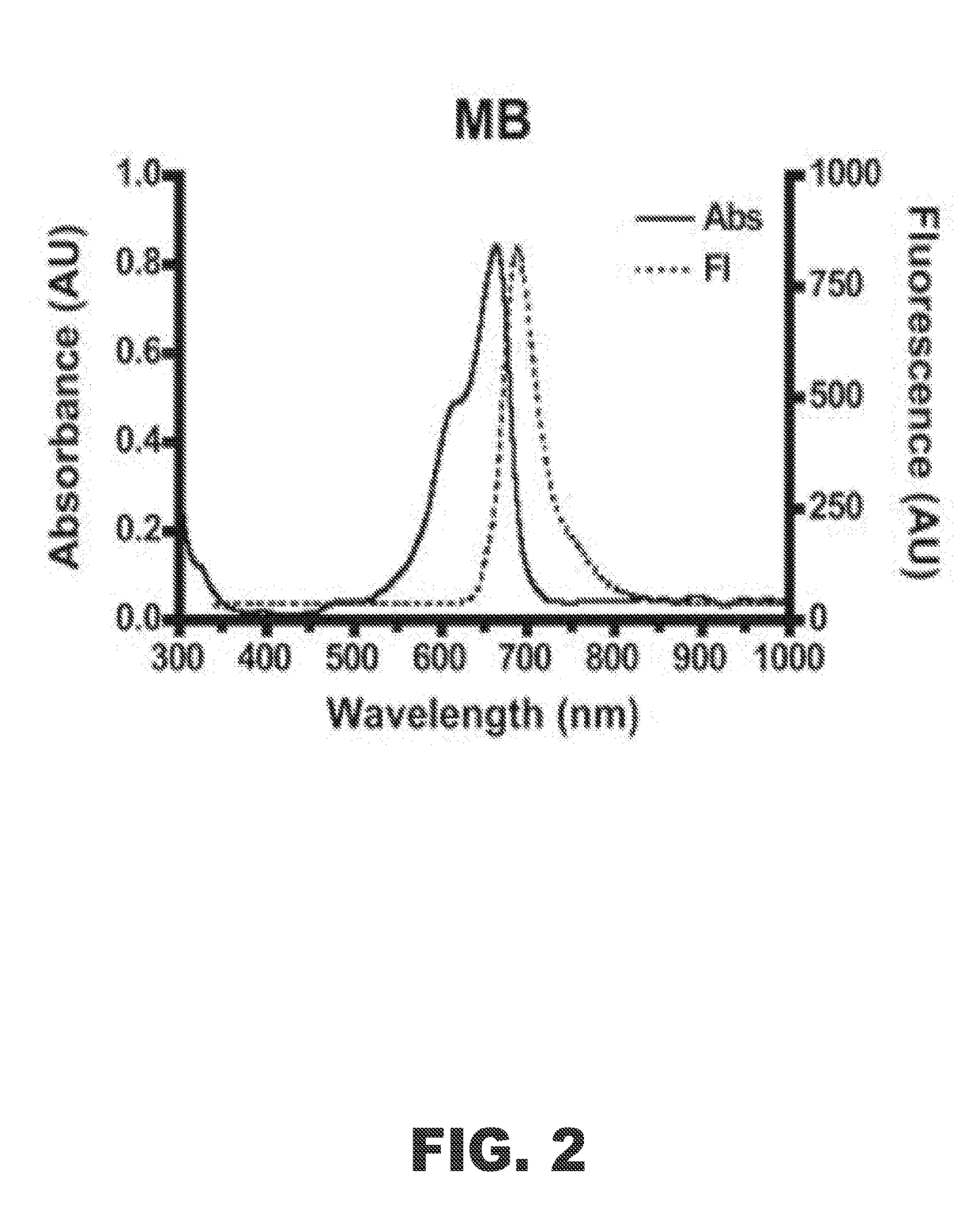
Methods for detecting the presence of atherosclerotic structures in order to diagnose or prevent atherosclerosis are provided herein. In particular, it has been found that methylene blue injected intravenously acts as an excellent indicator because the compound targets high-risk plaque, atheroma, macrophages, and other atherosclerotic structures formed within the endothelial walls of a vessel of a subject. Because the compound provides a unique binding profile with uptake only in plaque or atheroma, and not the normal or healthy vascular interstitial tissue, methylene blue maintains a good plaque-to-background ratio for imaging purposes. This enables healthcare providers to determine the status of atherosclerosis development in vivo within a patient with higher certainty and at lower costs. The disclosed methods allow for high-resolution mapping of plaque build-up, plaque pathobiology, and other atherosclerotic structures within a vessel of a subject by using methylene blue as an imaging agent.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus for assessing muscle quality
ActiveUS10327692B2Increase the differenceImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMuscle tissueFiber
Owner:TANITA CORP
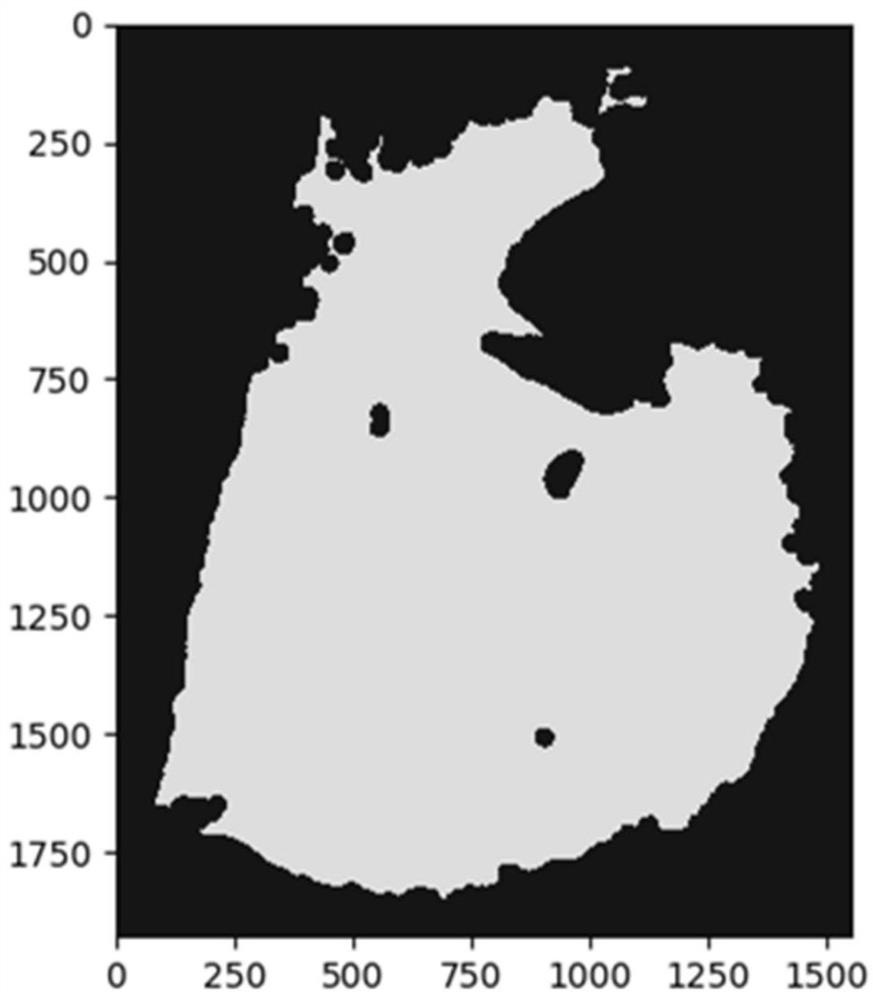
Colorectal cancer pathological image prognosis auxiliary prediction method and system
ActiveCN113313680AShorten the timeReduce the burden onImage enhancementImage analysisEpitheliumFeature extraction
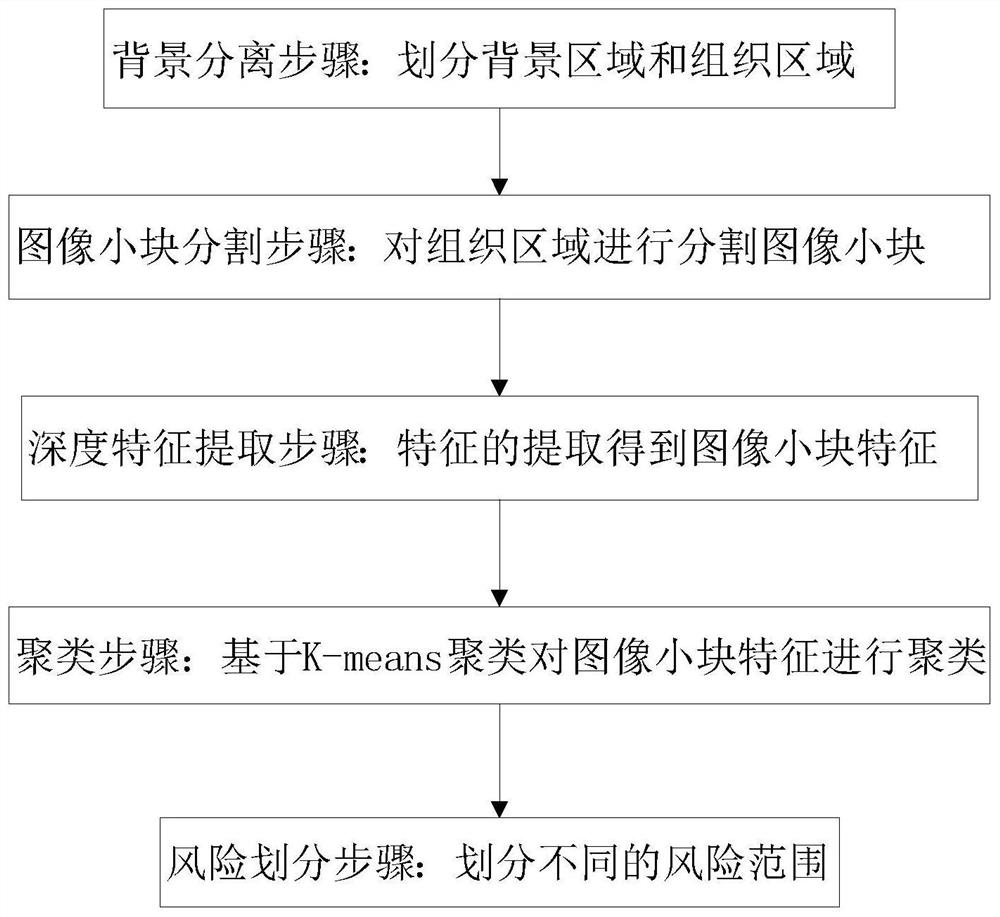
