External rotor alternating current (AC) independent excitation permanent magnet reluctance motor
A reluctance motor and outer rotor technology, applied to synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, electric components, magnetic cores/yokes, etc., can solve problems affecting the magnetic stability of permanent magnet salient pole pairs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
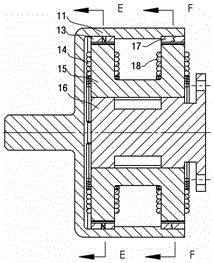
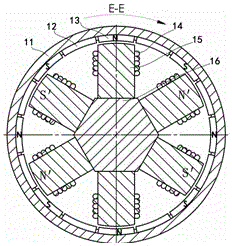
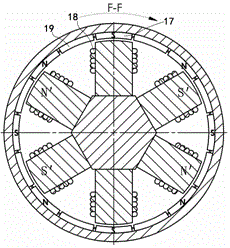
[0071] The structure of this embodiment is as attached Figure 1-5 shown.
[0072] Sixteen permanent magnets are arranged in pairs. Each group of permanent magnets is arranged on the inner wall of the rotating magnetic conduction cylinder 11 along the axial direction of the motor. Each group of permanent magnets forms a permanent magnet unit through the magnetic conduction cylinder 11 . as attached figure 1 middle. The permanent magnet 13 passes through the magnetic cylinder 11 . Together with the permanent magnet 17, a permanent magnet unit is formed. Eight sets of permanent magnet units are symmetrically arranged on the inner wall of the rotating magnetic cylinder. Sixteen magnetizers 12, 19 are in pairs. Each group of magnetizers is also arranged on the inner wall of the rotating magnetizer cylinder 11 along the axial direction of the motor. Each group of magnetizers forms a magnetizer unit through the magnetizer cylinder. The eight groups of magnetizer units are b...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The structure of this embodiment is as attached Figure 6-10 shown.
[0081] The structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the first embodiment. The difference is just that. The locations of the excitation coils wound around the periphery of the laminated iron core of the exciter unit are different.
[0082] The operating mechanism and torque formation of this embodiment are the same as those described in Embodiment 1. The description is not repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0084] The structure of this embodiment is as attached Figure 11 And attached Figure 12 shown.
[0085] The rotor support in this embodiment is disc-shaped. Twelve permanent magnets and twelve magnetizers take the axis of the rotating shaft as the axis of symmetry. Inner rings and outer rings are alternately arranged on one side of the magnetic conduction disk 37 . The intervals between the inner ring permanent magnets 38 and the magnetizers are equal. The intervals between the outer ring permanent magnets 36 and the magnetizers 39 are also equal. Due to the magnetic conduction disc 37 conducts magnetism. The inner ring permanent magnet 38 and the outer ring permanent magnet 36 arranged on the same radial line form a permanent magnet unit. The N pole surface of the inner ring permanent magnet 38 is close to the magnetic conduction disk 37 , the S pole surface of the outer ring permanent magnet 36 is close to the magnetic conduction disk 37 , and the magnetic polarities...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com