Railway vehicle axle heat-treatment technology for full pre-annealing by use of residual forging heat
A complete annealing technology for railway vehicles, applied in heat treatment furnaces, heat treatment equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems that are difficult to eliminate, achieve the effects of reducing unqualified grain size, reducing production costs, and preventing fatigue fracture of axles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A heat treatment process for a railway vehicle axle that utilizes forging waste heat to carry out complete annealing in advance, comprising the following steps:
[0026] (1) When the axle steel of railway vehicles is forged, the final forging temperature is ≥750°C. After the final forging, the axle is placed in a heat treatment furnace at 790±10°C for complete annealing, and cooled to 400°C with the furnace at 30-40°C / h The following are out of the oven and air-cooled.
[0027] (2) Normalize the axle after complete annealing in step (1) at 810°C±10°C, and keep it warm for 3-3.5 hours.
[0028] (3) Temper the axle after normalizing in step (1) at 510°C±10°C, and keep it warm for 4-4.5 hours.
Embodiment 2-10
[0029] Embodiment 2-10, comparative example 1-3
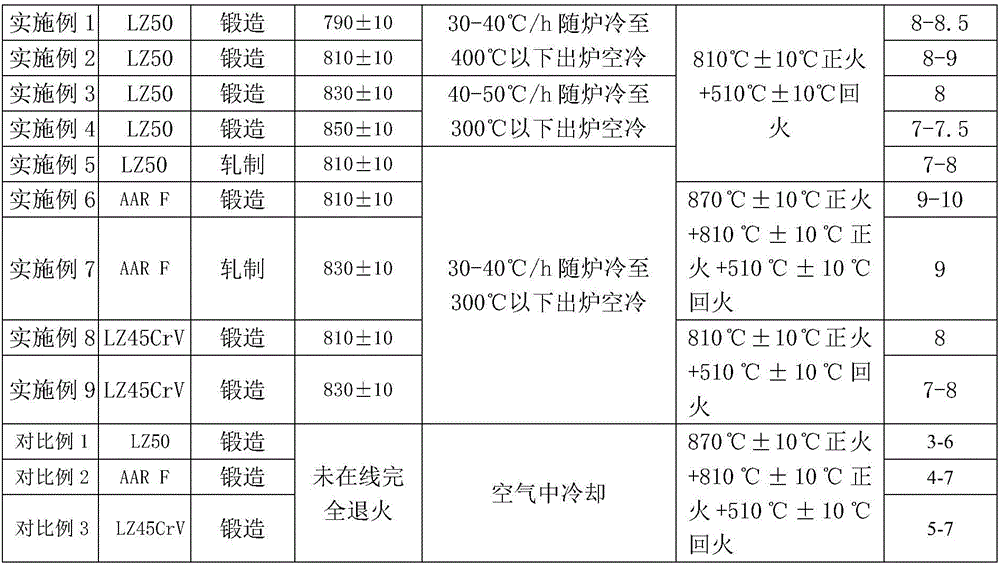
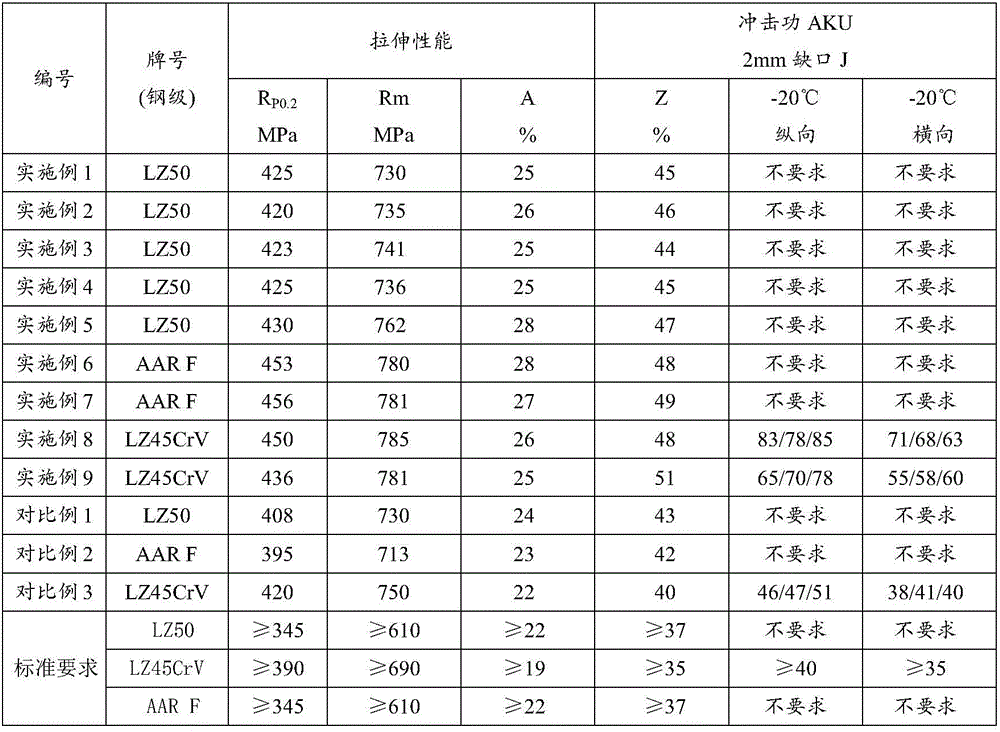
[0030] See Table 1 for the specific treatment process, grain size and mechanical performance test results of the axles of Examples 2-10 and Comparative Examples 1-3.
[0031] Other quality inspection results of the embodiment all meet the requirements of corresponding product standards. The grain size sample is taken at the 1 / 2 radius of the axle. The grain size of LZ50 and LZ45CrV is tested according to GB / T6394 standard, and the grain size of AAR F is tested according to ASTME112G standard. See Table 1 for the grain size and mechanical performance test results of the axles of Examples 1-10 and Comparative Examples 1-3.
[0032] Grain size, mechanical property test result of table 1 embodiment 1-10 and comparative example 1-3 axle
[0033]
[0034]
[0035] continued
[0036]
[0037] *Final forging (rolling) temperature ≥ 750 ℃.
[0038] **Normalizing holding time for follow-up heat treatment is 3-3.5 hours, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com