The invention discloses a colorectal cancer pathological image prognosis auxiliary prediction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: a background separation step: dividing into a background region and a tissue region; an image small block segmentation step: carrying out image small block segmentation on the tissue region according to a preset pixel size; a depth feature extraction step: extracting features of the segmented small image blocks based on a convolutional layer and a pooling layer of a colorectal cancer survival time prediction model to obtain features of the small image blocks, and encoding the small image blocks into a one-dimensional array form after processing of the convolutional layer; a clustering step: clustering the features of the small blocks of the image based on K-means clustering, and dividing tumor epithelial tissues, interstitial tissues, mucus, normal tissues and necrotic parts; and a risk division step: dividing a risk range. According to the invention, the image small blocks of the whole pathological image are automatically classified through K-means clustering, and then different types of image small blocks are selected for joint training, so that the survival time prediction of the prognostic patient of the colorectal cancer patient is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Alcohol immobilizer having an emergency drive option
InactiveUS8469135B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesAlcohol contentEngineering
A device for preventing the start-up or initial operation of a vehicle, in particular of a motor vehicle, by a vehicle driver who is under the influence of alcohol, as well as a vehicle equipped with such a device. The device includes a device for determining the alcohol content in the breath, blood, tissue, sweat of the skin, or in the interstitial tissue fluid of the vehicle driver, as well as an immobilizer which prevents the start-up or the initial operation of the vehicle when the alcohol content in the vehicle driver's breath, blood, tissue, sweat of the skin, or interstitial tissue fluid, that is ascertained by the device, exceeds a specified threshold value. Means are provided for bypassing or disabling the immobilizer.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Medicinal composition containing nitrate esters for treating ventricular hypertrophy or myocardial fibrosis
ActiveCN101120939AEasy to acceptSimple route of administrationEster active ingredientsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsCoronary artery diseaseTreatment effect
Myocardial hypertrophy is a pathological change of a plurality of kinds of angiocardiopathy. The main mode is the heart remodeling comprising cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy and change of the interstitial tissue component mainly. In the present invention, the nitrate medicine is used in treatment for myocardial hypertrophy caused by various reasons and excellent therapy effect is obtained. Currently the nitrate medicine is extensively applied in treatment for the coronary heart disease, the heart colicky pain and heart failure. Preload of the heart and myocardial consumption of oxygen are reduced by extension of the venous system. The drugs used in clinical field currently comprise Nitroglycerin, Amyl Nitrite, dicho nitric acid sorbite, sorbide dinitrate, 5-isosorbide dinitrate, Nitroglycerin, pentanitrol ters and itramine tosylate.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Insertion stabilizers for implants
