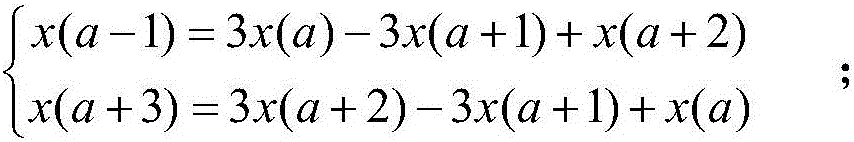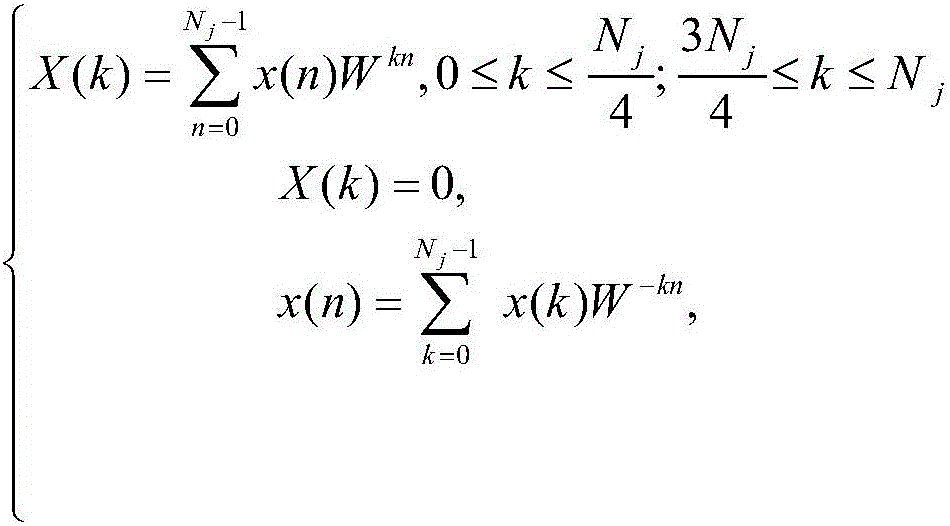Patents
Literature
169 results about "Arthroscopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
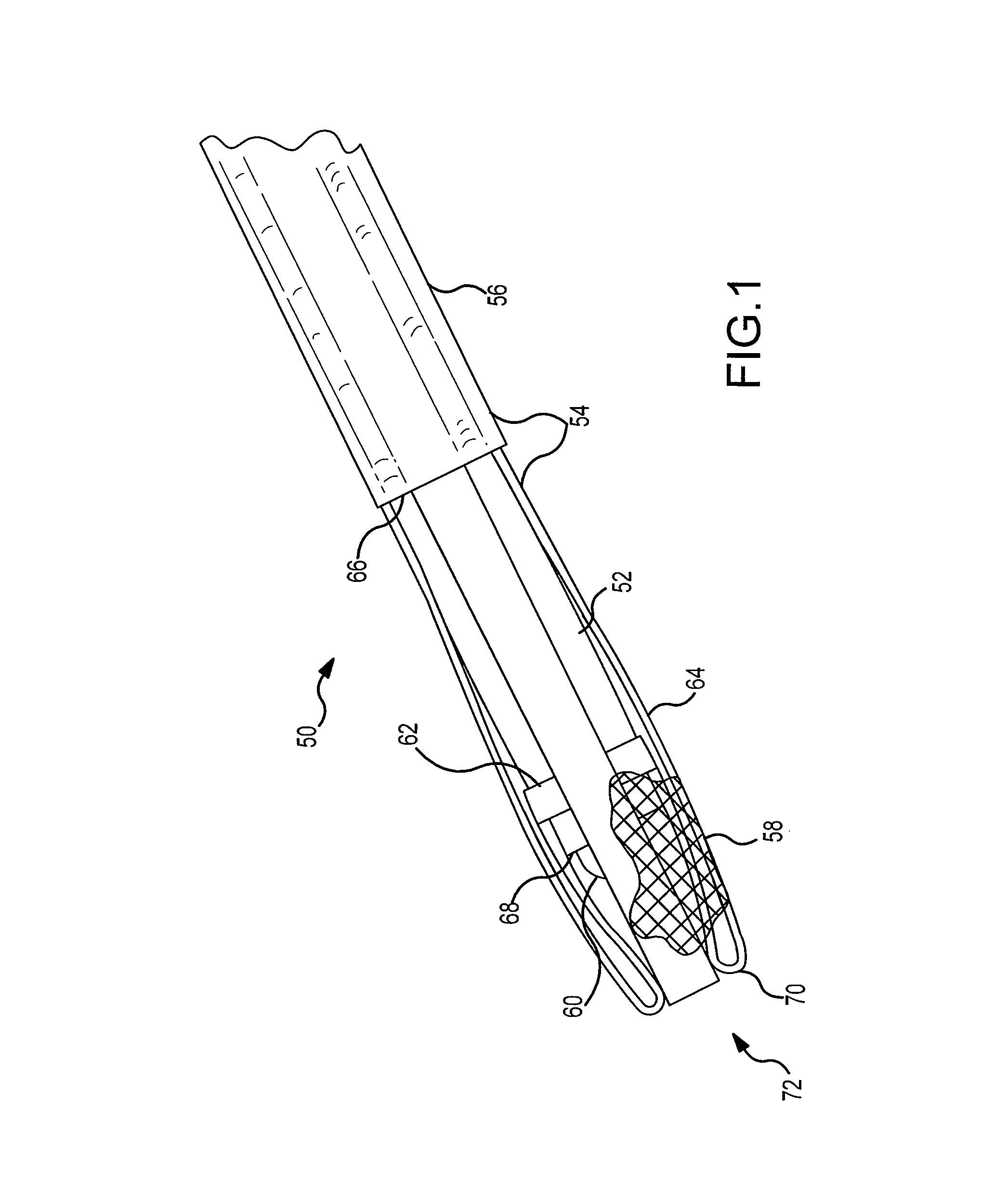
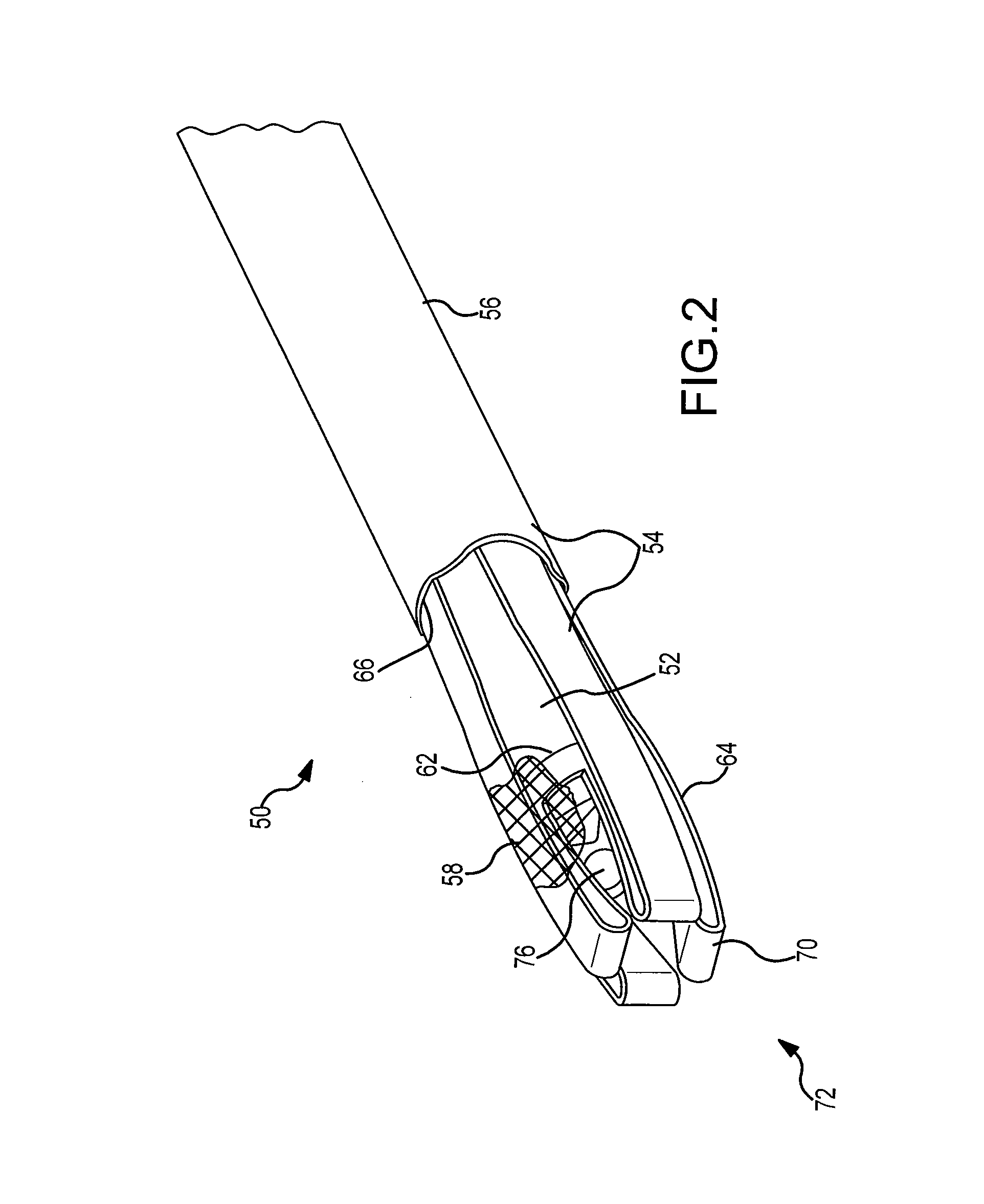
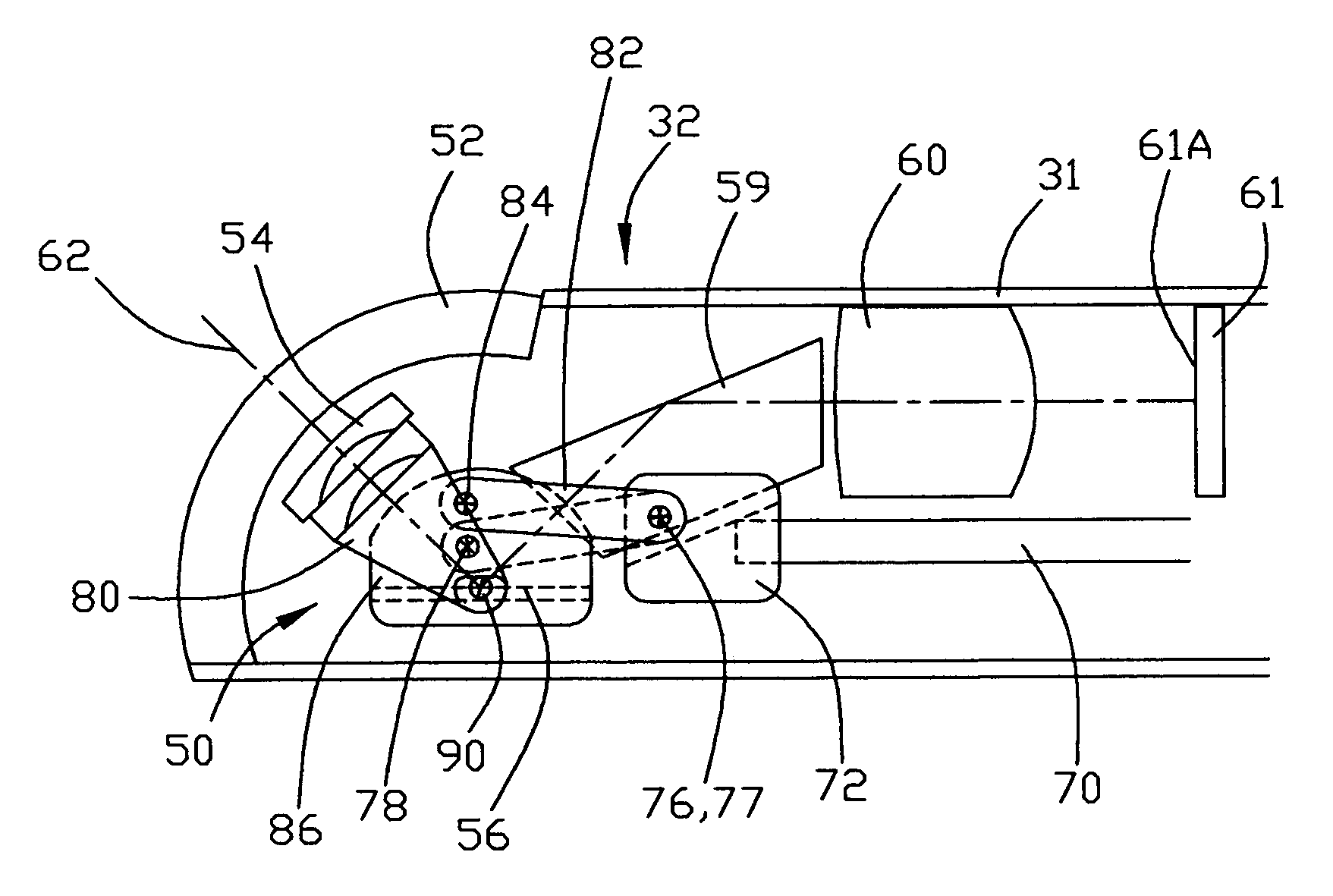
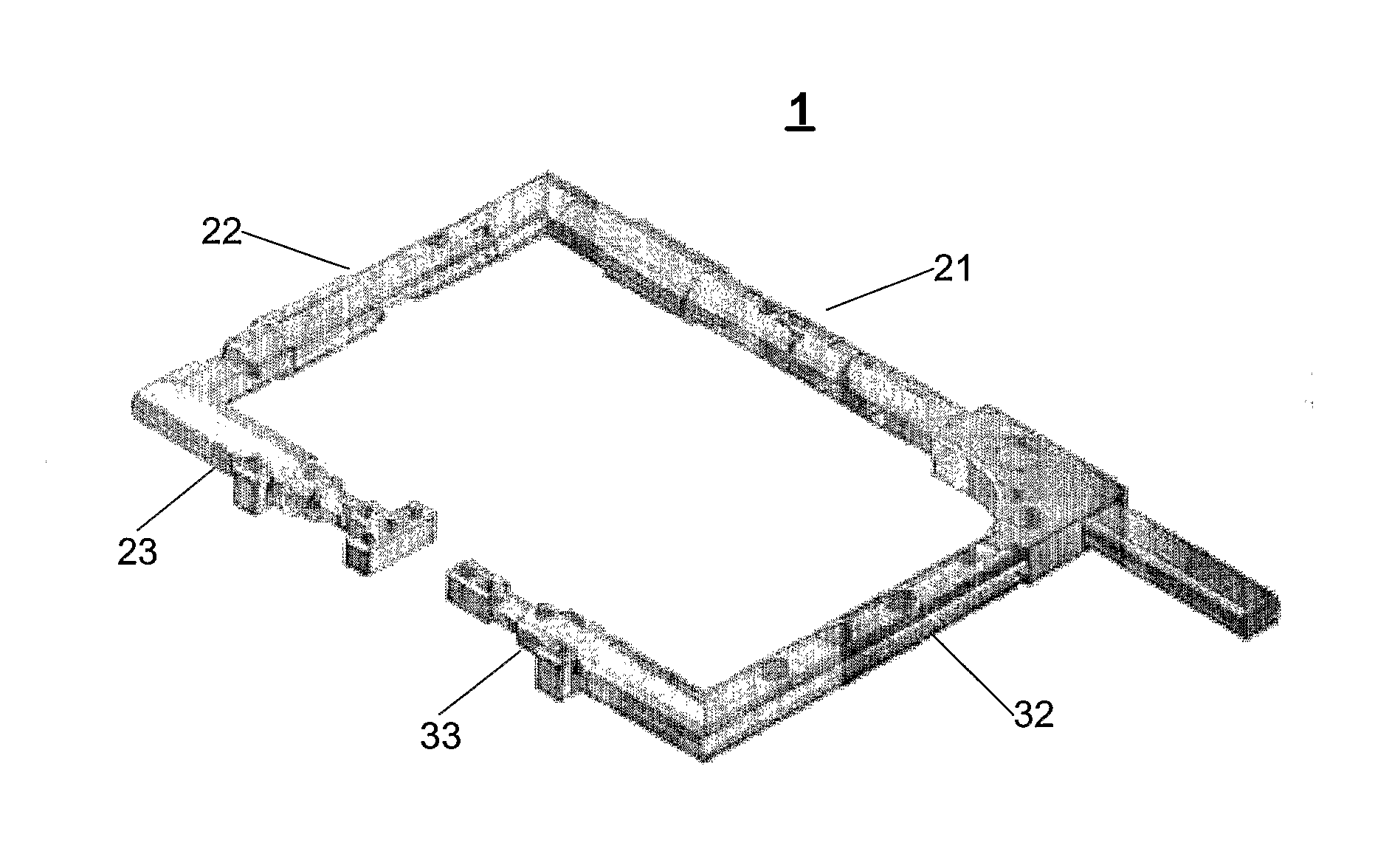
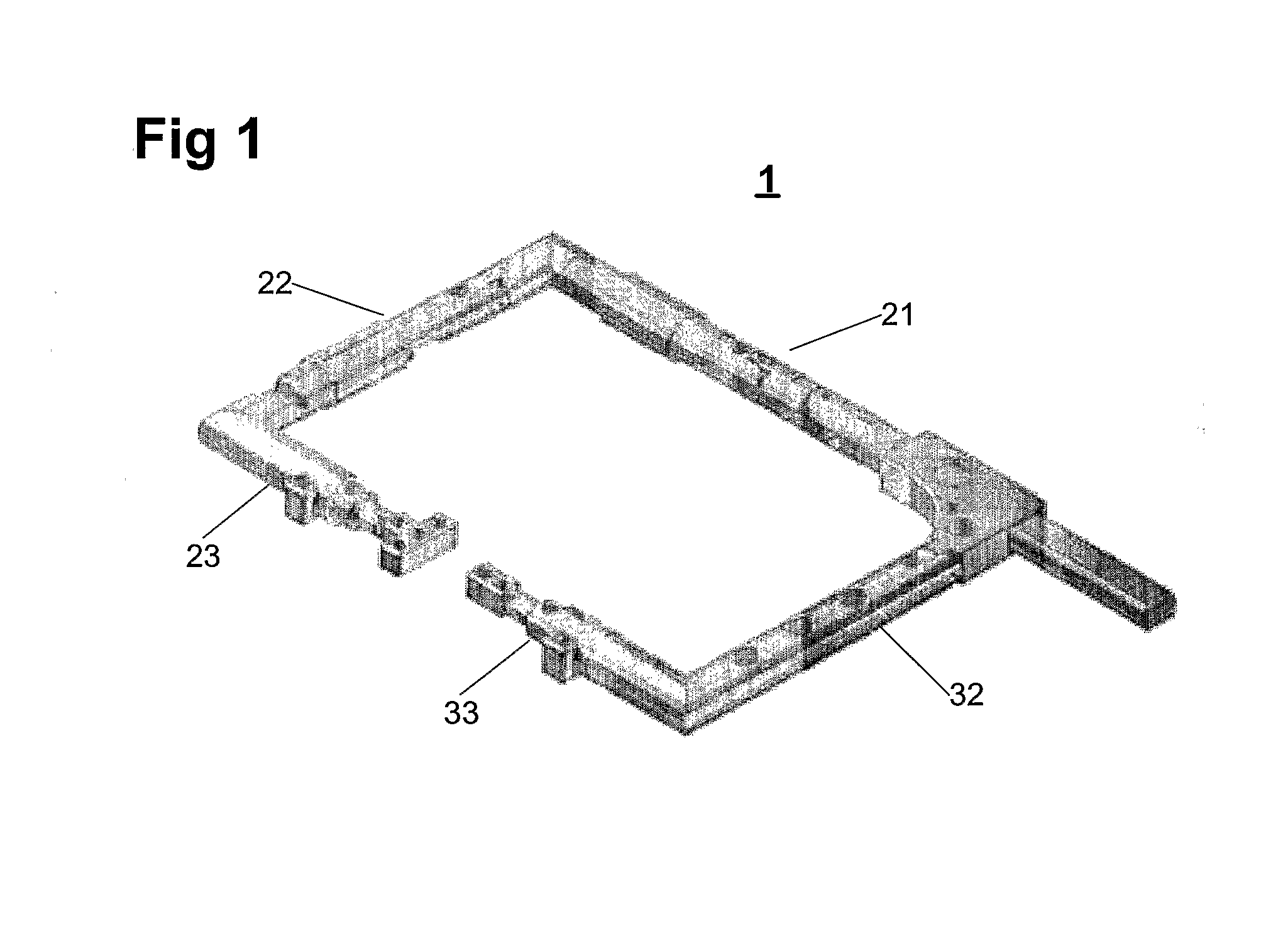
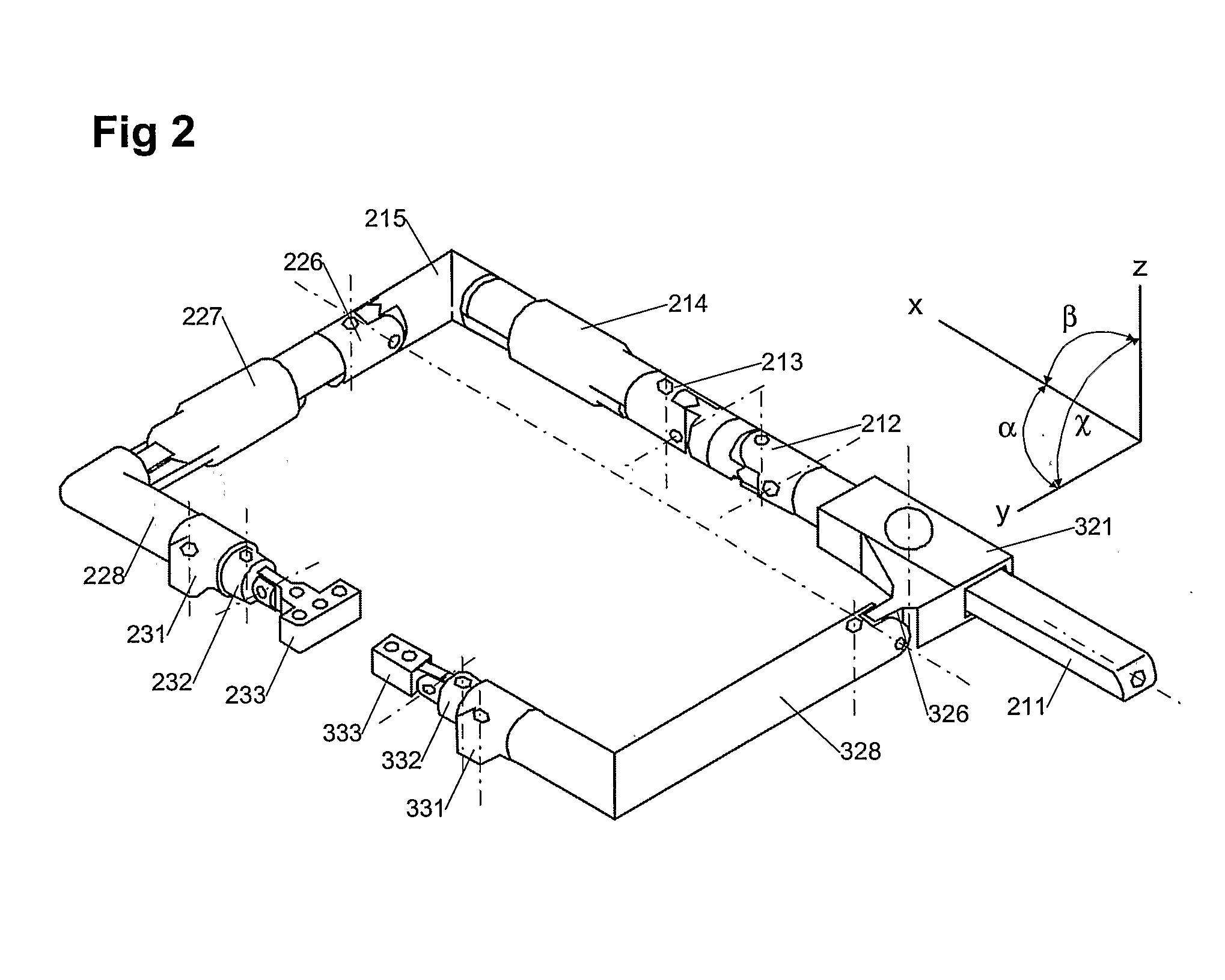
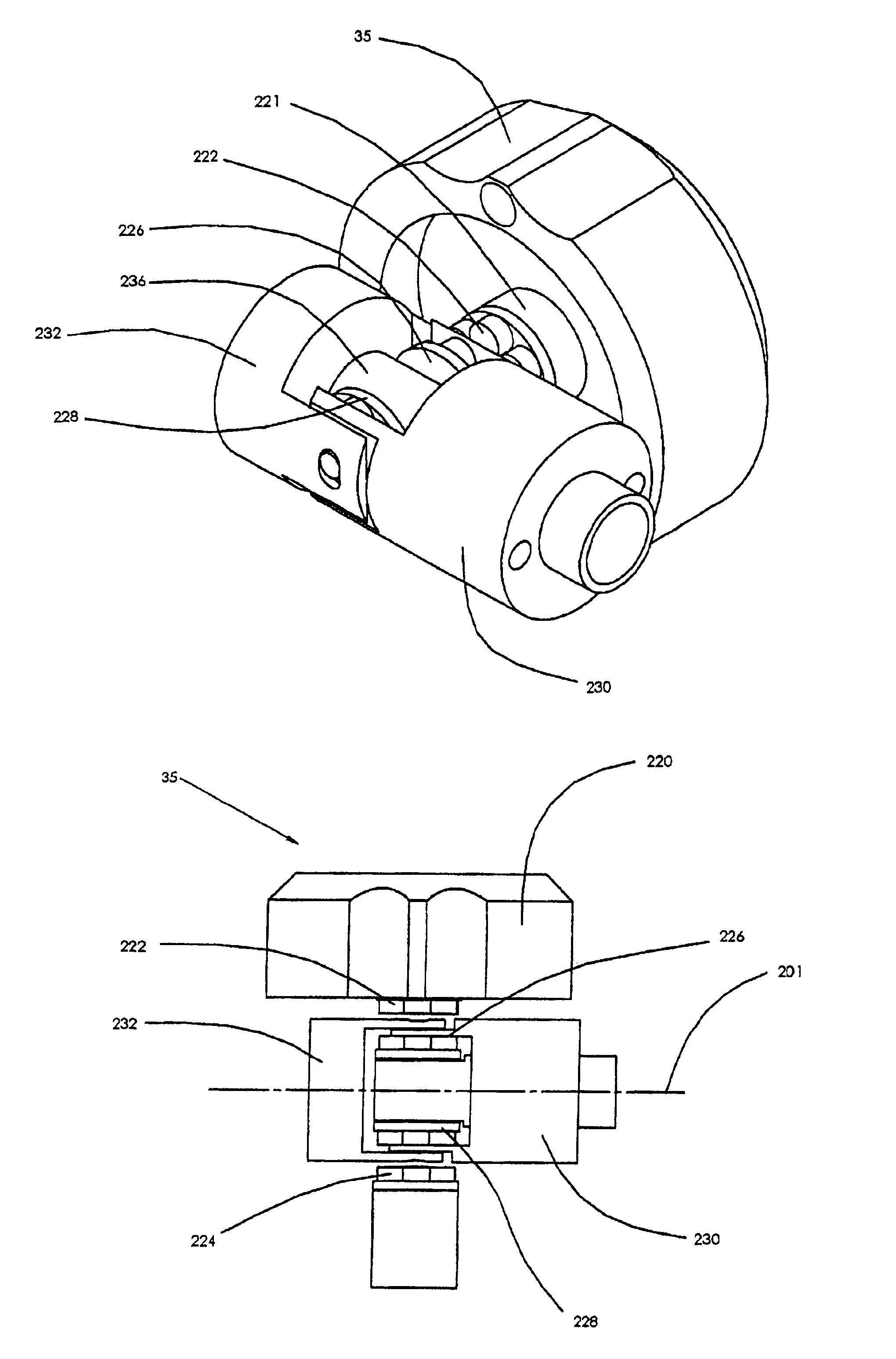
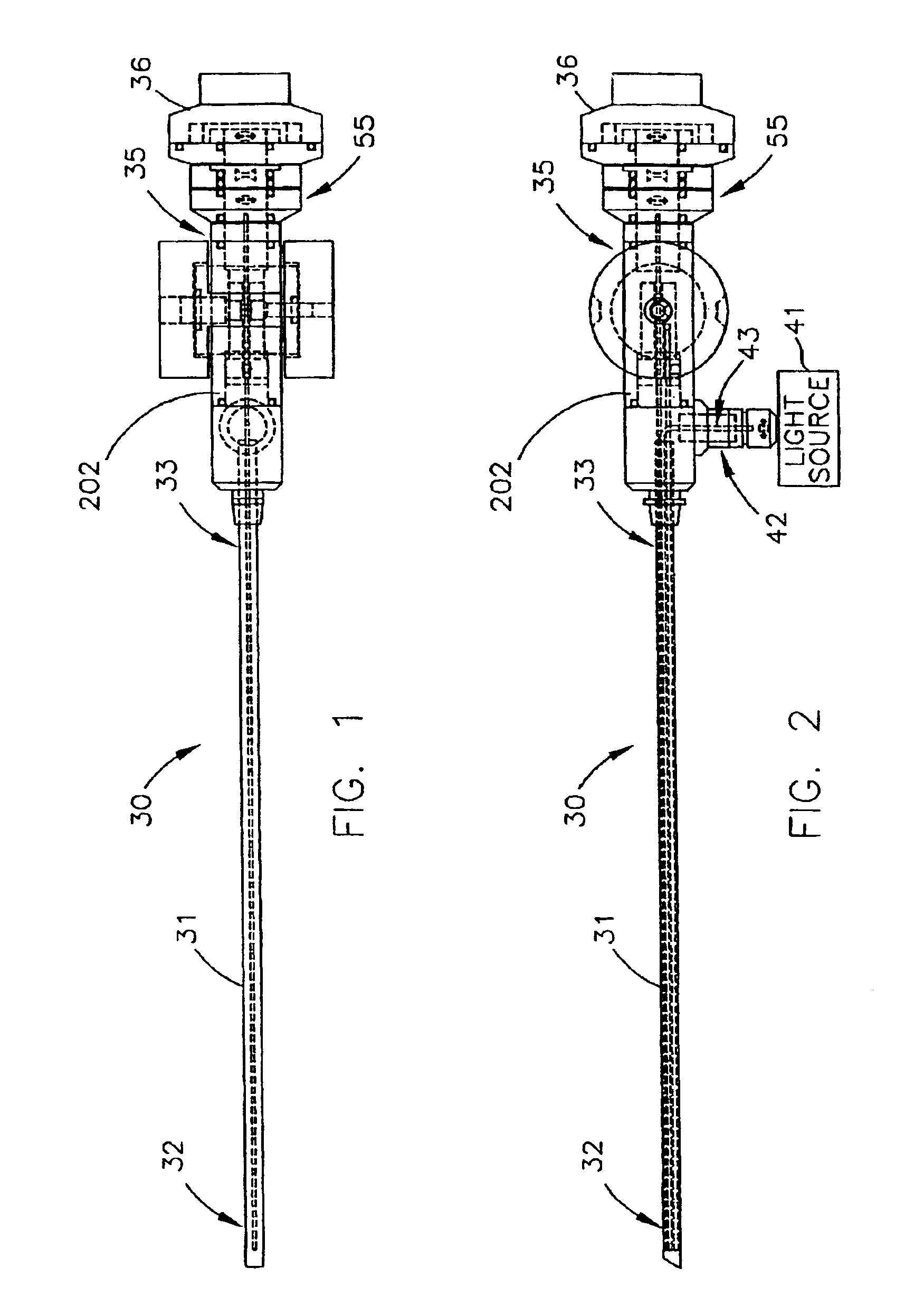
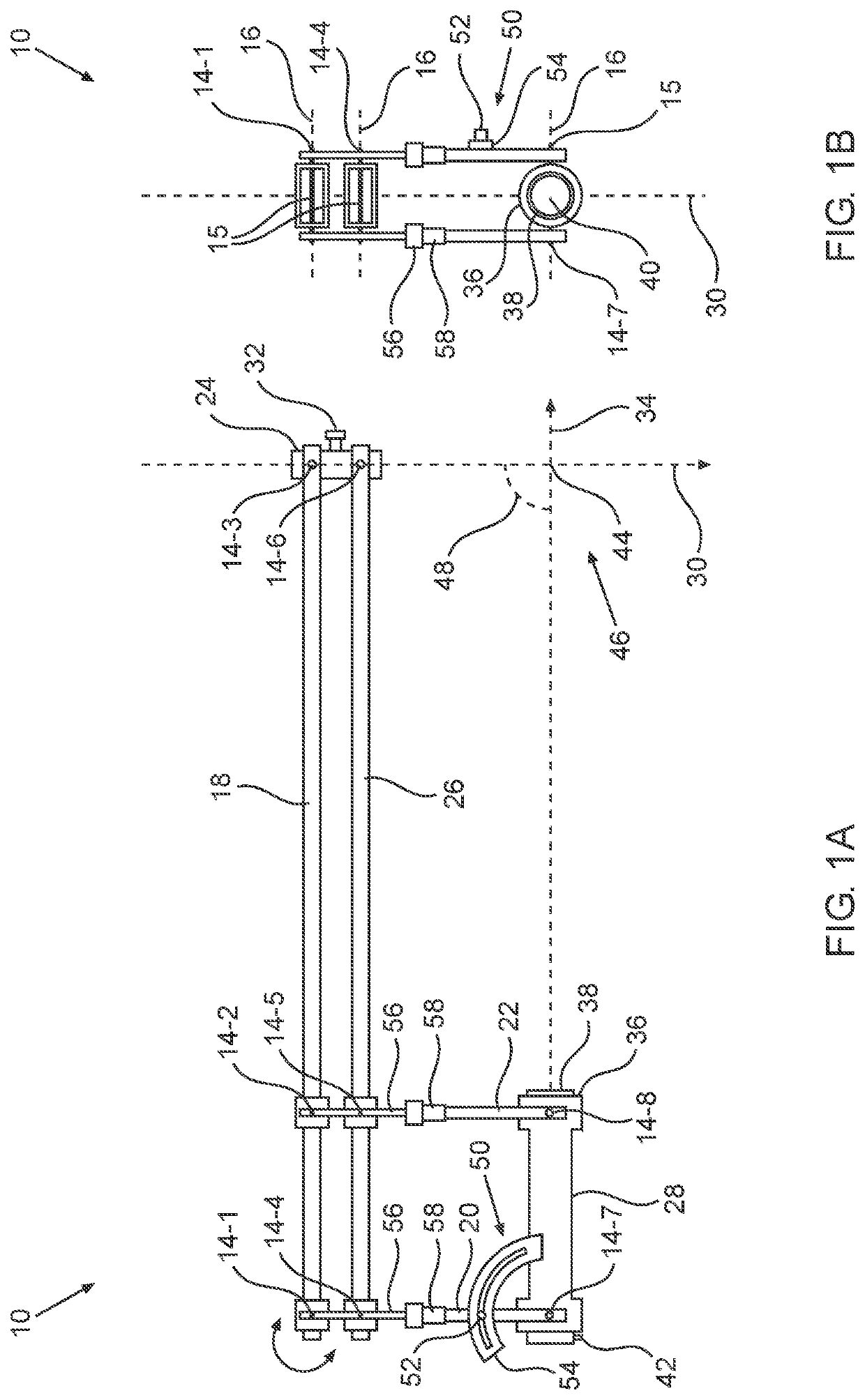
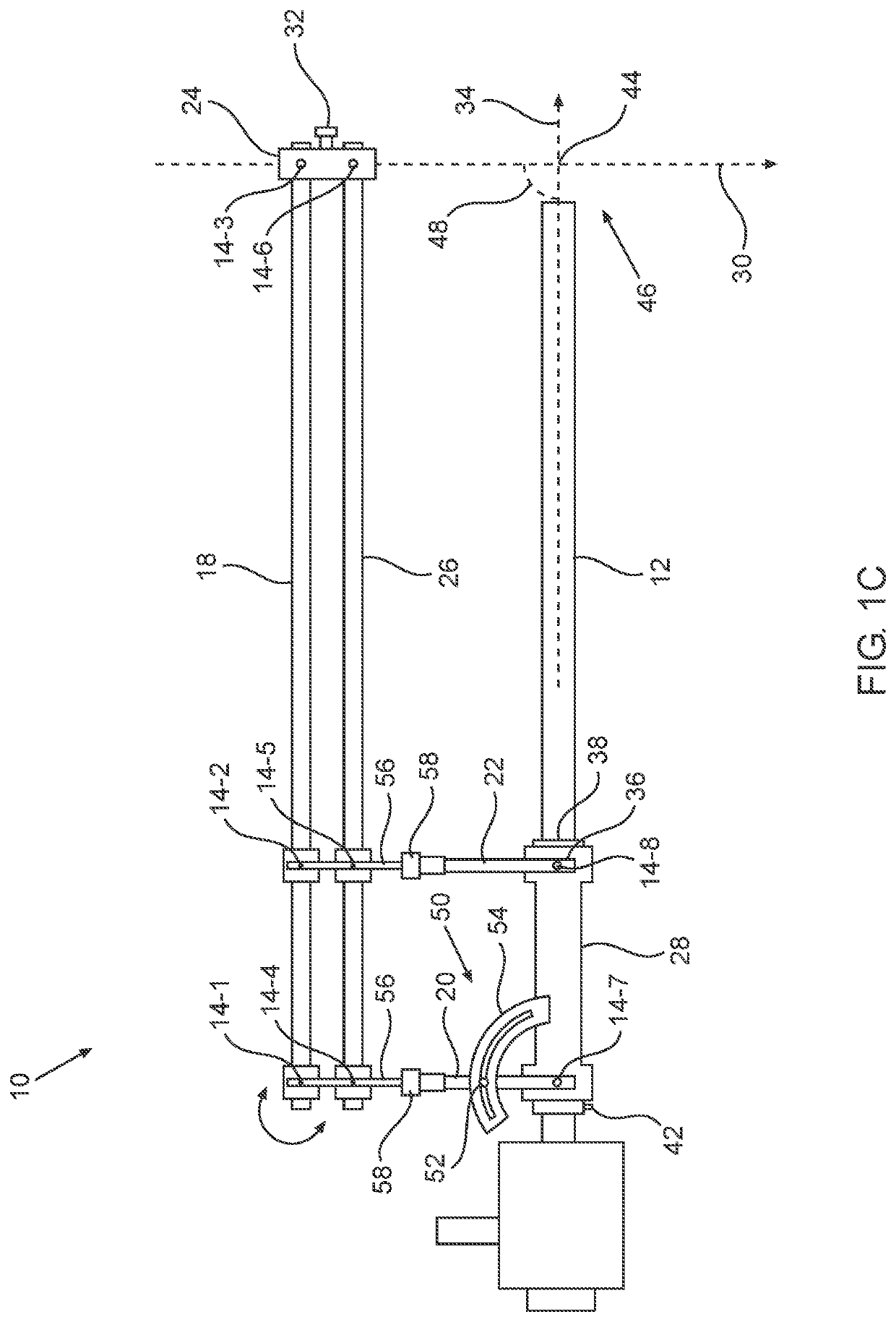
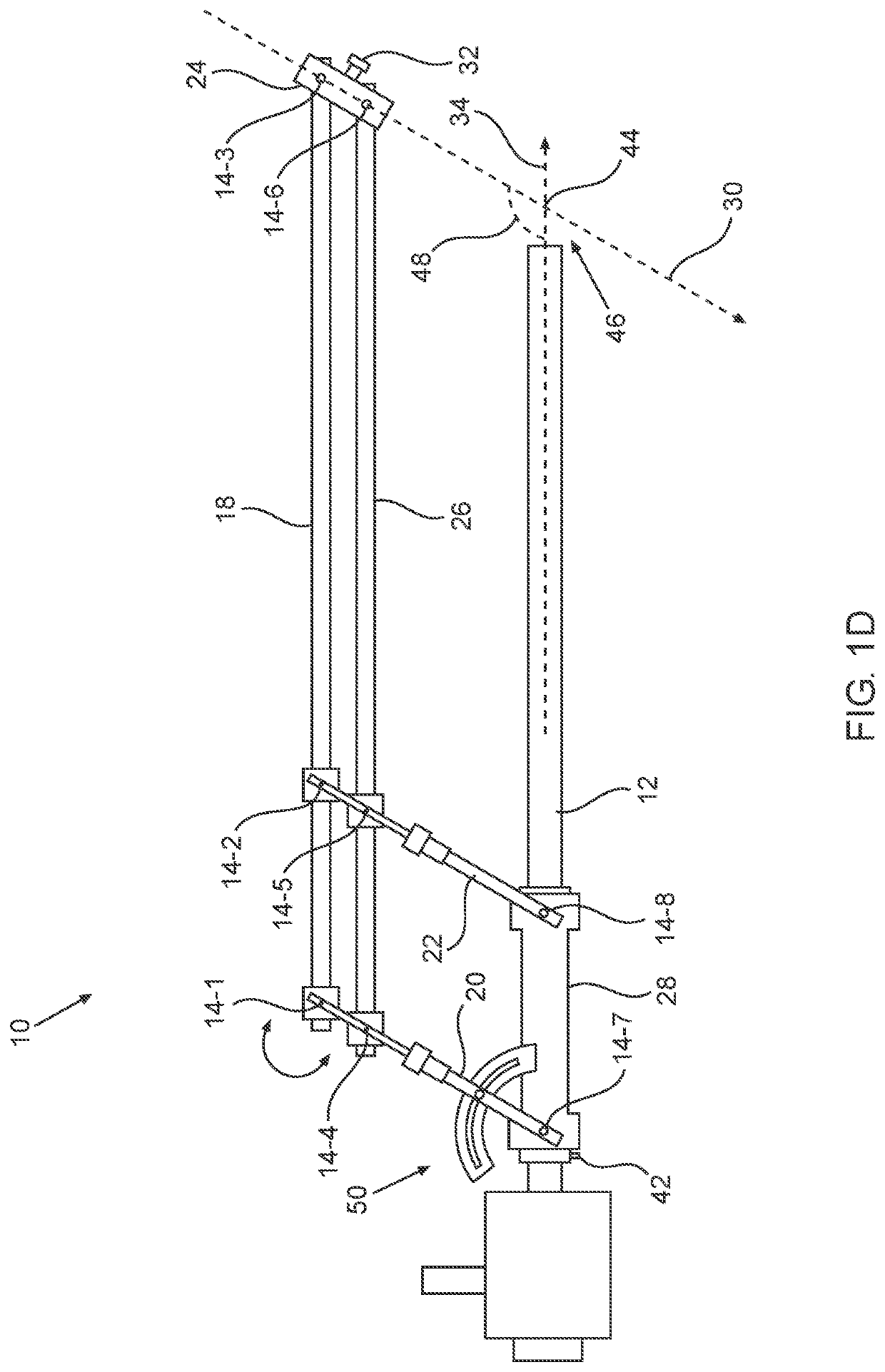
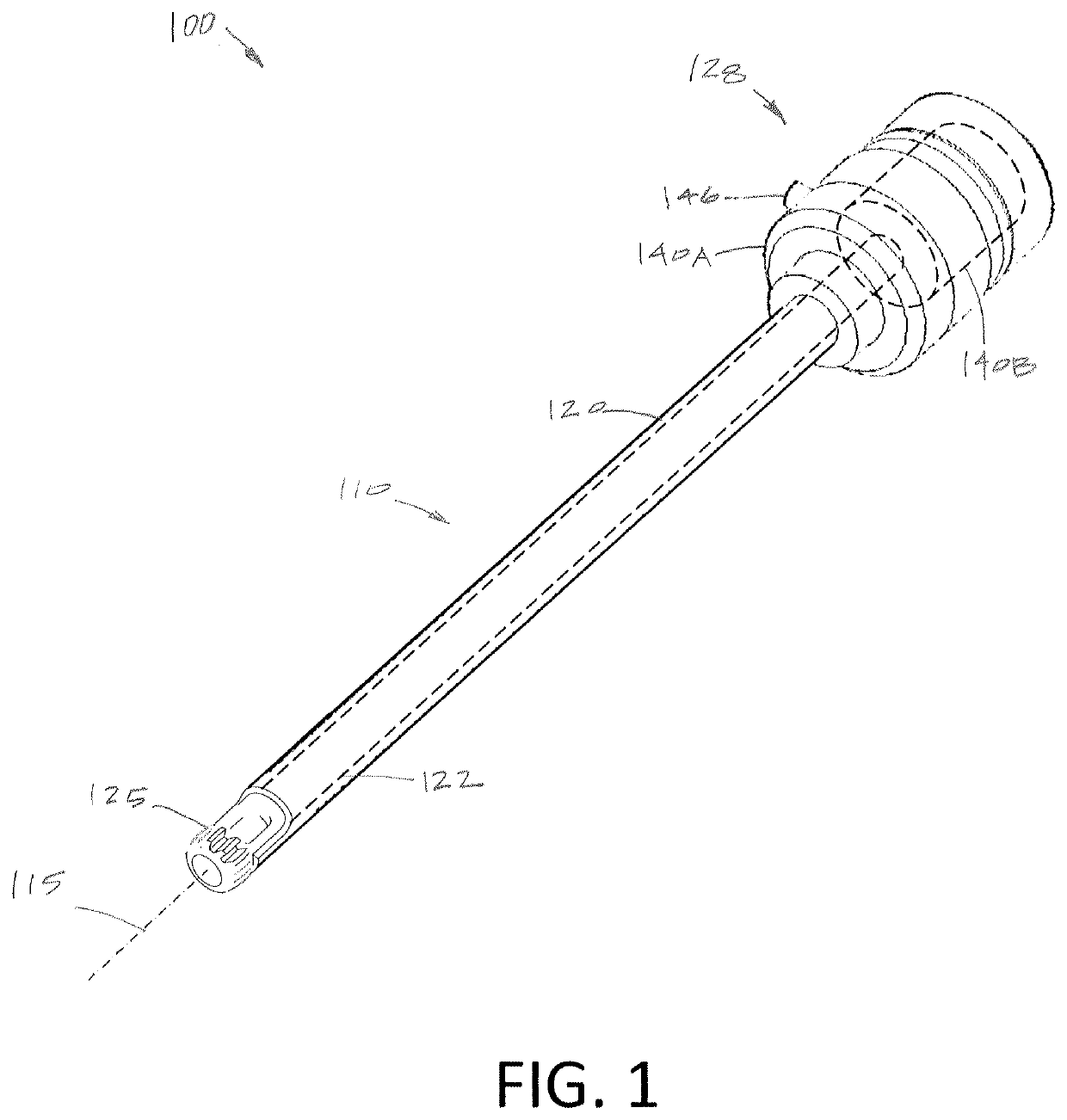
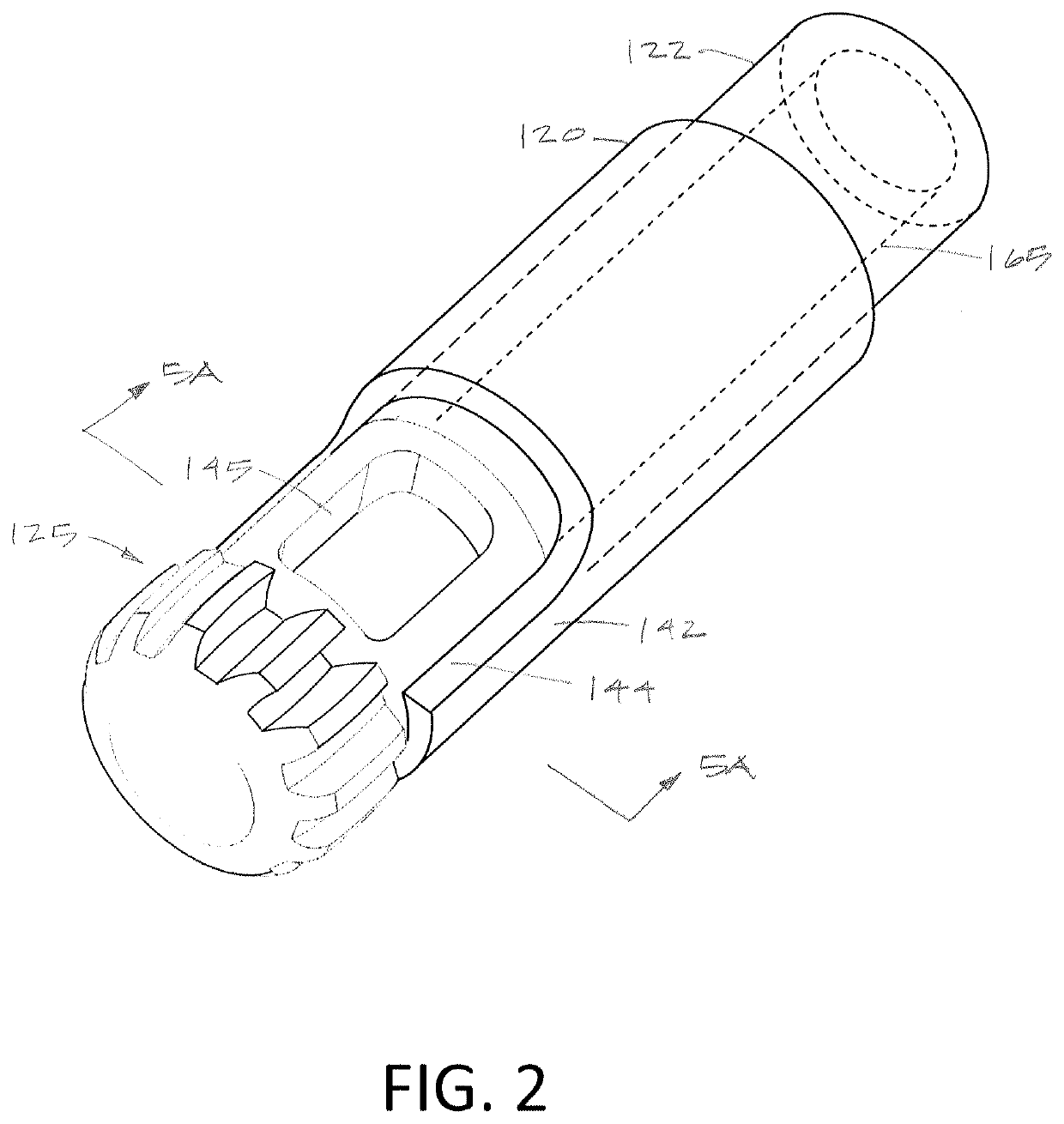
Illuminated Telescoping Cannula
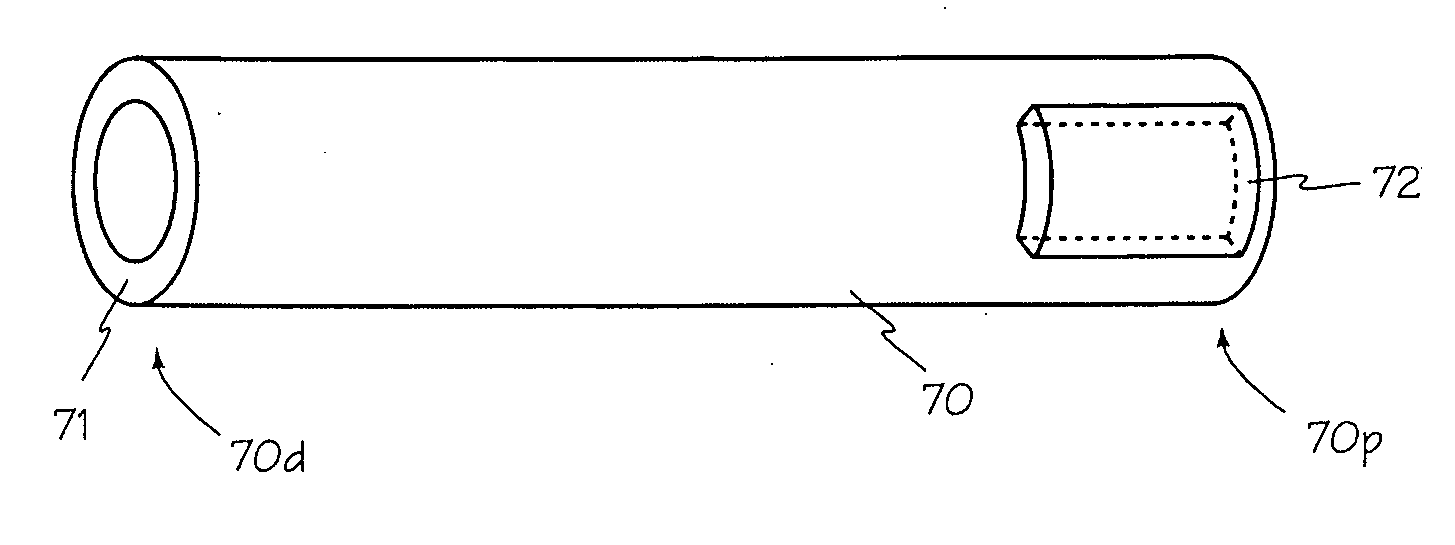
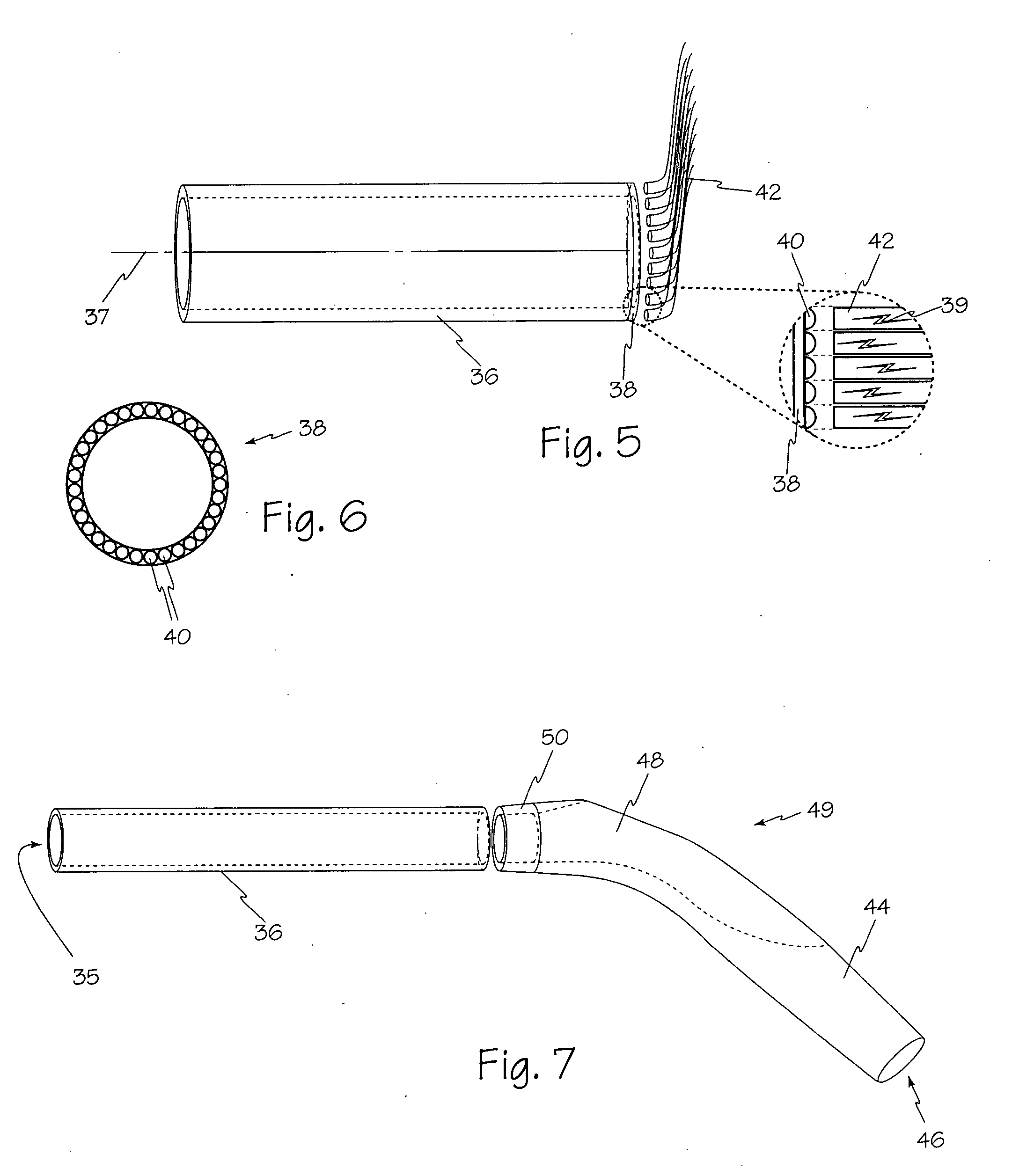
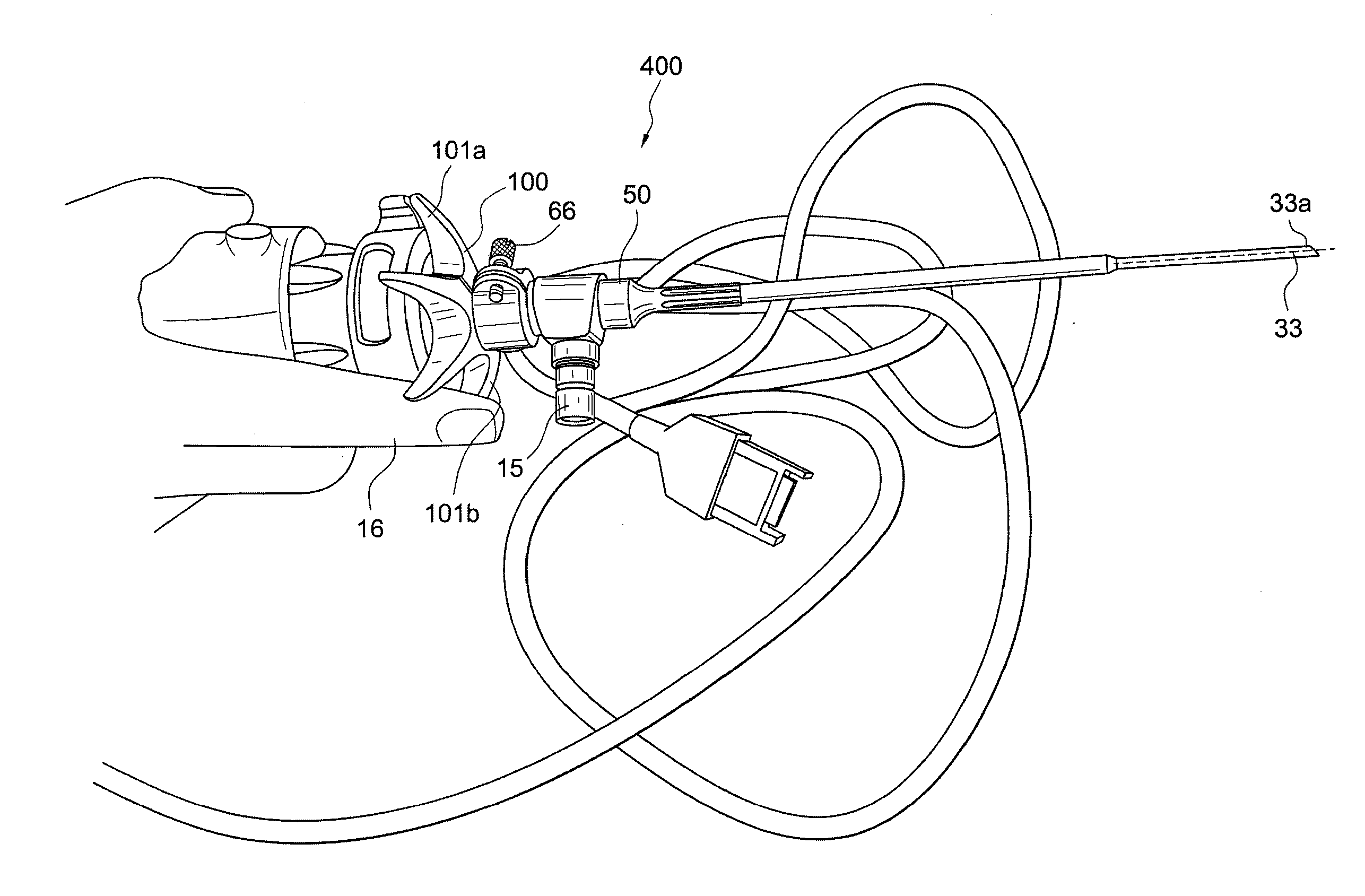
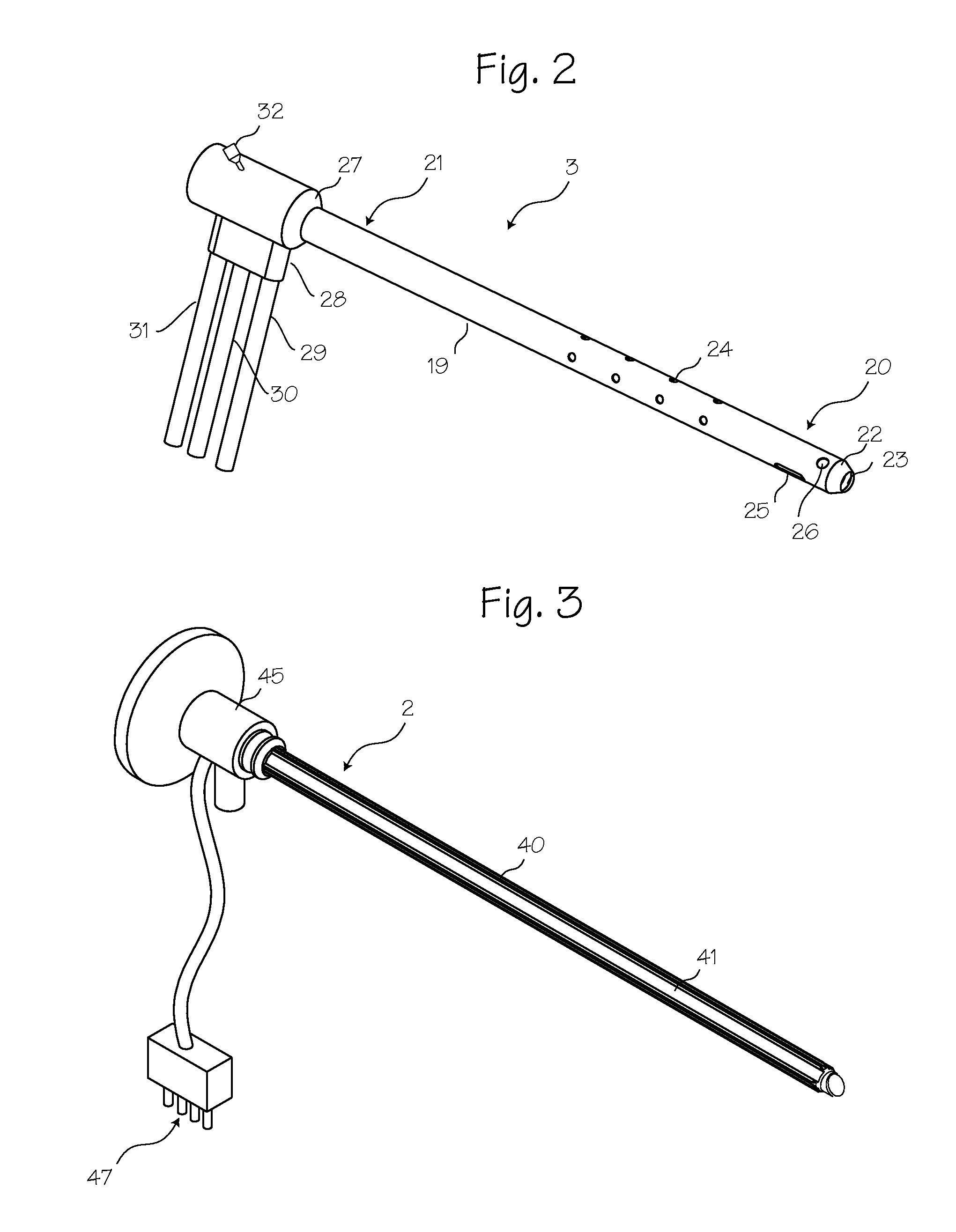
The illumination system described below comprises an arthroscope, endoscope or other suitable surgical tool and an attachable cannula comprising a transparent or semi-transparent material capable of carrying light from the proximal end of the cannula to the distal end of the cannula, thereby illuminating the surgical field. The surgical field is thus illuminated through components that do not occupy space that may otherwise by used for the optics of the arthroscope. The arthroscopic illumination system further comprises one or more illumination sources disposed at the proximal end of the cannula. The illumination source may be optically coupled with the cannula at the hub or other appropriate location. The cannula comprises a sterilizable polymer which functions as a waveguide. A waveguide is a material medium that confines and guides light. When in use, the light source connected to the hub provides light which may be guided to the distal end of the cannula or any other suitable location. Thus, the sheath provides structure-guided illumination resulting in the illumination of the surgical site.
