Device for automatically detecting two-dimensional morphology of wafer substrate
An automatic detection and chip technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems affecting consistency, system error, and complex structure of light-passing devices, and achieve simple structure, consistency assurance, and high coating accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] For ease of understanding, Embodiment 1 of the present invention only provides one of the light beams in the first direction and the light beam in the second direction.
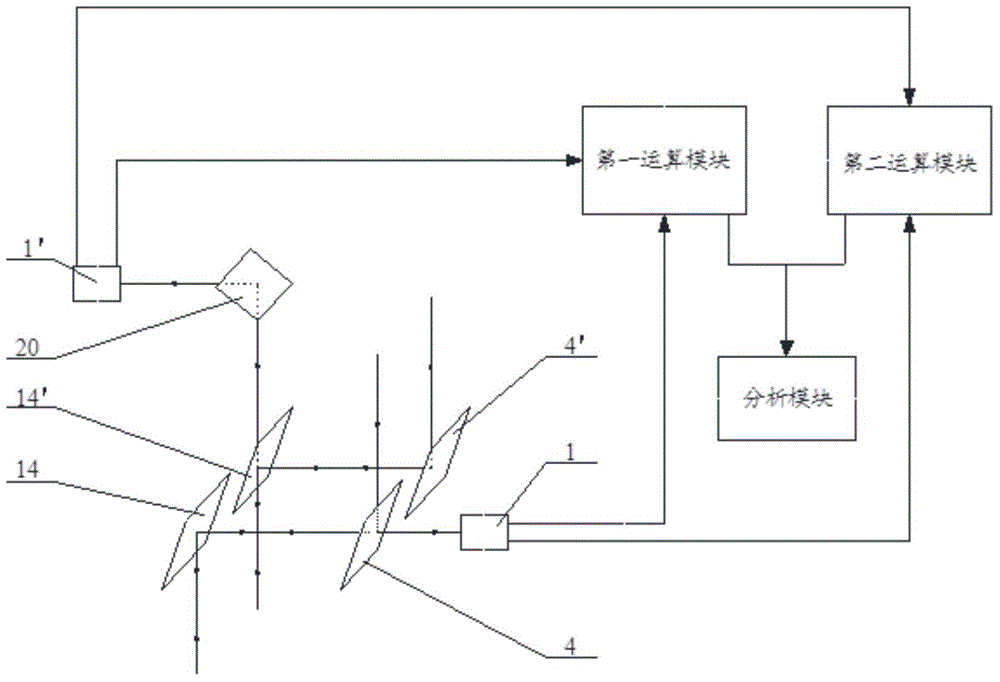
[0025] See attached figure 1 The device for automatically detecting the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided by the present invention includes N PSDs 1 or 1', N beams of the first type of laser light, and N first beam splitters 4 or 4 corresponding to the N beams of the first type of laser light one-to-one. ', N second beam splitters 14 or 14' corresponding to the N beams of the first laser one-to-one, the first computing module, the second computing module and the analysis module, the N beams of laser light are arranged along a straight line, wherein N is 3 The above natural numbers, N PSD1 or 1' correspond to N beams of lasers one by one, and N PSD1 or 1' are respectively arranged on the left and right sides of N beams of lasers, including left PSD1' and right PSD1;
[0026] Ea...
