An Extensible RFID Two-way Authentication Method
A two-way authentication and algorithm technology, applied in the field of RFID two-way authentication, can solve the problems of inability to prevent denial of service attacks, protocol retransmission and counterfeiting attacks, and easy access by eavesdroppers, so as to reduce query overhead, ensure confidentiality, and avoid security. hidden effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
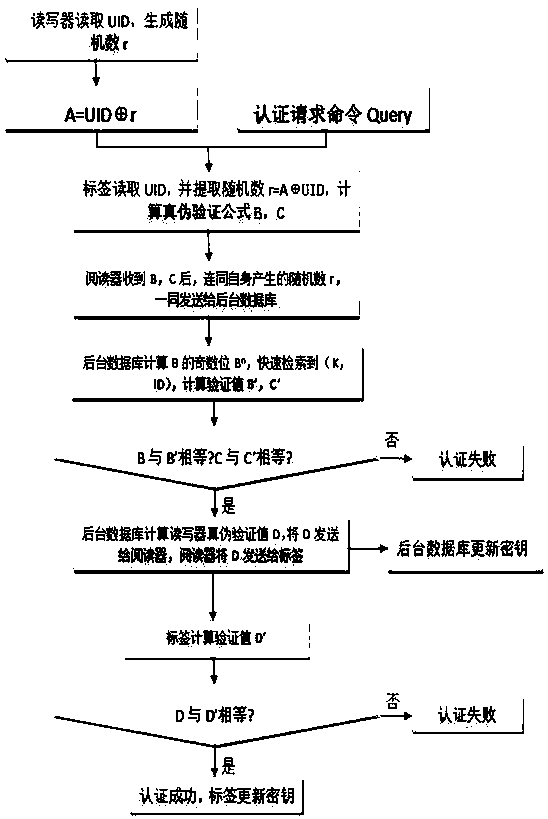
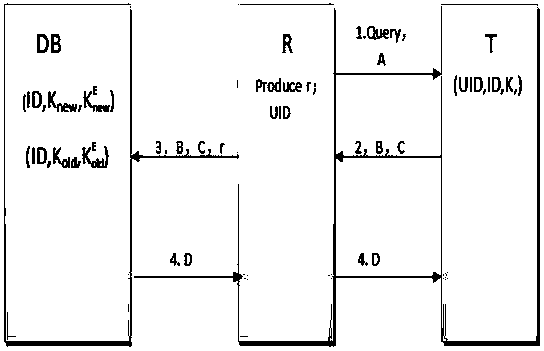
[0024] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the embodiments of the present invention are not limited thereto.
[0025] First give the meaning of each symbol involved in the method described in this embodiment:
[0026] R: reader;
[0027] T: label;
[0028] DB: background database;
[0029] UID: an identifier shared by all tags and readers;
[0030] ID: tag unique identifier;
[0031] K new : the shared key of this round;
[0032] The even number of bits of the current round shared key;
[0033] K old : the shared key of the last round;
[0034] The even-numbered bits of the shared key in the previous round;
[0035] L: the length of the key;
[0036] N: selected Mersenne number, N=2 L -1;
[0037] r: random number generated by the reader;
[0038] XOR operation;
[0039] [] L : Take the first L bits of the operation result
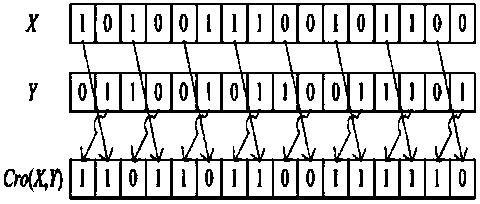
[0040] Cro(X,Y): Cross bit operation, specifically, s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com