Led with scattering features in substrate
A substrate and light scattering technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as reducing the light extraction efficiency of LED dies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
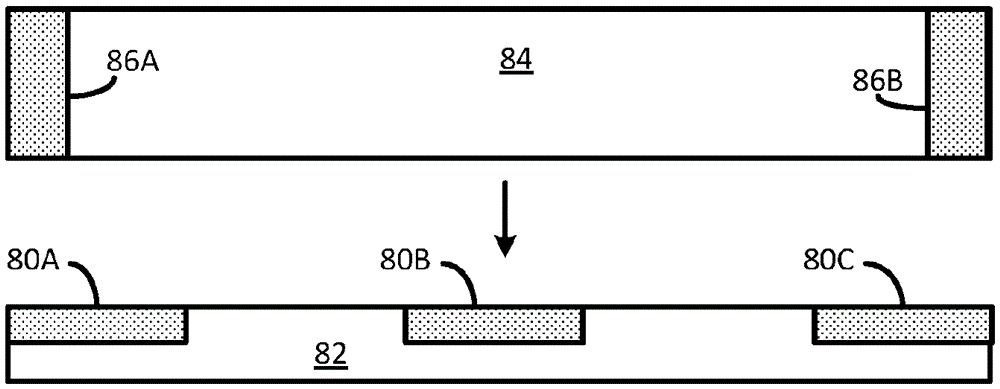
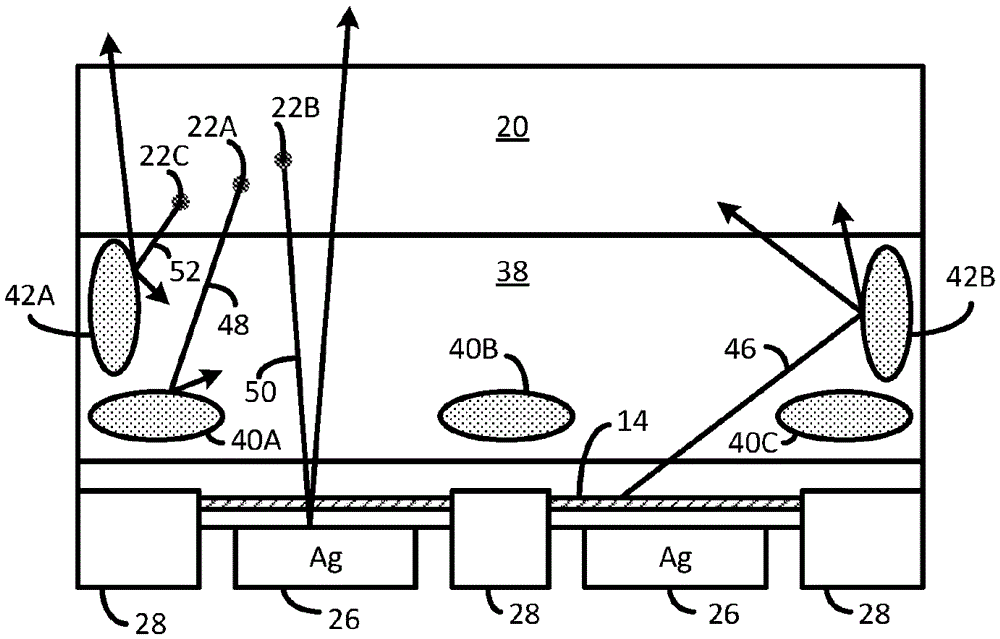
[0023] figure 2 Illustrates that in addition to the substrate 38 can be used with figure 1 The LED die 10 in the same LED36. Substrate 38 may be a growth substrate on which the LED semiconductor has been epitaxially grown, or may be a substrate that has been attached to the LED semiconductor layer after the growth substrate has been removed.
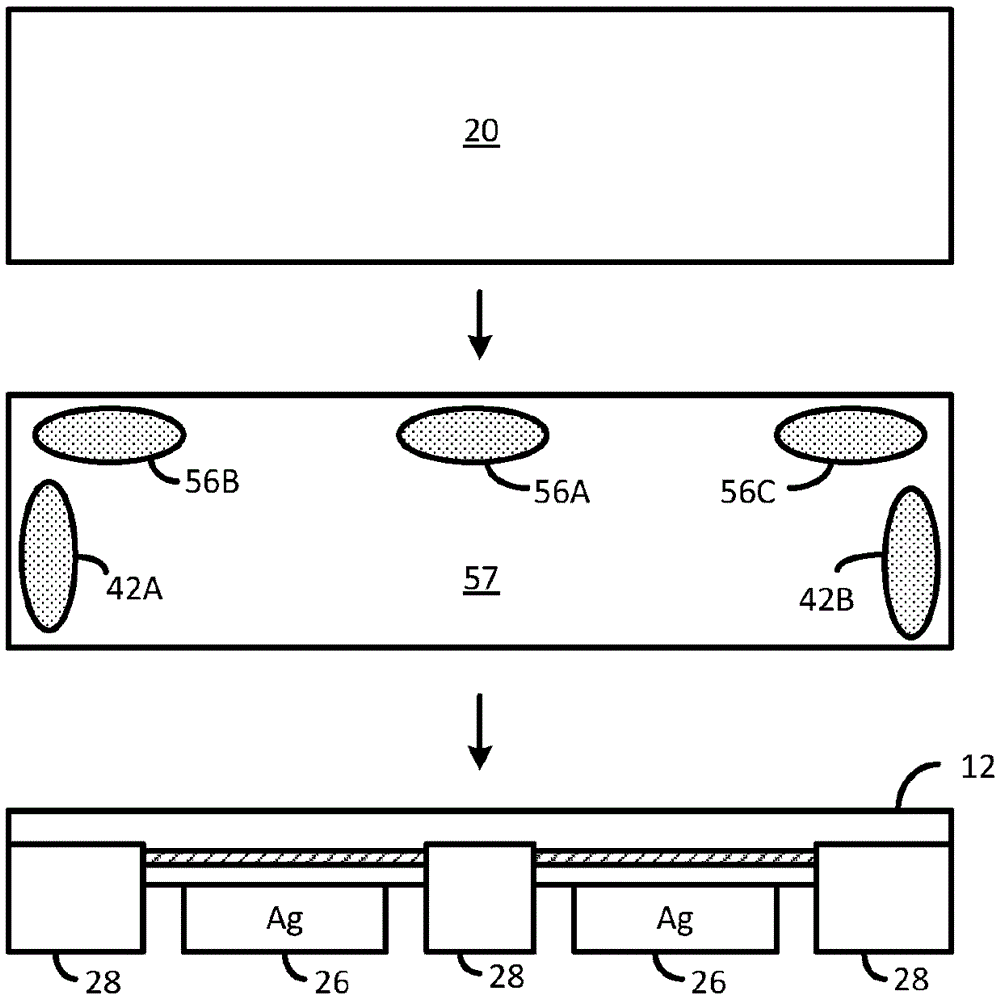
[0024] Substrate 38 is formed with light scattering regions 40A, 40B, and 40C over some or all of the light absorbing regions and with light scattering regions 42A and 42B over some or all of the sidewalls to reduce light guidance within substrate 38 . Scattering regions 42A and 42B may be part of a continuous ring of scattering regions around the sidewalls.
[0025] In one embodiment, substrate 38 is a sapphire growth substrate on which LED semiconductor layers have been epitaxially grown. Scattering regions 40A- 40C, 42A and 42B may be formed as an array of voids before or after growing the semiconductor layer. Scattering regions ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com