Owner:INVUITY
Ultraviolet sterilizer for surgery
InactiveUS20110054574A1Prevent moistureAvoid burnsLight therapyRadioactive sourcesUv disinfectionArthroscopy
An ultraviolet sterilizer for use during surgery is mounted in a base cabinet. The UV light source can be a laser, or an LED. An optical frequency multiplier can be used that outputs UV of less than 280 nm, or greater than 320 nm, to avoid burning the patient. A visible LED aiming light directs the UV light toward the surgery. A crosshair image can be projected to position the light.One lamp has a housing, a cavity, a handle, and an ocular plate to pass the UV and the aiming light. An articulated arm allows selective positioning of the lamp. Another lamp has a stylus, a handle, and a tip small enough for easy insertion into a small incision for arthroscopy. A fiber optic cable connects the UV and the aiming light to the lamp. Lenses or filters can be used with the fiber optic cable.An electronic power supply and a CPU connect to the UV and the aiming light sources. A keyboard inputs commands to the CPU. A sensor provides feedback.Another UV sterilizer is mounted on a ceiling of the operating room. A lamp has a housing with a cavity. Either a curved or a flat substrate is mounted in the cavity. Solid state UV elements are arrayed on the substrate, along with visible LEDs for aiming. Either a curved or a flat mirror is disposed behind the substrate. An ocular plate passes the UV and the aiming light, and protects the elements from damage. The ocular plate is a diffuser, a filter, or a fresnel lens.
Owner:FELIX PERRY
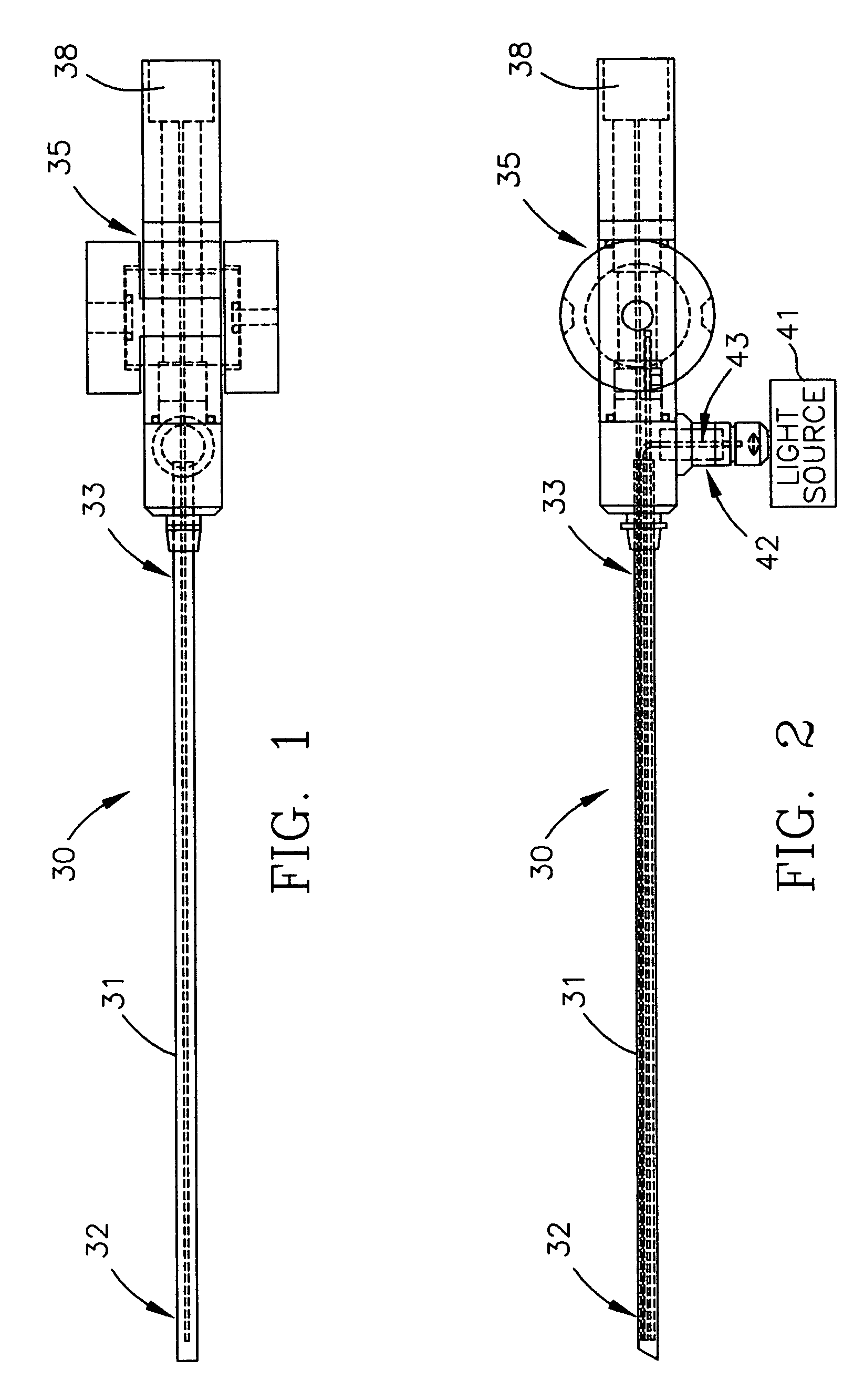
Illuminated cannula
ActiveUS20070270653A1Increasing the aperture of endoscopes without increasing the overall dimension of the endoscopePrintersCannulasSurgical siteLighting system
The illumination system described below comprises an arthroscope, endoscope or other suitable surgical tool and an attachable cannula comprising a transparent or semi-transparent material capable of carrying light from the proximal end of the cannula to the distal end of the cannula, thereby illuminating the surgical field. The surgical field is thus illuminated through components that do not occupy space that may otherwise by used for the optics of the arthroscope. The arthroscopic illumination system further comprises one or more illumination sources disposed at the proximal end of the cannula. The illumination source may be optically coupled with the cannula at the hub or other appropriate location. The cannula comprises a sterilizable polymer which functions as a waveguide. A waveguide is a material medium that confines and guides light. When in use, the light source connected to the hub provides light which may be guided to the distal end of the cannula or any other suitable location. Thus, the sheath provides structure-guided illumination resulting in the illumination of the surgical site.
Owner:INVUITY
Arthroscope rotation mechanisms and methods of endoscopic rotation
A rotation mechanism (rotating device) that can be easily accessed by the surgeon's finger to rotate an endoscope or similar instrument. The rotation mechanism is a device / component with a “starfish” configuration, which can be attached to the endoscope / arthroscope just distal to the eyepiece (or to an alternate attachment to a camera). The starfish component has a plurality of projections that extend radially from the endoscope axis, and beyond the diameter of the mechanism on the camera head that grasps the arthroscope eyecup. The projections can be easily accessed by the surgeon's finger to rotate the endoscope.
Owner:ARTHREX
Arthroscope guide
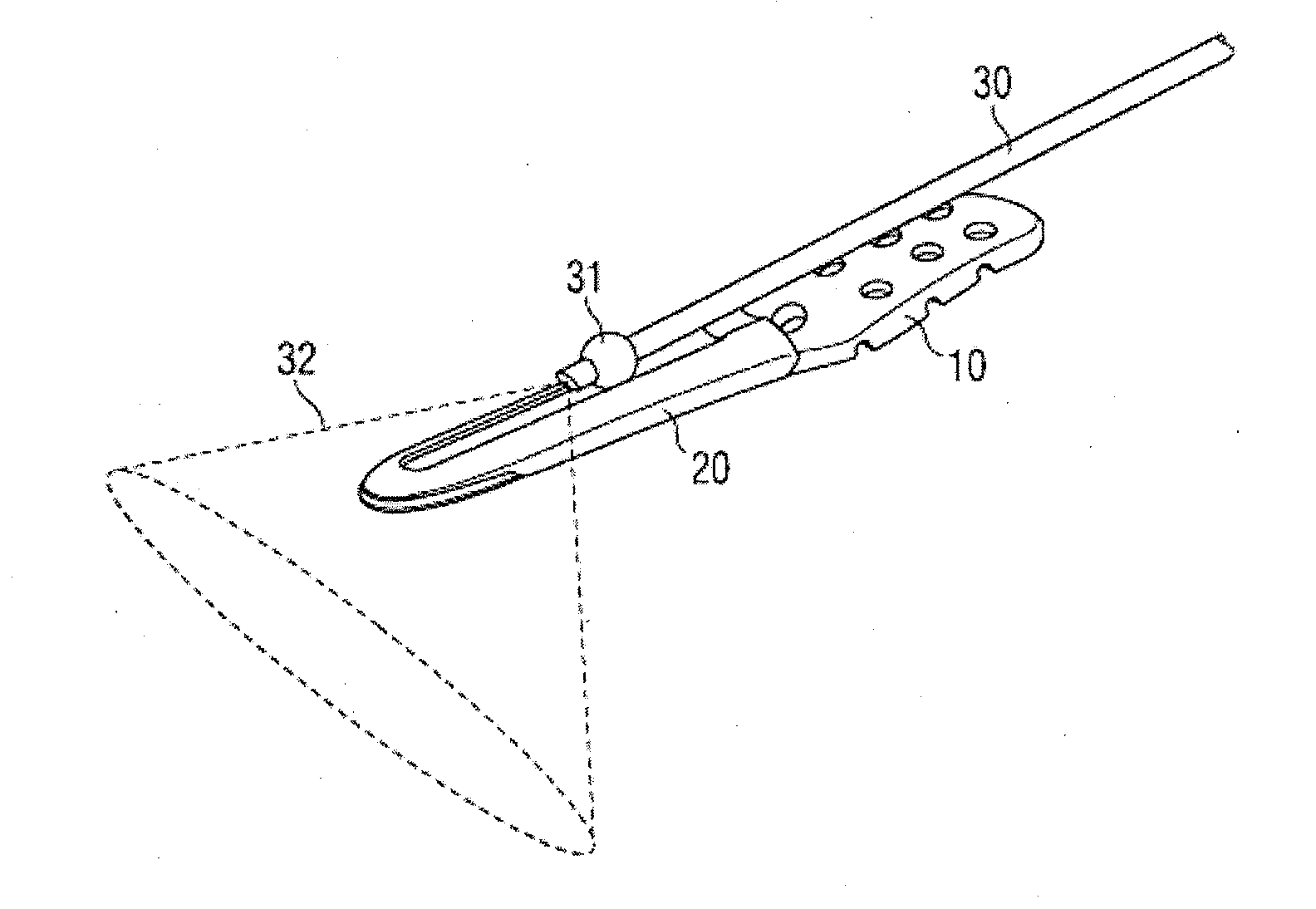
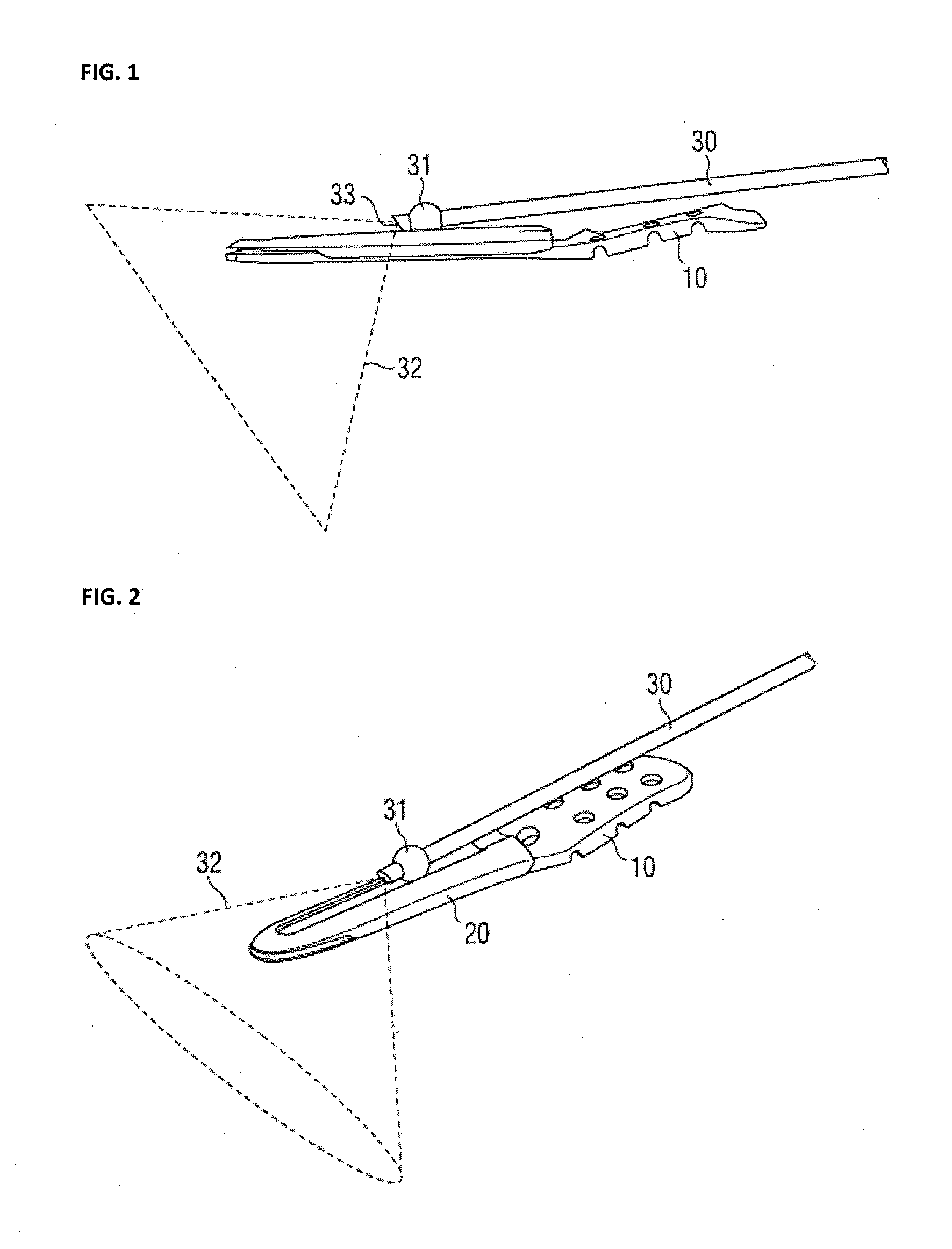
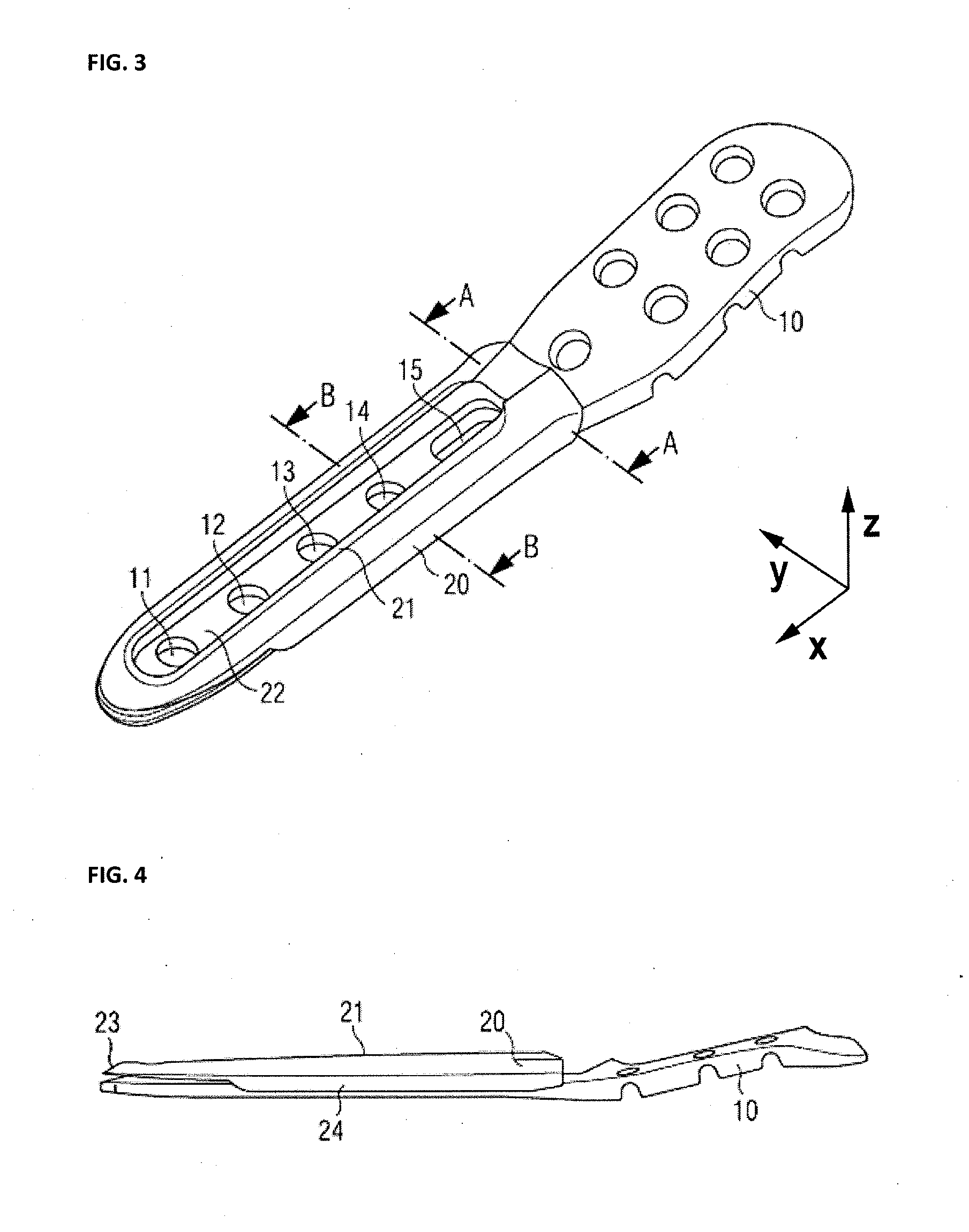
InactiveUS20130103104A1Precise positioningPrevent movementInternal osteosythesisLaproscopesArthroscopesBiomedical engineering
A guide for guiding the distal end of an arthroscope above the surface of a bone plate is disclosed. The guide is located on top of the bone plate. It has a body with cutouts and / or grooves to guide the arthroscope. Furthermore the arthroscope has a ball shaped slider close to its distal end. This slider is adapted to interface with the guide and allows movement of the distal end of the arthroscope along the cutouts or grooves.
Owner:ARTHREX MEDIZINISCHE INSTR
Arthroscopic System
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Rigid Arthroscope System
A reinforced arthroscope comprising external ribs to provide for a number of separate fluid channels, such as inflow, outflow and interstitial tissue drainage, when the arthroscope is slipped into a disposable external sheath. The arthroscope is constructed to be sufficiently rigid so as to penetrate and move within a joint without damaging the rod optics inside. The externality of the arthroscope channels allow for cleaning and sterilizing the scope between uses.
Owner:PSIP2 LLC
Small single-port arthroscopic lavage, directed tissue drying, biocompatible tissue scaffold and autologous regenerated cell placement delivery system
InactiveUS20150025311A1Increase chanceMore accurateCannulasSurgical needlesPort of entryDegradative enzyme
A system for performing arthroscopic lavage, directed tissue drying, and the accurate placement of a biocompatible tissue scaffold for the adherence of autologous regenerated cells through a small single port of entry into a joint compartment. The system is comprised of a handpiece having valves for irrigation and suctioning and a dual valve swivel cannula attached to the handpiece. The system includes a mobile cart, high resolution camera, light source, optical coupler, high-resolution monitor, an air compressor to power individually controlled irrigation pumps to deliver irrigation fluid to a handpiece and a vacuum suction console to collect fluid. The system also includes an insufflator to maintain distension immediately following the lavage and to dry tissue in preparation for directed tissue scaffold and regenerative cell placement. The delivery system achieves accurate biocompatible tissue scaffold placement to a specific tissue site or sites within the joint utilizing a small diameter arthroscope for direct visualization while inserting and advancing a grasping instrument or device through one of two valves located on the cannula. While holding the tissue scaffold in the jaws of the grasping device, it is advanced through the cannula lumen and extended beyond the distal tip and placed on the dried tissue site. Removing the grasping device, a catheter is then inserted and advanced through a cannula valve into the lumen and extended beyond the distal tip to the scaffold placed and prepared tissue site. A means of applying torque to the catheter tip further enhances the ability for accurate, exact placement of cells to a specific scaffold receptive tissue site. The cells are then injected into and through the catheter and applied under direct visualization to the scaffold. As comprised, the small single-port system allows a physician to perform the diagnosis, clean the joint space of debris and degradative enzymes using pressurized irrigation and suction, followed by a rapid conversion from a sterile saline fluid distension media to a dry gas CO2 distension media and directed tissue drying, and the accurate placement of a biocompatible tissue scaffold for the adherence and accurate placement of regenerated cells through a catheter to a specific tissue site within a joint.
