Extraction method of dietary fiber from sweet potato dregs as well as application thereof in adjusting intestinal flora
A technology for regulating intestinal flora and dietary fiber, applied in food extraction, application, function of food ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution, economic loss, emission, etc., to increase colonization capacity, increase water content, and increase ratio Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Experimental procedures: 1) Shandong Hongba sweet potatoes were purchased from farmers’ markets; 2) Wash the sweet potatoes and cut them into sweet potato pieces with a length, width and height of 5cm; 3) Put the sweet potato pieces and water in a high-speed beater at a weight ratio of 1:2 Crush; 4) After the above-mentioned beating liquid is filtered through two layers of gauze, the residue is collected, which is the sweet potato residue; 5) The sweet potato residue is washed 4 times with tap water to fully remove the residual starch; 6) The sweet potato residue is dried in an oven at 60°C Dry to constant weight; 7) Put the dried sweet potato residue into a pulverizer to pulverize, pass through a 100-mesh sieve, and store at 4°C for later use. The yield of sweet potato residue was 3.7%.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Weigh 1.0 g of sweet potato residue, add 40 mL of MES-TRIS buffer solution (0.05 mol / L, pH 8.2, 24° C.), stir and disperse for 1 hour with a magnetic stirrer. Add 50 μL of α-amylase (3000 U / mL) to remove the starch dissolved in the potato residue, and enzymatically hydrolyze in a water bath at 95°C for 35 minutes. Add 100 μL of protease solution (50 mg / mL), and enzymatically hydrolyze in a water bath at 60 °C for 30 min. Adjust the pH to 4.5 with 3 mol / L acetic acid, add 100 μL amyloglucosidase, and enzymatically hydrolyze in a water bath at 60°C for 30 minutes. After the enzymatic hydrolysis is completed, suction filter and collect the filtrate, wash twice with 70°C pure water (about 10 mL), combine the filtrate, add 4 times the volume of 95% ethanol (60°C), stir while adding, and alcohol precipitation at room temperature for 1 h, Centrifuge (3000rpm, 15min), and the precipitate is sweet potato residue dietary fiber after drying. The yield of sweet potato dietary fib...
Embodiment 3
