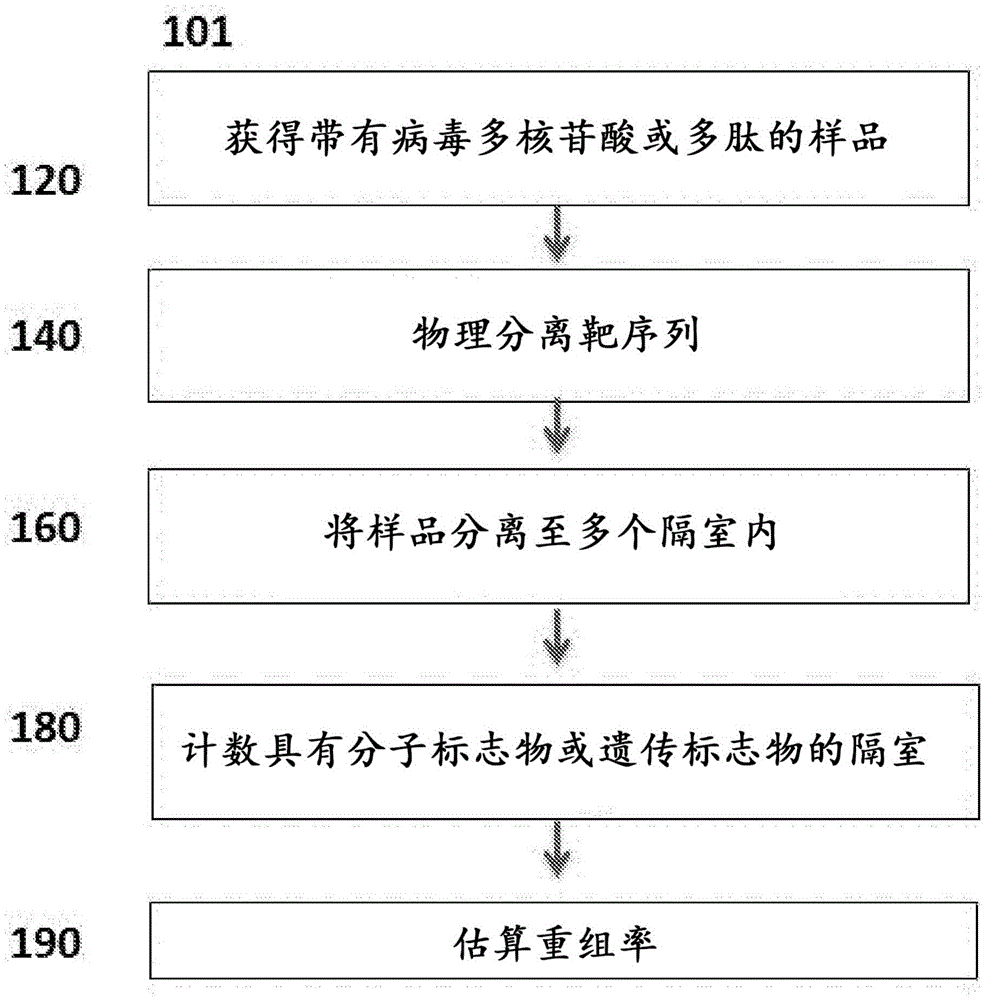
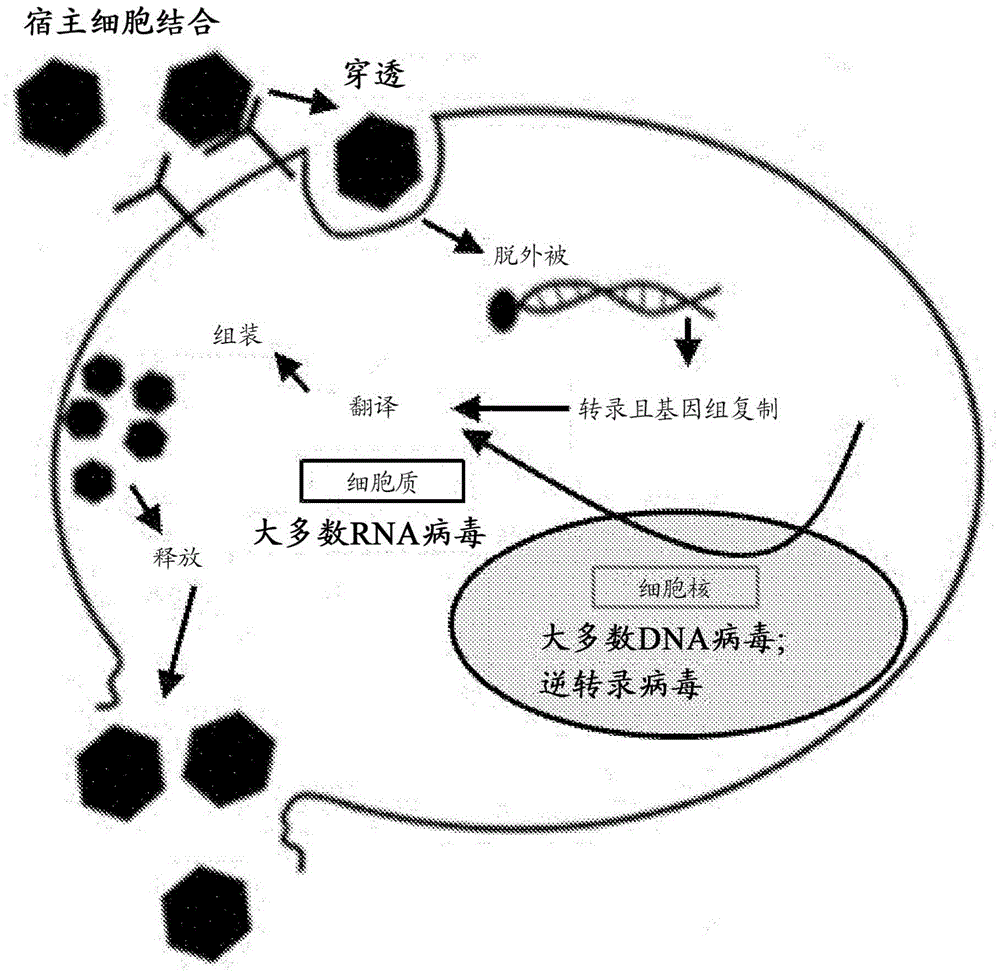
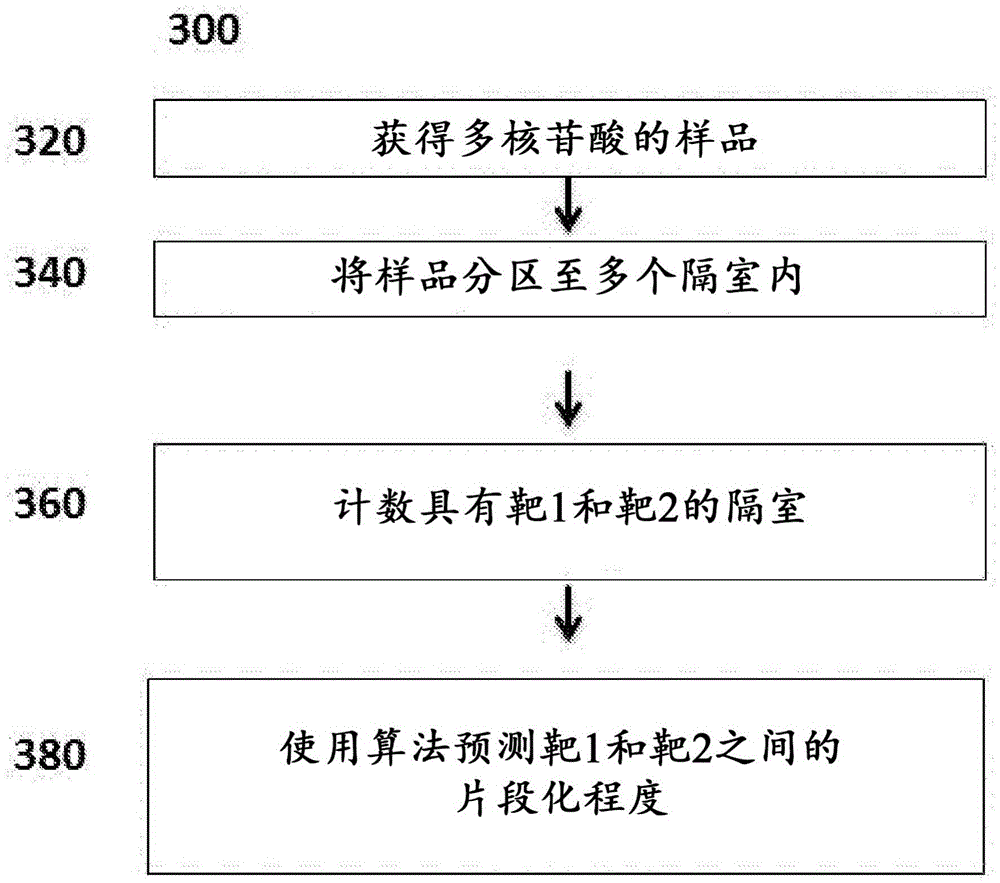
Genetic assays
A sequence and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of virus recombination, which can solve the problems of inaccuracy, time-consuming, and overestimation of the recombination level.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0289] Example 1 - Droplet cluster identification and classification
[0290] Samples may be obtained by swabbing the throat or nose of subjects suspected of being infected with a particularly virulent recombinant strain of influenza virus. Nucleic acids from the sample are extracted, bound to specific probes and / or amplification reagents, and partitioned into aqueous droplets within a water-in-oil emulsion. Virulent strains can be characterized by an A allele at the A / a locus and a B allele at the B / b locus. Primers comprising probes attached to fluorophores are designed to detect the A locus by emitting a signal with a specific color, and the B locus by emitting a signal with a different color. Although the fluorescent probes were designed for