Priori knowledge based microblog user group division method
A technology of user groups and prior knowledge, applied in the field of social networks, can solve problems such as high complexity, poor algorithm accuracy, and inability to define when to stop, and achieve stable performance, improved accuracy, and efficient detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The above-mentioned features and advantages of the present invention will be described in more detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
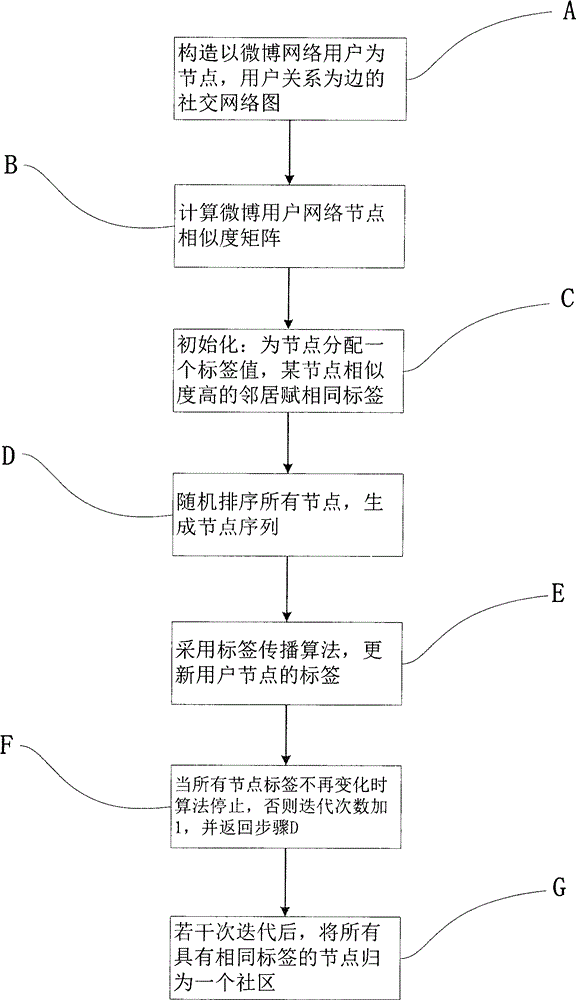
[0035] figure 1 It is an implementation flowchart of a microblog user group division method based on prior knowledge of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0036] Step A: read social network data, and construct a social network graph with social network users as nodes and user relationships as edges.
[0037] For example, in a social network such as Weibo, each user is regarded as a node in the network, and users with the same characteristics or opinions are regarded as an edge of the network. As a result, many communities with the same characteristics have been formed, which is of great significance to the monitoring of public opinion on the Internet; on the World Wide Web, if you know a small amount of information about some web pages, you can f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com