Molecular markers for identifying PHYB wild type and mutant of rice phytochrome gene
A phytochrome and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular markers, can solve the problems of out-of-stock, increased identification cost, large amplified fragments, etc., to reduce costs and improve breeding efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Establishment of a molecular marker for identifying rice phytochrome gene PHYB wild type and mutants
[0037] (1) Primer design
[0038] It is known that the phyB1 mutant inserts a base C at 1644 bp inside the PHYB gene, thereby causing premature translation termination (Takano et al., 2005, Plant Cell, 2005, 17:3311-3325). Select 175bp sequences before and after the mutation site for comparison ( figure 1 ), according to sequence differences, practical dCAPS Finder 2.0 online design software ( http: / / helix.wustl.edu / dcaps / dcaps.html ) design primers, the primer sequences are as follows:
[0039] Upstream primer PHYBF4: 5'-TGTCACACAAAGCCCCAGCATCATGGATC-3'(Seq No.3);
[0040] Downstream primer PHYBR1: 5'-AAGGCTATCTGTGCTGAGCC-3' (Seq No.4).
[0041] (2) Theoretical analysis of amplified fragments
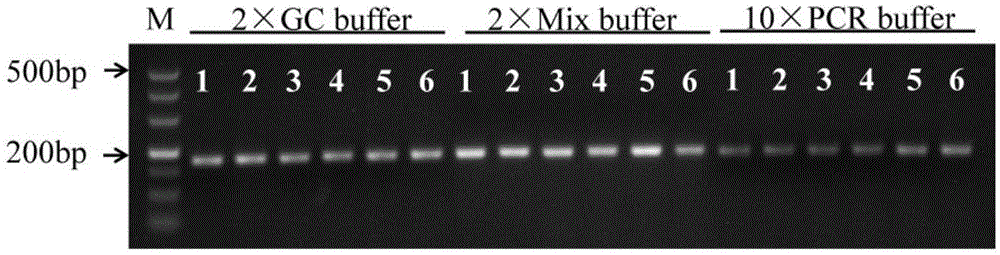
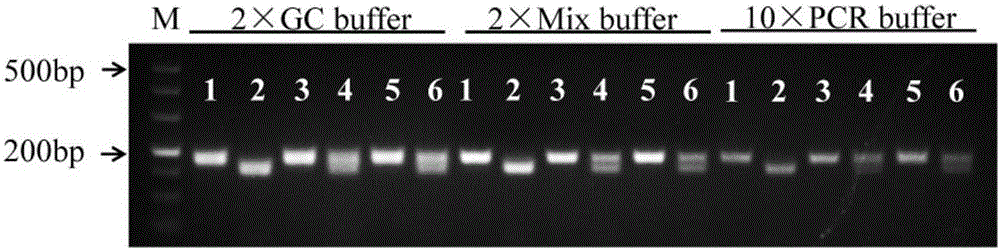
[0042] A 175bp fragment (sequence 1) can be amplified from wild-type rice genomic DNA; a 176bp fragment can be amplified from phyB mutant genomic DNA (seque...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Using the molecular markers of the rice phytochrome gene PHYB wild type and mutants to analyze the PHYB genotypes of 6 rice materials
[0048] (1) Extraction of genomic DNA from rice leaves
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com