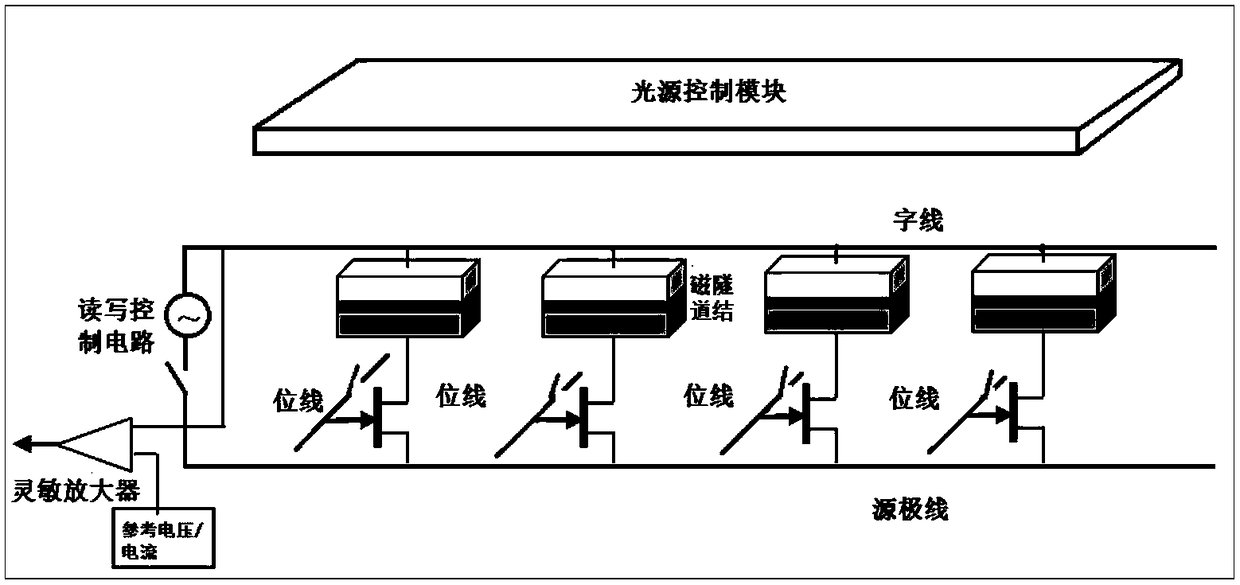
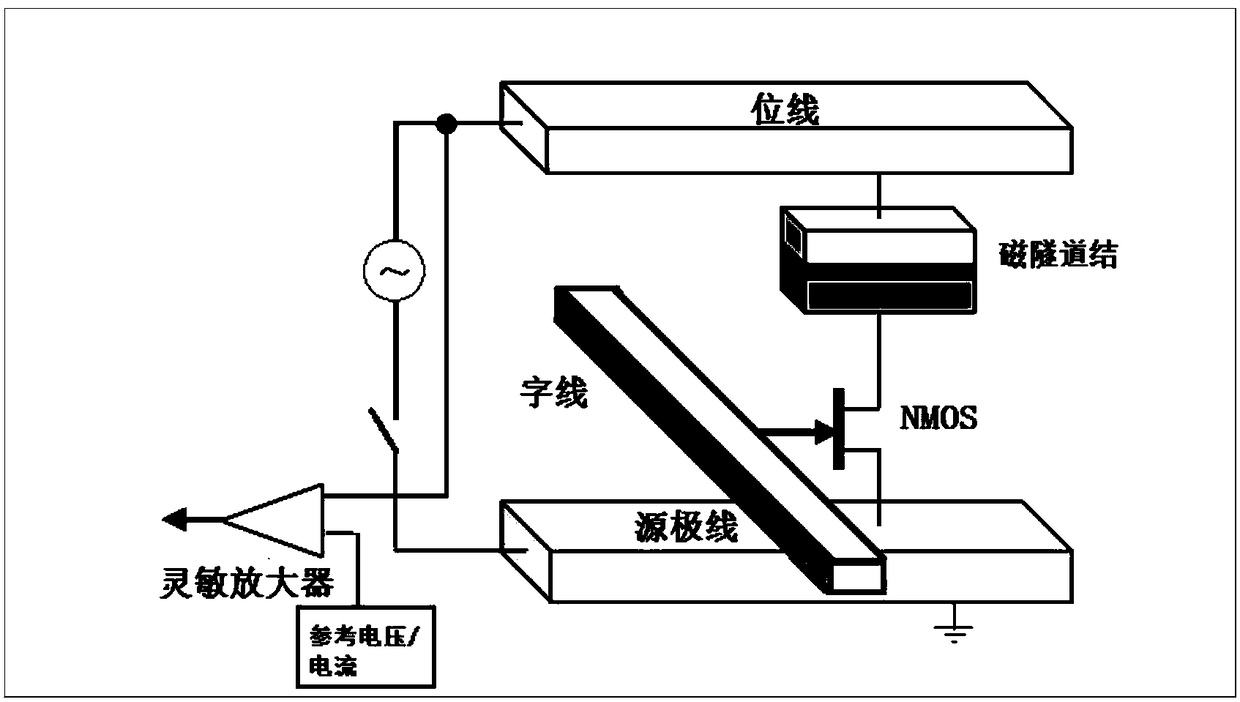
An optically written non-volatile magnetic memory
A magnetic memory and non-volatile technology, applied in the field of non-volatile memory, can solve the problems of high write delay, high current, increased manufacturing and processing costs, etc., to reduce energy consumption and delay, and reduce power consumption , The effect of reducing the tunneling current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The invention proposes an optically written nonvolatile memory, which has the characteristics of fast writing speed, low writing power consumption and non-volatile by realizing the optical writing of storage state.
[0036] The substantive features of the present invention are further described with reference to the accompanying drawings. The drawings are all schematic diagrams, and the thicknesses of the functional layers or regions involved are not actual dimensions, and the resistance and voltage values in the working mode are also not actual values.
[0037] Detailed exemplary embodiments are disclosed herein, specific structural and functional details are merely representative for purposes of describing exemplary embodiments, therefore, the invention may be embodied in many alternative forms and should not be construed as It is to be construed as being limited only to the exemplary embodiments set forth herein, but to cover all changes, equivalents, and alternative...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com