Embodiment 2
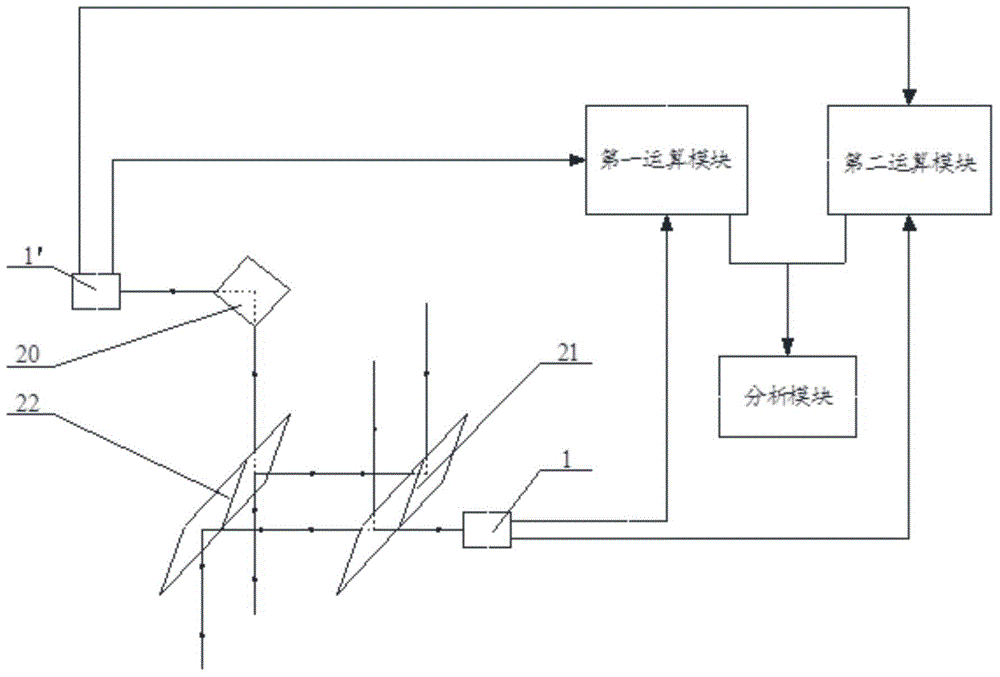
[0062] See attached figure 2 The difference from the device for automatically detecting the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention is that in the device for automatically detecting the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided in the embodiment of the present invention, the N beams of lasers are used one by one The corresponding N first beam splitters 4 or 4' and / or the N second beam splitters 14 or 14' corresponding to the N beams of laser light are respectively integrated into one piece, and figure 2 Among them, N first light splitters are integrated into one piece, and the label is 21, and N second light splitters are integrated into one piece, and the number is 22; corresponding to the area of the light beam in the first direction, the coating of the first light splitter 21 makes it in ( The reflectance in the wavelength range of λ-10nm, λ+10nm) is 50%, corresponding to the area of the ligh...
Embodiment 3
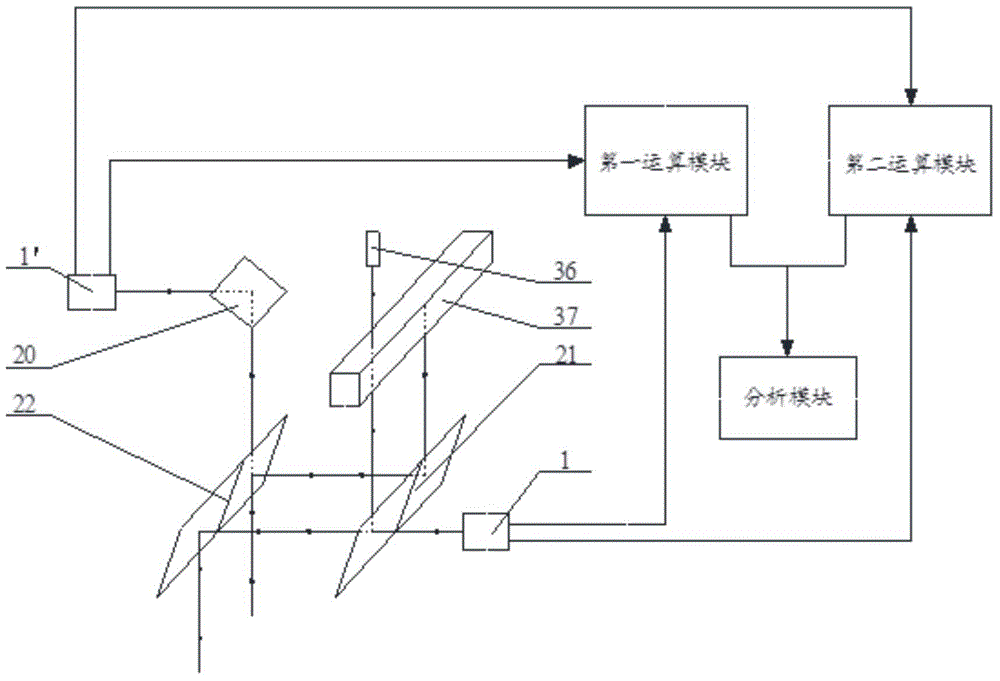
[0069] See attached image 3 And attached Figure 7 , the difference from the device for automatically detecting the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided in the second embodiment of the present invention is that in the device for automatically detecting the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided in the third embodiment of the present invention, the N beams of laser light are composed of a plurality of issued by the laser emitting device.
[0070]The multi-channel laser emitting device includes a multi-channel beam splitting prism 37 and a laser 36. The multi-channel beam splitting prism 37 includes a plurality of beam-splitting surfaces parallel to each other, and the included angle α between the multiple beam-splitting surfaces and the horizontal direction is 45° respectively. The centers of the multiple beam-splitting surfaces are on the same straight line, and the laser light emitted by the laser 36 is directed to one of the outerm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com