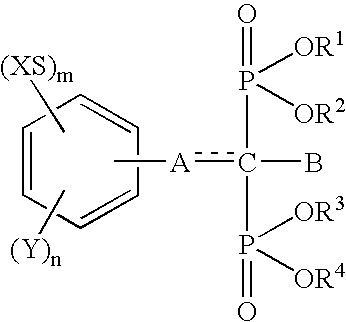
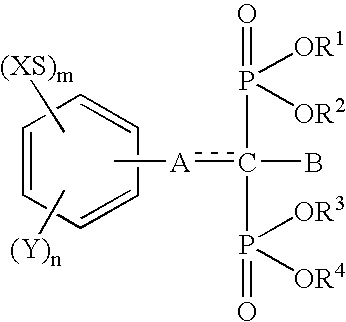
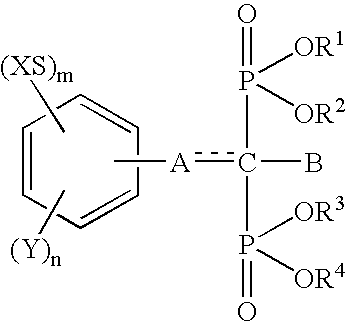
InactiveUS6692758B1Organic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsArtificial jointsAcid derivative
The present invention relates to an implant attachment stabilizer having, as an effective component, a methanebisphosphonic acid derivative represented by general formula (I)[where, in the formula, X, Y, m, n, <CUSTOM-CHARACTER FILE="US06692758-20040217-P00900.TIF" ALT="custom character" HE="20" WI="20" ID="CUSTOM-CHARACTER-00001" / >, A, B, R<1>, R<2>, R<3 >and R<4 >are as defined in the Specification], or hydrate thereof.The methanebisphosphonic acid derivatives represented by general formula (I) or the hydrates thereof, to which the present invention relates, have an interstitial tissue proliferation inhibiting action and an osteolytic factor production inhibiting action and, in particular, since they inhibit osteolysis through the inhibition of the interstitial tissue proliferation which accompanies implant attachment and the inhibition of osteolysis factor production at the implant periphery, they are effective in the prevention of implant loosening and detachment, and it is possible to extend the implant attachment period in the case of implants such as artificial joints, and implants in the oro-dental field.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
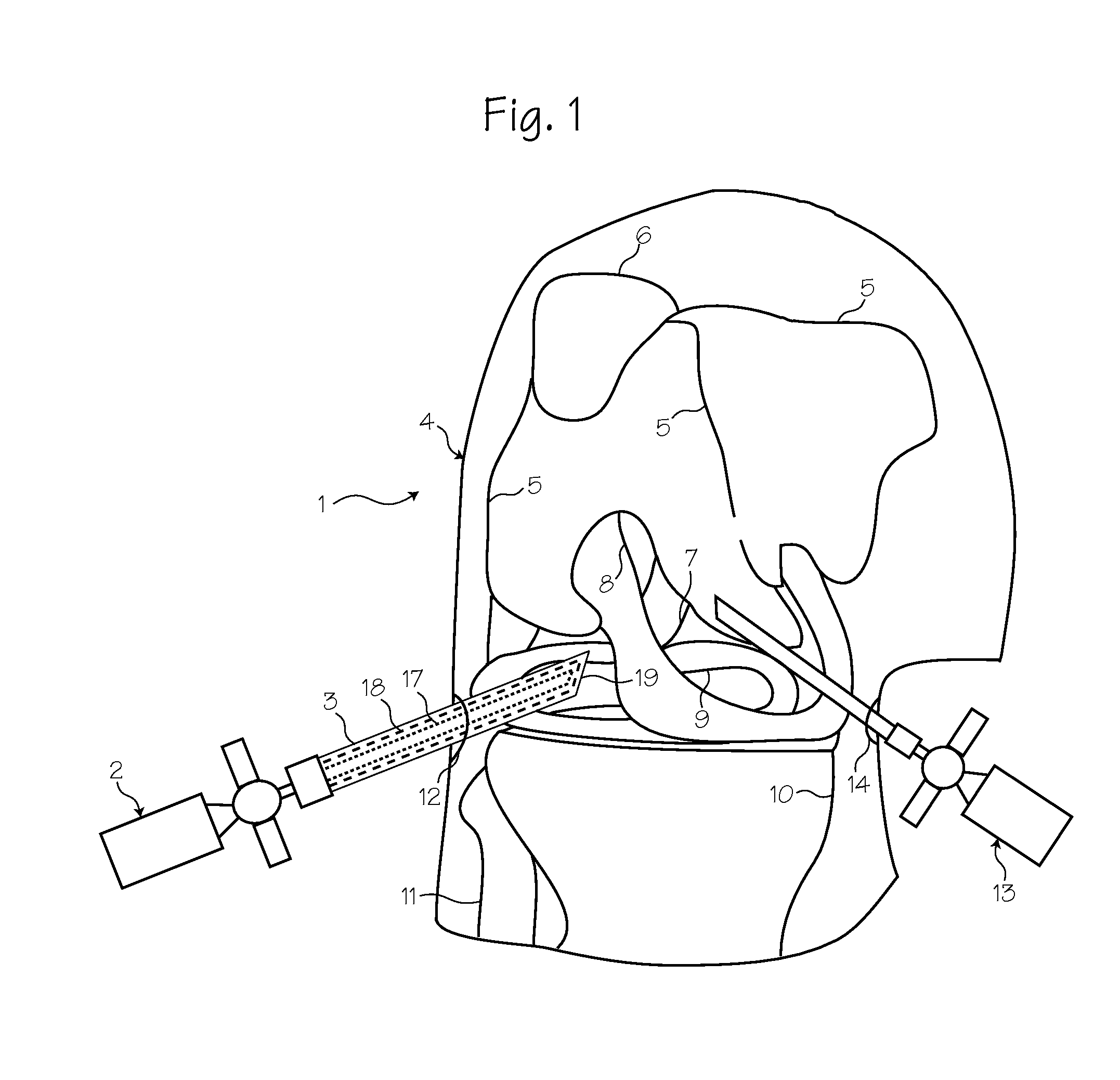
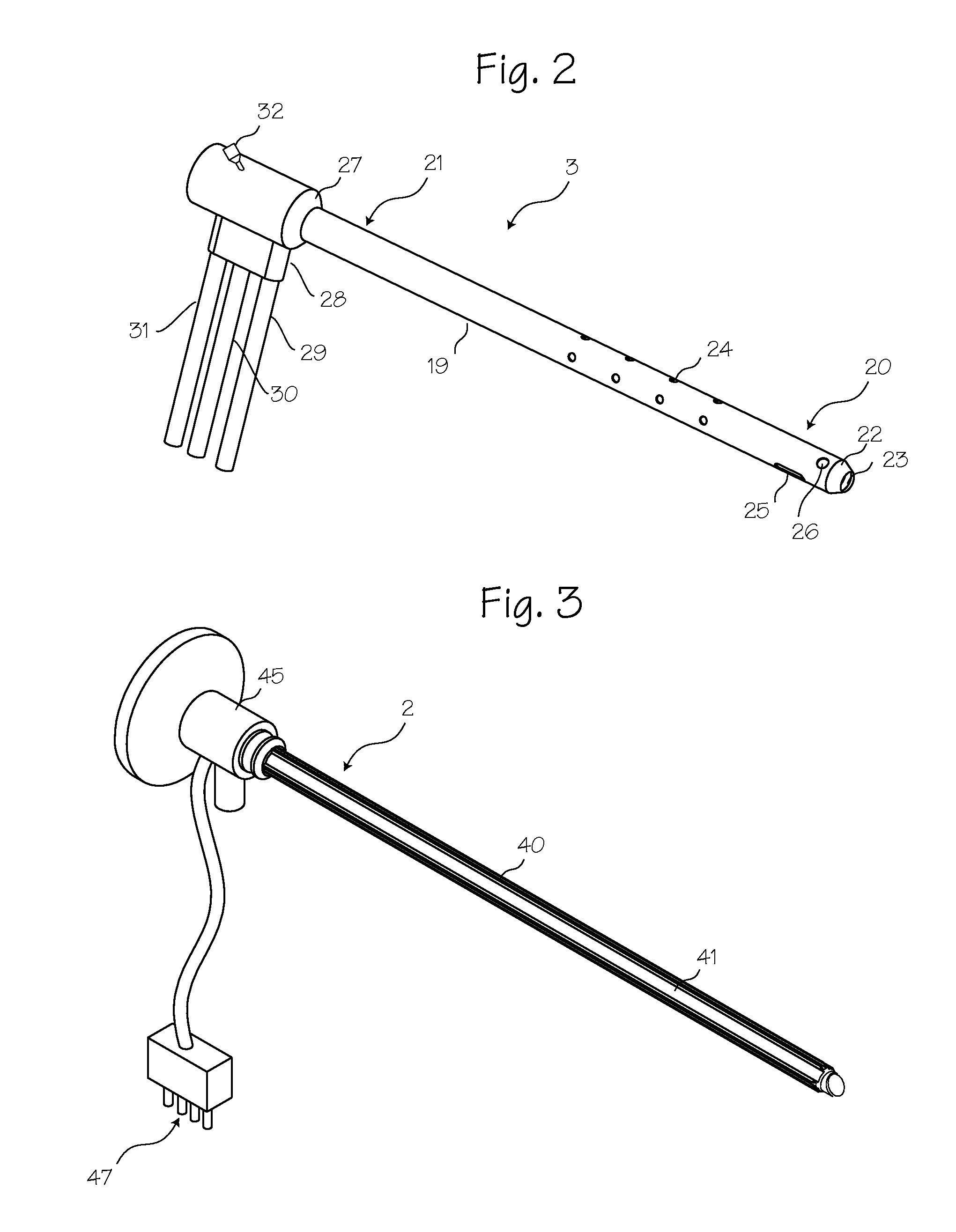
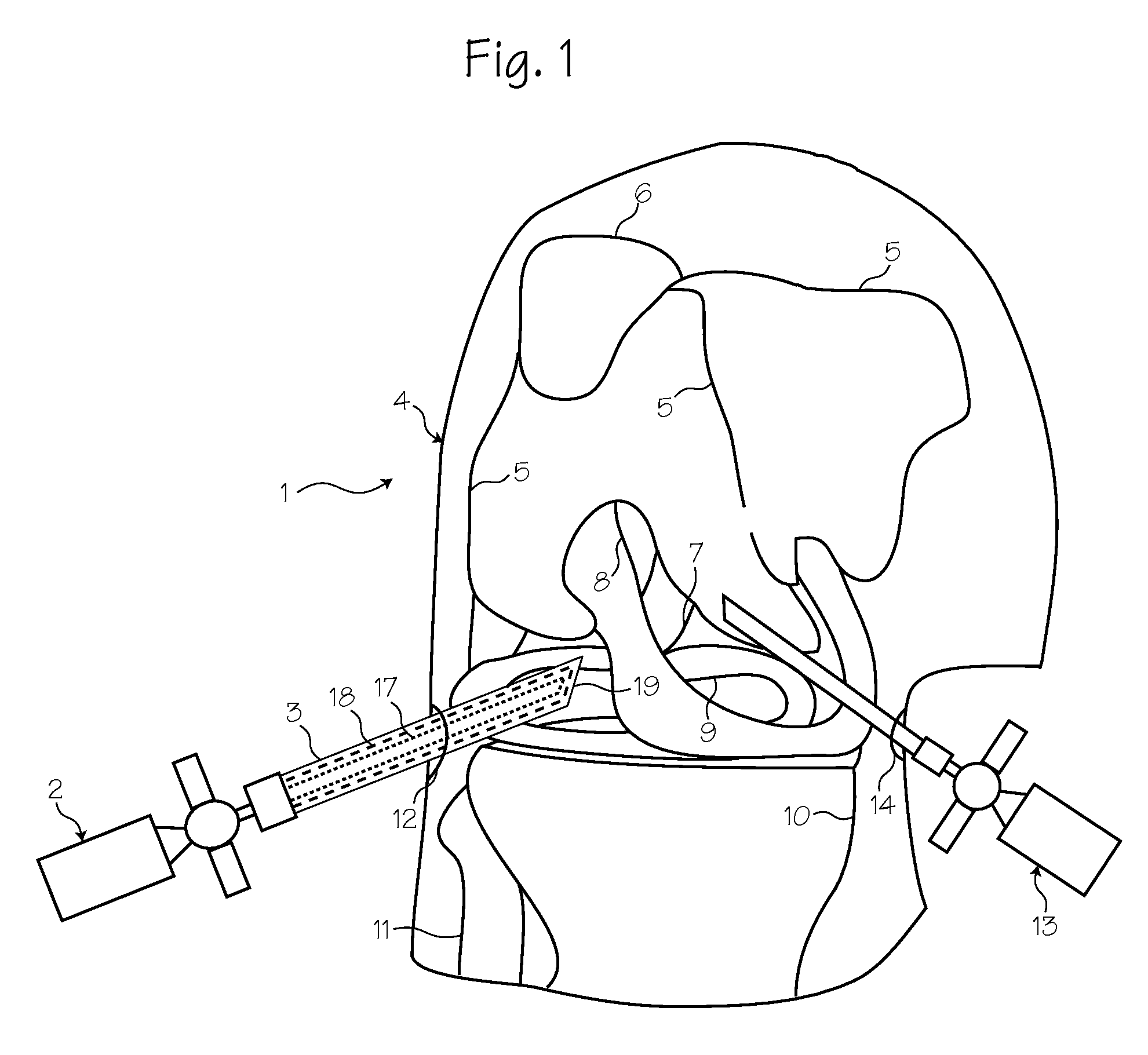
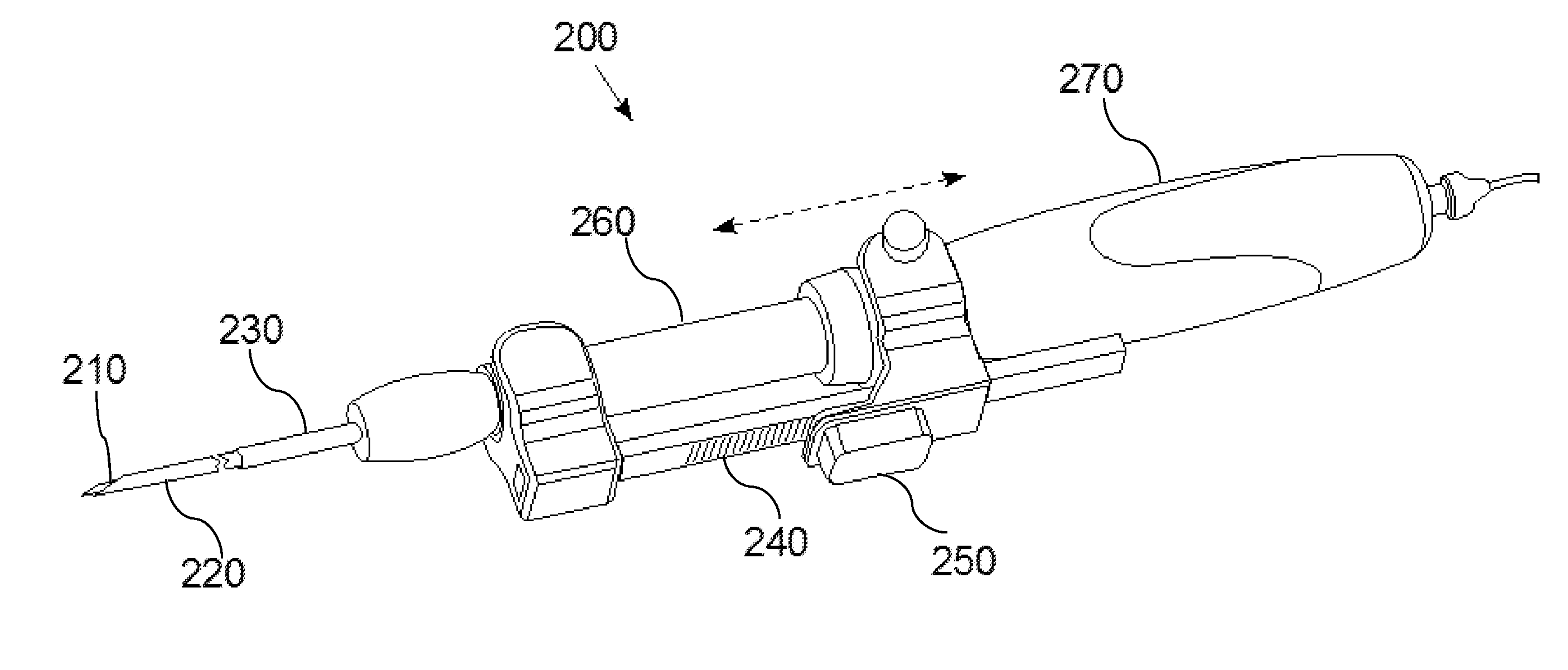
Apparatus and Method for Assessment of Interstitial Tissue
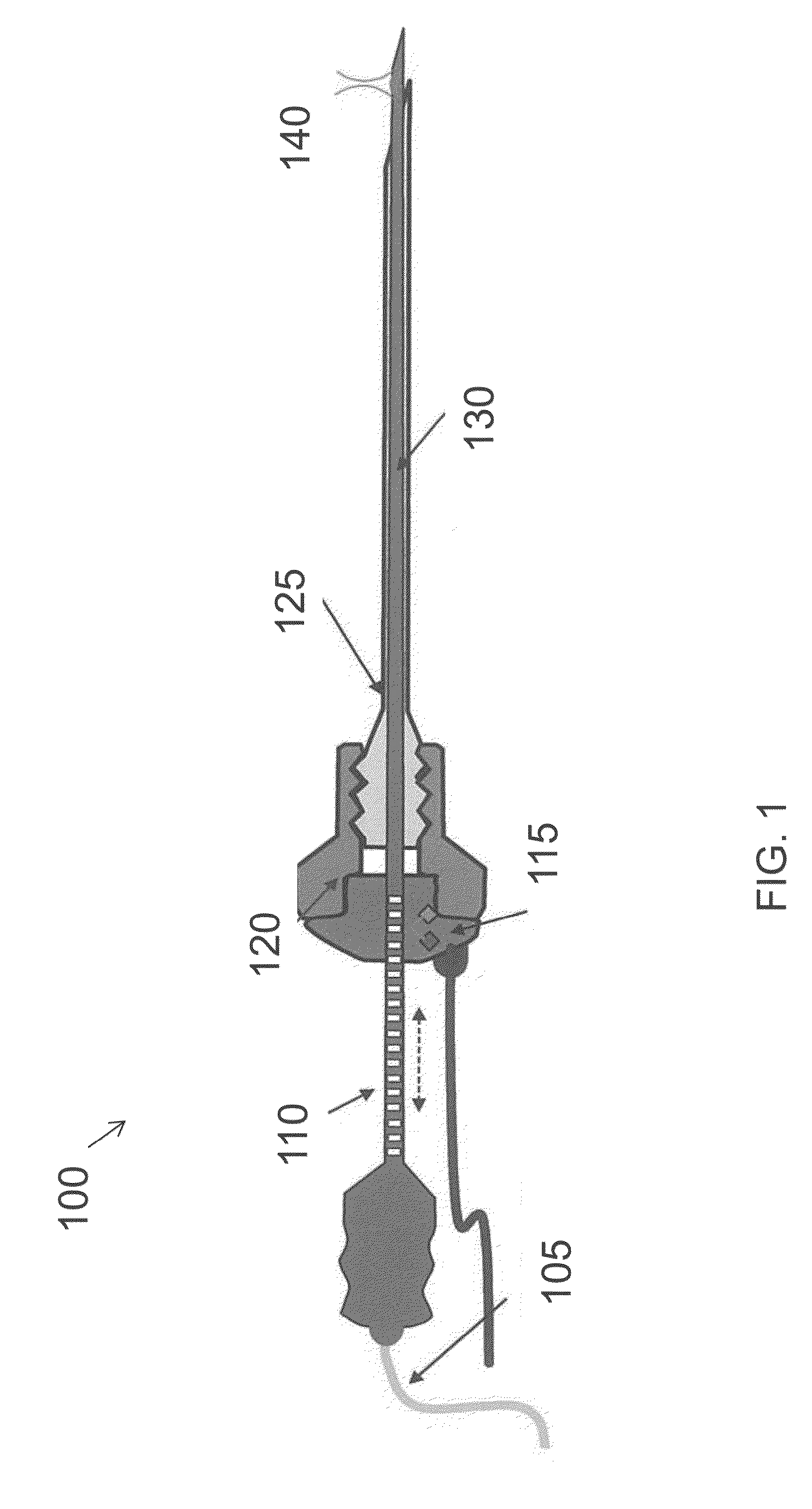
