Method for pressure mediated selective delivery of therapeutic substances and cannula
a selective delivery and therapeutic substance technology, applied in the direction of trocars, catheters, other medical devices, etc., can solve problems such as microanatomical barriers, and achieve the effect of improving regional- and organ-
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Delivery Device and Infusion Data
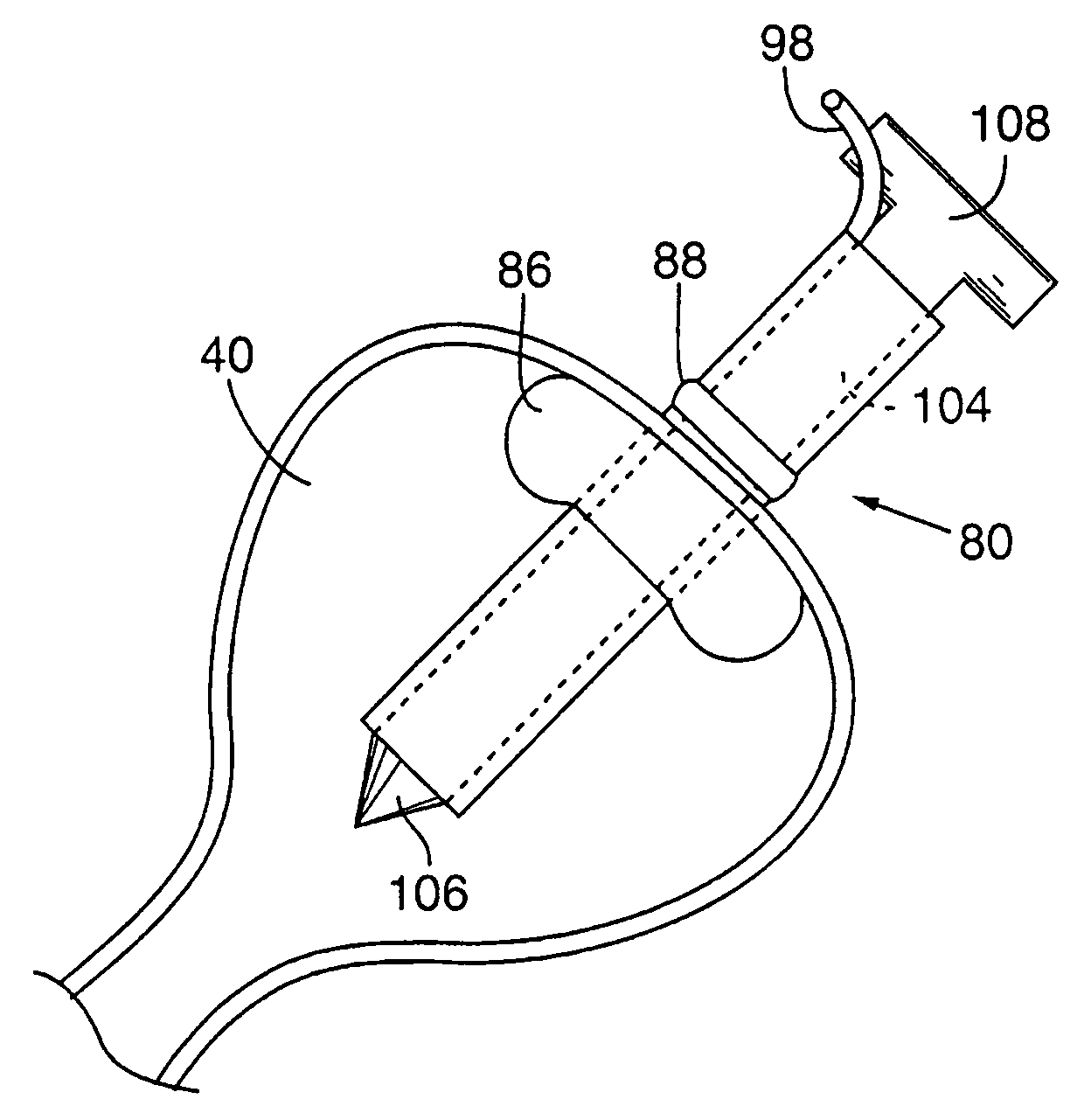
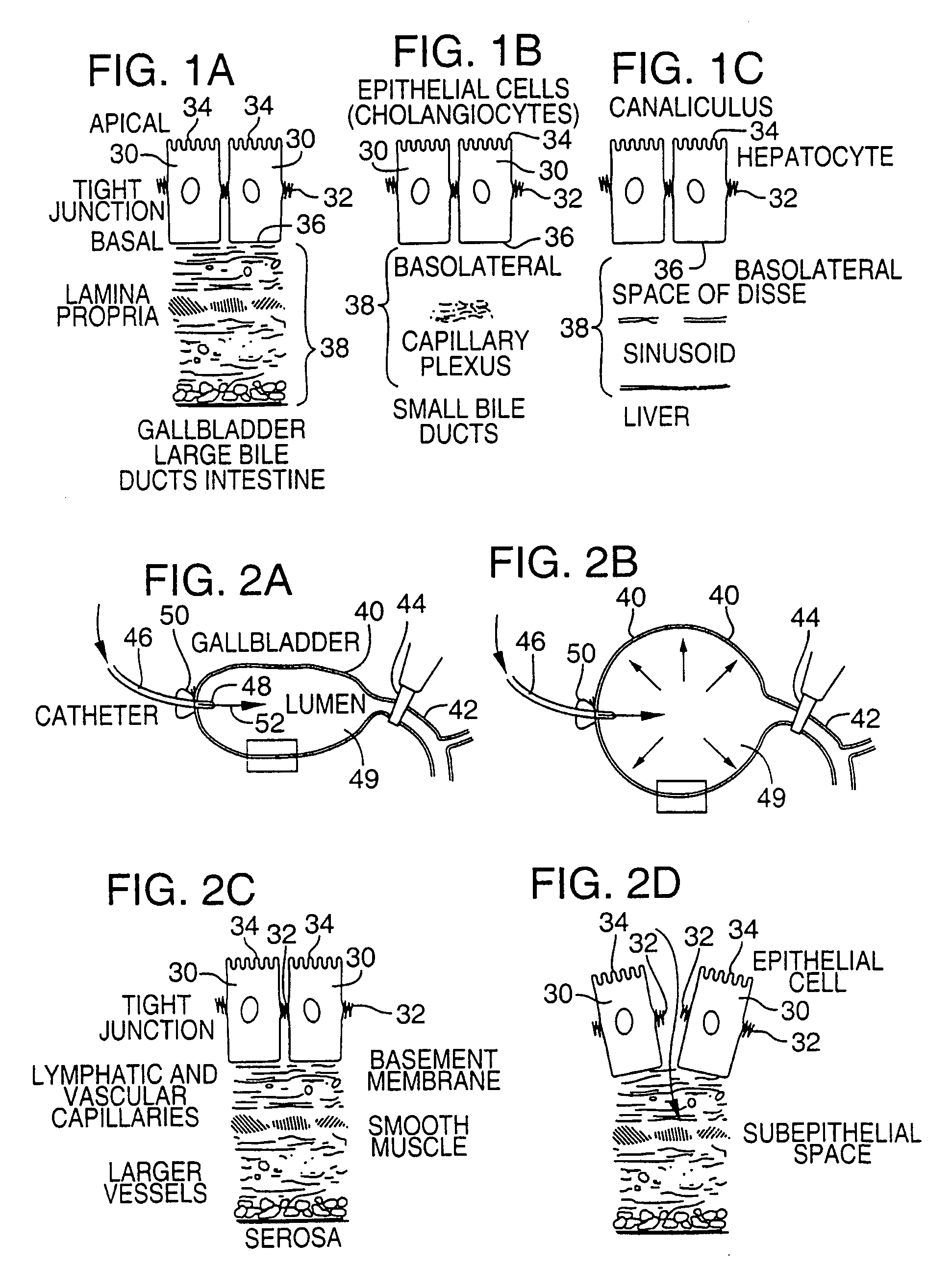
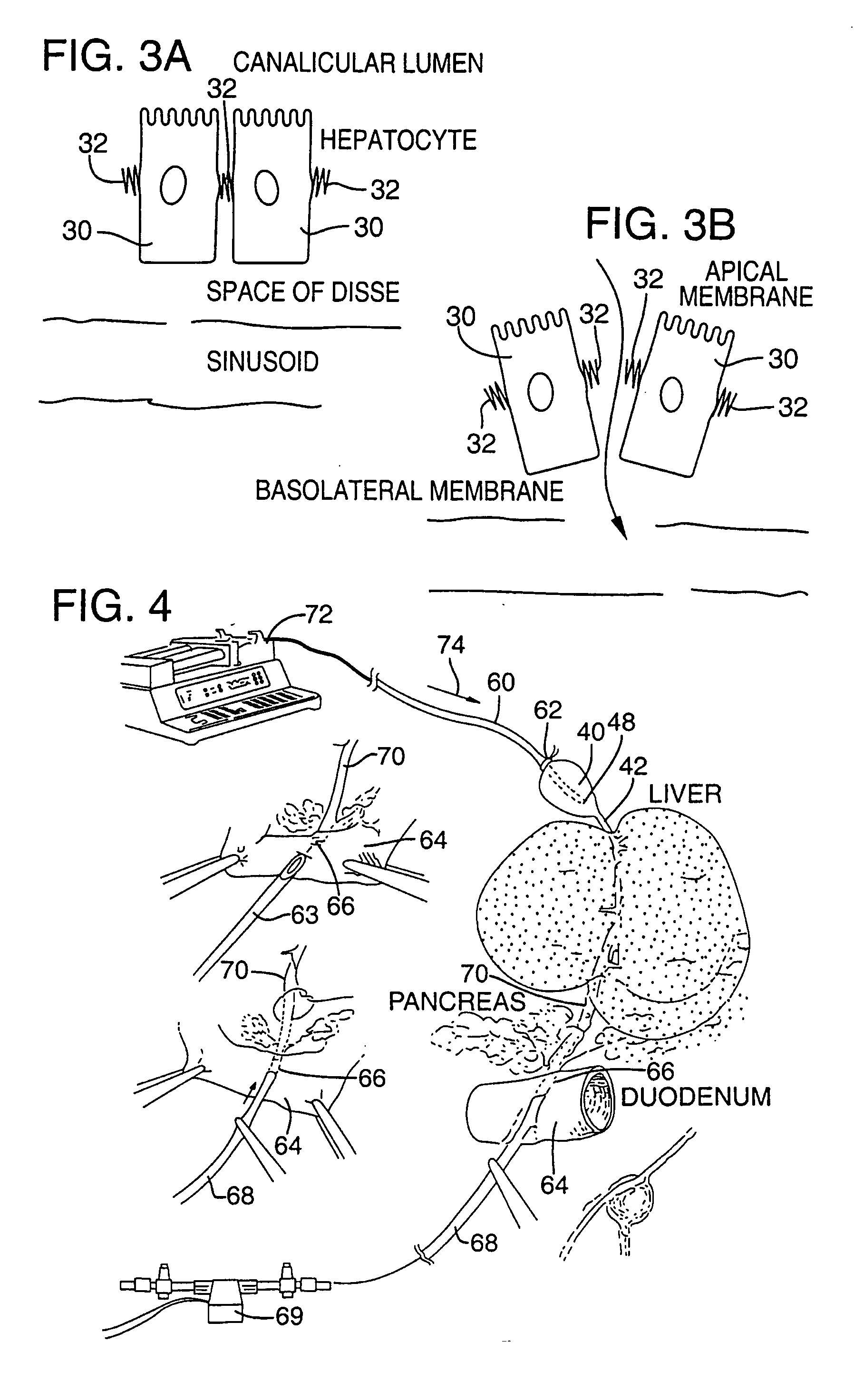
[0081]FIG. 4 illustrates an apparatus used for demonstrating the effect of retrograde biliary infusion on intrabiliary pressure, and the site specific delivery of agents to the cells. Twenty to forty gram anesthesized CD-1 male mice (Charles River) were used as experimental subjects. Following a midline laparotomy, the gallbladder 40 was manually drained through the cystic duct 42. A cholecystotomy catheter 60 (silastic tubing, 0.012″ ID / 0.025 OD) was introduced through the wall of the gallbladder 40, and secured within the gallbladder lumen with the catheter tip 48 advanced so that it was immediately proximal to the junction with the cystic duct 