Method for recovering intertidal zone salt marsh wetland
A restoration method and intertidal zone technology, applied in the field of restoration of intertidal salt marsh wetlands, can solve problems such as slow results, imperfect wetland ecosystems, unsuitable habitat conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of improving water quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described in detail in conjunction with the following specific embodiments and accompanying drawings. The process, conditions, experimental methods, etc. for implementing the present invention, except for the content specifically mentioned below, are common knowledge and common knowledge in this field, and the present invention has no special limitation content.
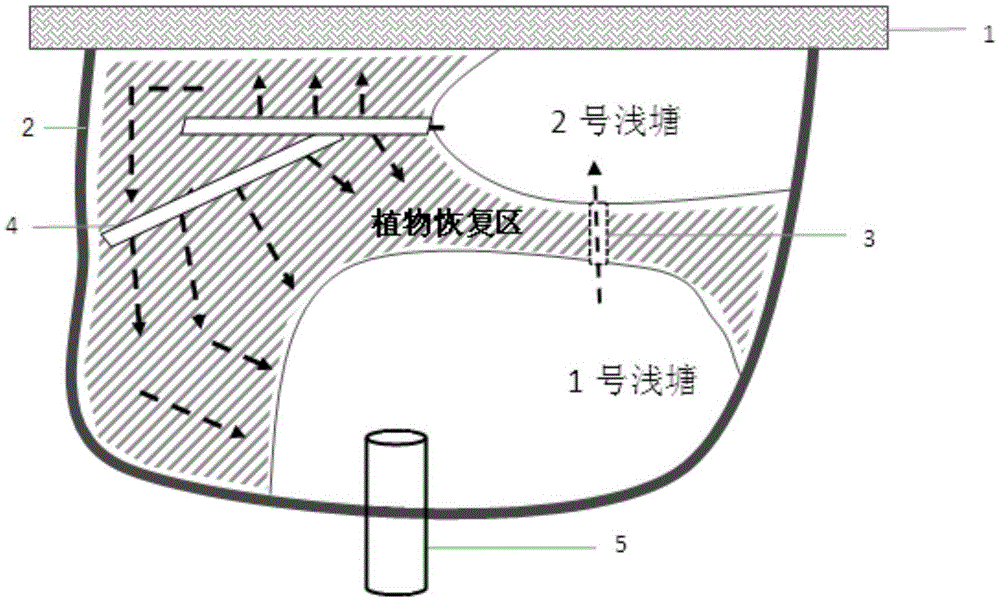
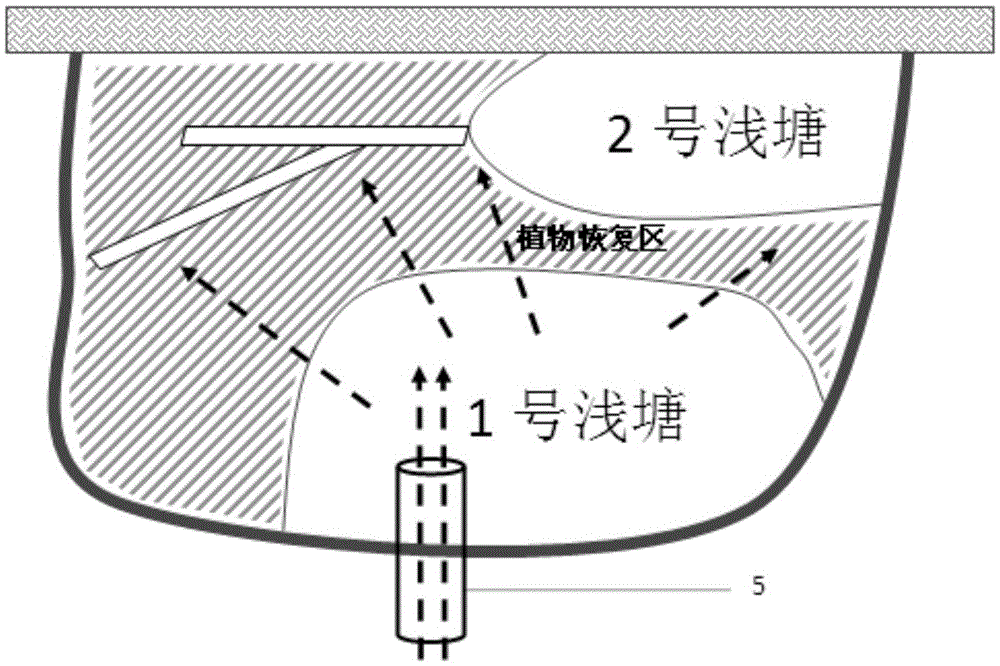
[0028] Such as figure 1 Shown, the recovery method of intertidal zone saline wetland of the present invention comprises the steps:
[0029] Step 1: Find restoration areas suitable for wetland restoration and wetland vegetation growth in the intertidal zone, such as smooth beaches with high bases or original degraded wetlands;
[0030] Step 2: Build an ecological dam 2 on the outer edge of the restoration area (such as between the restoration area and the external sea area) to protect the beach and prevent the loss of the wetland base; install a culvert 5 under the ecologi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com