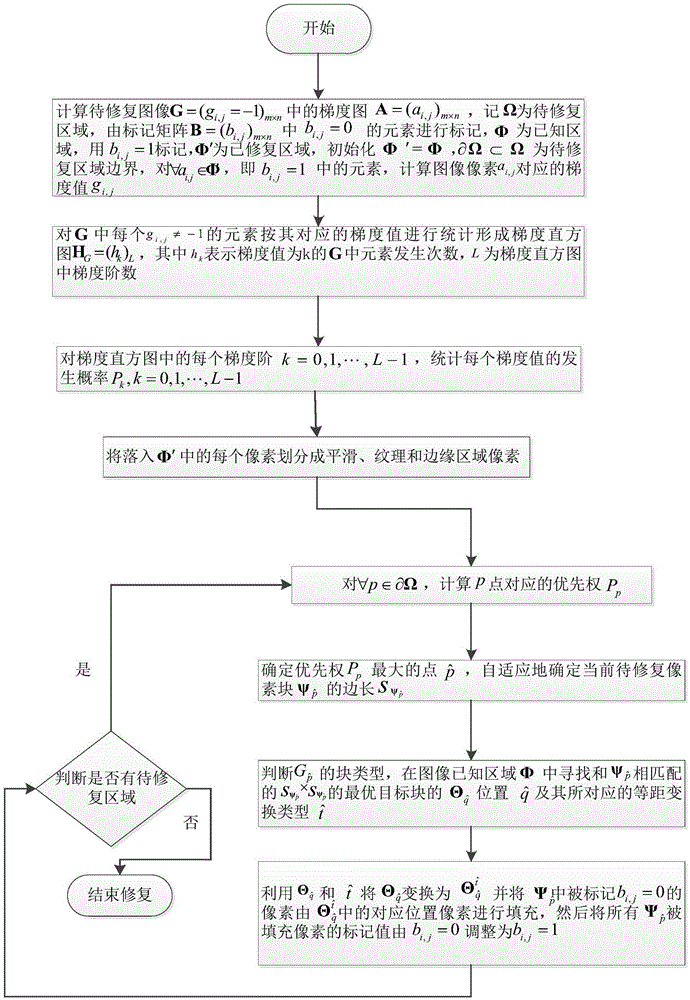
[0005] ①The priority model of the Criminisi method is designed as the product of the confidence item and the data item. With the continuous filling of the patch, the confidence item drops sharply and tends to zero value after multiple iterations, but the data item keeps changing smoothly, which leads to Data items are subject to a confidence term that tends to zero, making the priority calculation unreliable, thus leading to wrong filling order, which affects the quality of
image restoration;
[0006] ②The Criminisi method does not analyze the information of the block to be repaired in detail, which may lead to unreliable calculation of the priority, and it is easy to mistake the texture part for the edge part, causing the image block originally belonging to the texture part to be repaired first, so that the texture extension affects the final image repair quality;
[0007] ③The Criminisi method looks for suitable matching blocks in all areas of known information in the entire image, while ignoring the local self-similarity of the natural image itself, which will bring high matching calculation costs;
[0008] ④The Criminisi method only uses the
Euclidean distance between blocks, and there is a lack of direct matching, which will lead to inaccurate similarity measurement, and cause the directly matched target block to be not the best target block, thus affecting the quality of image restoration
[0010] For problem ②, the literature (Ren Shu, Tang Xianghong, Kang Jialun. Criminisi
improved algorithm using texture and edge features [J]. Chinese Journal of Image and
Graphics, 2012, 17(9): 1085-1091.) by treating the repair block has been Find the mean and variance of the known pixels, use their normal direction to segment the block to be repaired, and use the two factors of
mean difference difference and variance difference to distinguish the texture edge of the image block to be repaired, and then introduce the difference factor to improve the priority The model overcomes the texture extension in the restoration process, but still cannot solve the restoration
distortion caused by the absence of suitable matching blocks, and the unreasonable classification of the edge texture of the block to be repaired; in order to solve the restoration
distortion caused by the existence of inappropriate matching blocks Problem, literature (Ren Shu, Tang Xianghong, Kang Jialun. Image inpainting
algorithm combining texture and edge features [J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design and
Graphics, 2013, 25(11): 1682-1693.) on the process of inpainting The poor matching area is located, and the image
repair method based on image
decomposition is used for repair; but these two articles use the
mean difference and variance difference to judge the image block to be repaired when judging the edge texture information of the image block to be repaired. The texture edge is distinguished, and all the information in the known area of the image is not divided. When matching the best target block of the block to be repaired, the information of the block to be repaired is not classified and searched, so the matching calculation cannot be effectively reduced. cost
[0011] For problem ③, in order to reduce the calculation cost, literature (Ren Shu, Tang Xianghong, Kang Jialun. Improved Criminisi
algorithm using texture and edge features [J]. Chinese Journal of Image and
Graphics, 2012, 17(9): 1085-1091.) Adjust the search method of the matching block in the restoration process. On the basis of the global search, add a search condition to judge the distance between the center of the two image blocks between the block to be repaired and the target matching block. If the distance is too large, stop the repair. Change the repair target to a sub-priority repair block. If the same situation still occurs, continue to transfer the repair target, and the number of transfers is up to 3 times. After 3 times, ignore this condition and perform a matching search according to the original search method. In terms of efficiency It has been improved, but the global search is still used, and the
time complexity is high; in order to change the global search to local search, literature (Dai Shimei, Zhang Hongying, Zeng Chao. A fast image restoration
algorithm based on examples[J] .
Microcomputer and Applications, 2010(22):34-36.) Improve the efficiency of the method by reducing and limiting the search space of matching blocks. Although the calculation cost is alleviated, the simple search space will lead to the loss of reasonable matching blocks, thus Reduce the visual repair quality of the image
However, when searching for the
best matching block, the above
repair method does not take into account the problem that the target block after
equidistant transformation may have a higher similarity with the sample block
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More