42. An absorbent cellulose (X0-Med, Jacksonville, μl) packing 62 was packed around the entrance site of the catheter into the gallbladder to prevent bile from leaking into the peritoneum.
[0082]A twenty-three gauge needle 63 was used to make an opening in the duodenum 64 and to perform a sphincterotomy on the...
example 2
Radiopaque Tracer Studies
[0091]A silastic catheter was placed in the gallbladder as described above. Straight (1 mm×3 mm) or curved (1 mm×5 mm) Kleinert-Kutz microvascular clips (MVC; Pilling-Weck, Research Triangle, North Carolina) were then placed rostral to the junction of the superior pancreatic duct with the common bile duct to turn the hepatobiliary system into a closed pressure system. Infusions were administered as in Example 1, and the microvascular clip occlusion caused the infusion to move retrograde into the hepatic duct and then into smaller hepatic ducts and ductules. At the end of the administration period (infusion plus dwell time) the clip was removed and the cholecystotomy catheter was withdrawn.
[0092]To evaluate the impact of hepatic venous drainage on the distribution of radioopaque dye and adenovirus following retrograde biliary infusion, the suprahepatic inferior vena cava was temporarily occluded for 5 to 10 minutes with a curved microvascular clip at a level ...
example 3
Latex Microsphere as Model for Vector Delivery
[0097]In order to both corroborate the digital fluoroscopic studies and histologically evaluate the distribution of infusate, 100 nm and 200 nm diameter fluorescent latex microspheres were administered by retrograde biliary infusion. Spheres of this diameter were selected since they are close in diameter to adenoviral (80 nm) and liposomal (200-500 nm) vectors. Yellow green (490 nm peak excitation wavelength) carboxylate-modified fluorescent latex microspheres (Molecular Probes, Eugene, Oreg.) were diluted in 1×PBS and extensively sonicated prior to use. Sphere concentration was maintained constant at 1×1011 spheres per animal, while the volume and rate of infusion were varied between animals. Following the completion of infusion, fresh frozen sections were prepared from the liver and lung and evaluated under fluorescent microscopy. To visualize histologic detail more completely, some slides were stained with Evans Blue (0.05% for 20 sec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com