one viral allele, they also fluoresced (with reduced intensity) when they cross-reacted with other alleles. For example, a FAM-labeled probe is designed to detect the A allele, and the droplets exhibit four levels of fluorescence: th...
Embodiment 2
[0291] Example 2 - Determining recombination rates in RNA samples
[0292] RNA was taken from blood samples of cells from HIV-infected patients. The sample was partitioned into aqueous droplets in a water-in-oil emulsion. Allele-specific fluorescent probes (FAM; and HEX) were used to detect viral alleles at two distinct loci on the HIV virus. After RT-ddPCR, droplets were positive for one fluorophore, positive for both fluorophores or positive for neither fluorophore depending on the viral allele they contained at the beginning of the reaction. Viral alleles configured in trans partitioned independently into droplets. Viral alleles configured in cis tend to cosegregate into the same droplet because they are physically linked, see Figure 14 . Restriction enzyme digestion at sites between the viral alleles configured in cis abrogates copartitioning of the two viral alleles (not shown). This quantitative difference or ratio between trans-configured and cis-configured viral ...
Embodiment 3
[0293] Example 3 - Determining recombination rates in DNA samples
[0294] DNA is taken from blood samples of cells from HIV-infected patients. The sample was partitioned into aqueous droplets in an oil-water emulsion. Allele-specific fluorescent probes (FAM; and HEX) were used to detect viral alleles at two distinct loci on the HIV virus. After ddPCR, the droplets were positive for one fluorophore, positive for both fluorophores or positive for neither, depending on the viral alleles they contained at the beginning of the reaction. Viral alleles configured in trans partitioned independently into droplets. Viral alleles configured in cis tend to cosegregate into the same droplet because they are physically linked, see Figure 14 . Restriction enzyme digestion at sites between the cis-configured viral alleles abrogates copartitioning of the two viral alleles. This quantitative difference or ratio between trans-configured and cis-configured viral alleles determines the reco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com