Owner:KADAN JEFFREY S +1
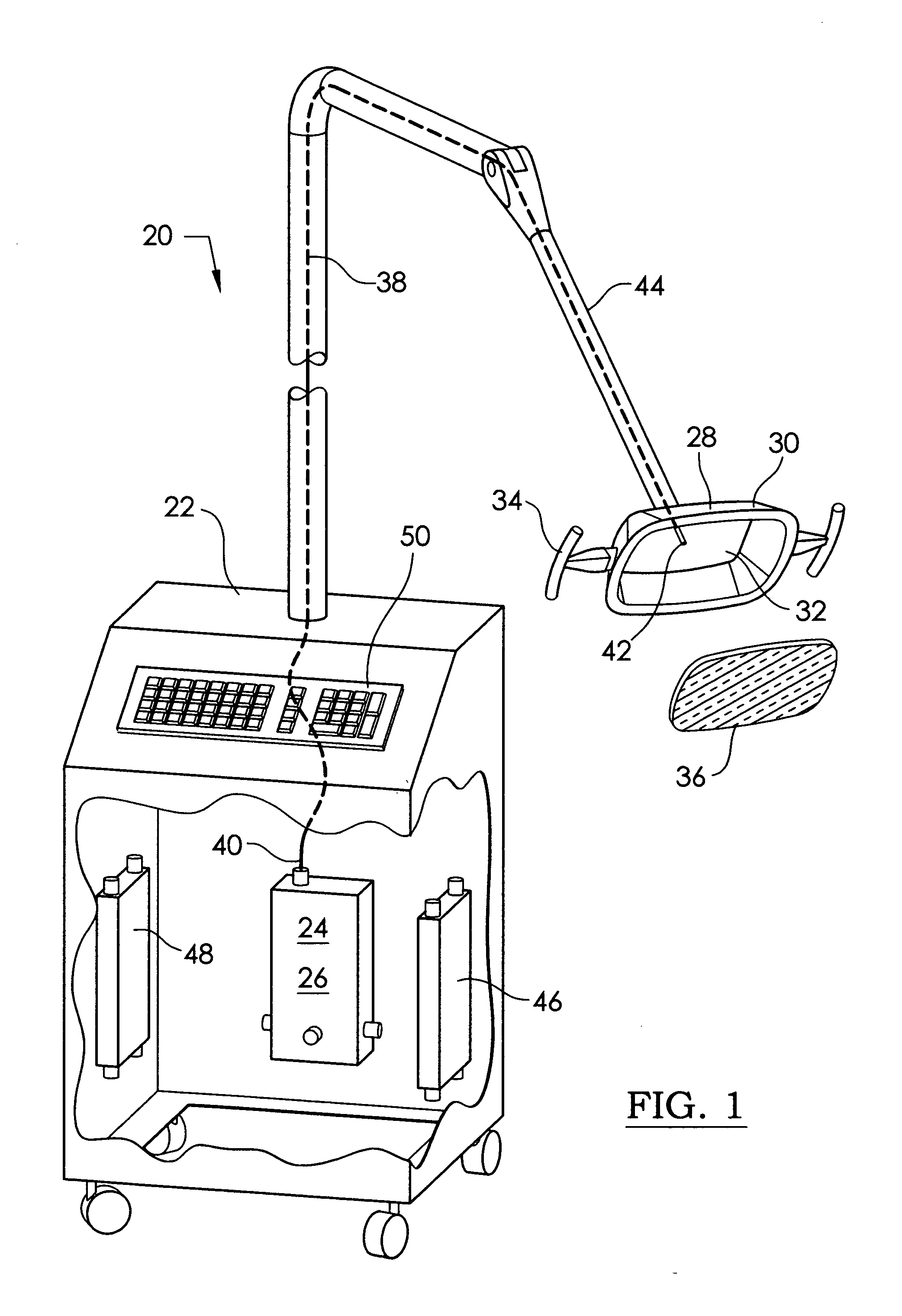
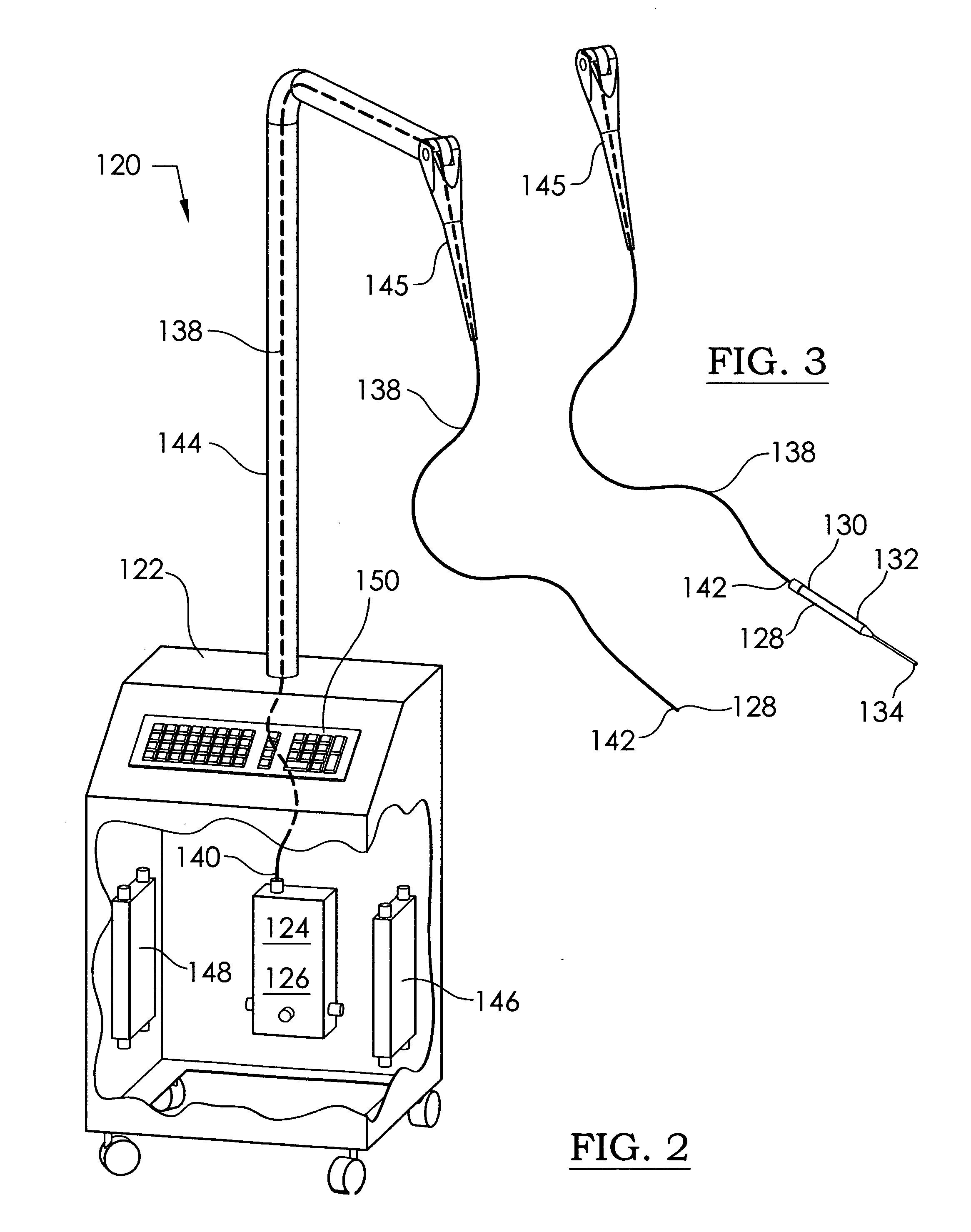
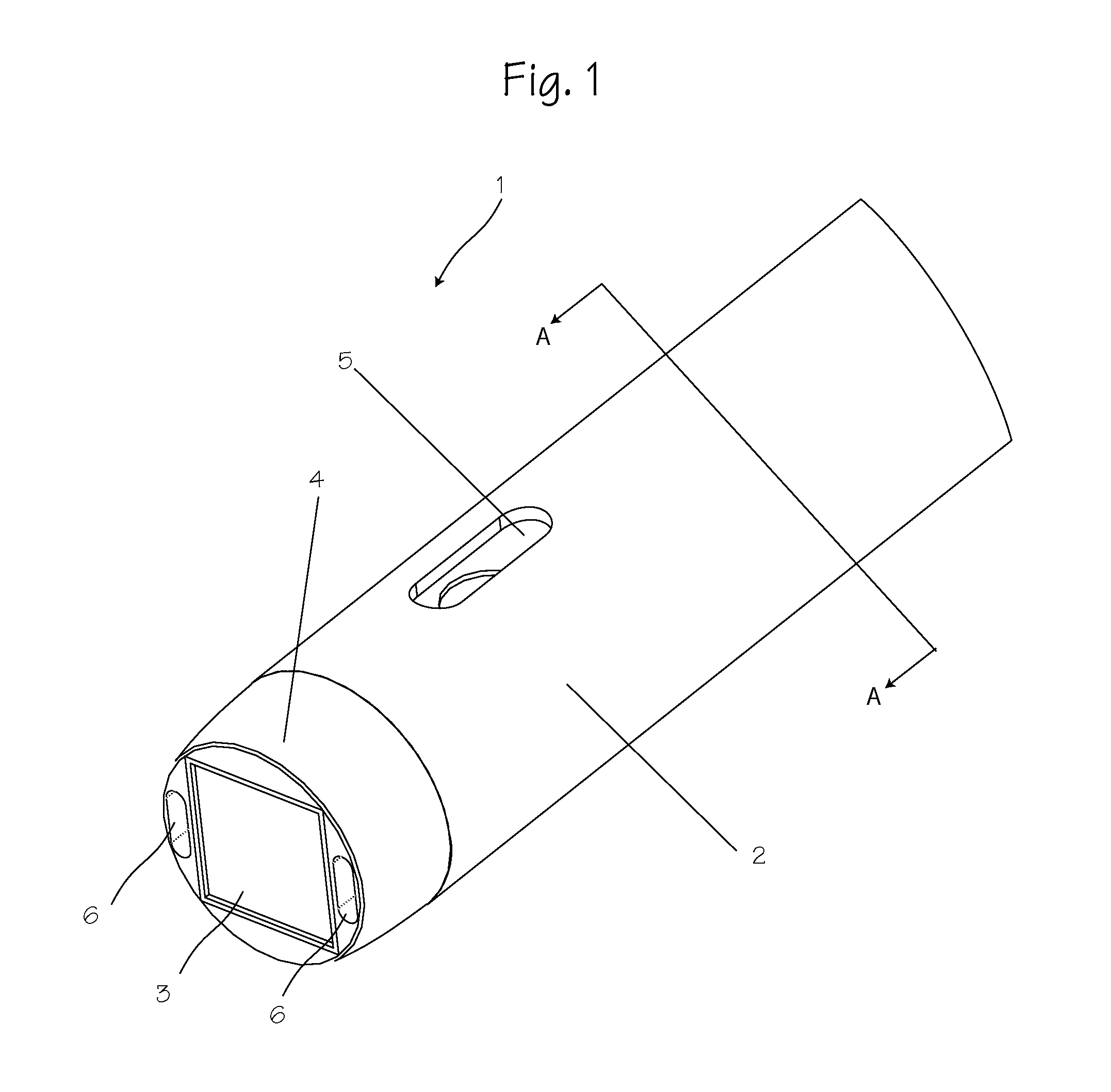
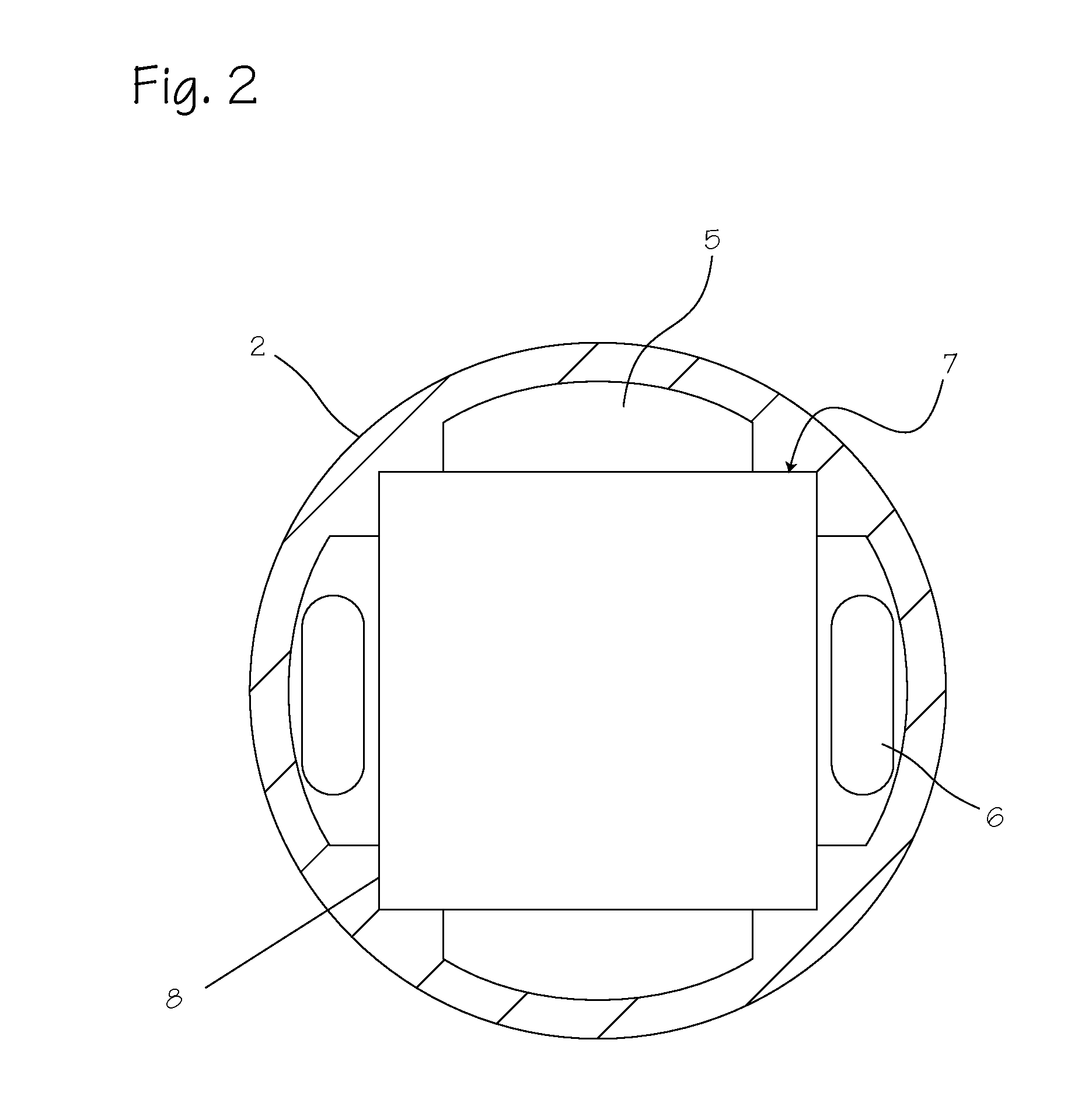
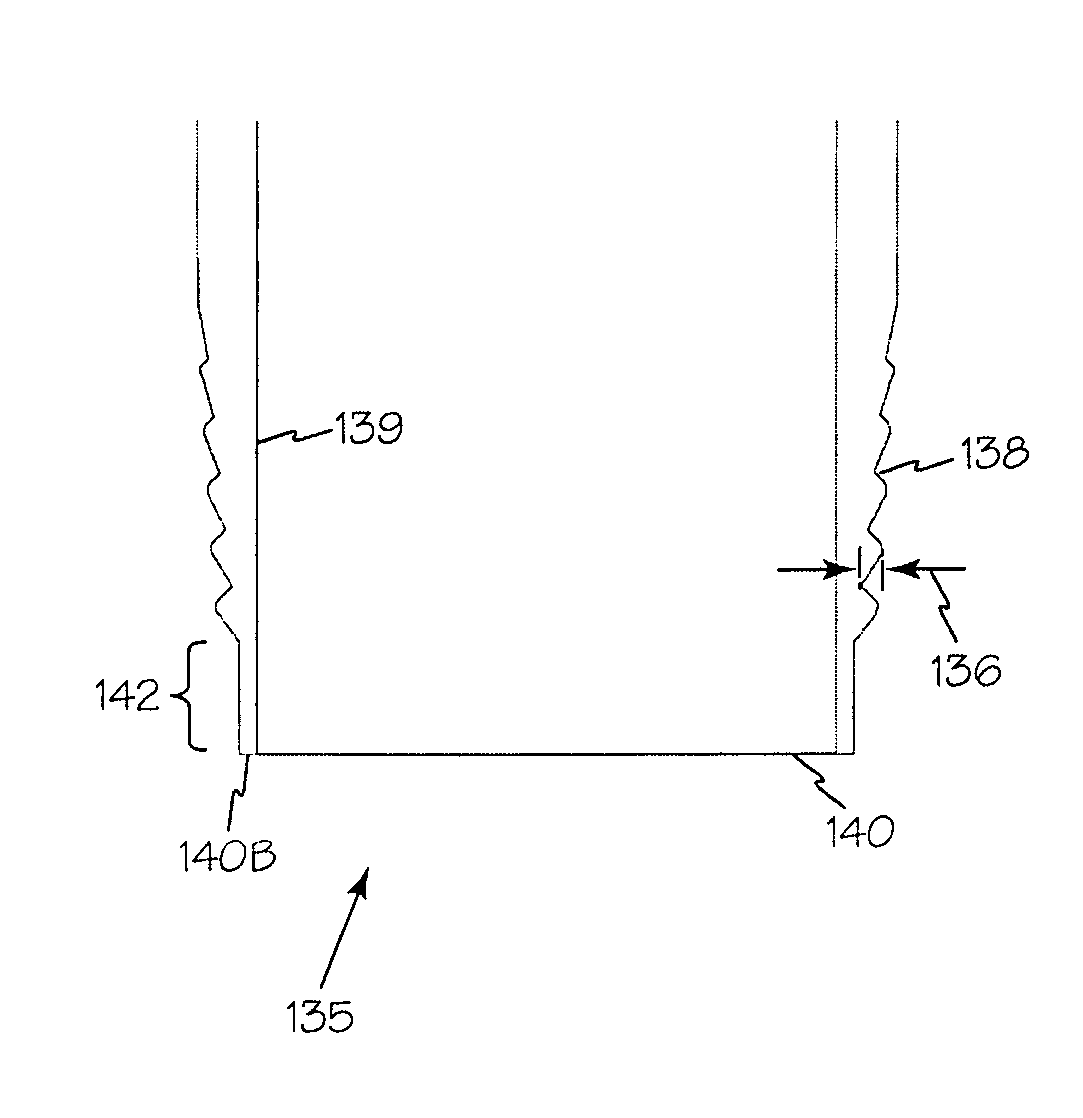
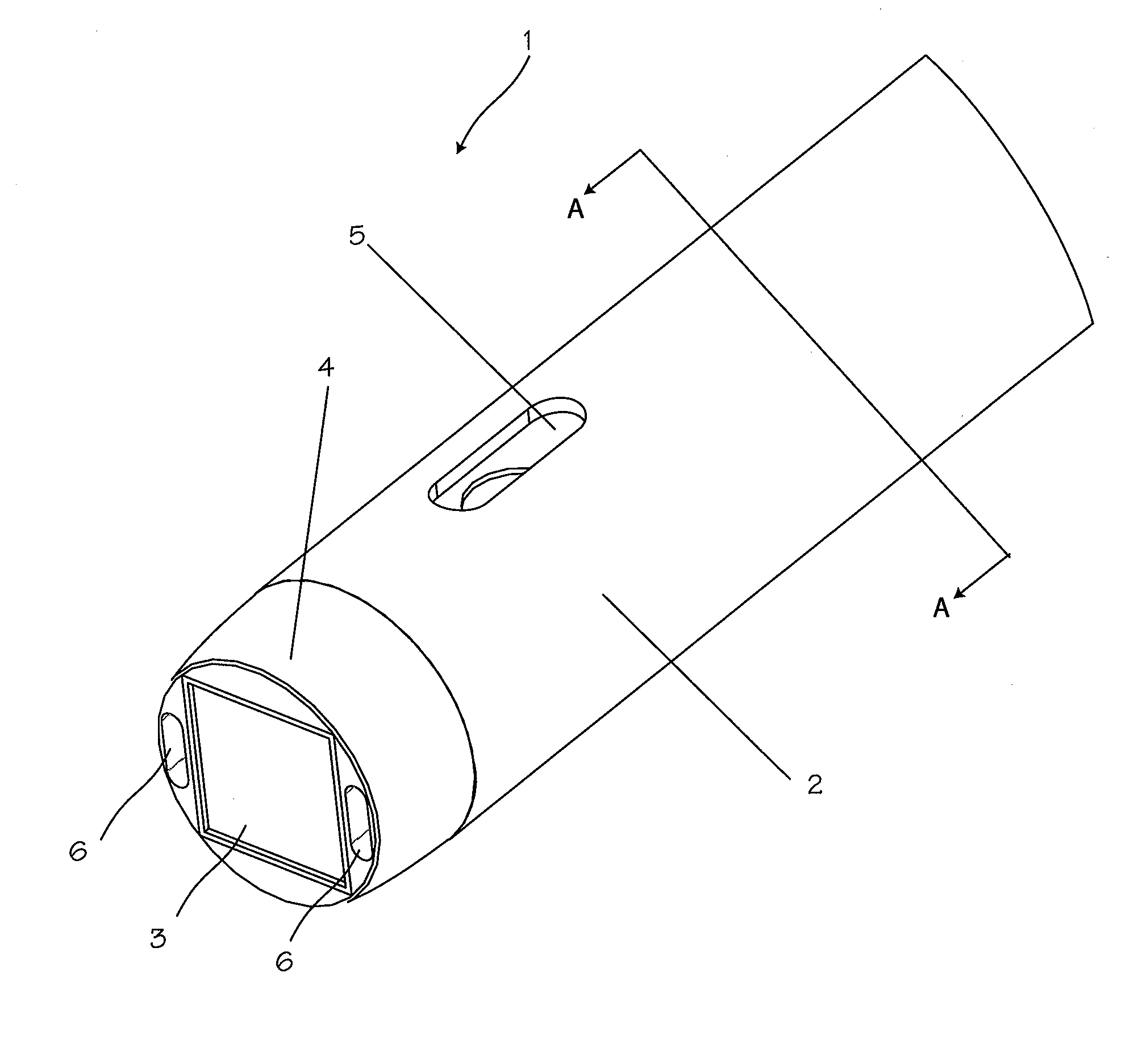
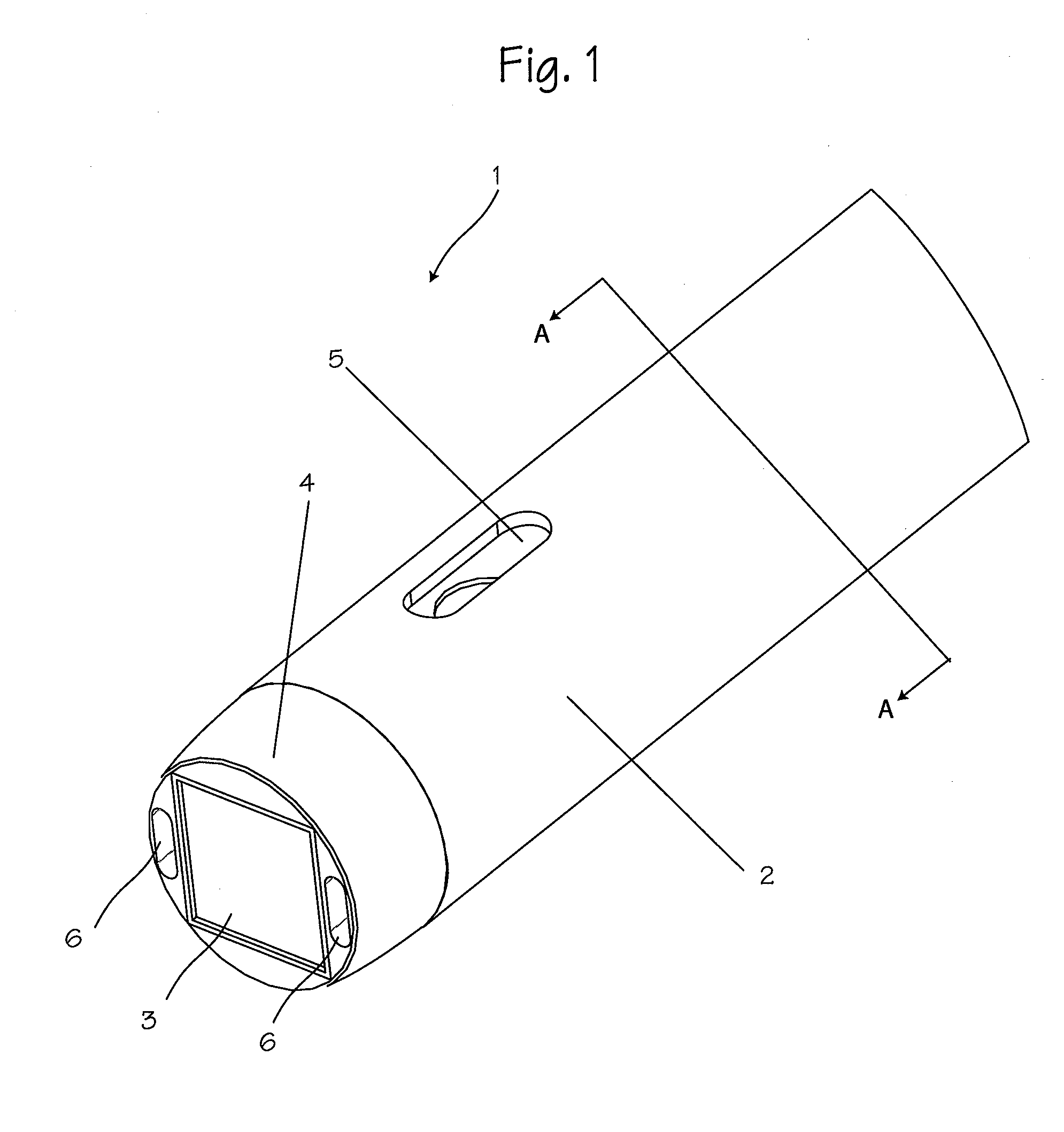
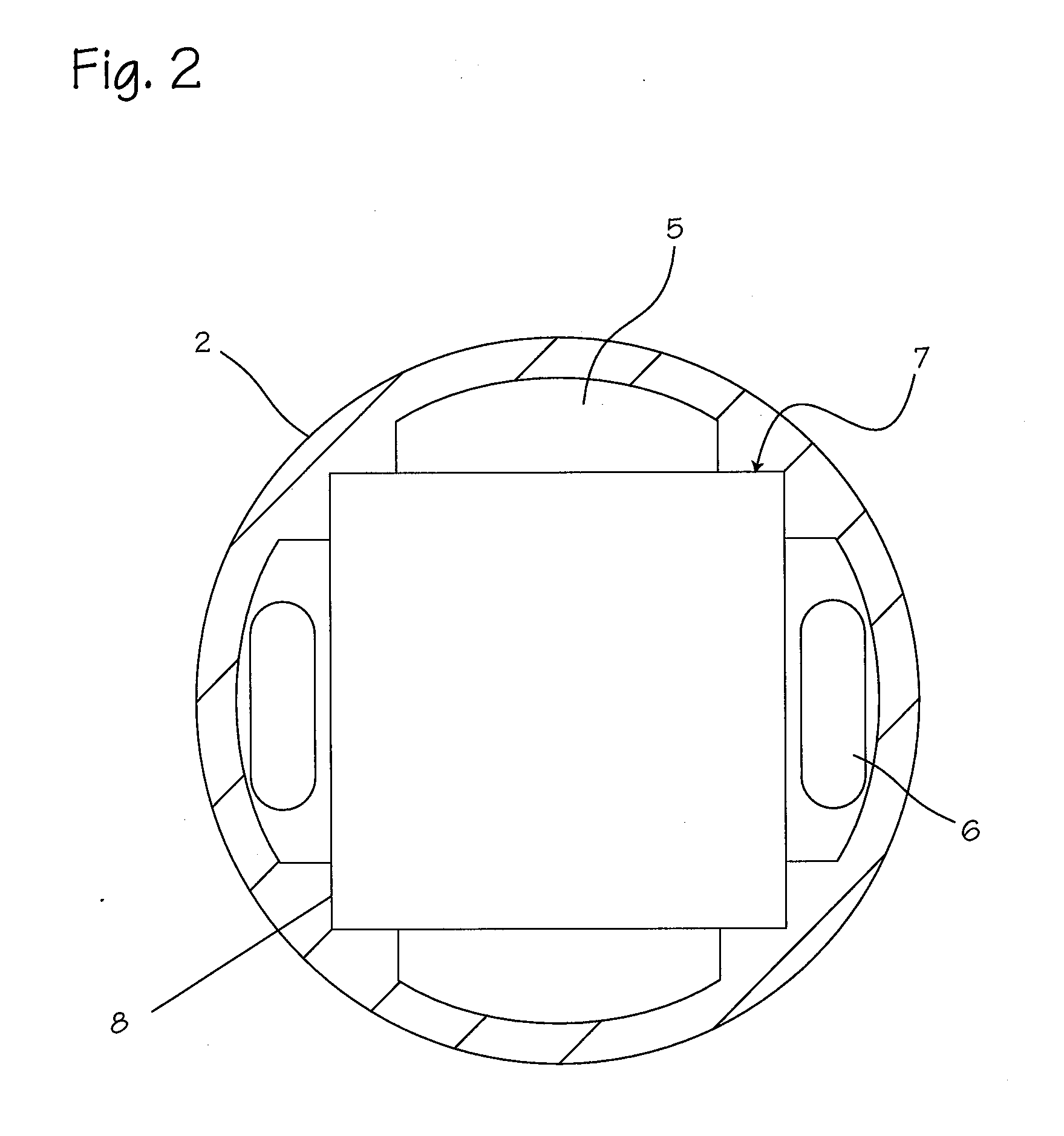
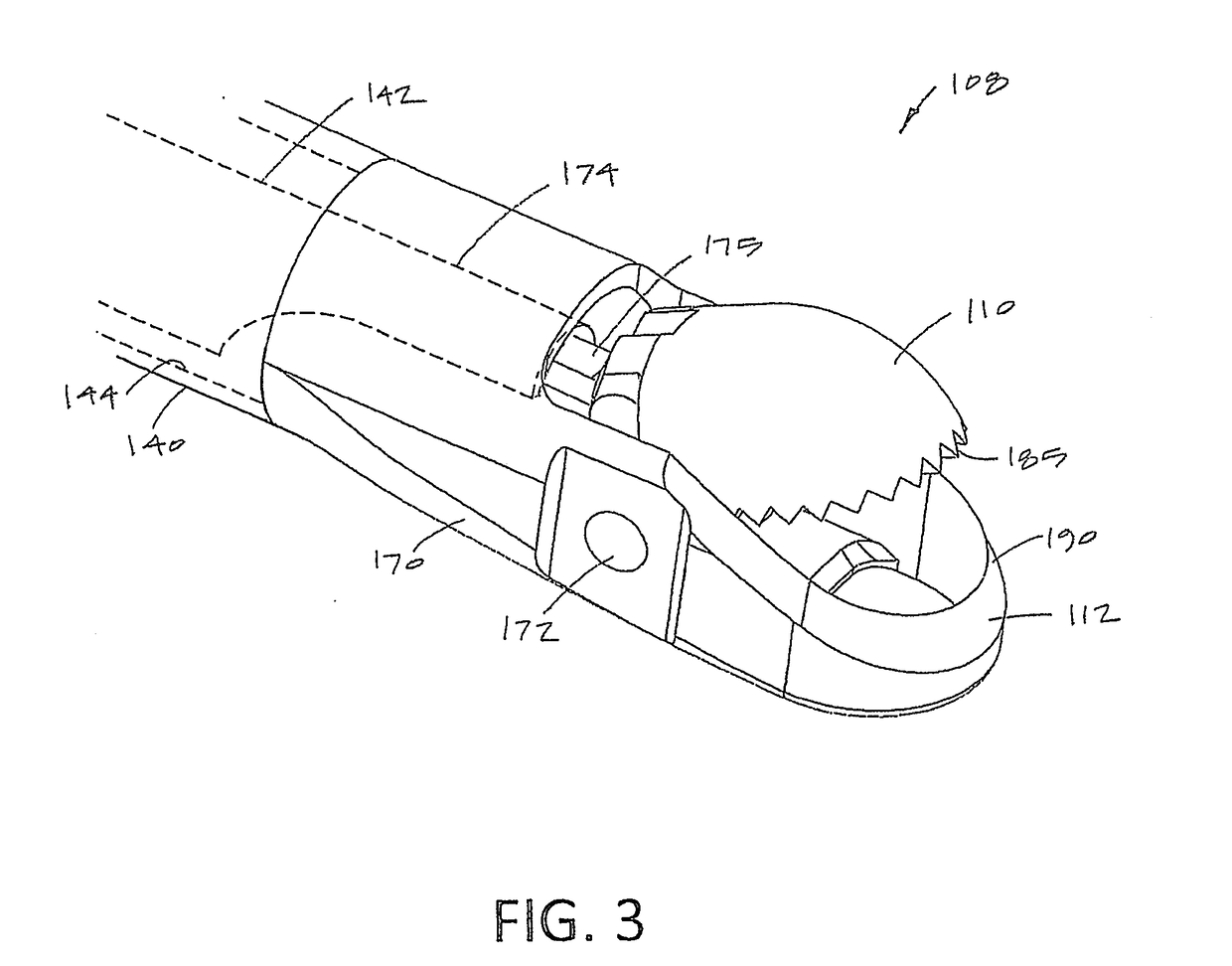
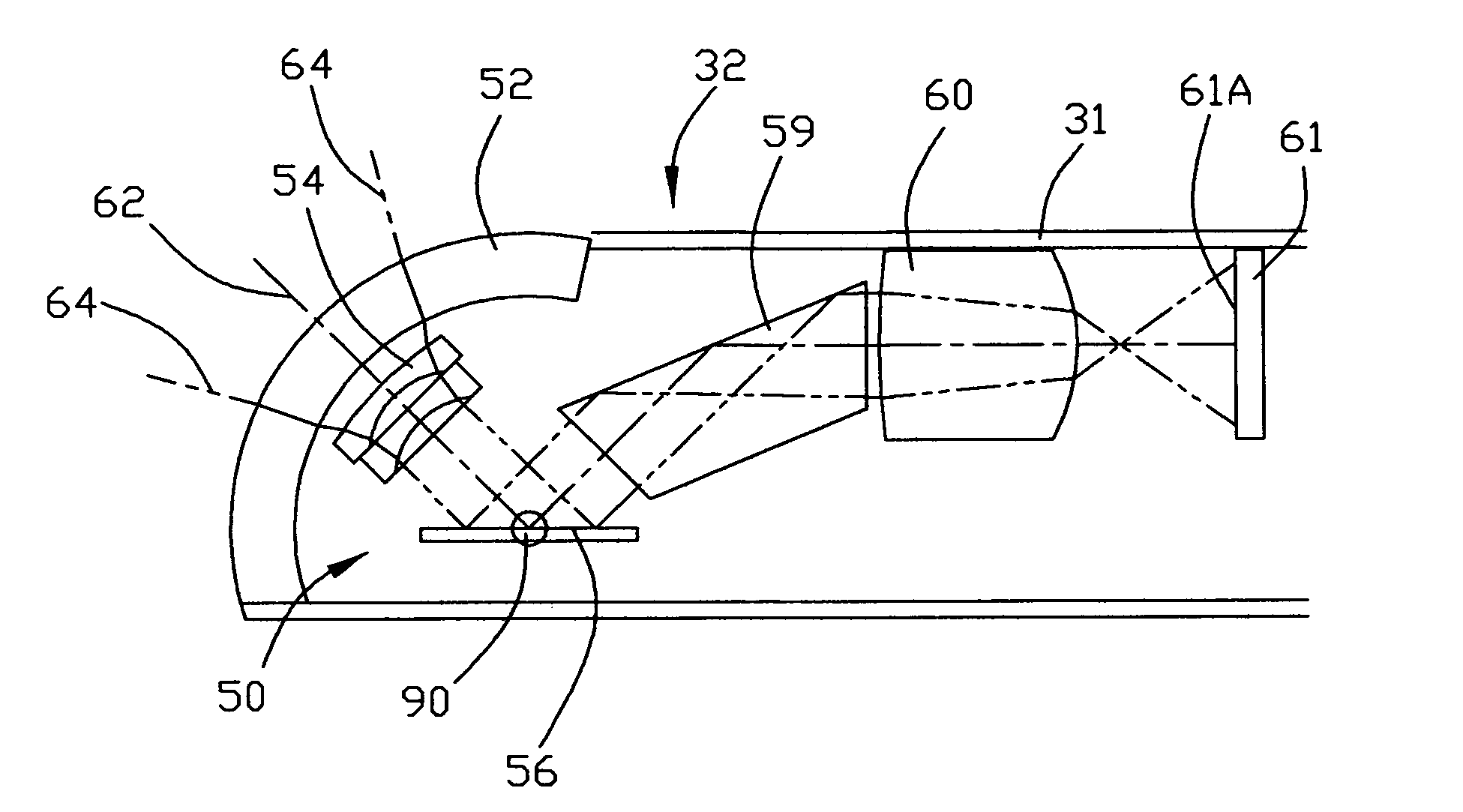
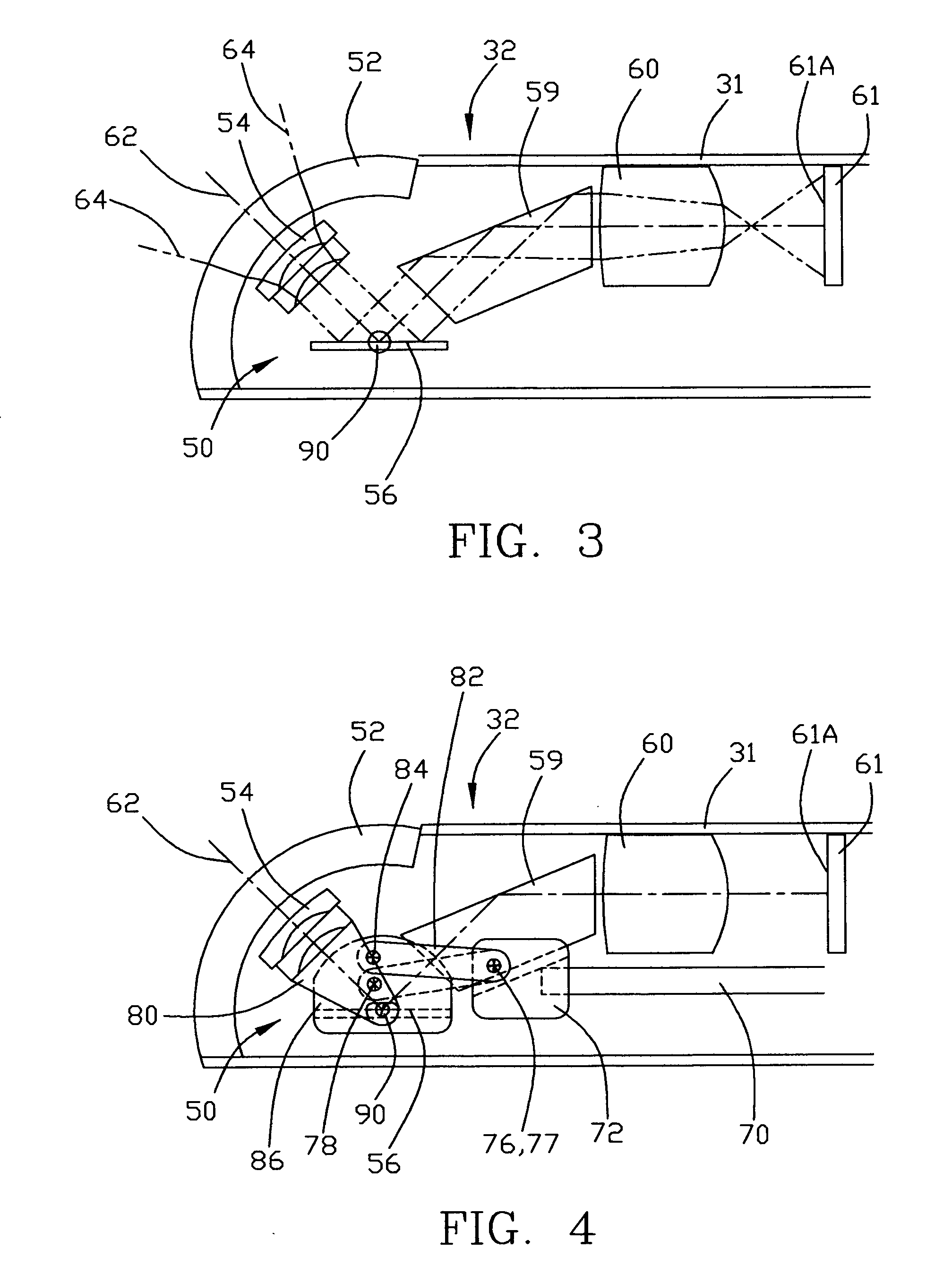
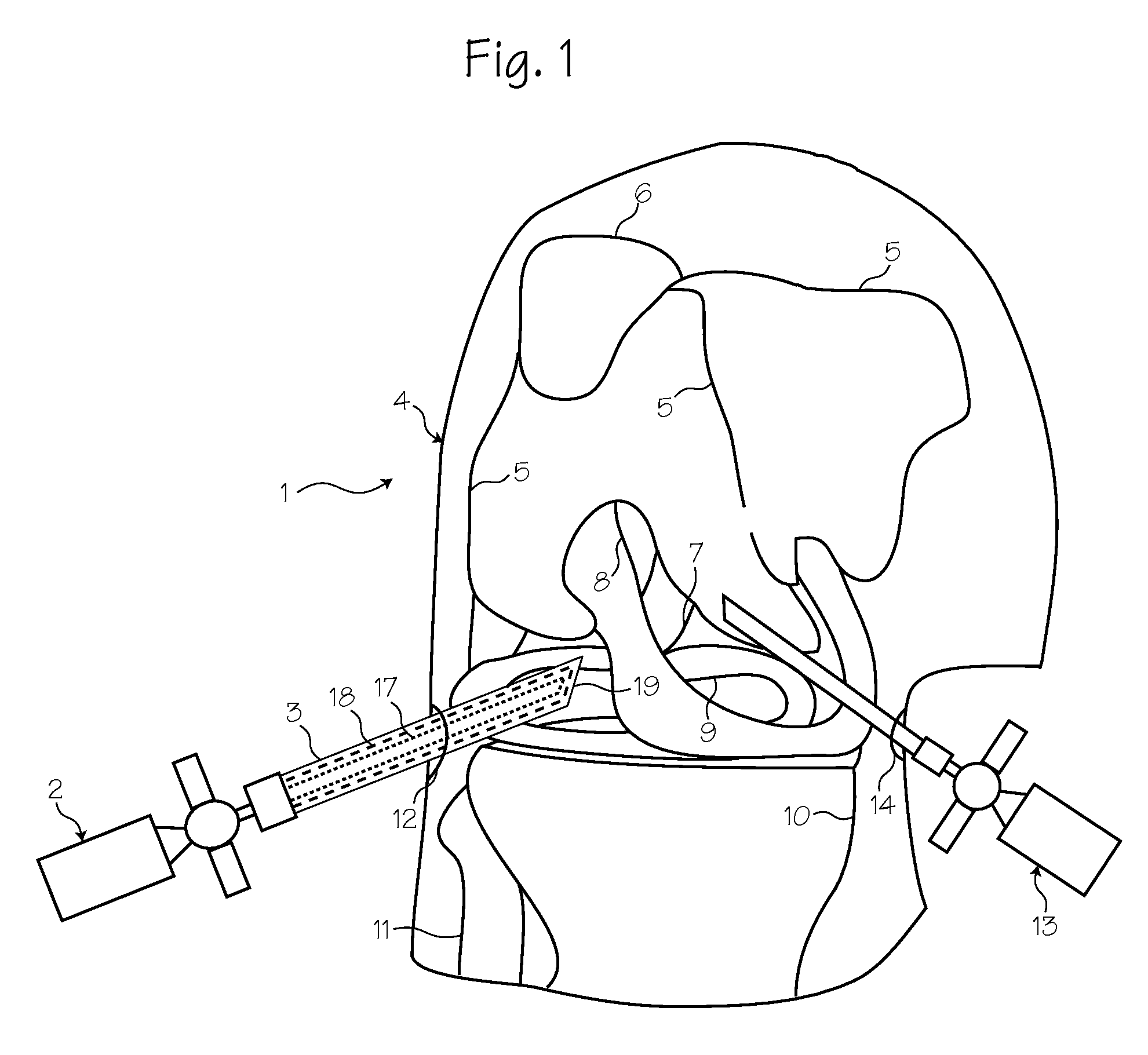
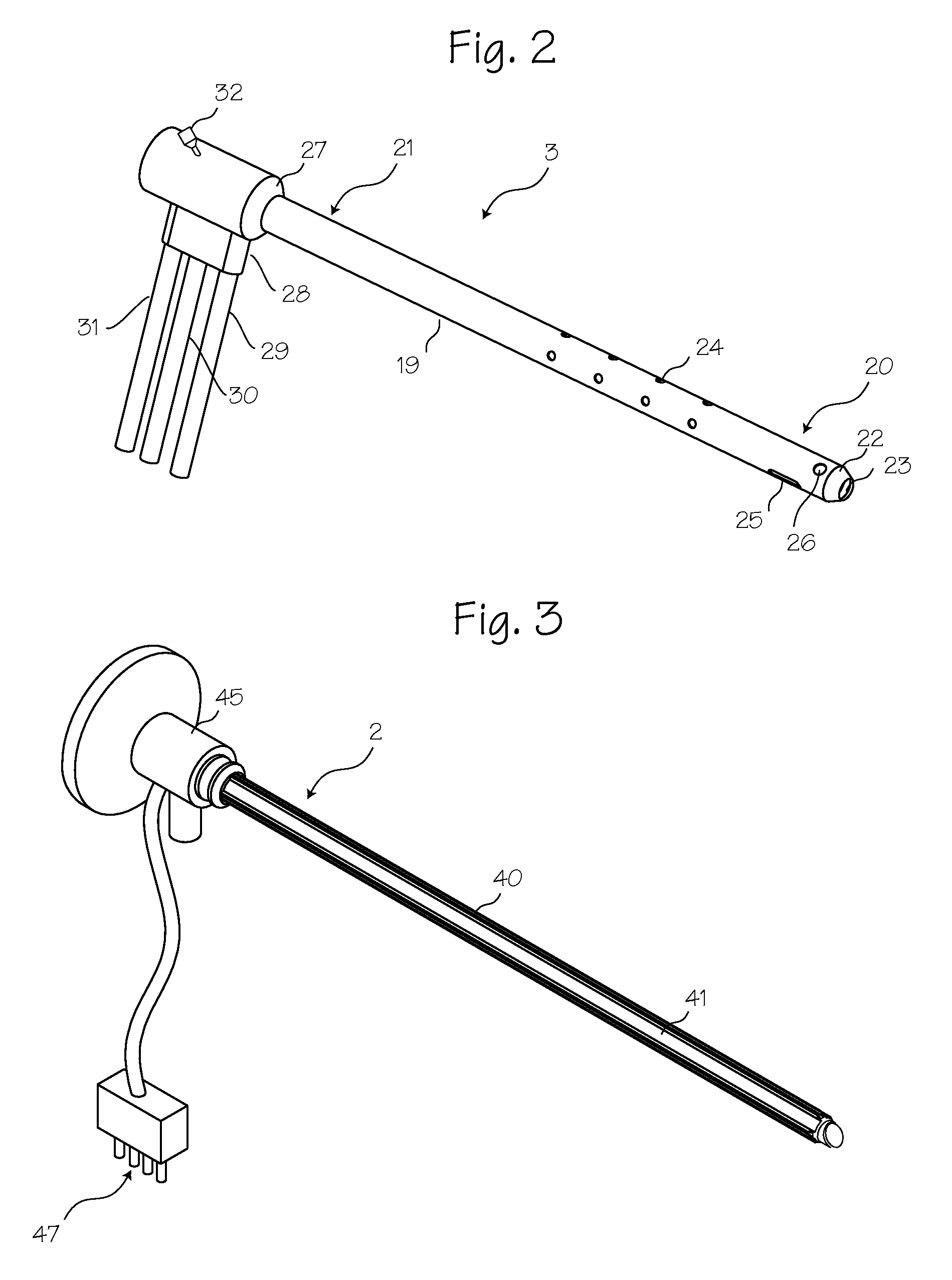
Illuminated telescoping cannula
An illumination system includes an arthroscope, endoscope or other suitable surgical tool and an attachable cannula comprising a transparent or semi-transparent material capable of carrying light from the proximal end of the cannula to the distal end of the cannula, thereby illuminating the surgical field. The surgical field is thus illuminated through components that do not occupy space that may otherwise be used for the optics of the arthroscope. The arthroscopic illumination system further comprises one or more illumination sources disposed at the proximal end of the cannula. The illumination source may be optically coupled with the cannula at the hub or other appropriate location. The cannula comprises a sterilizable polymer which functions as a waveguide. A waveguide is a material medium that confines and guides light. When in use, the light source connected to the hub provides light which may be guided to the distal end of the cannula or any other suitable location. Thus, the sheath provides structure-guided illumination resulting in the illumination of the surgical site.
