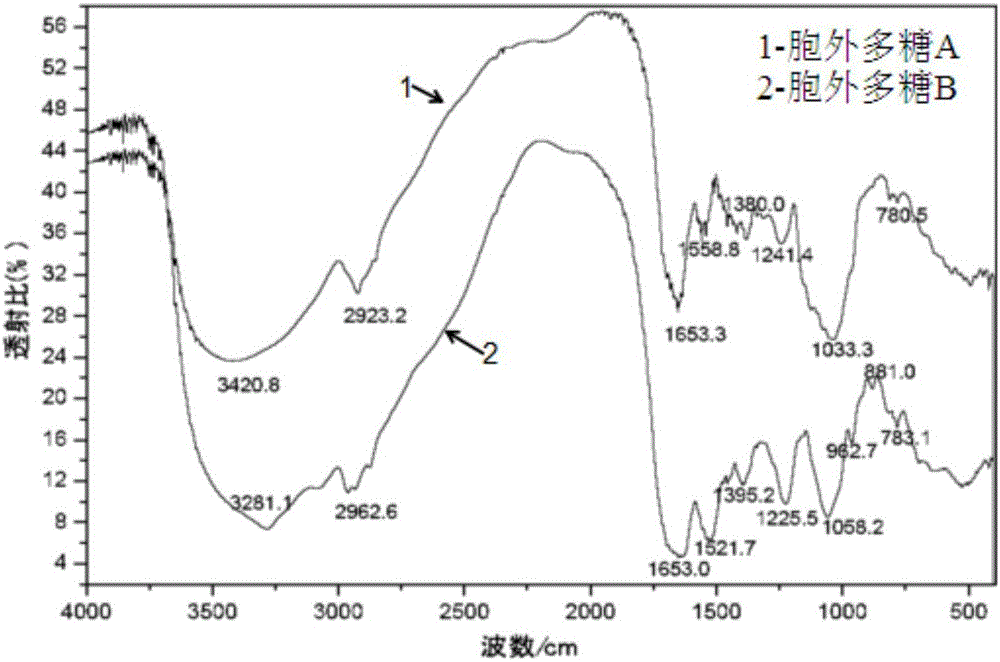
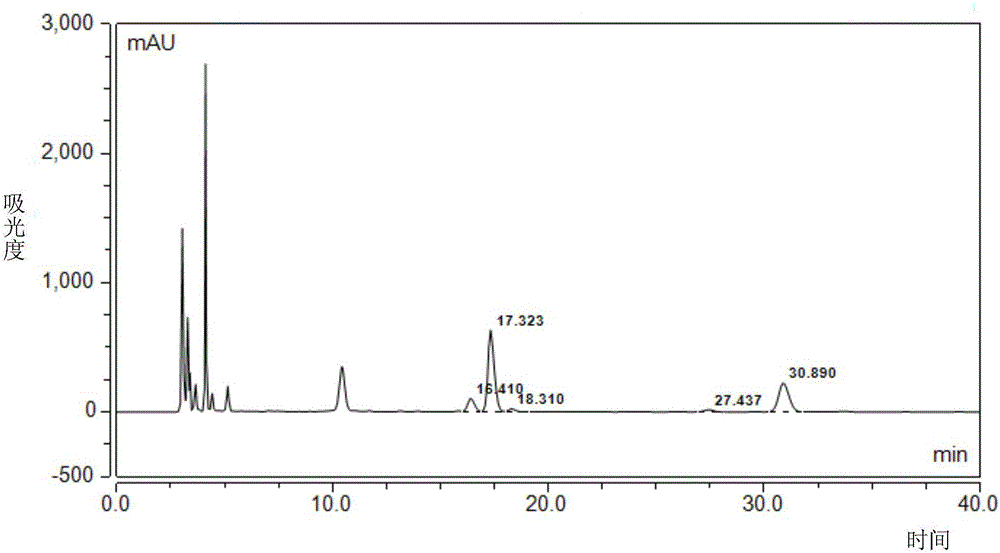
Method for extracting and isolating clostridium acetobutylicum exopolysaccharide
A technology of Clostridium acetobutylicum and extracellular polysaccharide, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems that the research on the biofilm of Clostridium acetobutylicum is still in its infancy and has little research, and achieves the effects of low cost and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
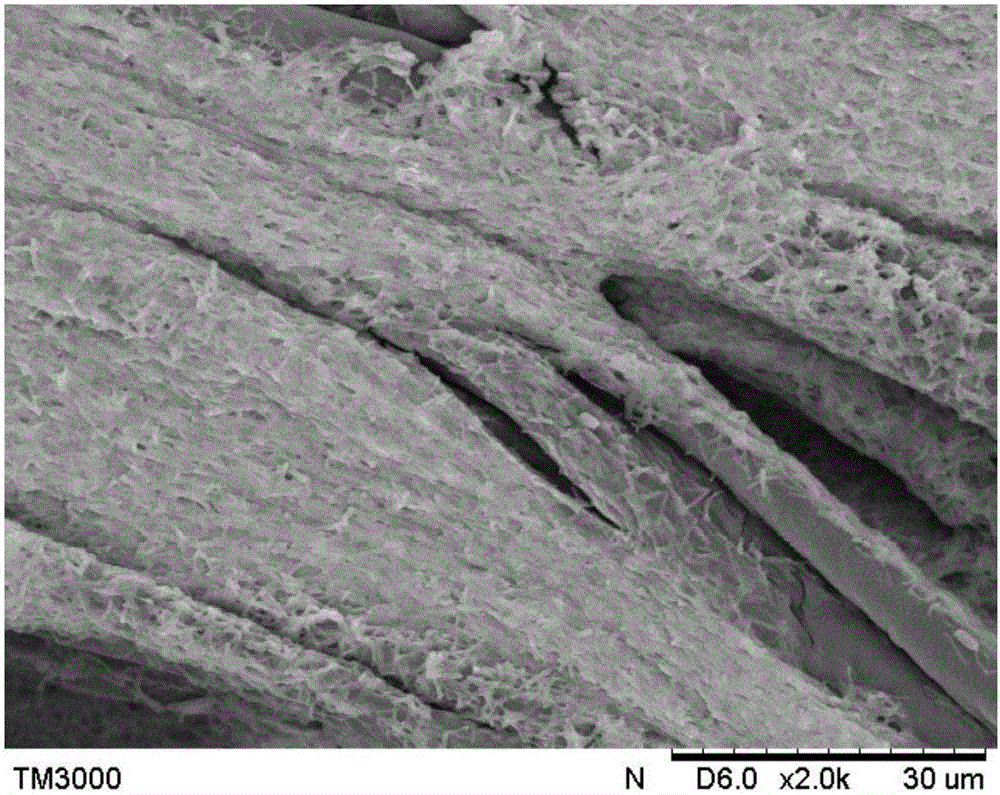
[0030] Inoculate 200ml of the cultured Clostridium acetobutylicum (Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824) seed liquid into an anaerobic fermenter equipped with 1.8LP2 fermentation broth, and place about 60 grams of fixed The immobilized material was cultured at a constant temperature of 37°C, and the culture was repeated for 12 batches, and each batch was cultivated for 12 hours. A thick layer of Clostridium acetobutylicum biofilm would grow on the surface of the immobilized material.
[0031] The cultivated biofilm was washed twice with ultrapure water to remove free bacteria and residual fermentation broth on the surface of the biofilm. The cultured biofilm was collected and centrifuged at a high speed (10000rpm, 10min, 4°C) to obtain a biofilm with a volume of about 50ml.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Take 12 5ml centrifuge tubes, labeled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, add 1ml of biofilm respectively, then add 0.075mol / L, 0.1mol / L, 0.125mol / L three concentrations of NaOH solution, Na 2 CO 3 Each 1ml of solution and EDTA solution was shaken for 1h, and the dissolution situation was observed (dissolution rate=10000rpm centrifugation after precipitation volume / volume of initial biofilm), as shown in the following table:
