Sintering method for neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A sintering method, NdFeB technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inorganic materials, etc., can solve the problems of rare earths being easily oxidized, and the coercive force of magnetic properties is not ideal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Preparation of 38SH Sintered NdFeB
[0079] First, weigh Pr and Nd according to the mass percentage composition: 25.1wt%, Dy: 2wt%, Ho: 4wt%, Al: 0.44wt%, B: 0.94wt%, Cu: 0.15wt%, Co: 1.5wt%, Zr: 0.15wt%, Ga: 0.2wt%, and the rest of Fe, through ingot casting, crushing, grinding, magnetic field orientation, and press molding to obtain the NdFeB green body.
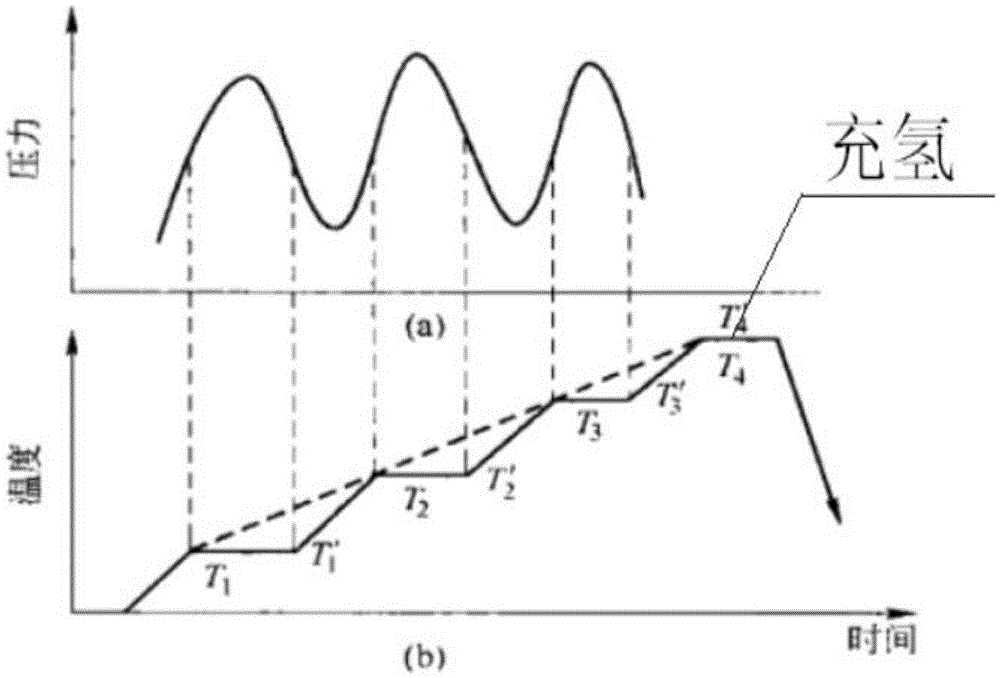
[0080] Then put the green body into the vacuum sintering furnace, evacuate the vacuum to 0.3Pa, and burn the NdFeB magnet green body at 200°C for the first time at a constant temperature for 90 minutes to obtain the first intermediate; then the above steps are obtained After the first intermediate is fired at 500°C for the second time at constant temperature for 60 minutes, the second intermediate is obtained; and the second intermediate obtained in the above steps is fired at 750°C for the third time at constant temperature for 90 minutes to obtain neodymium iron Boron magnet intermediate.
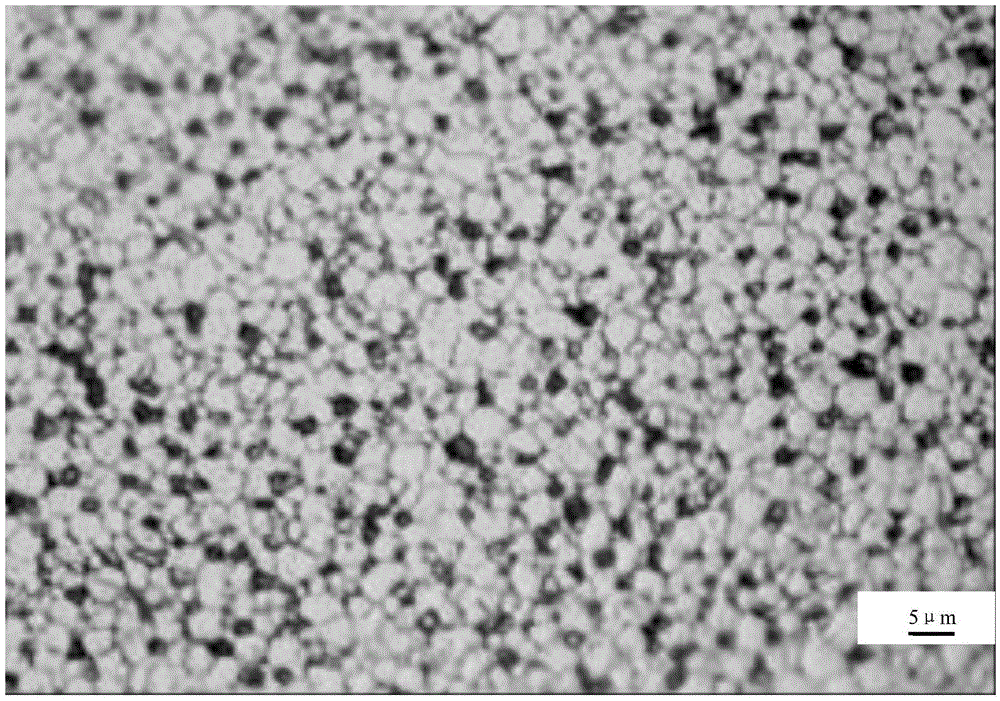
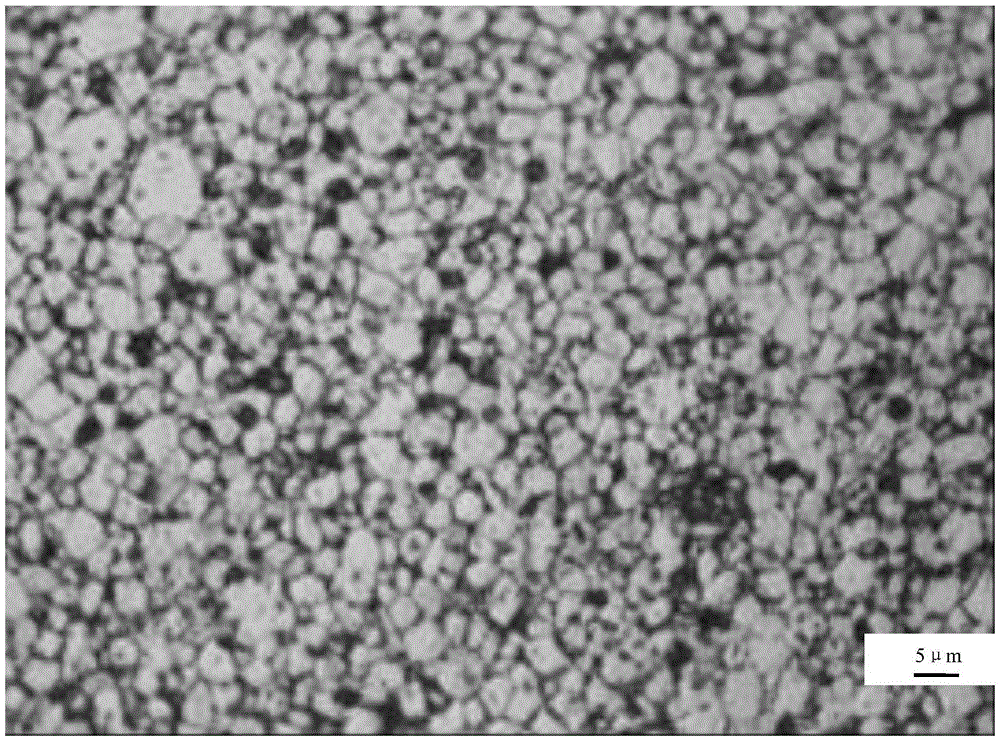
[0081] After the NdFeB...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Preparation of 42SH Sintered NdFeB
[0101] First, according to the 42SH formula, the NdFeB green body is obtained through ingot casting, crushing, grinding, magnetic field orientation, and pressing.