Owner:INVUITY
Endoscopic system for accessing constrained surgical spaces
A retractor instrument for minimally invasive surgery may include a housing with a longitudinal axis, an arm extending from a distal end of the housing, and an actuation mechanism, wherein actuation of the actuation mechanism causes radial expansion of the arm relative to the longitudinal axis. The device may be adapted for use with an endoscope or arthroscope or may be an integral part of one such scope. A method of performing surgery in constrained areas within the body is also included and may be applicable to the carpal tunnel of a wrist and palm or the cubital tunnel of an elbow.
Owner:SOCORRO MEDICAL
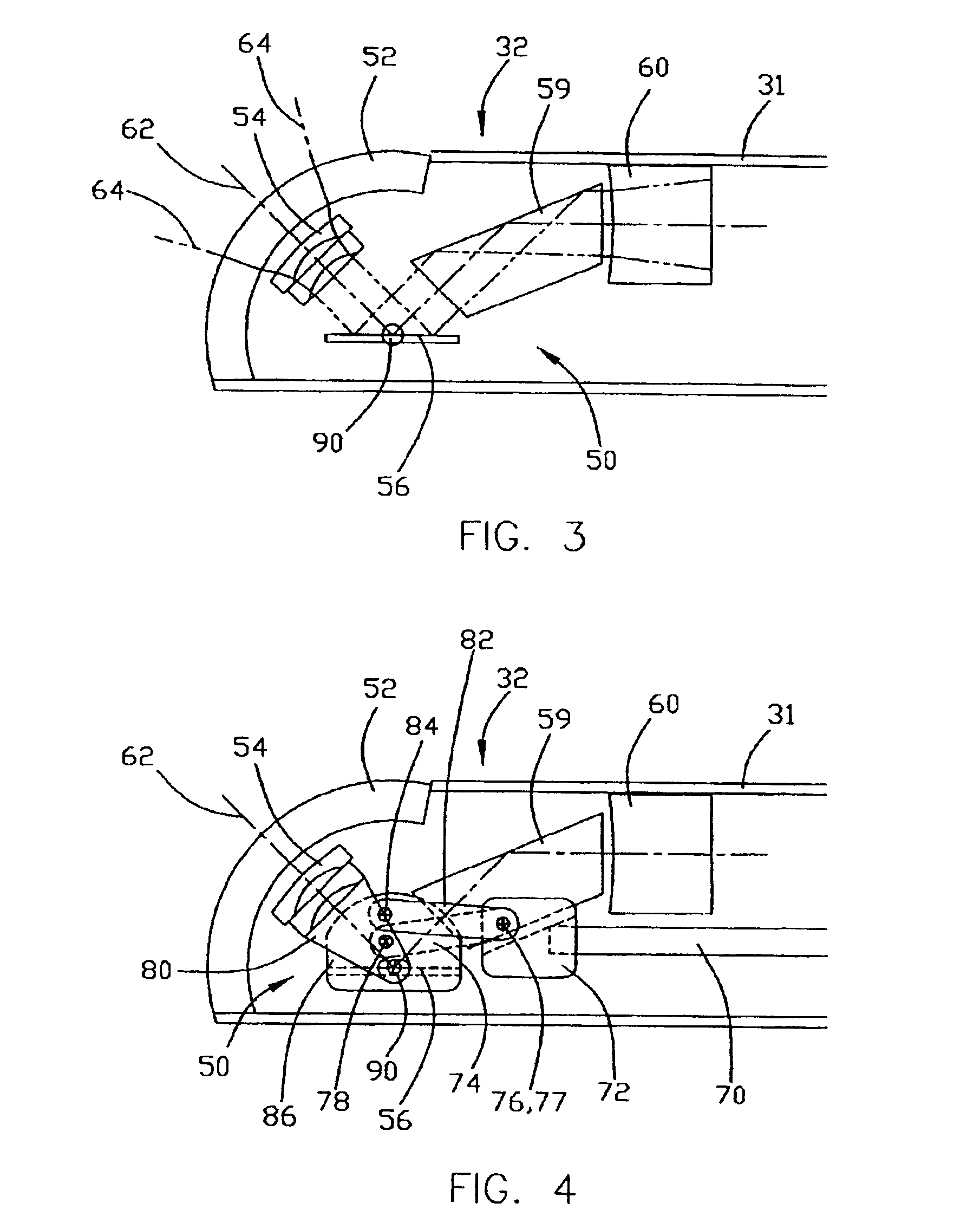
Variable view arthroscope with charge coupled device
A variable view arthroscope includes a tubular housing having a longitudinal axis and an input end, an input lens and a CCD in the input end of the housing for capturing and relaying an image object. In some embodiments, a variable view arthroscope with a plurality of viewing positions in a viewing range between a first end viewing position and a second end viewing position includes a tubular housing having a longitudinal axis and an input end, an input lens and a mirror in the housing for obtaining an image object, and a prism, a focusing lens, and a CCD in the housing for capturing and relaying the image object. The input lens and mirror are movable around an axis for varying the view of the arthroscope. In certain embodiments, the tubular housing has a longitudinal axis and an input end and the input lens and CCD are mounted in an input lens holder in the input end of the housing. The input lens and the CCD are movable for varying the view of the arthroscope. The CCD converts the object image into a digital image that can be viewed, for example, on a TV or CRT screen. The CCD can be used to replace a field and relay system, or additional focusing lenses and mirrors, thereby decreasing the cost and complexity of a variable view arthroscope.
Owner:DURELL & GITELIS INC
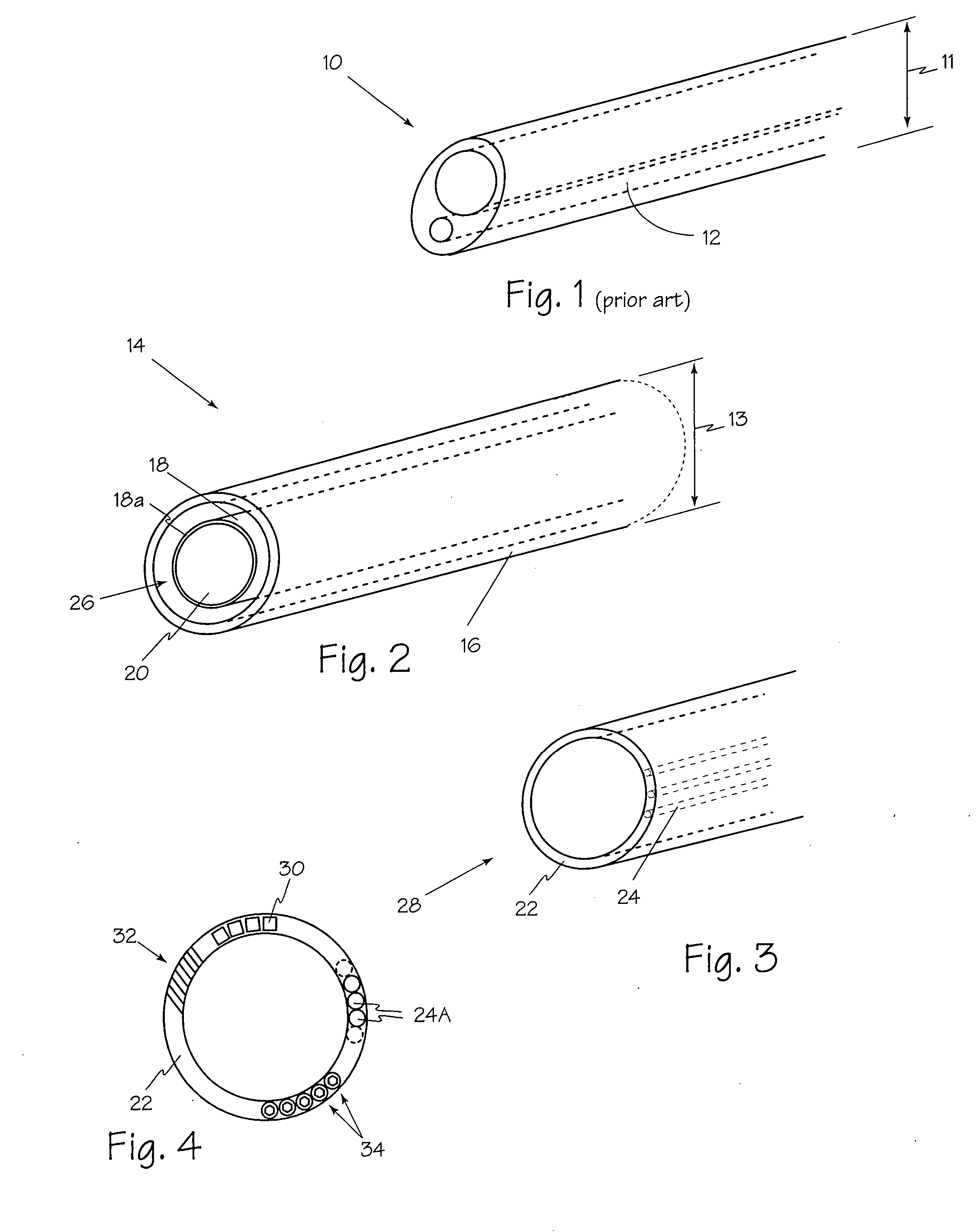
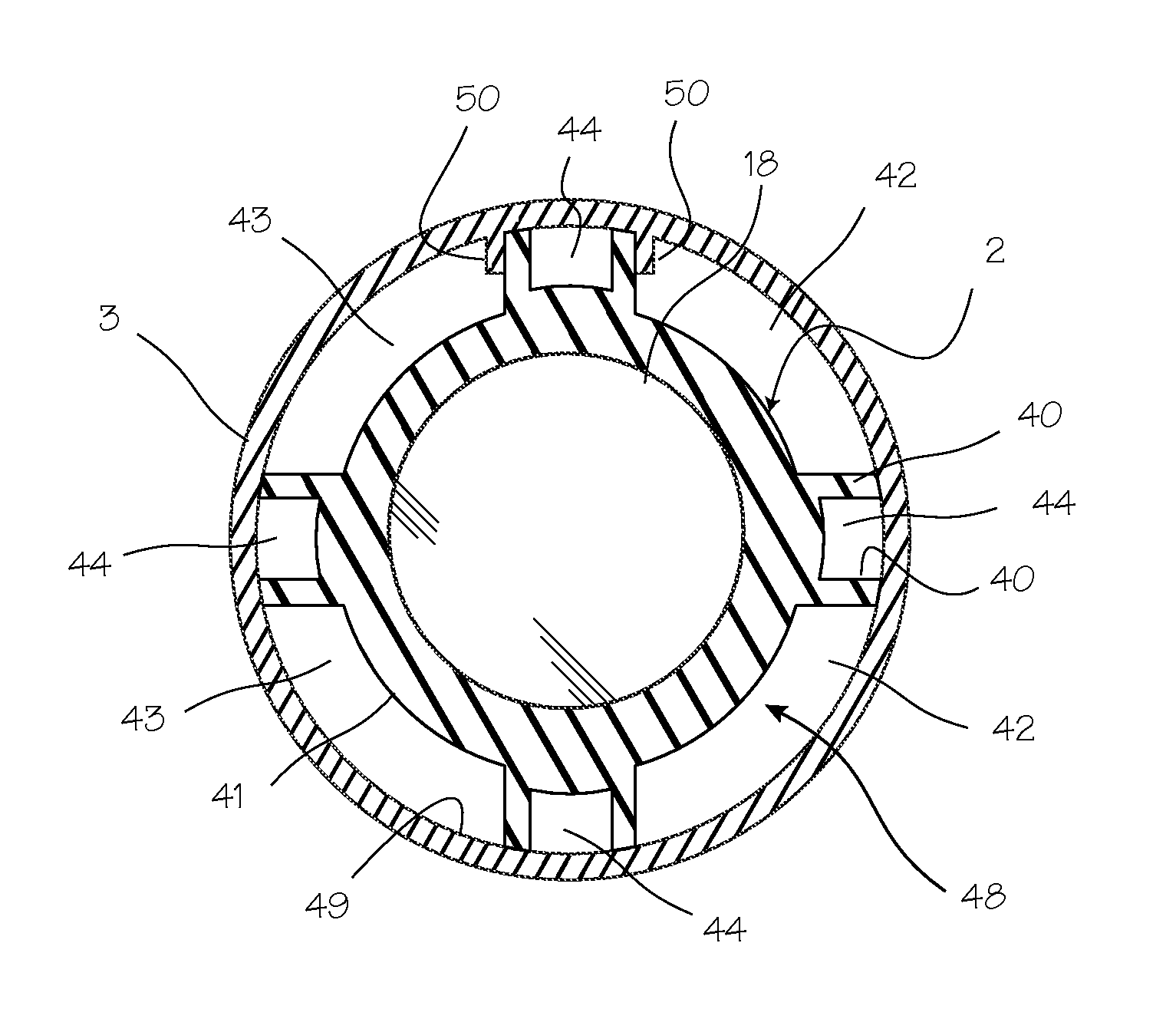
Simplified arthroscopy cannula
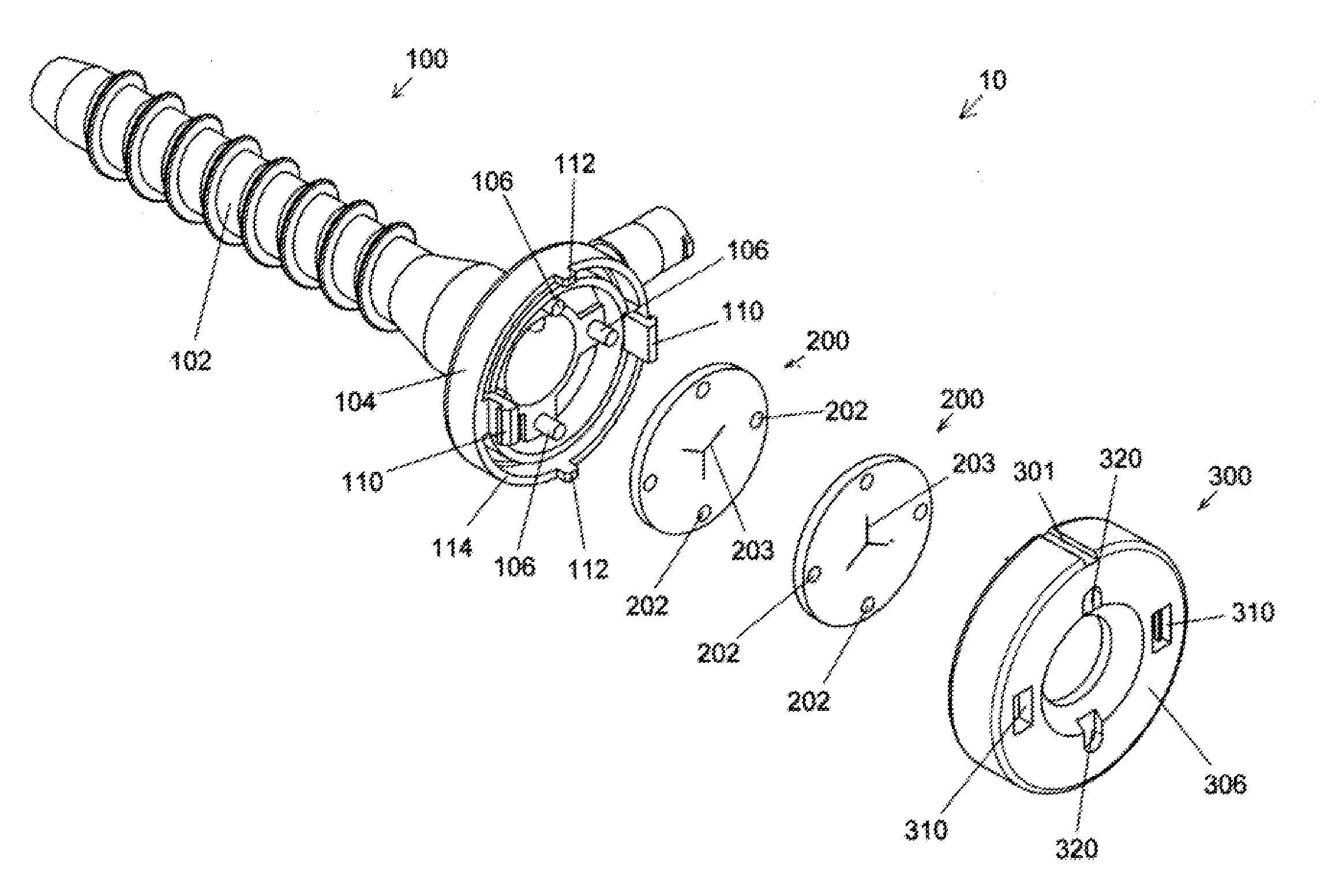
InactiveUS20150065808A1Firmly connectedImprove reliabilityCannulasSurgical needlesCapital equipmentArthroscopes
An arthroscopic sealing cannula having improved efficiency, access and reduced manufacturing costs is described herein. In particular, the present invention describes arthroscopic sealing cannulae in which the conventional thermal and chemical bonding means are eliminated and replaced with a mechanical joining system that utilizes mating fastener pairs integrally molded into the distal and proximal elements of a cannula so as to thereby provide a strong reliable joining of the elements. Such a mechanical system eliminates the need for costly capital equipment and specializing tooling as well as the material and environmental handling problems associated with conventional bonding techniques. Furthermore, in that the join may be readily confirmed through simple visual examination, the present invention also eliminates the need for complex, costly, and time-consuming validation procedures mandated by regulations in place to ensure proper integrity, strength, and reliability of the bond. Accordingly, arthroscopic sealing cannulae constructed in accordance with the principles of this invention are expected to have increased reliability and reduced manufacturing costs.
Owner:HANSHI
Cable-free arthroscopy
ActiveUS20080183028A1Reduce riskReduce the risk of infectionLaproscopesEndoscopesEngineeringArthroscopy
The present invention relates to an arthroscopy apparatus, comprising at least three elements selected from: a conventional arthroscopic lens (12), to which there is coupled a power supply device or capsule, in the inside of which is the power source (1), and a miniature camera (8), characterized by not comprising connecting cables.