[0034] Table 1 Dissolution of biofilm under different concentrations of different solutions
[0035]
NaOH solution
Na 2 CO 3 the solution
NaHCO 3 the solution
0.075mol / L
70%
40%
20%
50%
0.1mol / L
100%
45%
30%
60%
0.125mol / L
100%
45%
35%
65%
[0036] As shown in Table 1, the effect of dissolving biofilm with 0.1 mol / L NaOH is the best, and the dissolution rate reaches 100%, so 0.1 mol / L NaOH is finally chosen to dissolve biofilm.
[0037] Ta...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Take a 50ml centrifuge tube, add 10ml of biofilm, then add 20ml of 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, oscillate to completely dissolve the biofilm, and centrifuge at high speed to remove the sediment of the lower layer of bacteria, and collect about 28ml of supernatant 1.
[0040] Take nine 10ml centrifuge tubes, draw about 2ml of the above supernatant 1, slowly add 1.6ml, 3ml, 6ml of absolute ethanol, acetone and butanol respectively, shake evenly, the solution becomes turbid and precipitates, and centrifuge at a high speed (10000rpm , 10min, 4°C) to obtain a precipitate, that is, exopolysaccharide A, freeze-dry and measure the dry weight, as shown in the following table.
[0041] The dry weight of the polysaccharide precipitated under different concentrations of different solvents in table 2
[0042]
45%
14.3mg
8.5mg
7.2mg
60%
21.6mg
9.6mg
8.3mg
75%
21.5mg
10.3mg
9.8mg
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Relative molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com