InactiveUS20160007854A1High-resolution imageMinimally invasive OCT imagingDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterHand heldCatheter
A handheld optical coherence tomography imaging and tissue sampling system and method of imaging and sampling a tissue is disclosed. The method includes inserting a catheter probe into a biopsy needle. The biopsy needle can be attached to a hand-held scanning and sampling device. The biopsy needle is maneuvered to an investigation site. A three-dimensional image of the tissue at the investigation site is captured with the catheter probe.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
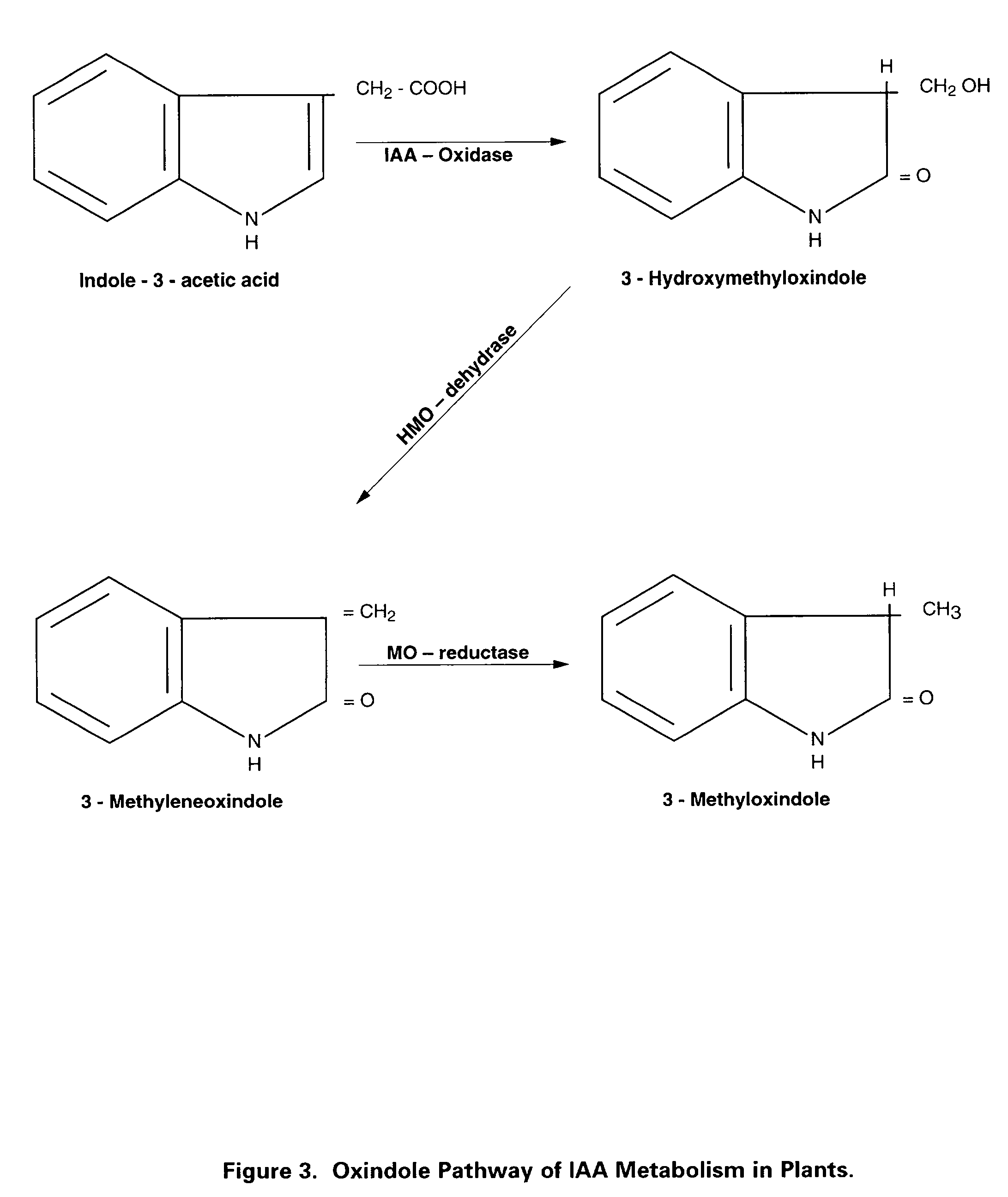
Preparation of biologically active 3-methyleneoxindole and definition of its application in stimulation of plant growth and tissue repair
InactiveUS20020055171A1Increased formationAvoid infectionBiocideOrganic chemistryShootSynthesis methods
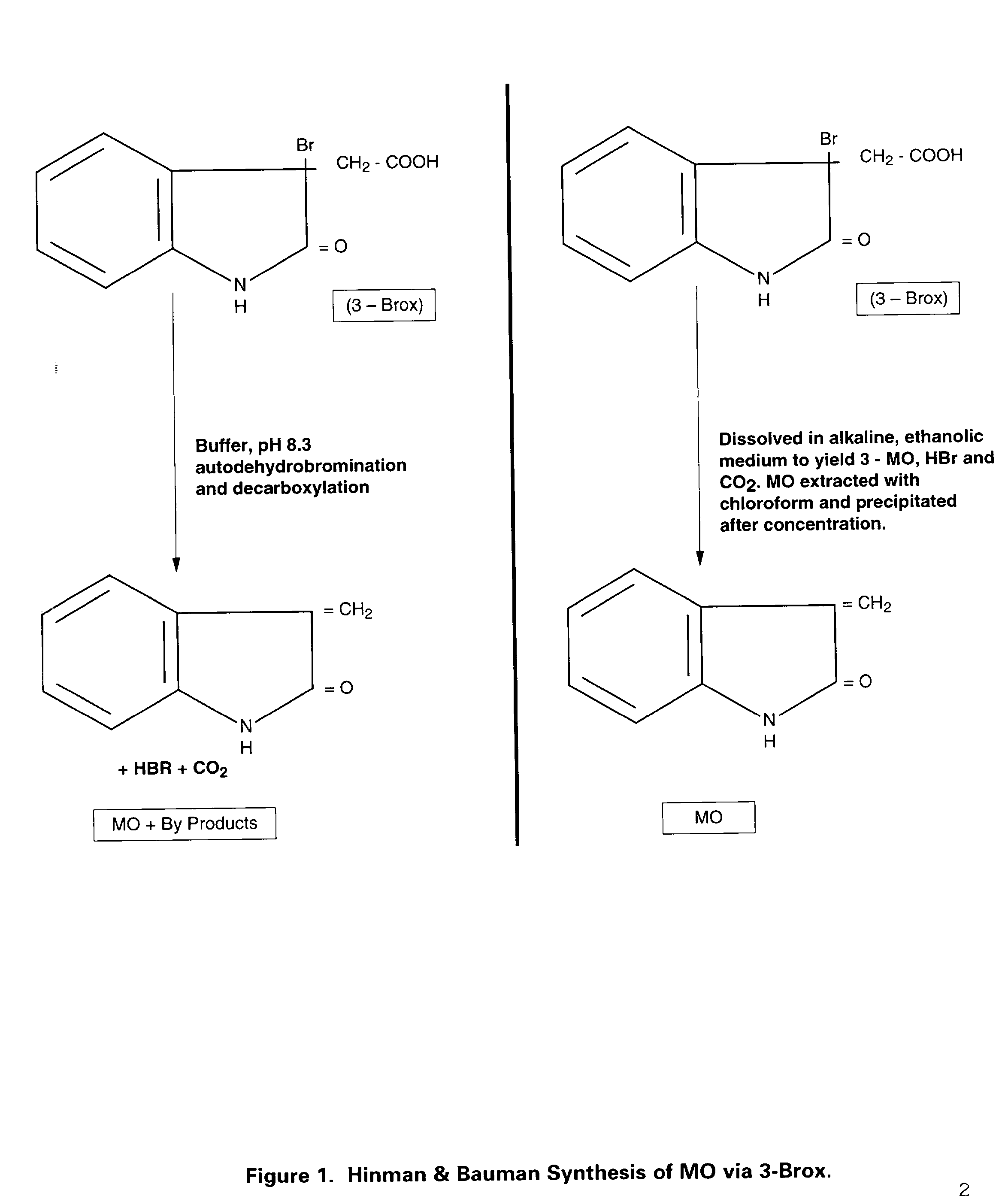
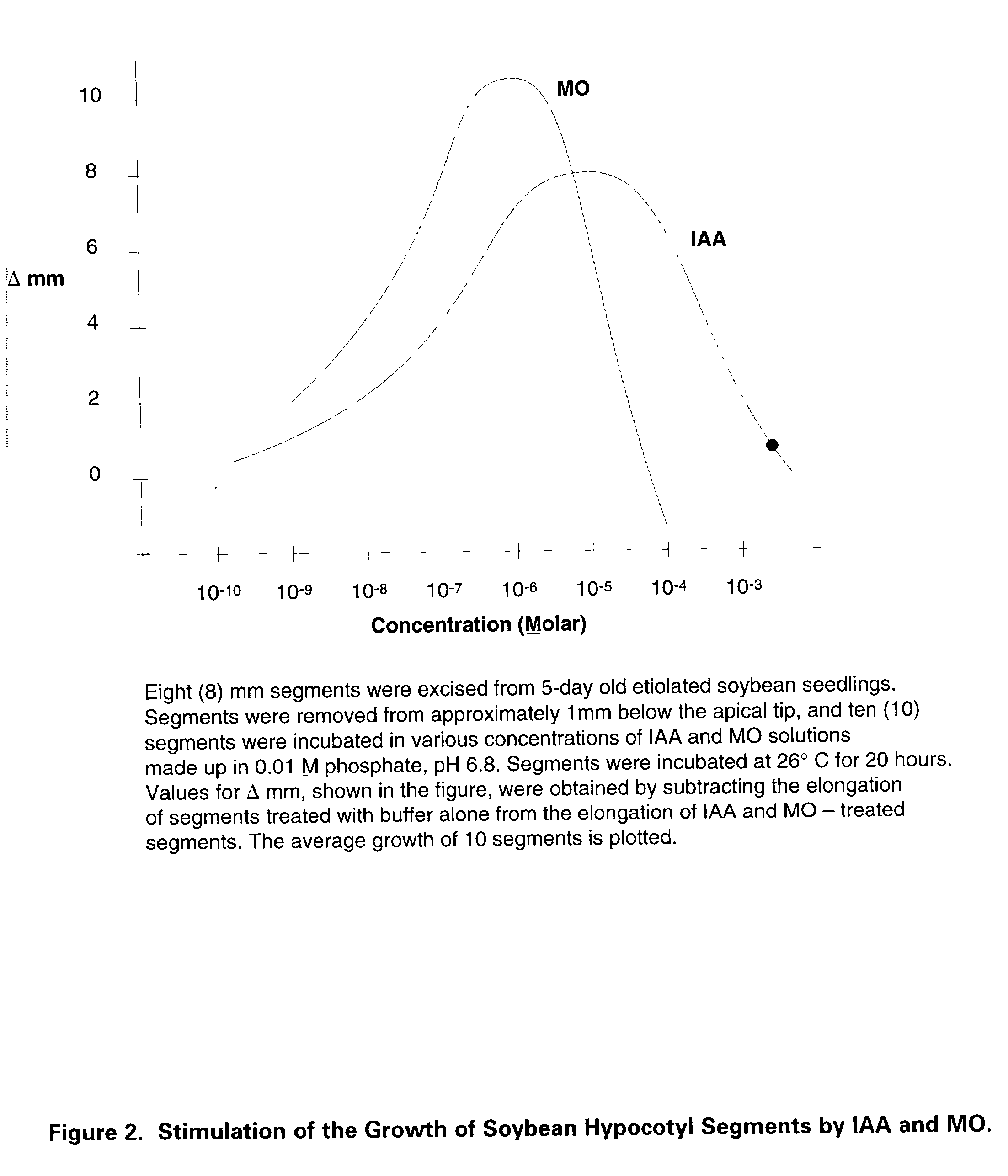
Identification of the true nature and metabolic action of 3-methyleneoxindole (MO), a naturally occurring catabolite of the plant auxin, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Description of the two novel methods of synthesis of MO which produce the pure, biologically active auxin compound of MO. Discovery and description of the causes for the erroneous classification of MO as an inert compound with no auxin activity. These findings and methods of synthesis correct the ubiquitous theoretical errors which have driven scientific investigation and plant science research of plant auxins for nearly forty years. Researchers have failed to observe the auxin activity of MO