Owner:GARCIA PEDRO GUILLEN
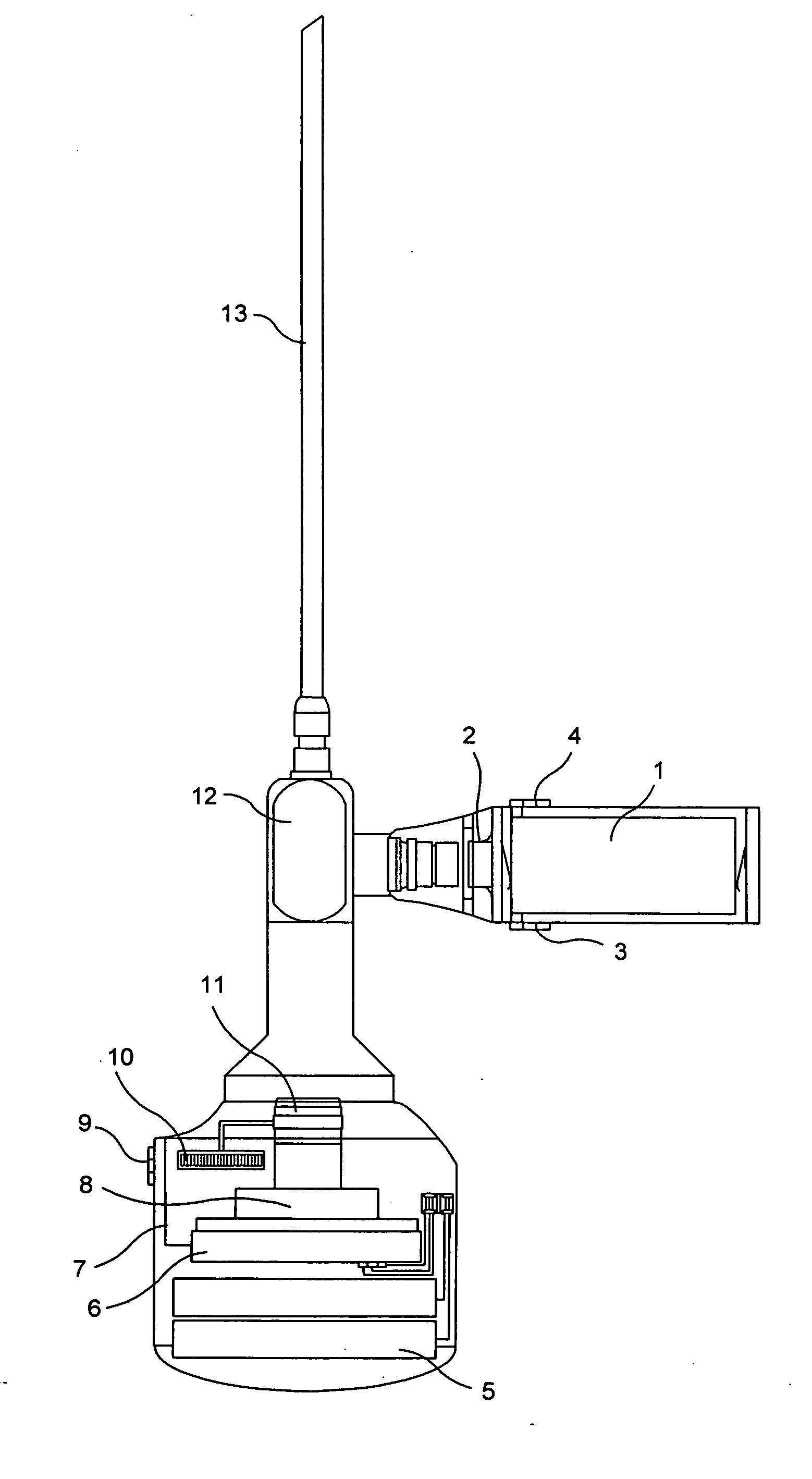
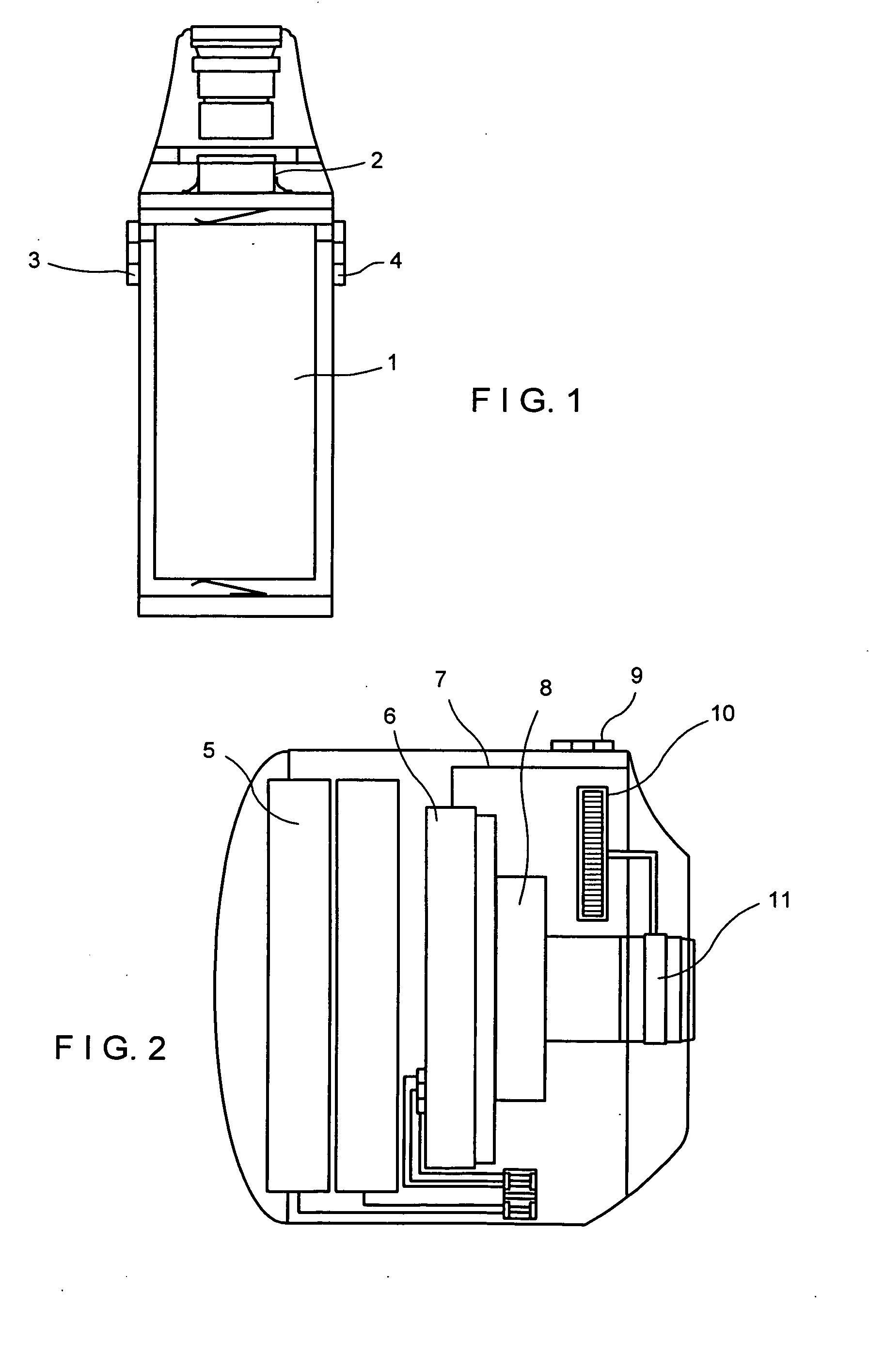
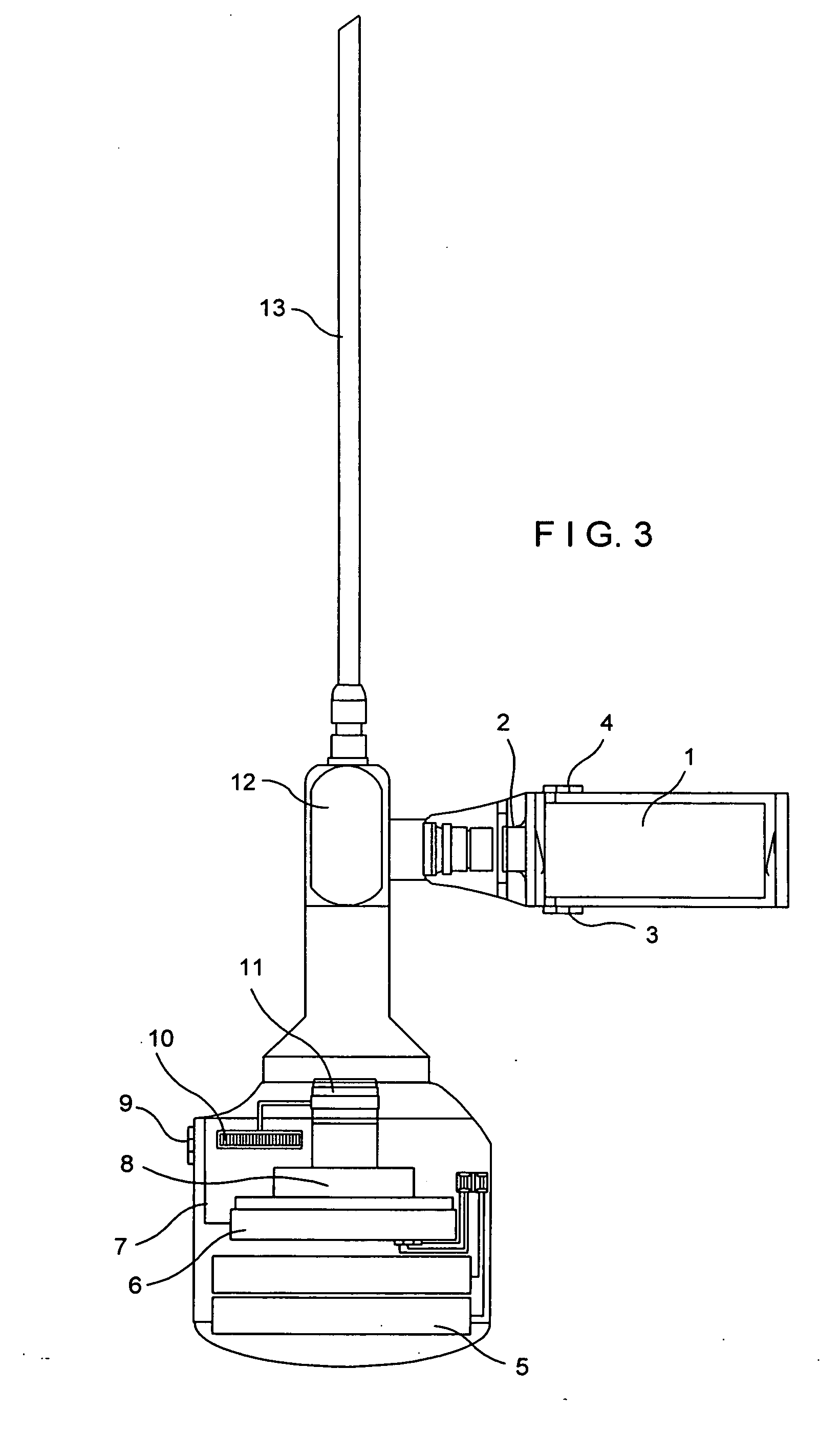
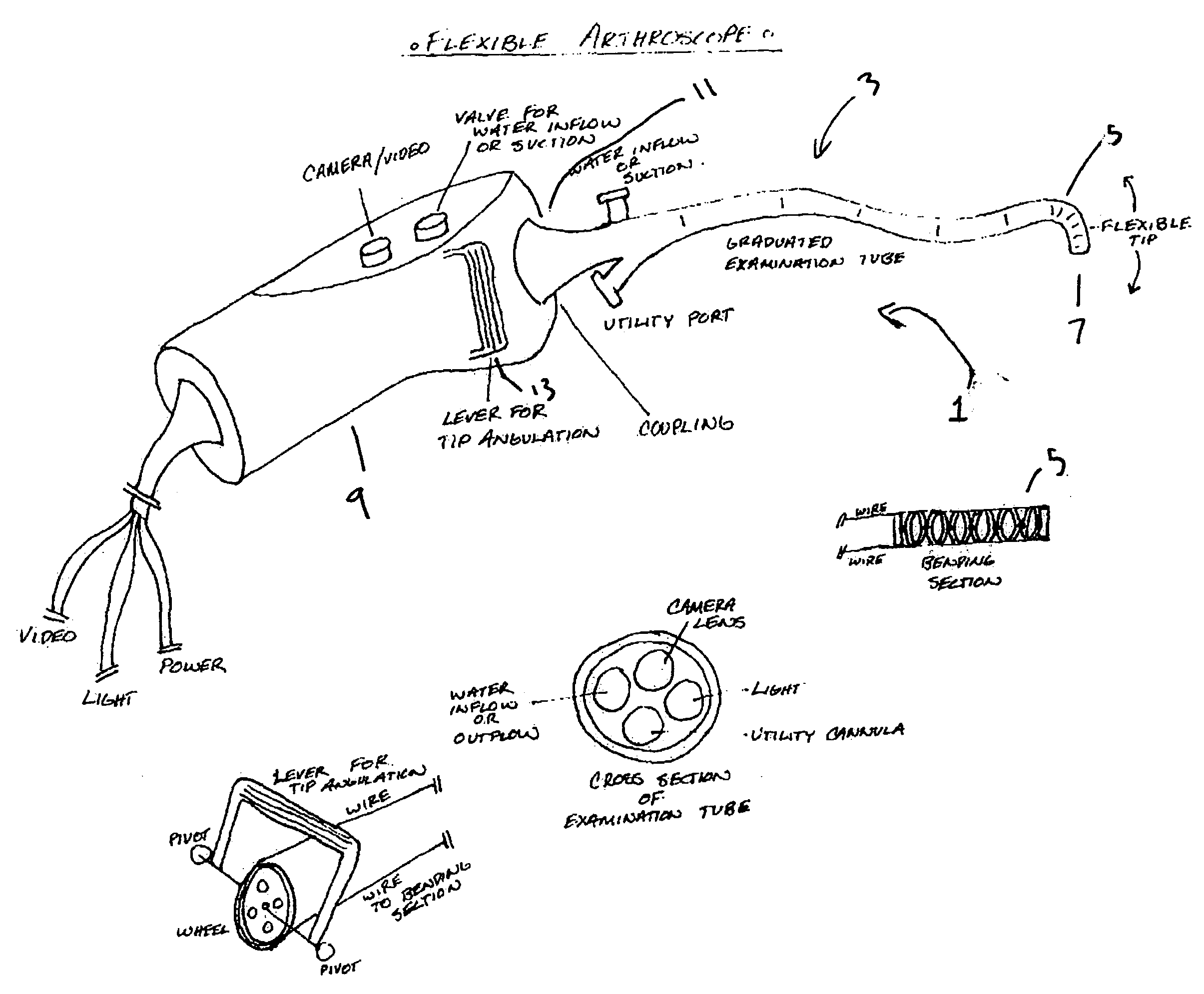
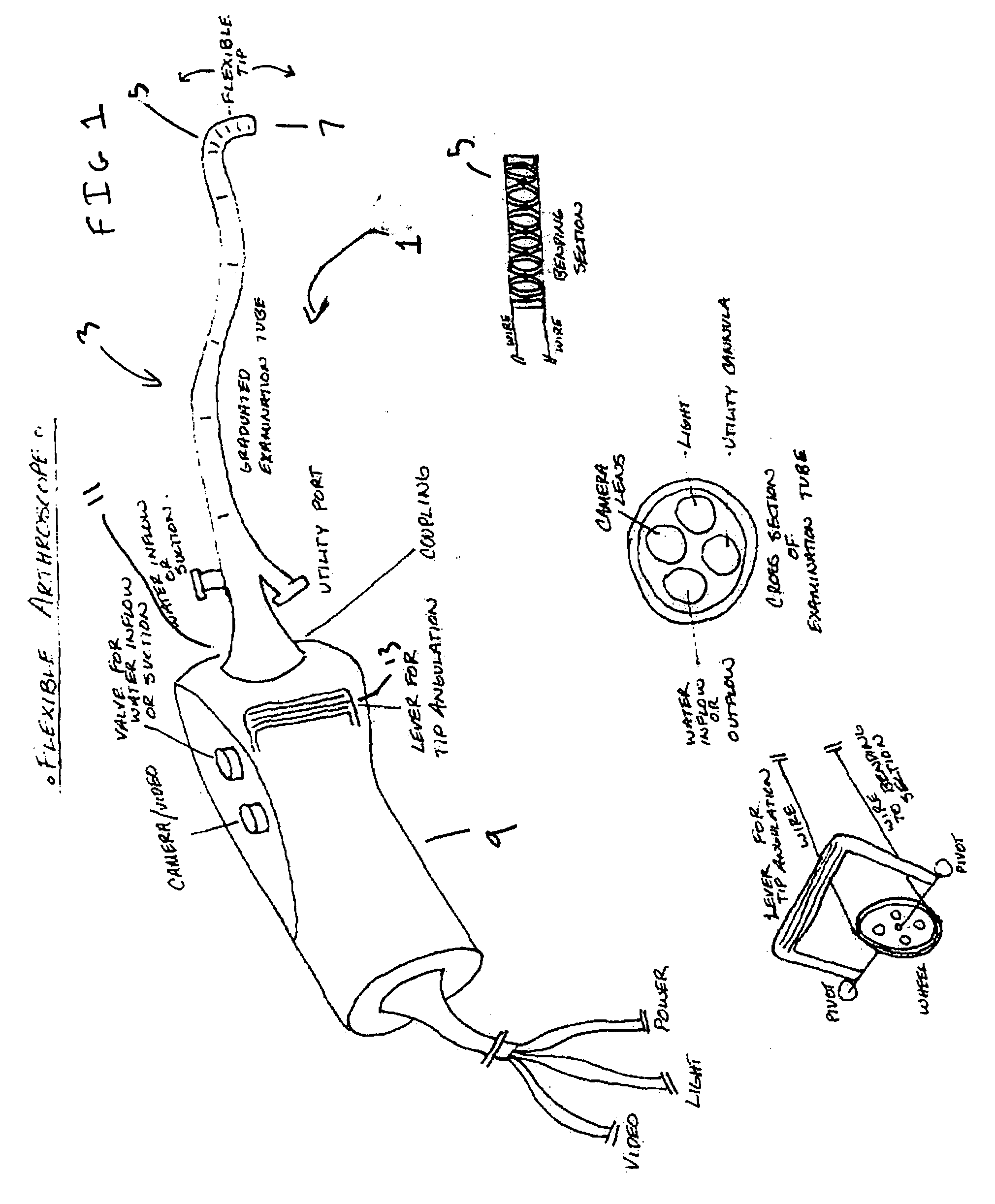
Flexible arthroscope and method of using the same
A flexible arthroscope comprising a semi-flexible examination tube having means for bending at its distal end, and removably connected to a handheld module at its proximal end. The semi-flexible examination tube coupled with its means for bending its distal end provides the user the ability to immediately alter his field of view in any direction and maintain the horizontal plane.
Owner:DIGIOVANNI CHRISTOPHER WILLIAM +2
Optical Cap for Use With Arthroscopic System
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
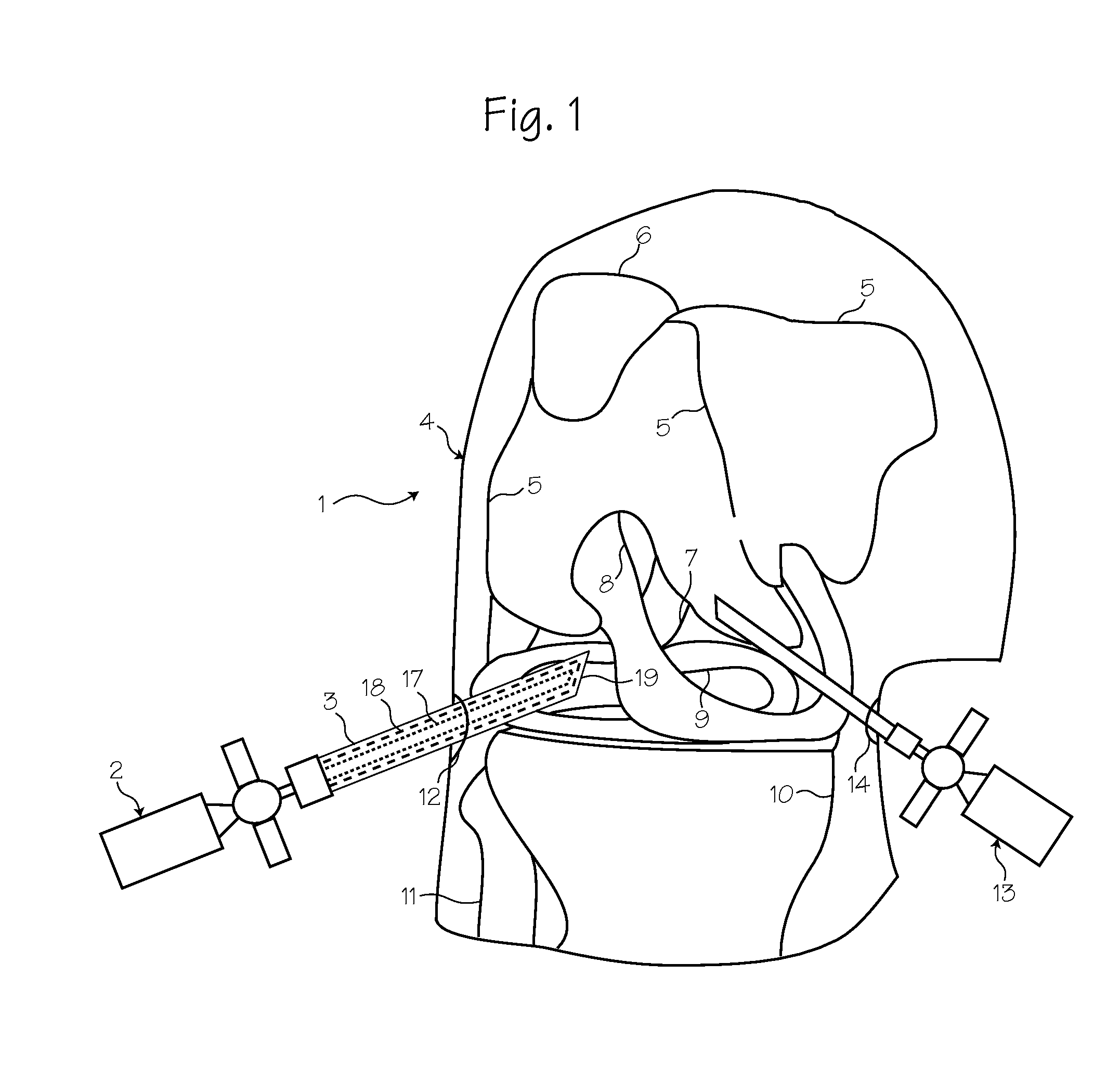
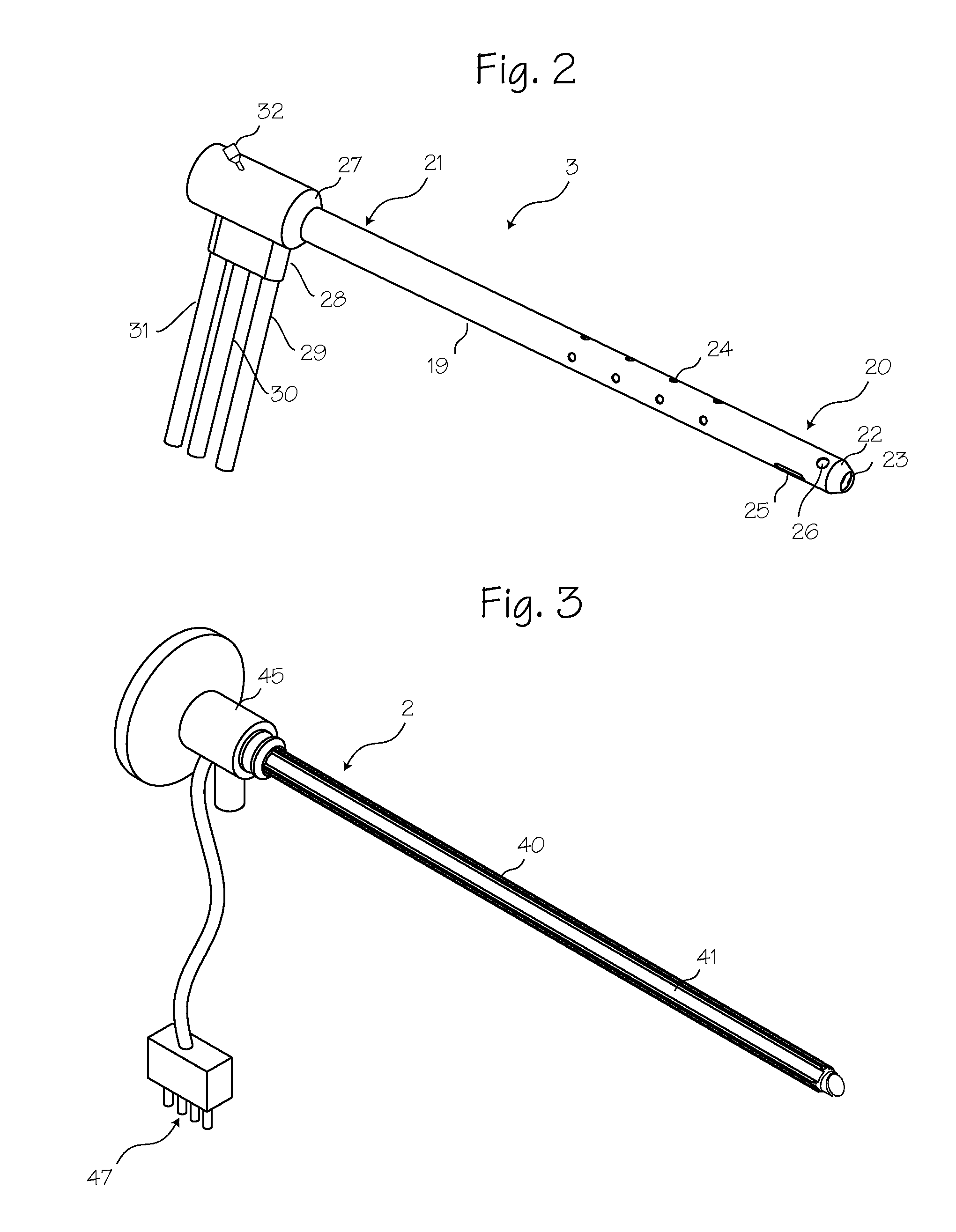
Invasive Distracter
InactiveUS20080109004A1Free working areaDampen applied forceProsthesisExternal osteosynthesisPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
An invasive distractor is proposed that has a form comparable to a conventional C-clamp or screw clamp. It permits spatially targeted positioning of two bones, so that the joint connecting these bones can be spread by means of distraction during an intervention, thereby creating the space needed to perform diagnosis and / or interventions by means of arthroscopic methods. The appliance is composed of a base (2) and of a slide (3) which can be displaced relative to one another in a controlled manner and secure against twisting. The base (2) and the slide (3) comprise various devices, such as worm gear, rotary gear and expansion gear, to ensure that the distraction of the two bones can be performed in a spatially exact manner adapted to the particular requirements.
Owner:ROLD ORLANDO +1
Variable view arthroscope
A variable-view arthroscope or similar instrument (endoscope, etc.) includes a housing tube with an input end. The housing tube contains an input assembly and a portion of a light relay assembly. A control varies the position of the input assembly to change the viewing position of the arthroscope. In certain embodiments, the control uses external master magnets that rotate around an axis orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the housing to drive internal slave magnets magnetically. This permits the housing to be sealed completely. In certain embodiments, a cam-axle assembly translates the rotational motion of the internal slave magnets to linear motion that drives a push rod that manipulates the input assembly.
Owner:DURELL & GITELIS INC
Artroscopic devices and methods
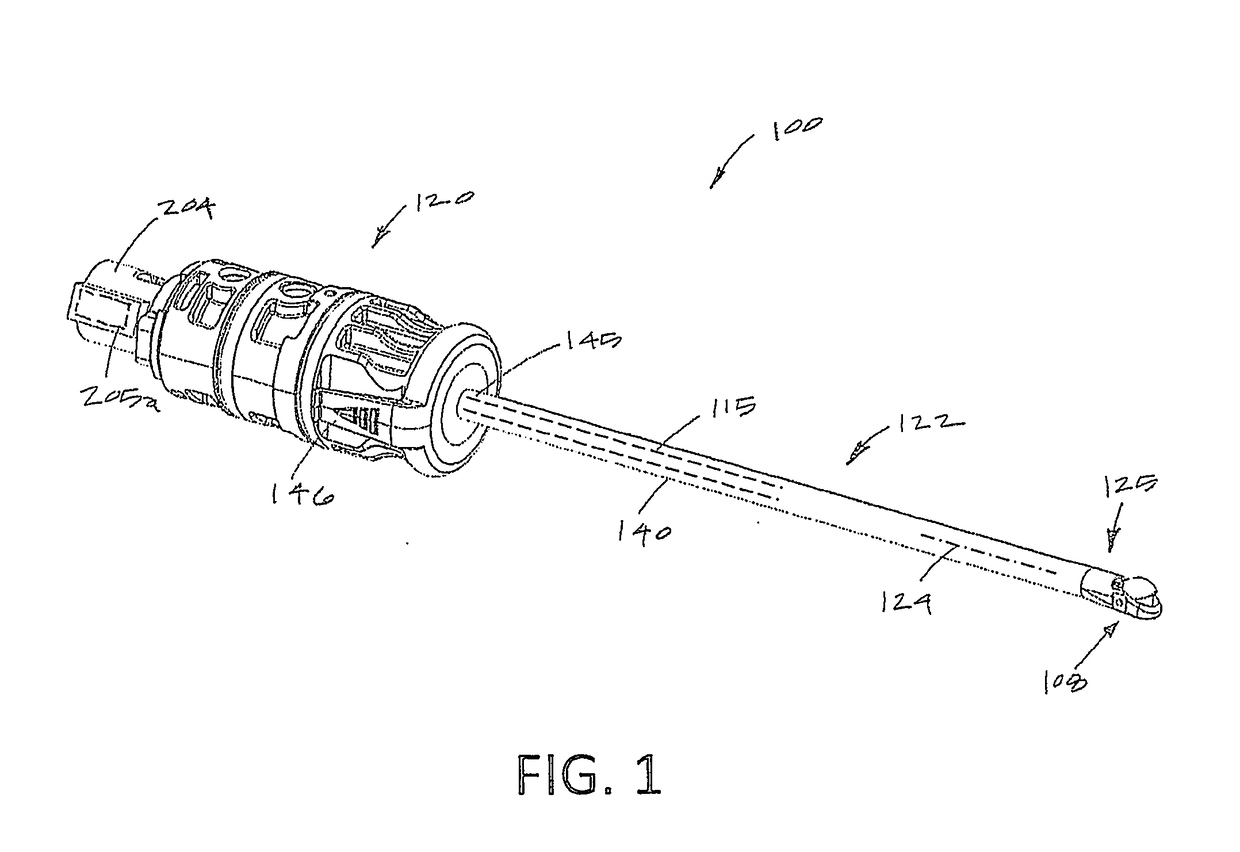
ActiveUS20190008541A1High strengthInhibition of translationSurgical instrument detailsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsDrive shaftEngineering
An arthroscopic device is used with a hand piece having a motor drive with a rotating drive shaft. An elongate probe extending along a longitudinal axis and includes a proximal hub on a proximal end. The proximal hub detachably couples to the hand piece, and an openable-closeable jaw structure is disposed on a distal end of the elongate probe. A conversion mechanism carried by the hub converts a rotational motion of the motor drive shaft to a longitudinal motion of an actuator member. The actuator member drives the jaw structure between jaw-open and jaw-closed positions to resect bone and other hard tissues.
Owner:RELIGN CORP
Rigid arthroscope system
A reinforced arthroscope comprising external ribs to provide for a number of separate fluid channels, such as inflow, outflow and interstitial tissue drainage, when the arthroscope is slipped into a disposable external sheath. The arthroscope is constructed to be sufficiently rigid so as to penetrate and move within a joint without damaging the rod optics inside. The externality of the arthroscope channels allow for cleaning and sterilizing the scope between uses.
Owner:PRISTINE SURGICAL LLC
Variable view arthroscope with charge coupled device
A variable view arthroscope includes a tubular housing having a longitudinal axis and an input end, an input lens and a CCD in the input end of the housing for capturing and relaying an image object. In some embodiments, a variable view arthroscope with a plurality of viewing positions in a viewing range between a first end viewing position and a second end viewing position includes a tubular housing having a longitudinal axis and an input end, an input lens and a mirror in the housing for obtaining an image object, and a prism, a focusing lens, and a CCD in the housing for capturing and relaying the image object. The input lens and mirror are movable around an axis for varying the view of the arthroscope. In certain embodiments, the tubular housing has a longitudinal axis and an input end and the input lens and CCD are mounted in an input lens holder in the input end of the housing. The input lens and the CCD are movable for varying the view of the arthroscope. The CCD converts the object image into a digital image that can be viewed, for example, on a TV or CRT screen. The CCD can be used to replace a field and relay system, or additional focusing lenses and mirrors, thereby decreasing the cost and complexity of a variable view arthroscope.
