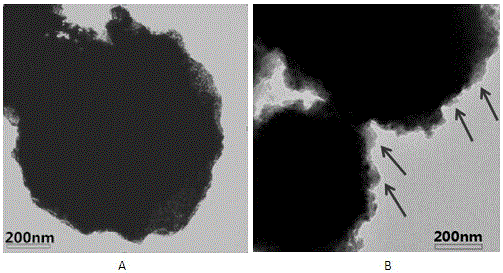
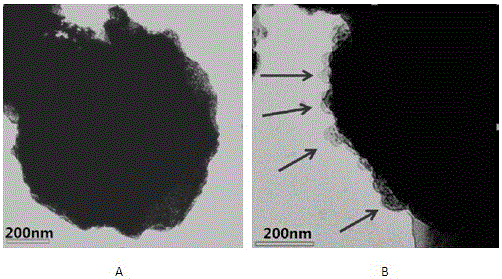
Method for separating exosomes from serum by using immunomagnetic beads
A technology of immune magnetic beads and exosomes, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of high cost, short time-consuming exosomes, time-consuming and labor-intensive problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1. Immunomagnetic Bead Separation of CD9 in Serum + Exosomes
[0023] one. method
[0024] (1) Collect fresh serum, put it in a centrifuge, and centrifuge at 2000g at room temperature for 30 minutes, discard the cell debris and precipitate, and take the centrifuged supernatant (if the serum is in a frozen state, it needs to be thawed in a water bath at 26°C before centrifuging).
[0025] (2) Vortex streptavidin-modified Dynabeads® MyOne™ Streptavidin T1 magnetic beads. After the magnetic bead suspension is uniform, take 5 microliters of the magnetic bead suspension and add it to 500 microliters of separation buffer, suspend and wash, and magnetically Magnetic beads were separated by rack and washed three times. After washing is complete, resuspend the beads in 500 µl of separation buffer.
[0026] (3) Take 5 microliters of the mouse anti-human biotinylated CD9 monoclonal antibody produced by Ancell Company and add it to the magnetic bead suspension obtained ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2. Immunomagnetic Bead Separation of CD63 in Serum + Exosomes
[0031] one. method
[0032] (1) Collect fresh serum, put it in a centrifuge, and centrifuge at 2000g at room temperature for 30 minutes, discard the cell debris and precipitate, and take the centrifuged supernatant (if the serum is in a frozen state, it needs to be thawed in a water bath at 26°C before centrifuging).
[0033] (2) Vortex streptavidin-modified Dynabeads® MyOne™ Streptavidin T1 magnetic beads. After the magnetic bead suspension is uniform, take 5 microliters of the magnetic bead suspension and add it to 500 microliters of separation buffer, suspend and wash, and magnetically Magnetic beads were separated by rack and washed three times. After washing is complete, resuspend the beads in 500 µl of separation buffer.
[0034] (3) Take 5 microliters of the mouse anti-human biotinylated CD63 monoclonal antibody produced by Ancell Company and add it to the magnetic bead suspension obtaine...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com