because of the use of standard but incorrect synthetic techniques which have consistently produced impure forms of 3-bromooxindole-3-acetic acid (3-Brox), the synthetic precursor of MO. In addition, the use of dimethylsulfooxide as a solvent for MO has been identified as a major source of contamination of MO during synthesis. This invention describes two novel methods for synthesizing (MO). By using purified MO and avoiding the use of dimethylsulfoxide, it was found that the resulting MO product to be 100 to 1,00 fold more effective than IAA in promoting rooting in plant cuttings; supporting tissue differentiation and growth in stage I, stage II and stage III media used for the micropropagation of explants; promoting the formation of callus tissue over wounded plant parts; and, stimulating the production of interstitial tissue between scion and rootstock to increase the success rate for grafting. Therefore, this invention identifies MO as the dominant auxin in shoot acceleration, root development, wound sealing and scion acceptance. Finally, the correct pathway from IAA to MO is presented.
Owner:TULI VIRENDA KUMAR
Method to mitigate morbidity and mortality in virally induced forms of ACE2 receptor pathology progressing to SARS or ARDS.
InactiveUS20210315910A1Reduce infectionMaximize resultTetracycline active ingredientsMucoid impactionBronchial epithelium
ACE receptors are affected in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome related coronaviruses. ACE genes are directly related to the morbidity and mortality of those with cystic fibrosis. The thick, sticky mucus in the respiratory, and digestive systems, is seen in the inherited disease cystic fibrosis. Viral