Owner:DURELL & GITELIS INC
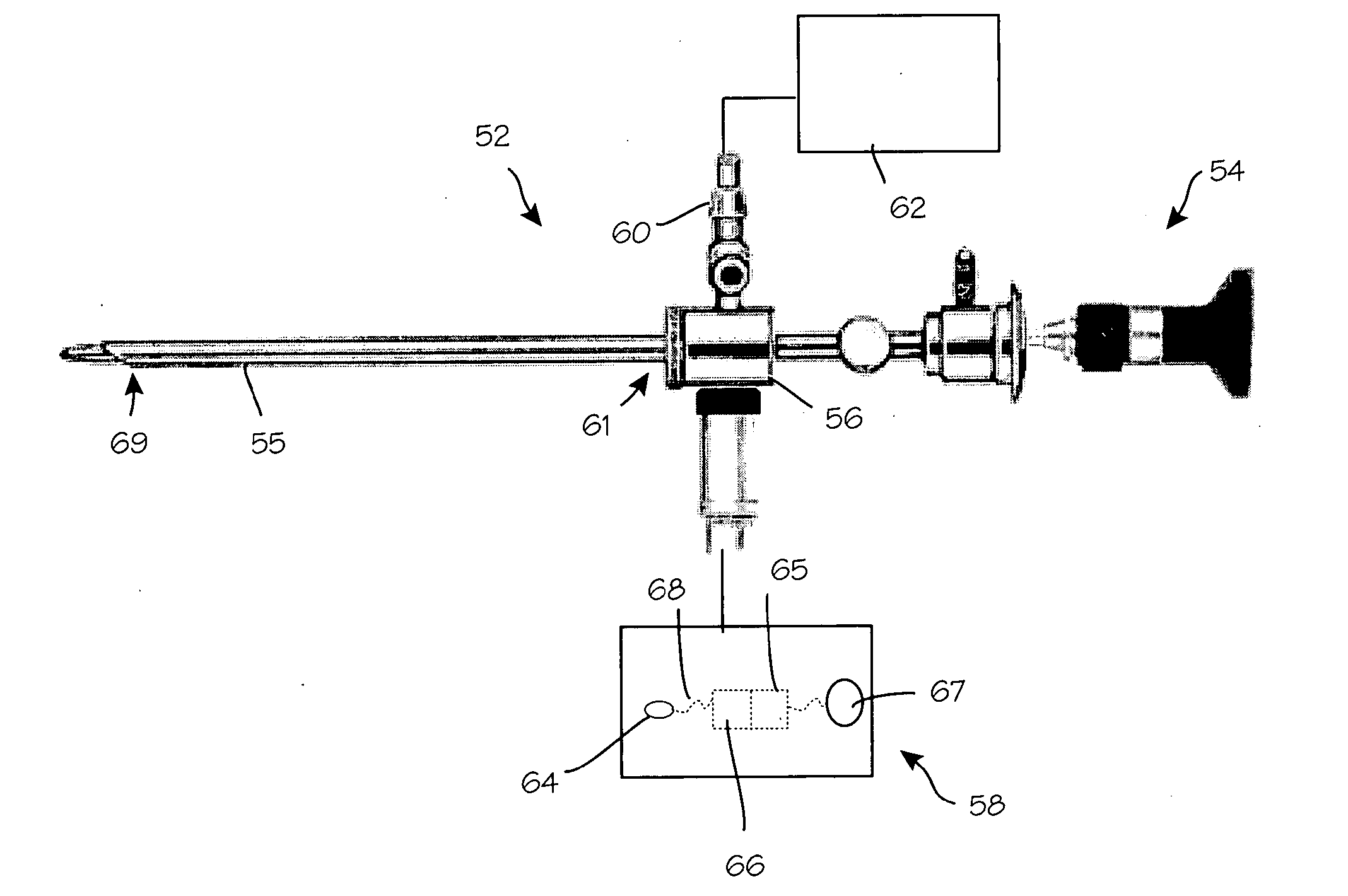
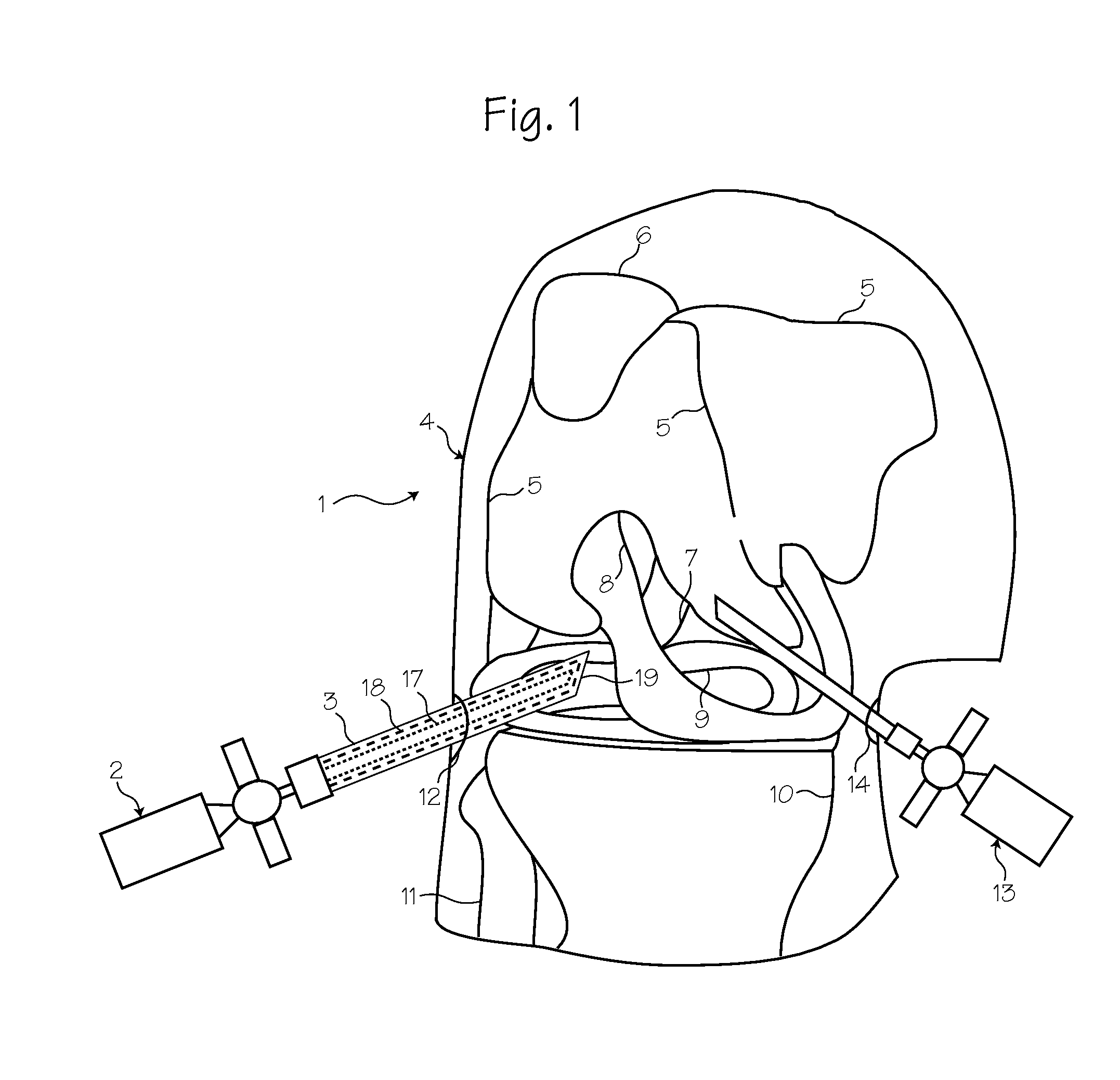
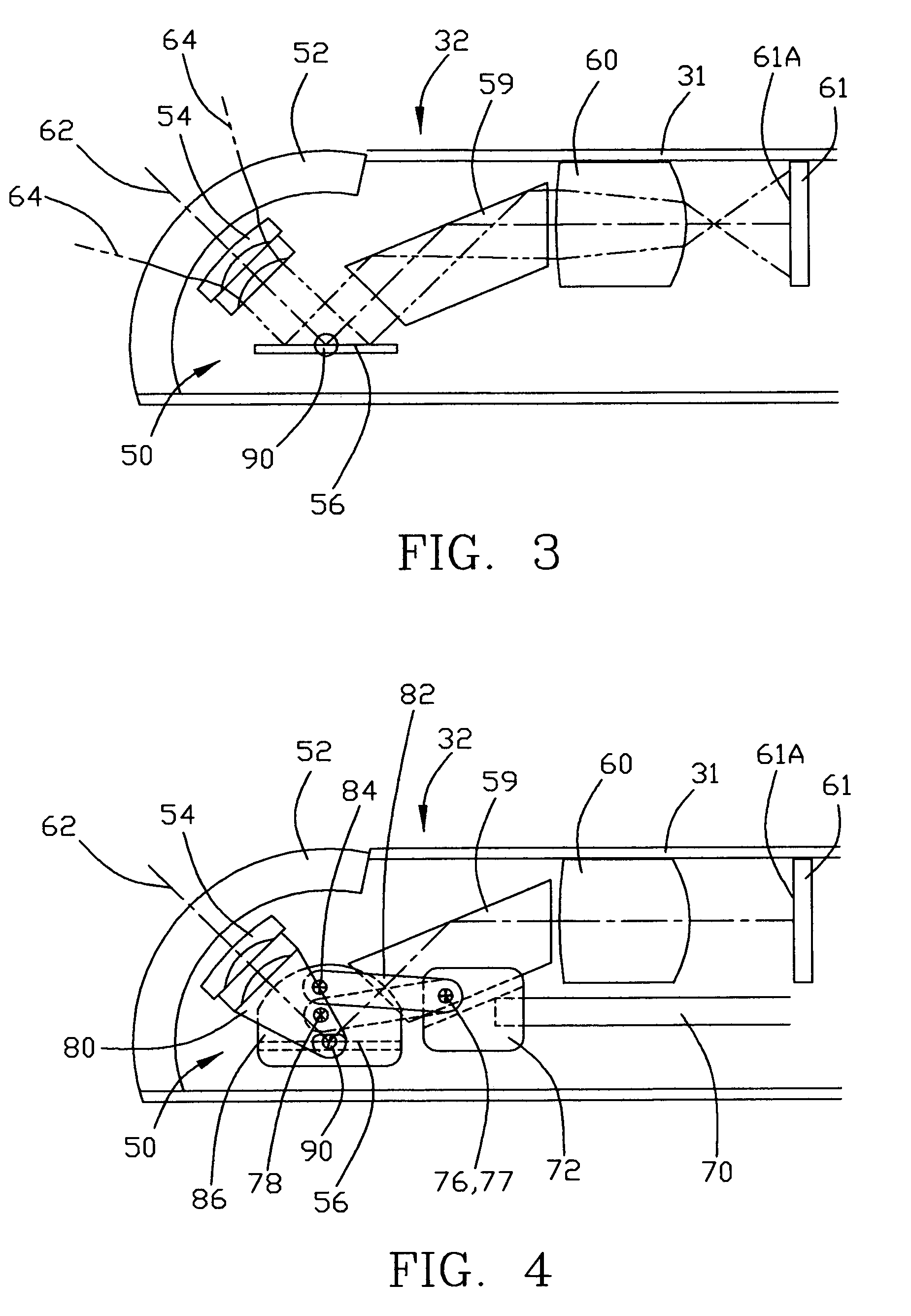
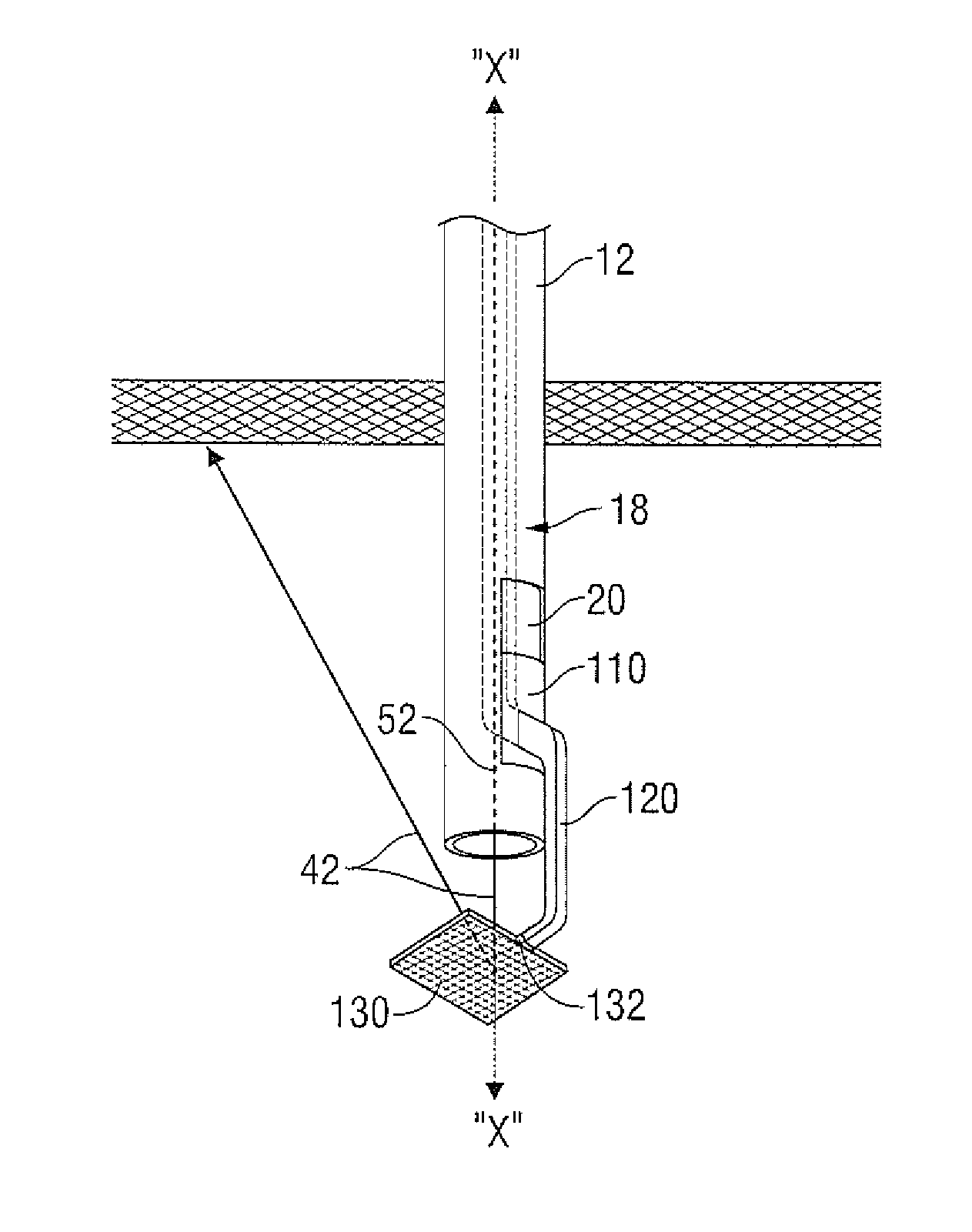
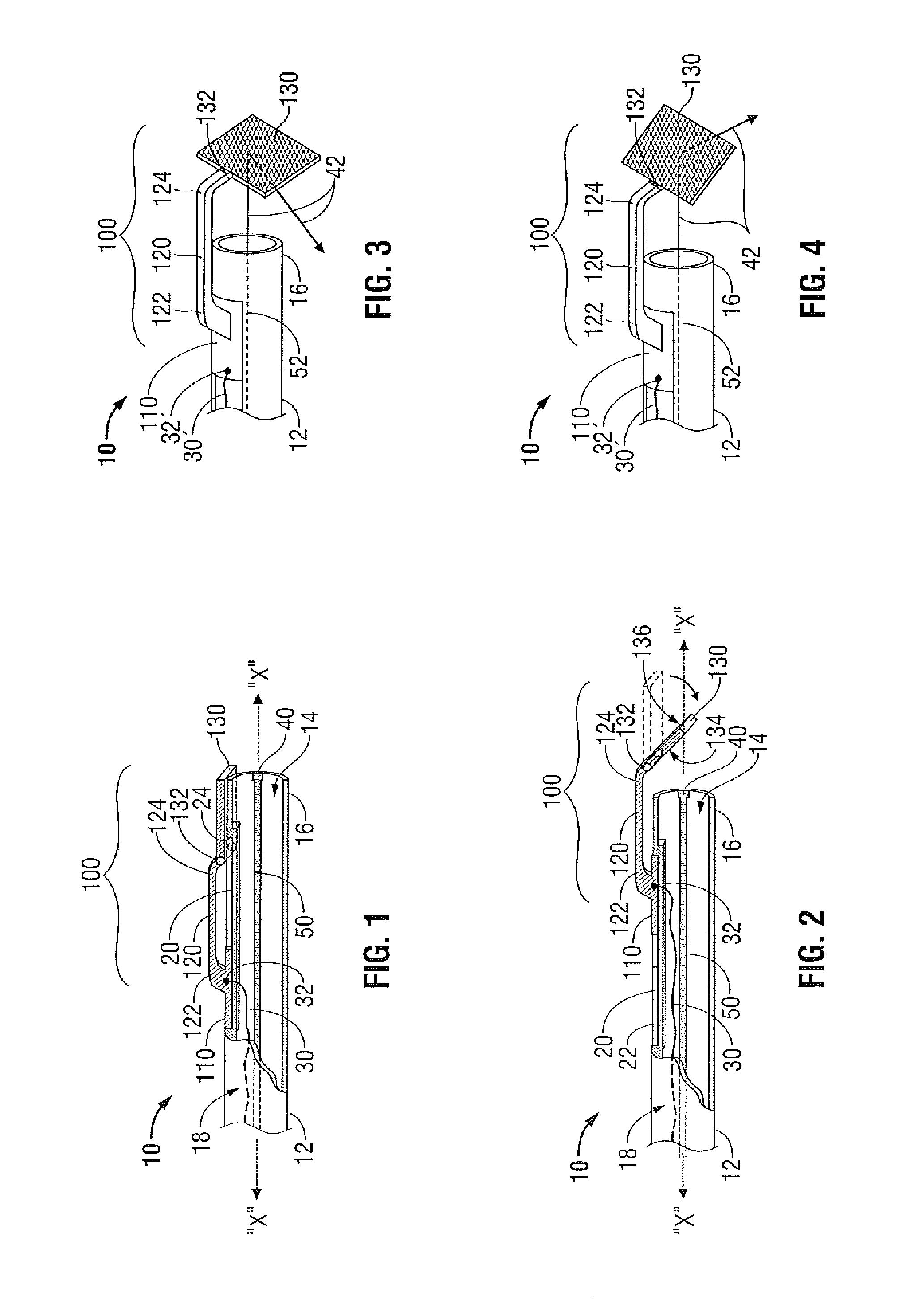
Arthroscopic instrument assembly, and method of localizing musculoskeletal structures during arthroscopic surgery
InactiveUS20150297073A1Promote localizationIncrease contrastDiagnostics using lightSurgeryDisplay deviceImage View
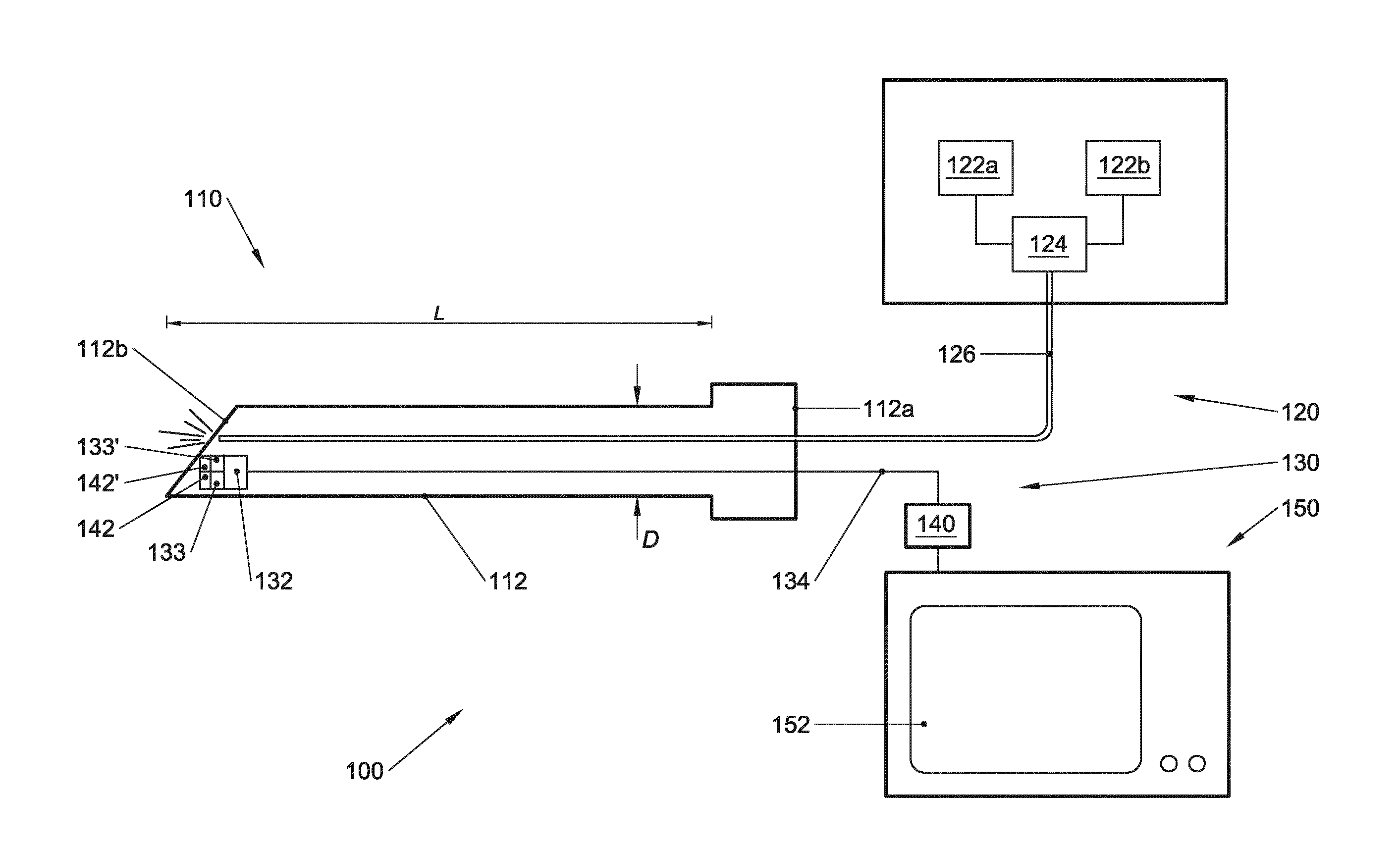
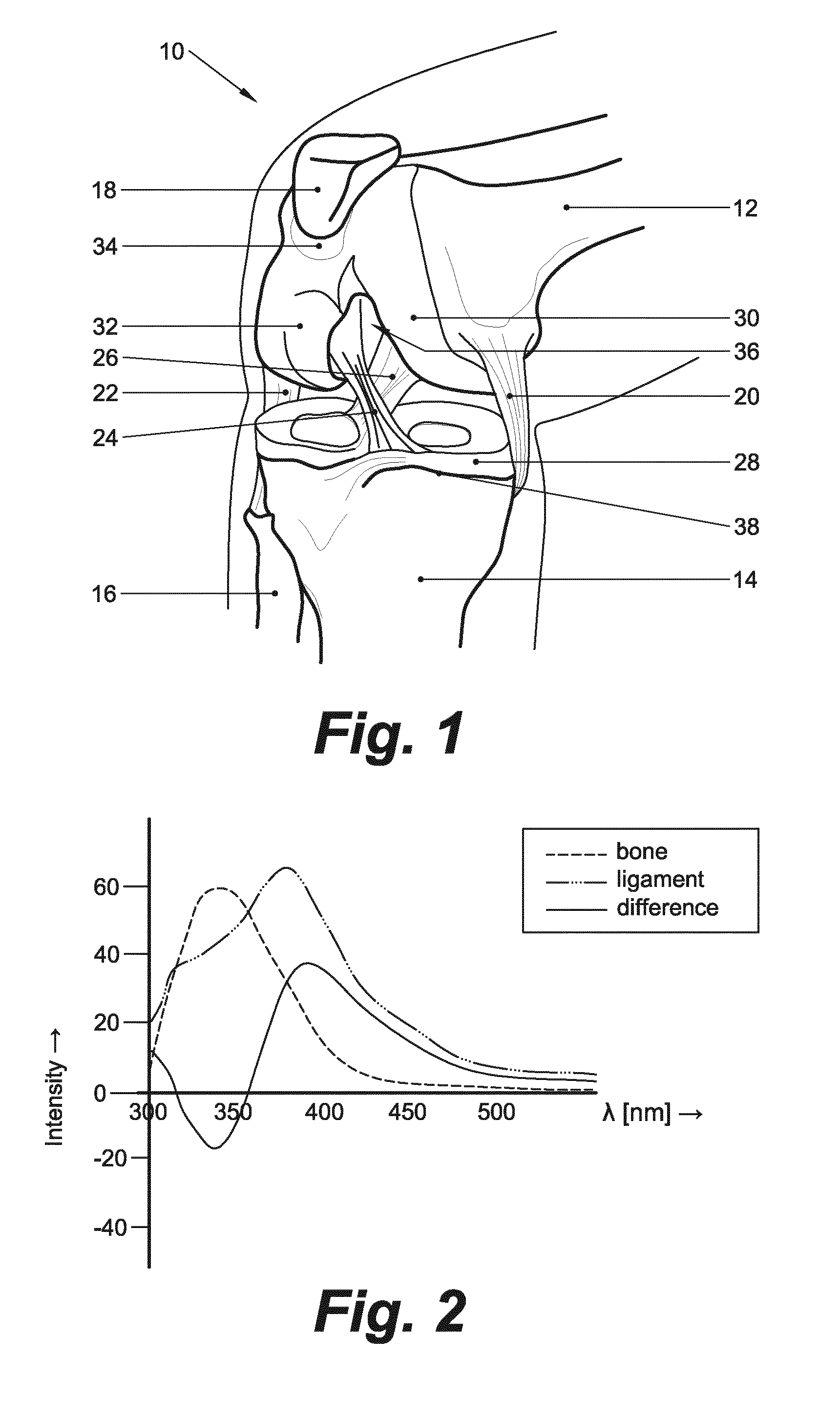
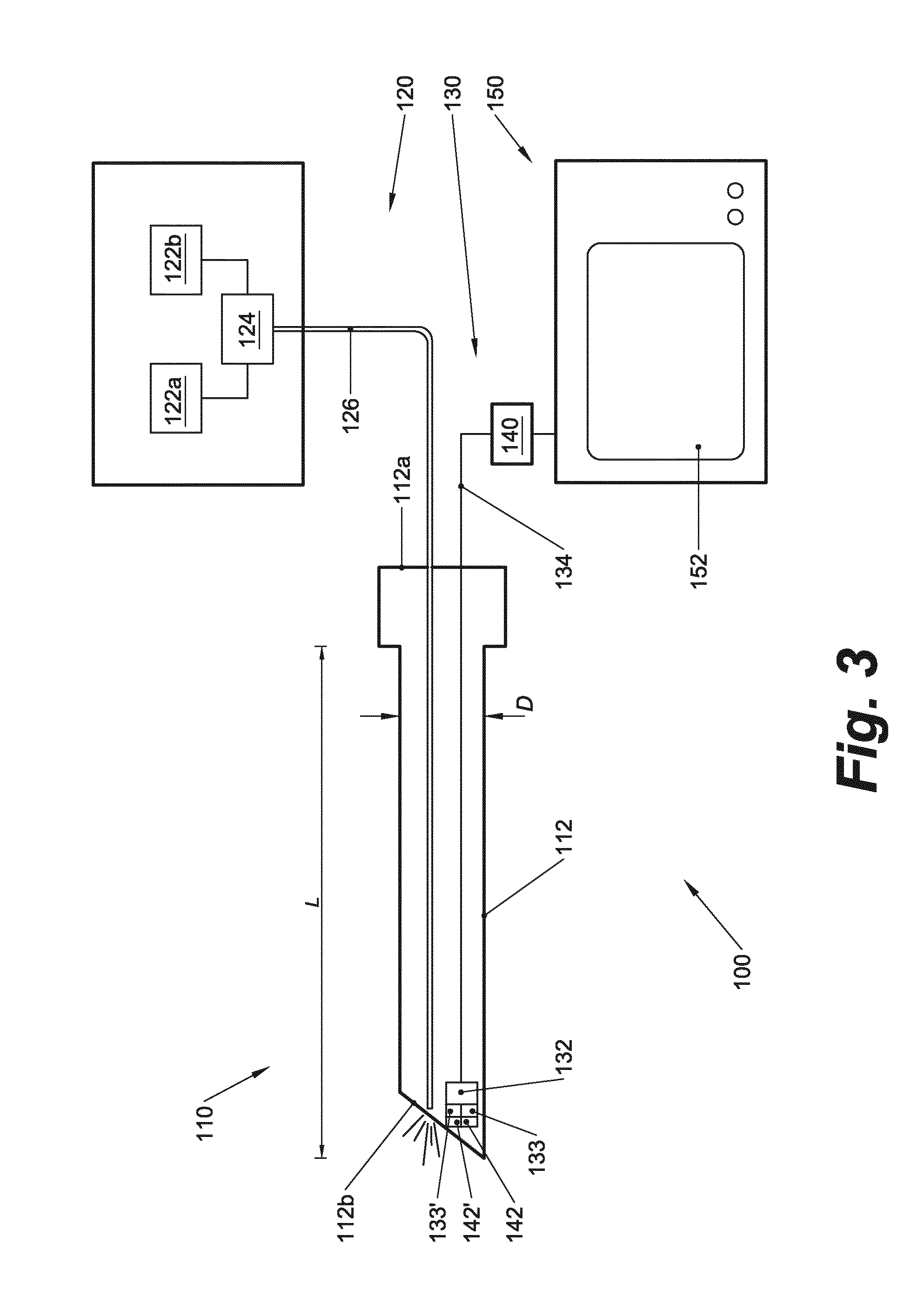
An arthroscopic instrument assembly (100), comprising: an illumination system (120) for illuminating an operative field, including a light source (122a) configured to produce light having at least one ligament excitation wavelength; an arthroscope (110); an image transmission system (130) configured to transmit a fluorescent image of the operative field at a distal end (112b) of the arthroscope (110) to an image viewing system (150); an image processing system (140) configured to process the fluorescent image as it passes through the image transmission system, so as to provide a false-color fluorescent image of the operative field in which a contrast between ligament and bone structures present in the operative field is enhanced relative to the unprocessed fluorescent image; and an image viewing system (150), operably connected to the image transmission system (130), and including a display (152) configured to enable viewing of the false-color fluorescent image.
Owner:ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT BIJ DE UNIV VAN
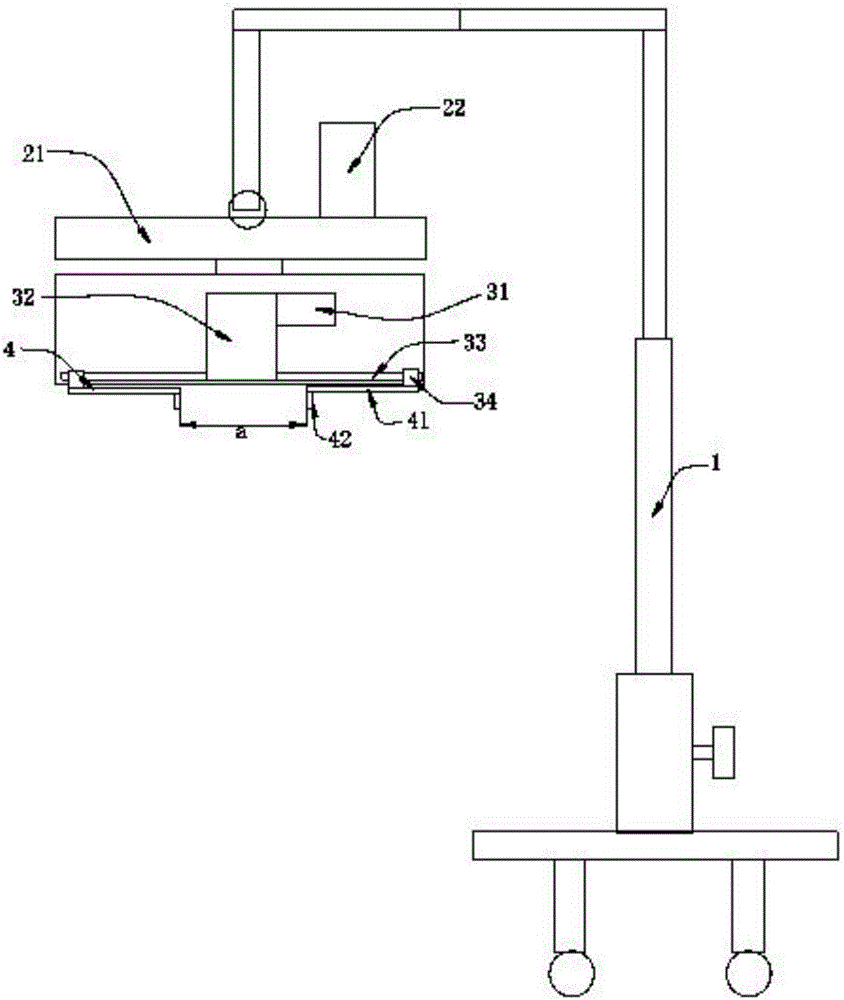
Knee arthroscope operation stent
InactiveCN102499843AMeet knee flexion requirementsKnee angle requirements are metOperating tablesInsertion stentKnee arthroscopic surgery
The invention discloses a knee arthroscope operation stent, which comprises a stent body fixedly connected with an operation table, a rotating disc I fixedly arranged on the stent body, a connecting rod I, a rotating disc II and a connecting rod IV. A locating hole I is arranged at the edge of the rotating disc I, one end of the connecting rod I is hinged to the center of the rotating disc I, a location pin I is arranged on the connecting rod I, and a connecting rod II is fixedly arranged at the other end of the connecting rod I. The rotating disc II is arranged perpendicular to the rotating disc I, a far end of the connecting rod II is hinged to the center of the rotating disc II, a locating hole II is arranged at the edge of the rotating disc II, and a location pin II matched with the locating hole II is arranged on the connecting rod II. A connecting rod III is fixedly arranged on the rotating disc II, one end of the connecting rod IV is hinged to a far end of the connecting rod III, and a fixing sleeve used for fixing ankles is arranged at the other end of the connecting rod IV. Angles at various directions can be adjusted and continuously fixed by the knee arthroscope operation stent according to operation requirements, a continuously stable and reliable operation environment can be provided for medical personnel, operation quality is guaranteed, manpower resources are saved, efficiency is improved, and the knee arthroscope operation stent is simple in structure, convenient to use and easy to manufacture.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Ligament reestablishing system
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments and discloses a ligament reestablishing system. After a ligament is reestablished for the first time by using the ligament reestablishing system, the ligament can be quickly replaced through a small incision outside a joint without using an arthroscope if a revision surgery needs to be carried out on the ligament. Because the technology has the character of quick revision, a ligament substitute material is not needed to be firmly combined with a bone channel any longer, so the ligament reestablishing system provides possibilities for reliable use of artificial materials except autologous / allogenic tendons. Moreover, the difficulty and cost of the revision surgery are reduced, the hospital time is reduced, and the indication of ligament reestablishment is expanded. The ligament reestablishing system comprises a first endosteal hollow channel, a second endosteal hollow channel, a ligament substitute, a first fixing piece and a second fixing piece. A bone penetrating through the near end of the joint and a bone penetrating through the far end of the joint are implanted into the first endosteal hollow channel and the second endosteal hollow channel respectively. The ligament substitute is placed into the first endosteal hollow channel and the second endosteal hollow channel.
