Tea making device that can degrade residual pesticides
A technology for pesticide residues and tea water, which is applied in water/sewage multi-stage treatment, separation method, multi-stage water treatment, etc., can solve the problem of ineffective washing of pesticide residues in tea leaves, and achieve the effect of reducing toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
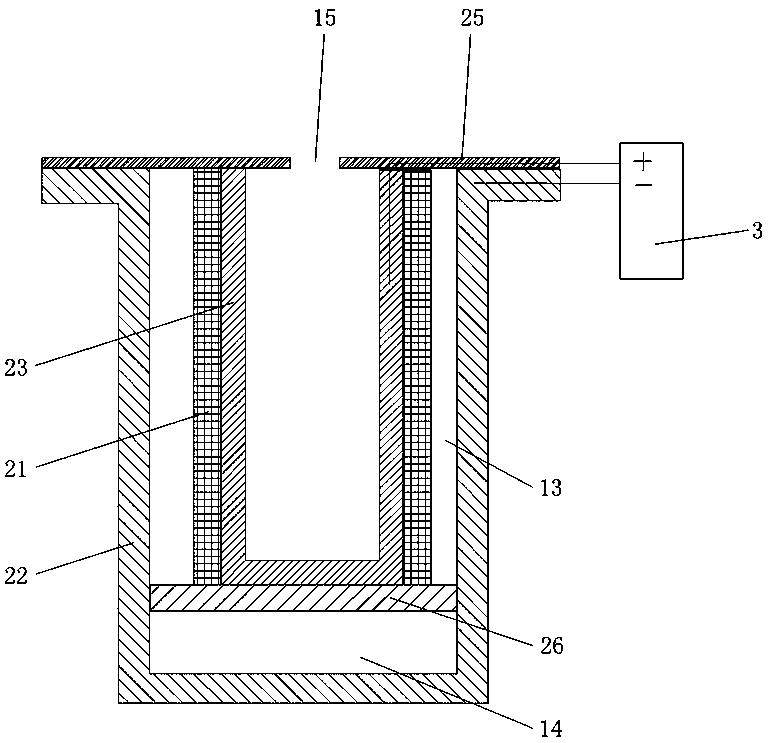
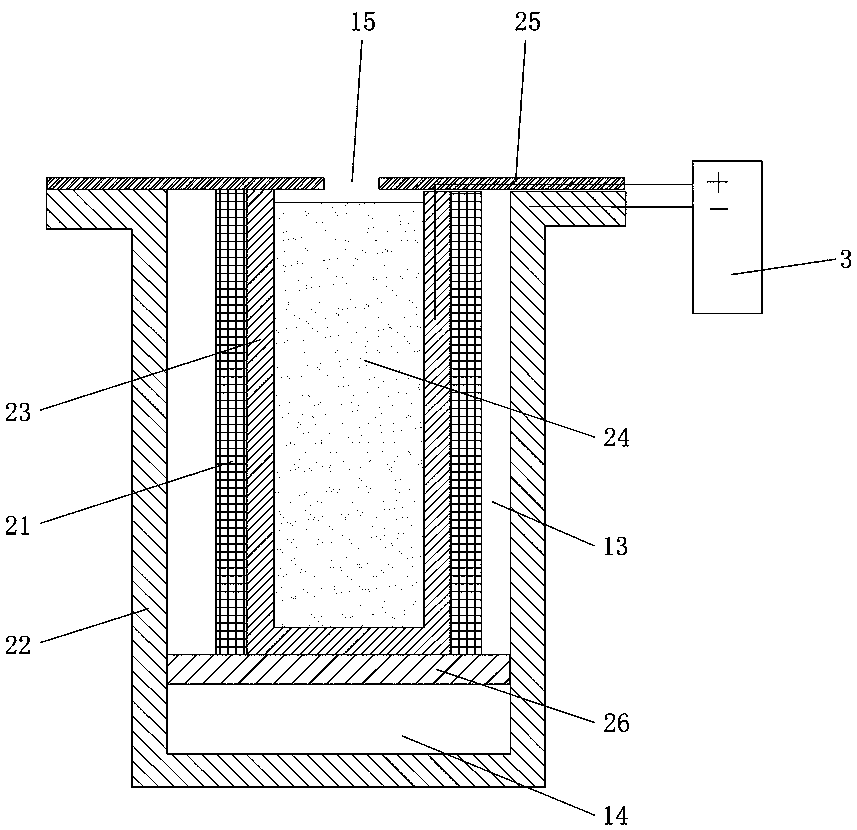
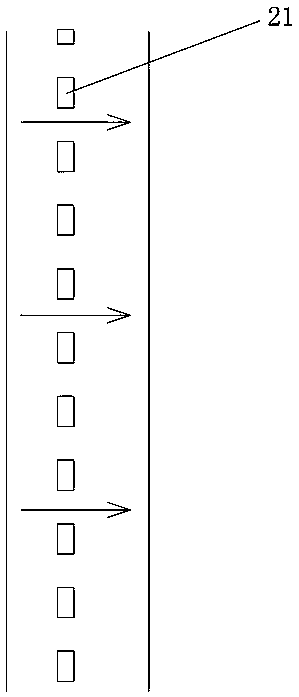
[0061] The tea-making device of the present embodiment that can degrade residual pesticides, see figure 1 , including a pair of cathode electrodes 22 and anode electrodes 23, an electrolysis power supply and an insulating frame 25 for supplying power to the cathode and anode electrodes. A water-permeable diaphragm 21 is provided between the cathode and anode electrodes.
[0062]Both the cathode electrode 22 and the anode electrode 23 are cylindrical electrodes fixed on the insulating frame 25. The cathode electrode 22 is formed with a mesh, and a separator is arranged inside the cathode electrode 22, and the interior of the cylindrical cathode electrode is divided into an upper cavity by the separator. Chamber 13 and lower chamber 14 for placing tea leaves. The positive electrode 23 is disposed in the upper chamber 13 . The water-permeable diaphragm 21 is fully covered on the outer surface of the anode electrode 23 . When in use, the negative electrode 22 is immersed in the...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The tea making device of this embodiment that can degrade residual pesticides is an improvement on the basis of Embodiment 1, and the difference from Embodiment 1 is:
[0085] In this embodiment, the kettle body is manually filled with tap water. Still taking the city supply tap water in Dalian, China as an example, the electrolytic power supply adopts an alternating pulse power supply with a forward voltage level greater than a reverse voltage level. The average voltage is 15V, and the water is permeable. The positive diaphragm 21 adopts a microfiltration membrane, and the distance δ between the microfiltration membrane and the anode electrode 23 located outside the membrane is 15 millimeters.
Embodiment 3
[0087] The tea-making device of this embodiment that can degrade residual pesticides is an improvement on the basis of Embodiment 1. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, there are several holes on the positive electrode 23 located on the outside of the water-permeable diaphragm 21. Through holes, the water-permeable diaphragm 21 adopts a nanofiltration membrane.
[0088] In this embodiment, the municipal tap water in Dalian, China is still taken as an example, and the distance δ between the water-permeable diaphragm 21 and the anode electrode 23 located outside the diaphragm is 0 mm and 10 mm, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com