induced sticky mucus in the respiratory and digestive systems can also be appreciated as a response to viral pathogens where the cycle of mucus production in vivo induces the recruitment of more mucus production to the extent that cellular damage occurs within the lower respiratory track requiring intubation as a life saving measure. In the most severe cases mechanical intubation fails due to the fact that no control over the recruitment of mucus production was achieved at the onset. SARS pathology shows inflammatory exudation in the alveoli and interstitial tissue, with hyperplasia of fibrous tissue and fibrosis. Inherited cystic fibrosis pathology shows atelectasis, mucoid impaction, acute and chronic inflammation, bronchiectasis, cyst formation, and fibrosis widespread. A virally induced disorder in relations to ACE2 receptors can be treated successfully at the early onset with inherited cystic fibrosis disease mimicking techniques with the efforts of minimizing the activity and utilization of the ACE2 receptor. Cystic fibrosis lung infections, and opportunistic pathogens contribute to chronic airway inflammation that is characterized by neutrophil / macrophage infiltration, cytokine release and ceramide accumulation. In terms of virally induced forms off ACE2 receptor pathologies, as it related to coronavirus such as Covid 19, presumably ceramide precursors which aid in intracellular transport of the virus into the cell via inflammation and remodeling is present in alveolar tissues of the lung in patients with cystic fibrosis while the same pathology occurs in patients with virally induced forms of ACE2 pathology which to often progresses to SARS or ARDS.