[0036] 3.1 In vitro model to simulate human digestion process
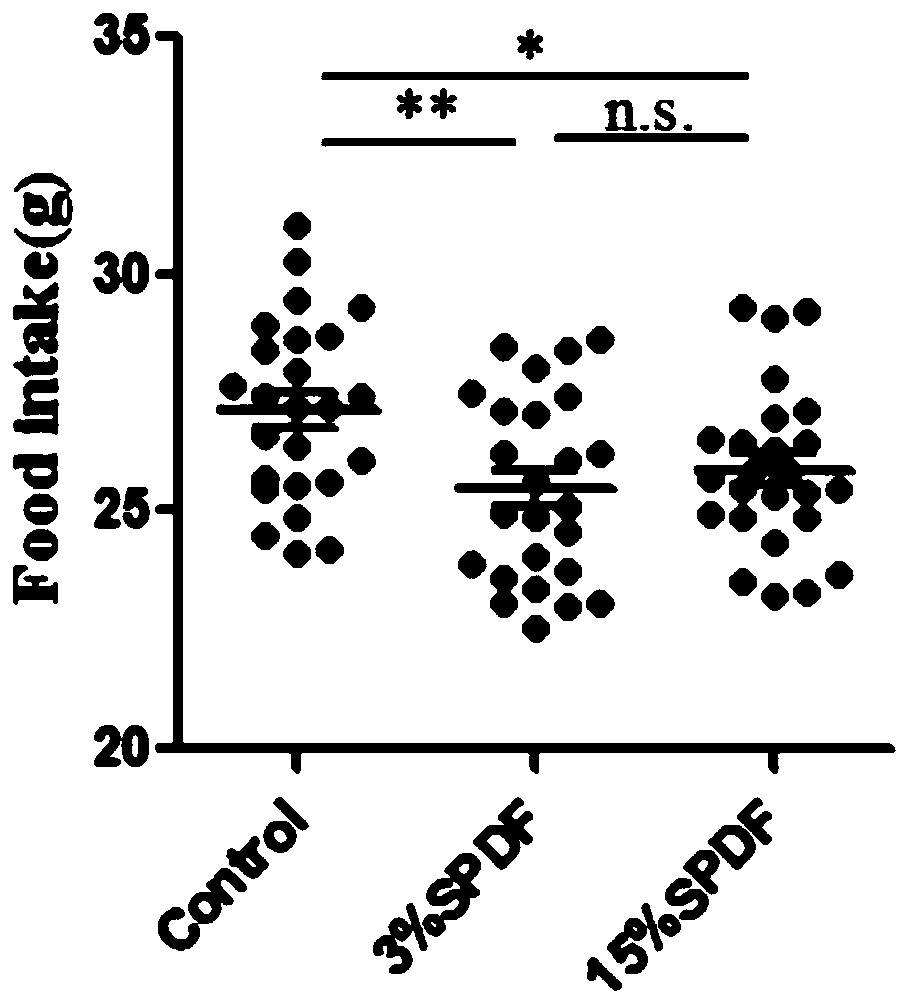
[0037] Accurately weigh 12g of sweet potato dregs dietary fiber and place it in an Erlenmeyer flask, add 200mL of distilled water, stir evenly, add α-amylase, shake the water bath at 37°C for 30min, then adjust the pH to 2.0 with HCl, add 0.54g of pepsin, and Shake in a water bath at 37°C for 2 hours; after the end, adjust the pH to 6.8, add pancreatin and bile, mix well, dialyze, freeze-dry, and store for in vitro simulated intestinal fermentation experiments.
[0038] 3.2 In vitro model to simulate intestinal fermentation process
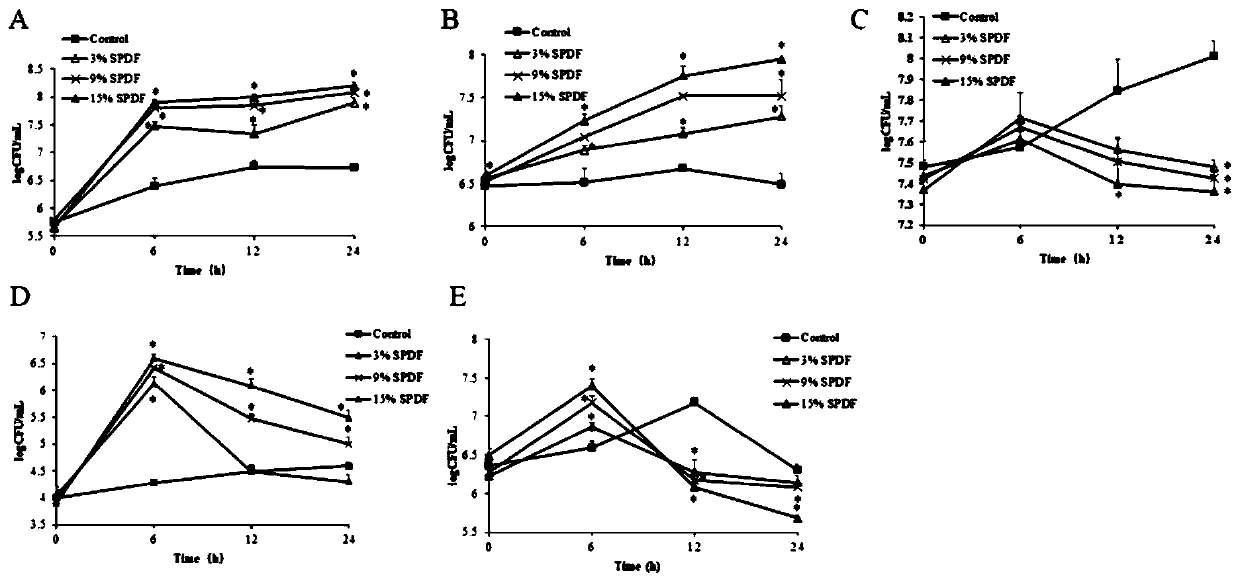
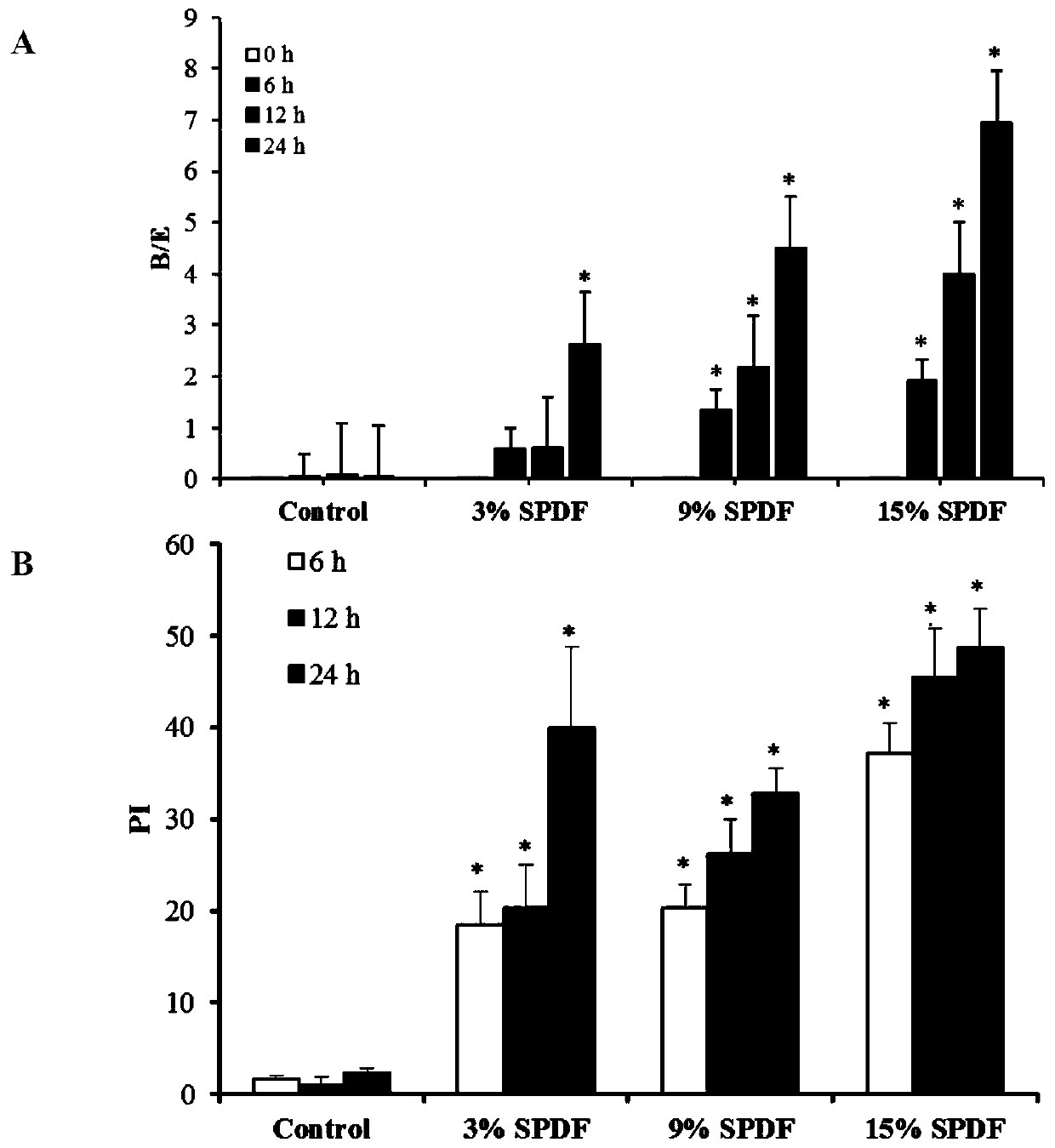
[0039] Add 90 mL of basal medium to a sterile fermentation bottle, and pre-reduce overnight at 37°C in an anaerobic workstation. Rat feces were aseptically collected, put into sterilized EP tubes, and immediately diluted with pre-reduced phosphate buffer saline (PBS, 0.1mol / L, pH7.0) at a ratio of 1:9. Take 10mL of feces dilution and add it to the pre-reduced basal medium, and the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com