[0102] Then put the green body into the vacuum sintering furnace, evacuate the vacuum until the vacuum degree is less than 0.3Pa, and after the first constant temperature firing of the NdFeB magnet green body at 230 ° C for 70 minutes, the first intermediate is obtained; then the above steps are obtained After the first intermediate is fired at 520°C for the second time at a constant temperature for 80 minutes, the second intermediate is obtained; after the second intermediate obtained in the above steps is fired at a third time at 780°C for 120 minutes, the neodymium iron is obtained Boron magnet intermediate.
[0103] After the NdFeB magnet intermediate obtained in the above steps is subjected to constant temperature liquid phase sintering at 1040 ° C for 30 minutes, t...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Preparation of 52M sintered NdFeB
[0123] First, according to the 52M formula, the NdFeB green body is obtained through ingot casting, crushing, grinding, magnetic field orientation, and pressing.
[0124] Then put the green body into the vacuum sintering furnace, evacuate the vacuum until the degree of vacuum is less than 0.2Pa, and burn the NdFeB magnet green body at 180°C for the first time at a constant temperature for 80 minutes to obtain the first intermediate; then the above steps are obtained After the first intermediate is fired at 480°C for the second time at a constant temperature for 70 minutes, the second intermediate is obtained; after the second intermediate obtained in the above steps is fired at a third time at 790°C for 150 minutes, the neodymium iron is obtained Boron magnet intermediate.
[0125] After the NdFeB magnet intermediate obtained in the above steps is sintered in a constant temperature liquid phase at 1038 ° C for 30 minutes, the above N...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com