Owner:STAFFORD VIVI ROBYN
Cell structure, non-human model animal, method for producing non-human model animal, and method for evaluating test substance
ActiveCN107921173AEffective evaluationRich interstitial tissueCompounds screening/testingMammal material medical ingredientsMesenchymeCancer cell
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a non-human model animal rich in interstitial tissue; a cell structure useful for production of the non-human model animal; a method for evaluatinga test substance using the non-human model animal; and a method for producing the non-human model animal. The present invention provides a cell structure comprising biocompatible polymer blocks and atleast cancer cells and mesenchymal cells. The multiple biocompatible polymer blocks are disposed in the space between the multiple cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Burn wound tissue activity evaluation system based on fluorescence development image
PendingCN114246553ADynamic display of perfusion rateDynamic Display IntensityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingRadiology
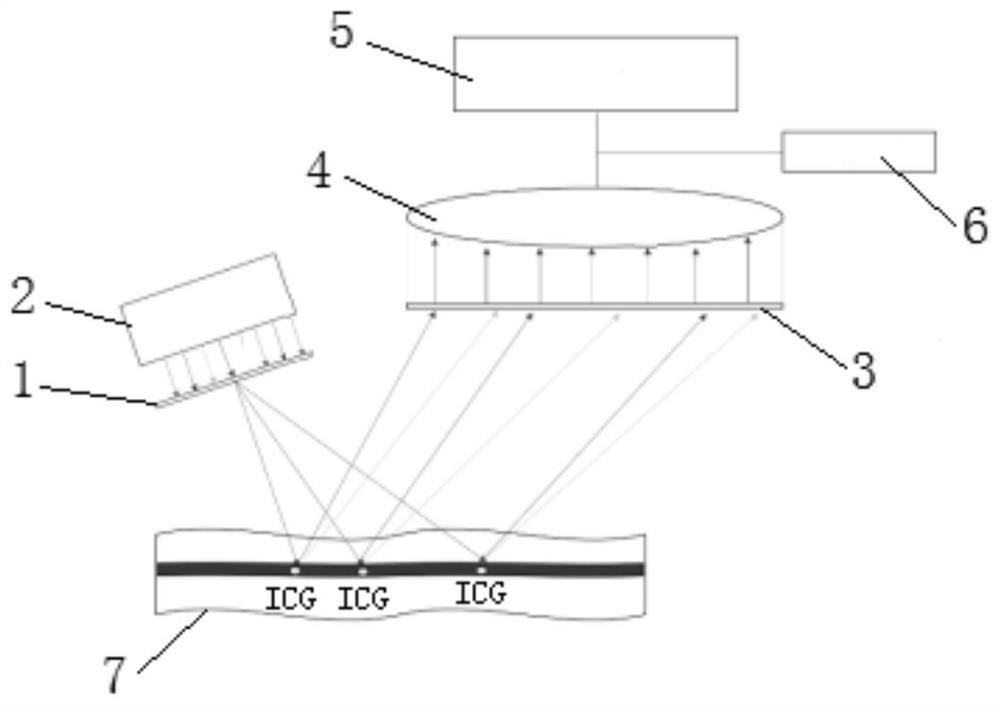
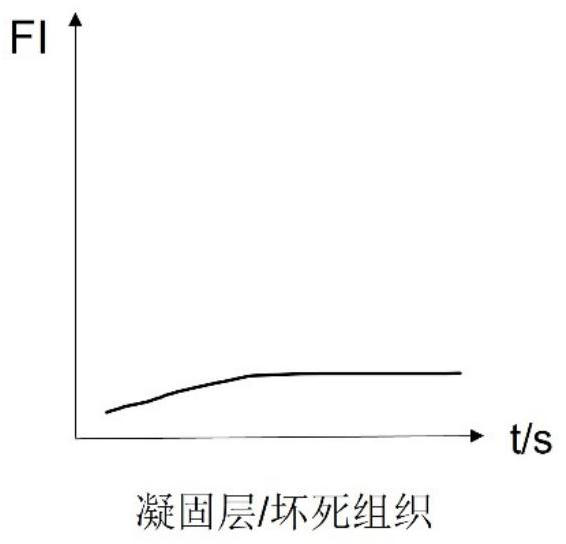
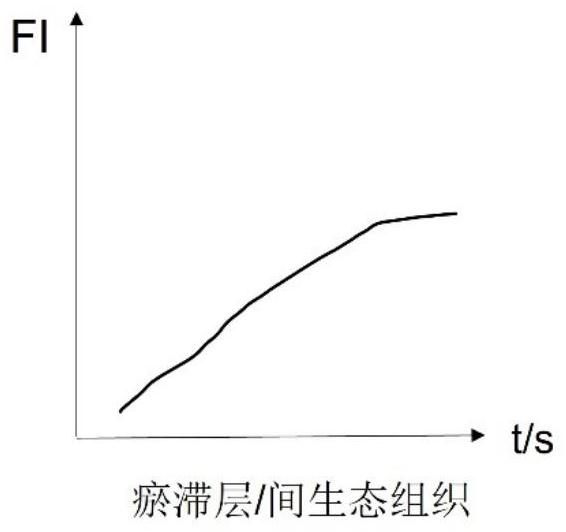
The invention discloses a burn wound tissue activity evaluation system based on a fluorescence development image, and relates to the technical field of burn wound evaluation, the burn wound tissue activity evaluation system comprises a fluorescence development acquisition module, a development image processing module and a tissue activity evaluation module, the fluorescence development acquisition module is used for performing fluorescence development on a burn wound and acquiring a development image; the developing image processing module is used for obtaining fluorescence intensity change data of the anchoring pixel sites according to the fluorescence developing time sequence, and obtaining a statistical value of each anchoring pixel site according to the fluorescence intensity change data; and the tissue activity evaluation module is used for evaluating the tissue activity of each anchoring pixel site according to the statistical value. According to the method, the solidification area, the stasis area and the hyperemia area of the burn wound surface are distinguished through the peak value and the slope of the fluorescence intensity curve, so that necrotic tissues and interstitial tissues of the wound surface are accurately identified, and the accuracy of deep diagnosis of the burn wound surface is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
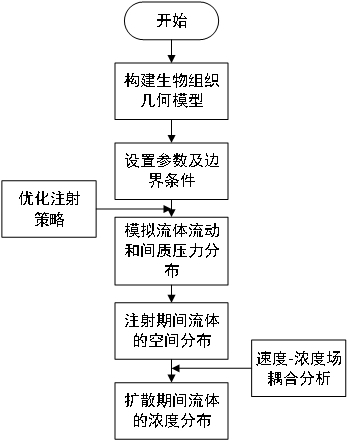
Prediction Method of Magnetic Fluid Concentration Distribution Based on Injection Strategy
ActiveCN113312684BPredicted Concentration DistributionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationPredictive methodsGeometric modeling
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for effectively treating varicocele by morida officinalis polysaccharide extracts through inhibiting testis blood vessel generation
InactiveCN107998143AImprove spermatogenic functionInhibition of lesionsOrganic active ingredientsSexual disorderDiseasePituitary gland
The invention discloses a method for effectively treating varicocele by morida officinalis polysaccharide extracts through inhibiting testis blood vessel generation. The method comprises the followingsteps of (1) building an experimental varicocele animal model; (2) extracting morida officinalis coarse polysaccharide; performing primary purification; then, studying and discussing the restorationeffect of the morida officinalis coarse polysaccharide on the experimental varicocele rat hypothalamus-pituitary gland-testis axis, particularly the restoration effect in the early stage and developing stage of the disease; (3) obtaining a result showing that 100mg / kg of morida officinalis coarse polysaccharide can restore the double-side testis sperm production function and epididymal sperm quality in the early stage of the varicocele; the mechanism can be relevant to the angiogenesis inhibition and interstitial tissue normal metabolism maintenance. The sperm production function of a subclinical or varicocele early-stage patient can be improved; the progressive lesion of the testis interstitial tissue and blood vessels can be inhibited.
Owner:MENGCHAO HEPATOBILIARY HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com