Owner:叶维光
Rigid Arthroscope System
A reinforced arthroscope comprising external ribs to provide for a number of separate fluid channels, such as inflow, outflow and interstitial tissue drainage, when the arthroscope is slipped into a disposable external sheath. The arthroscope is constructed to be sufficiently rigid so as to penetrate and move within a joint without damaging the rod optics inside. The externality of the arthroscope channels allow for cleaning and sterilizing the scope between uses.
Owner:PRISTINE SURGICAL LLC
Compositions and methods for treating cavity conditions
Compositions, methods and kits to be used as a lubricant and for treatment of a cavity pathology including joint pathology are provided. The composition comprises therapeutically effective amounts of at least one bioactive agent, such as magnesium compound, at least one lubricating agent, such as hyaluronic acid, and at least one cell membrane repairing agent, such as polyethylene glycol. The components of these compositions may be administered by a direct application, an application through a cannula, an intra-articular injection, as a flush fluid during an arthroscopy of the affected area, as a post-arthroscopy injection, or as part of a lavage of the area affected by the intra-articular pathology. In addition, the composition of the present invention may be administered to the patient from a pump or a depot.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Mirrored arthroscope
A surgical instrument includes an elongated tubular member defining a longitudinal axis and having a lumen extending therethrough. A light source is disposed within the elongated tubular member. The light source is configured to emit light from a distal end of the elongated tubular member. A mirror assembly is coupled to a distal end of the elongated tubular member. The mirror assembly is moveable between a retracted position and an extended position. In the retracted position, the mirror assembly is positioned adjacent an outer surface of the elongated tubular member. In the extended position, the mirror assembly extends distally from the elongated tubular member to re-direct light emitted by the light source.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
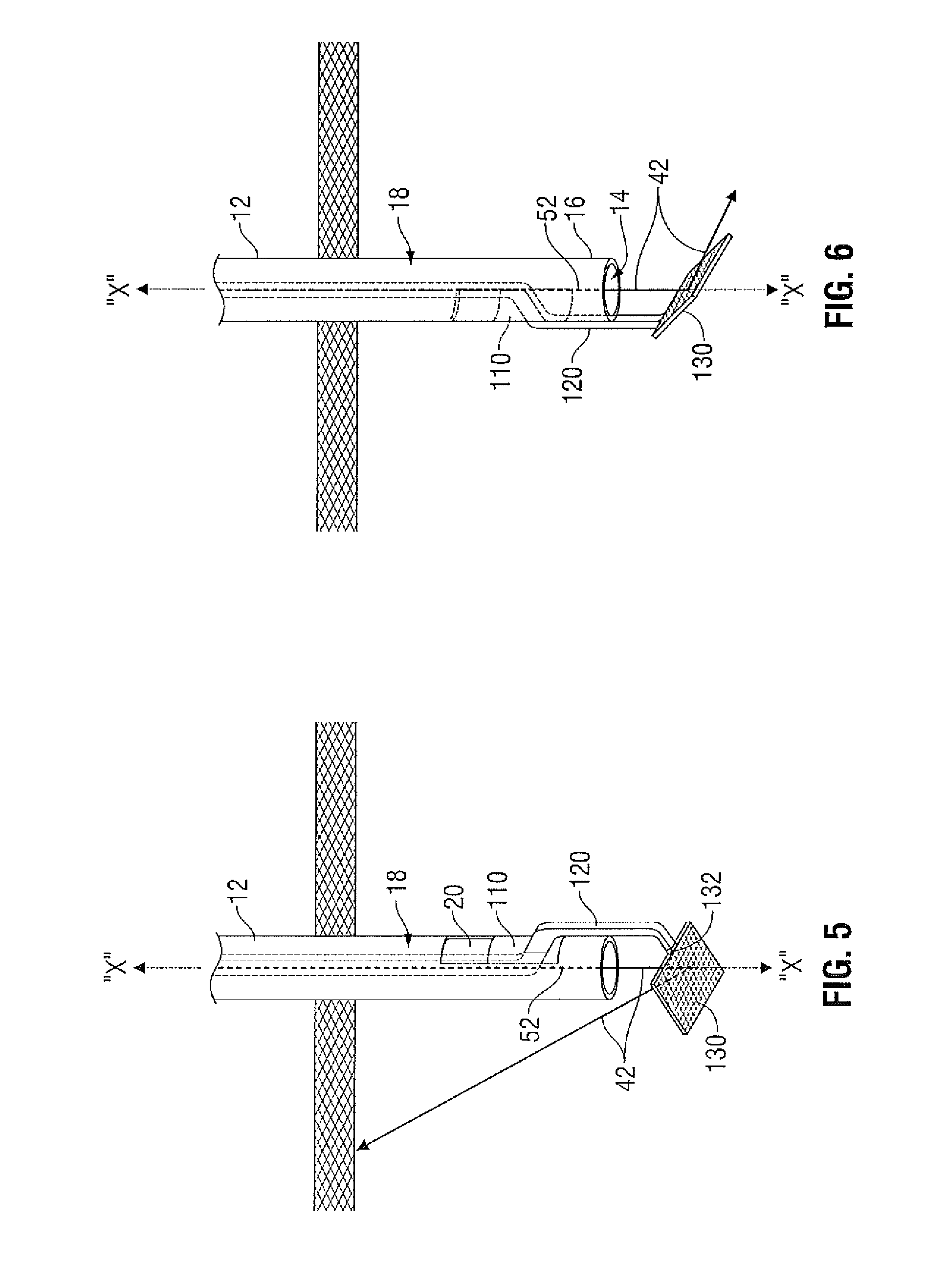
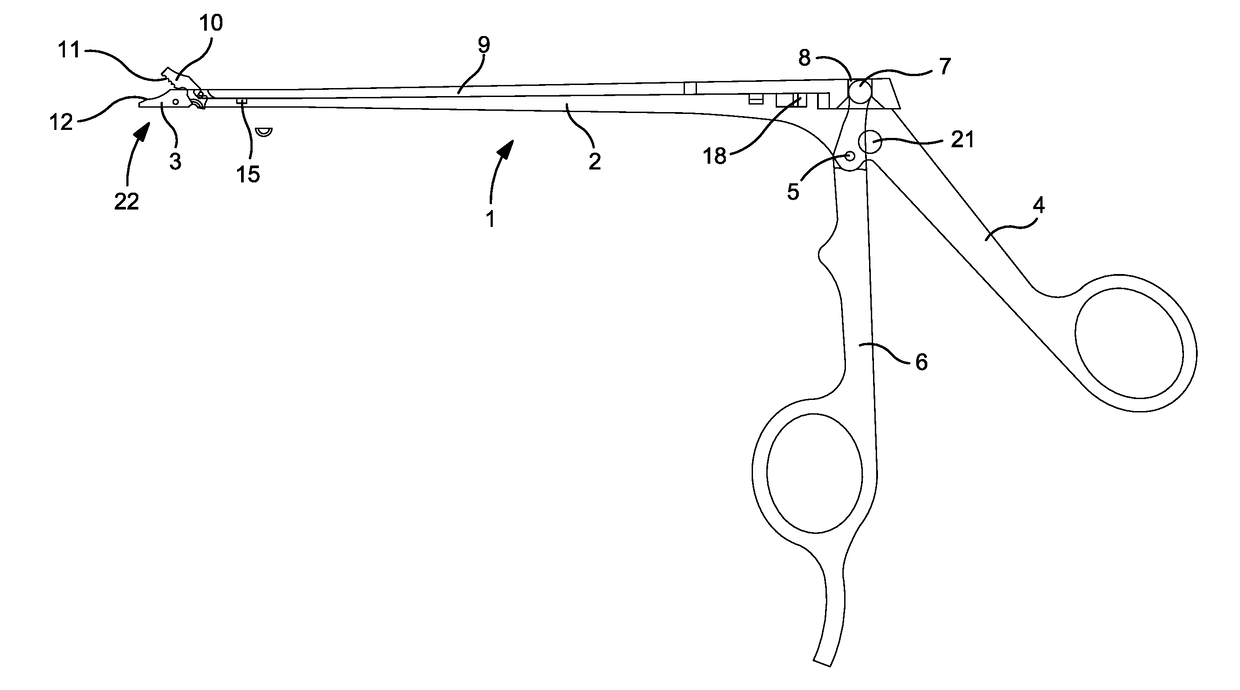
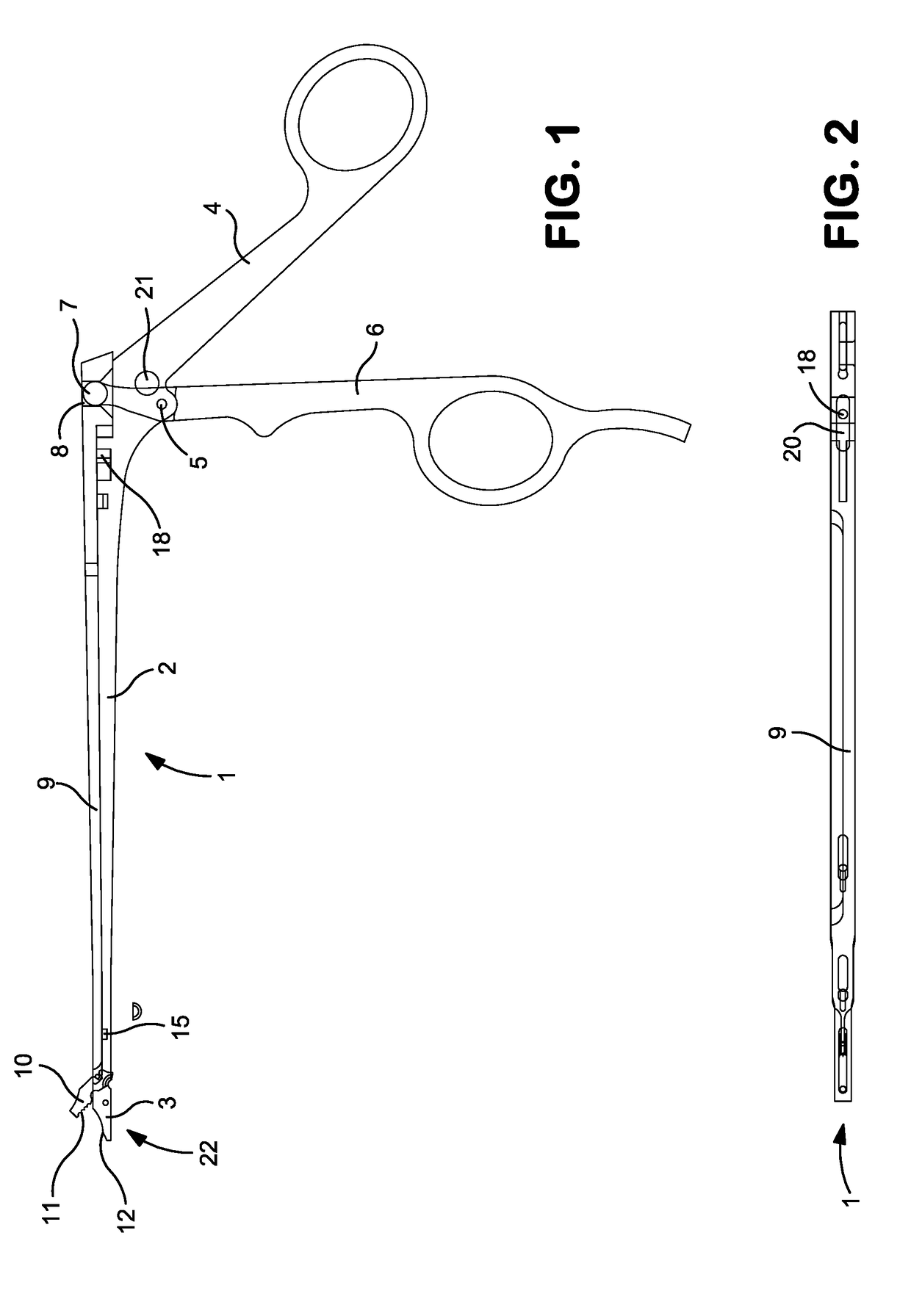
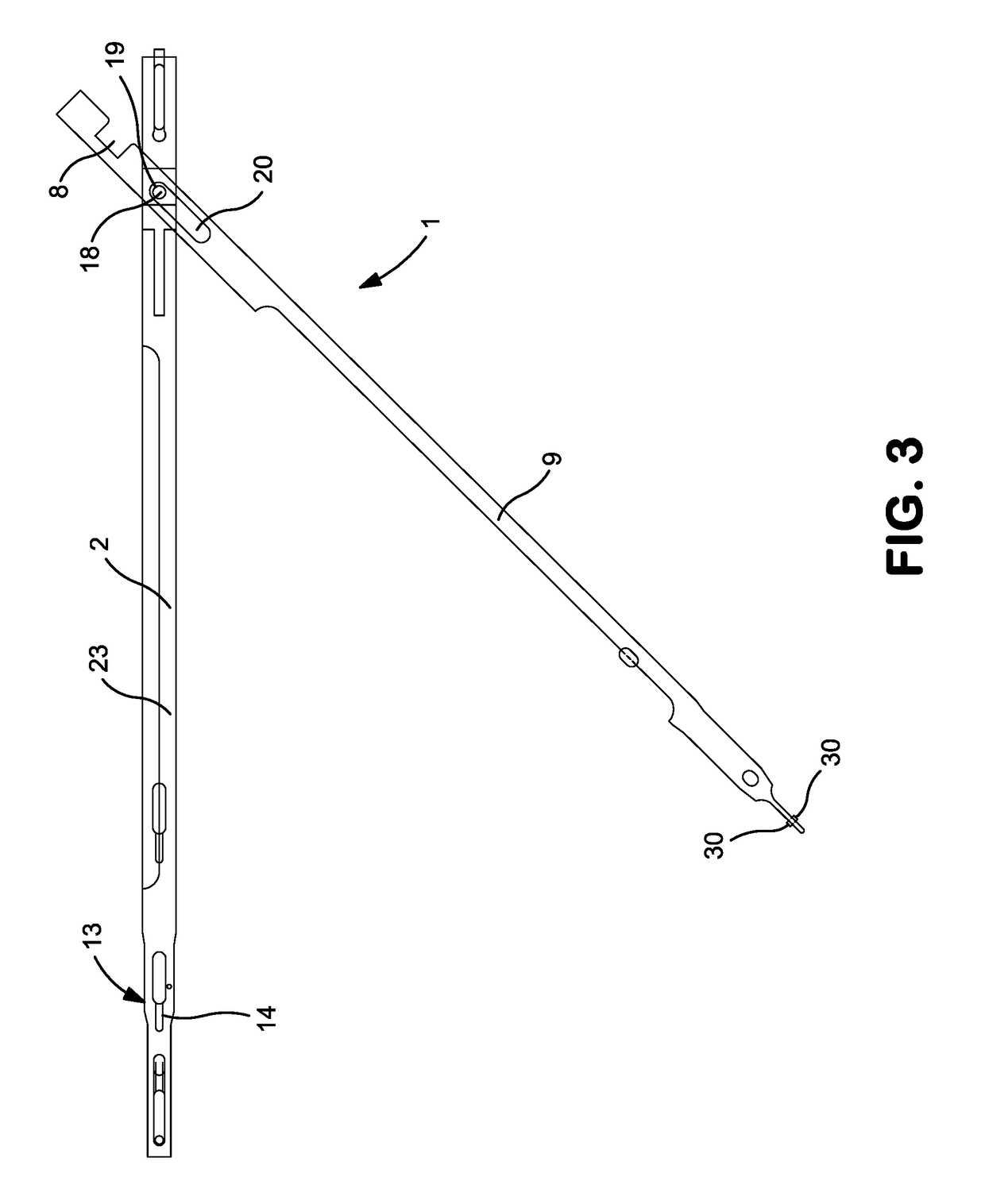
Surgical instrument
InactiveUS20170119402A1Easy to cleanDiagnosticsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsSurgical instrumentSurgical department
A surgical instrument, in particular an arthroscopy punch, with a jaw (22), includes a stationary jaw part (3) and a movable jaw part (10) which, by pivoting of a pivotable grip part (6), is displaceable relative to the stationary jaw part (3), between a closed position and an open position, in a slotted guide (26) along a curved guide path.
Owner:HEINEMANN NORBERT
Guide device suitable for performing temporomandibular joint arthroscopy
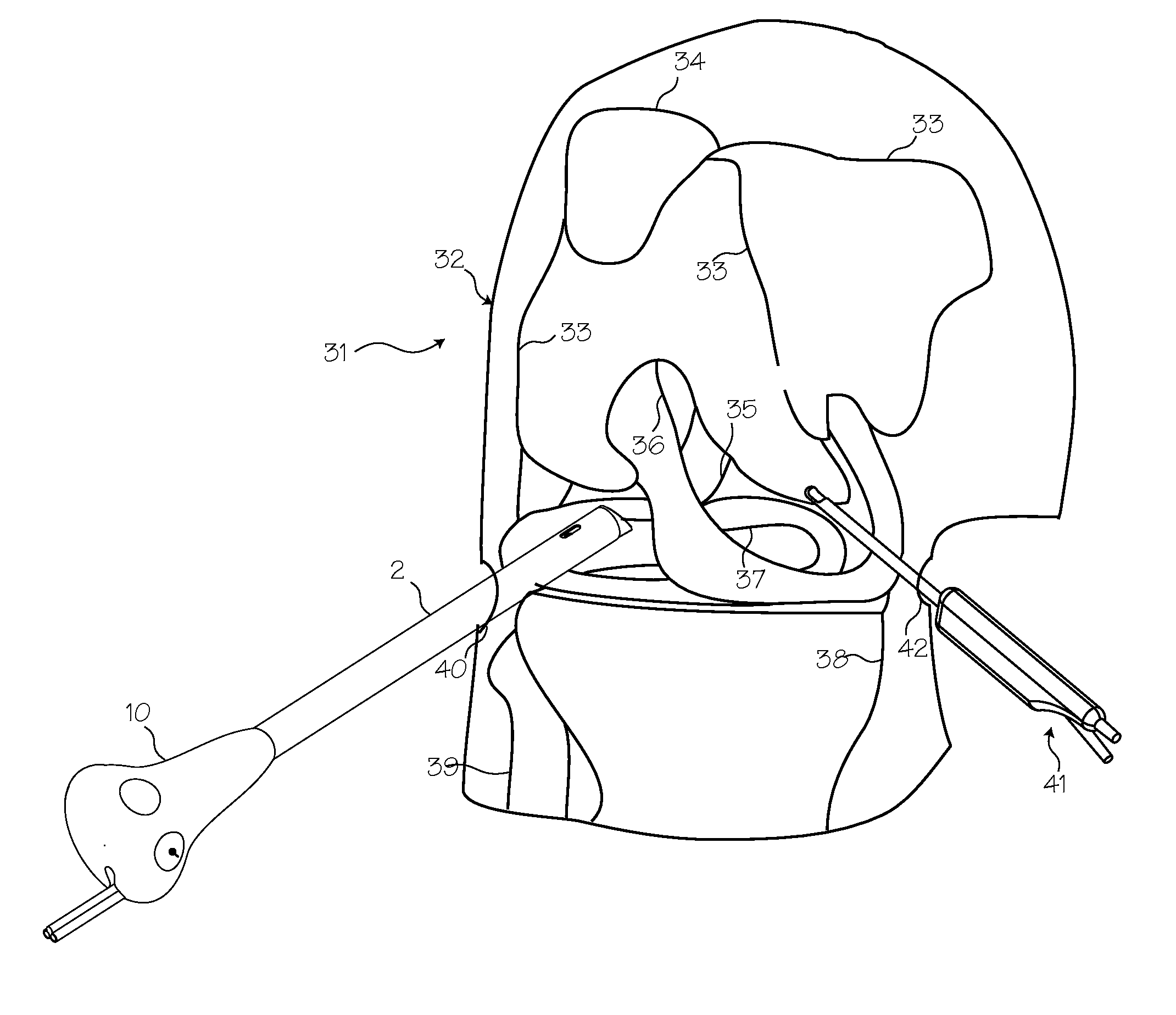
ActiveUS20200060724A1Accurate insertionPrecise positioningCannulasSurgical needlesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
A guide device for TMJ arthroscopy including one or more pairs of arms pivotly connected at one end to a working cannula holder and defining a working cannula axis; and at the opposite end to at one or more arms via one or more pivot connections to form with the arm one or more adjustable parallelograms, an end of the arm is connected to an irrigation cannula holder defining an irrigation cannula axis, the irrigation cannula axis intersecting with the working cannula axis at an intersection, intersection and one or more of the pivot connections between connecting the arms are located at opposing vertices of one or more of the adjustable parallelograms.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Sports medical arthroscope surgical equipment
InactiveCN106214192AStretch outWell exposedSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionArthroscopic procedureDistraction
The invention relates to equipment special for orthopedic operation, in particular to sports medical arthroscope surgical equipment. The surgical equipment comprises a support, a steering platform hinged to the support, a steering motor for driving the steering platform, and a distraction device arranged on the steering platform. The distraction device comprises a drive motor, a gearbox arranged on an output shaft of the drive motor, two screws meshed with the gearbox through gears in a transmission mode, and hooks arranged on the screws. The two screws are oppositely arranged. The movement directions of the hooks on the two screws are opposite. Each hook comprises a transverse hook handle and a hook body longitudinally arranged at the inner end of the hook handle. The distance between the two hook bodies is not larger than 6 cm. The hooks in the surgical equipment are driven by the drive motor, so a surgical incision is stably distracted and obviously exposed, and medical labor cost is saved.
Owner:姜文晓
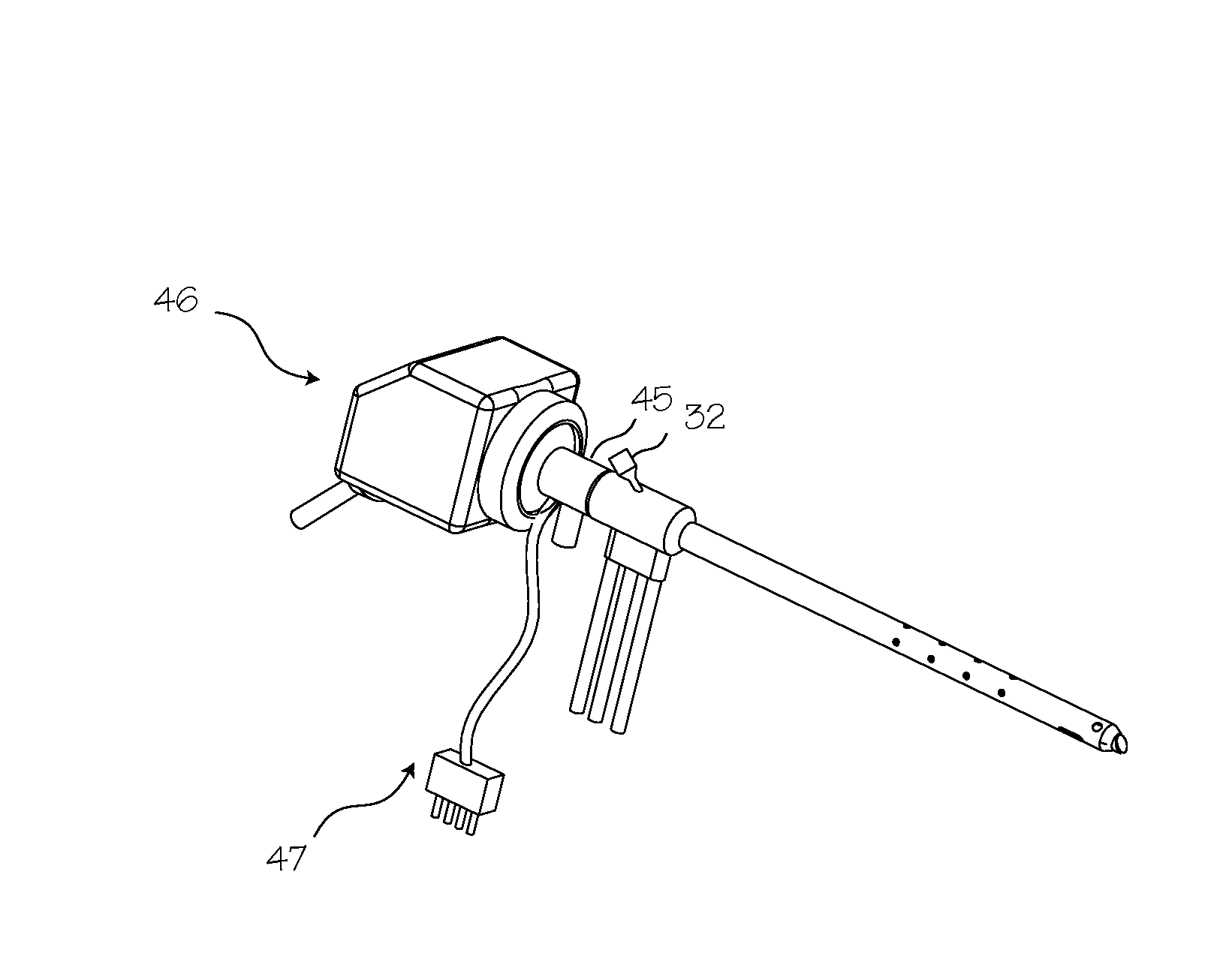
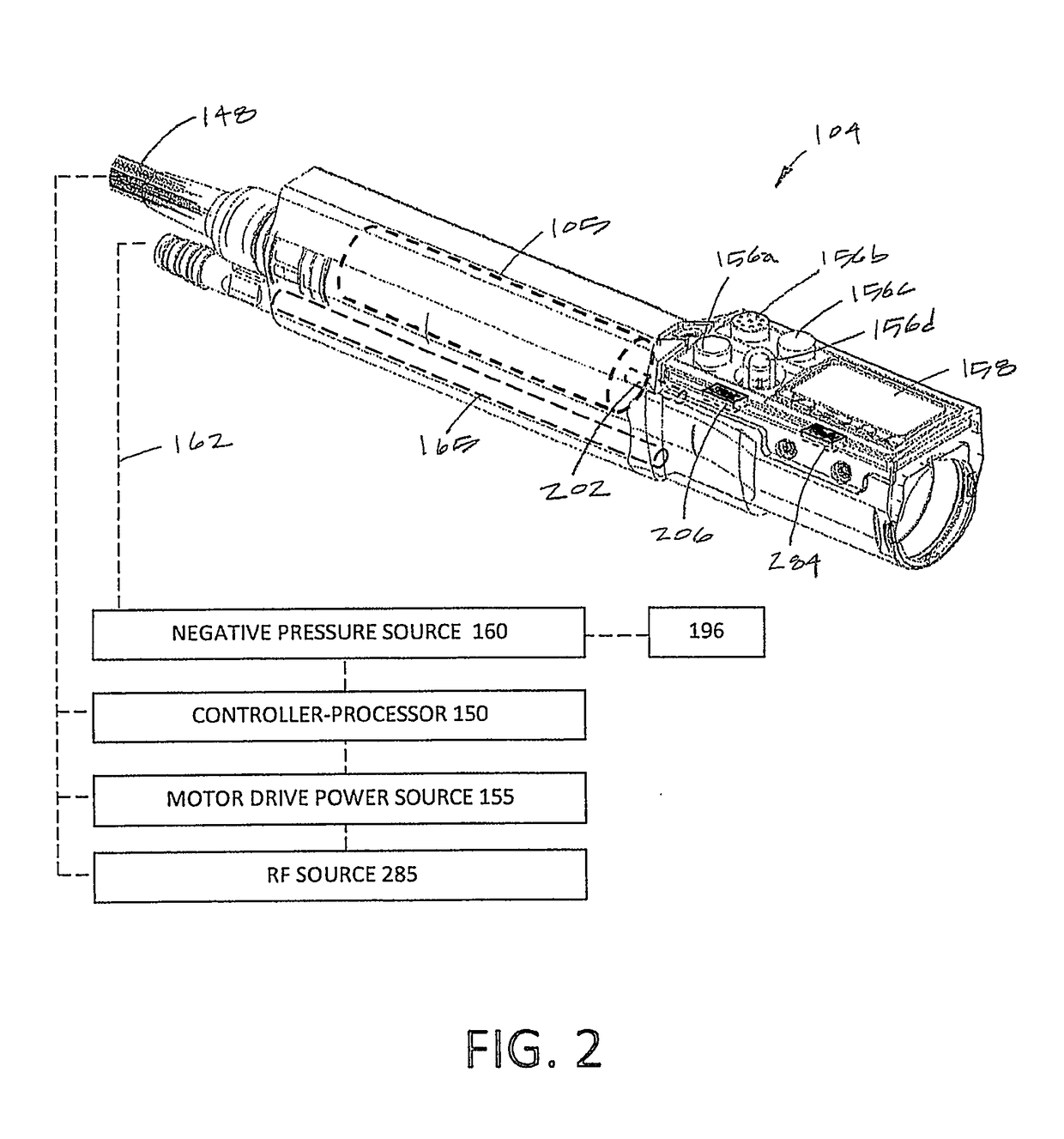
Arthroscopic devices and methods
ActiveUS20200060752A1Inhibit inflammationSurgical instruments for heatingEndoscopic cutting instrumentsRf ablationBone tissue
A medical device includes an elongated sleeve having a longitudinal axis, a proximal end and a distal end. A cutting member having a plurality of sharp edges is formed from a wear-resistant ceramic material is carried at the distal end of the elongated sleeve. A motor drive is coupled to the proximal end of the elongated sleeve to rotate the sleeve at cutting member at high RPMs to cut bone and other hard tissue. An electrode is carried in a distal portion of ceramic cutting member for RF ablation of tissue when the sleeve and cutting member are is a stationary position. In methods of use, (i) the ceramic member can be engaged against bone and then rotated at high speed to cut bone tissue, and (ii) the ceramic member can be held in a stationary (non-rotating) position to engage tissue and RF energy can be delivered to the electrode to create a plasma that ablates tissue.
Owner:RELIGN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com