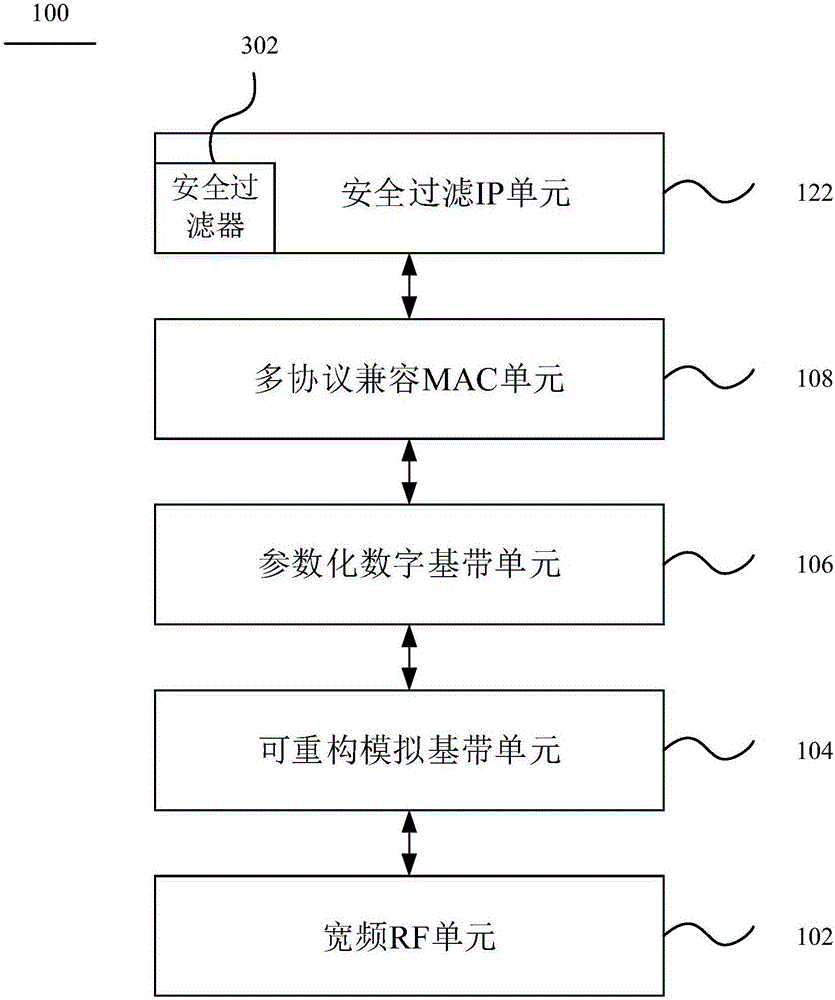
IP over RF network system
A network standard and signal technology, applied in electrical components, wireless communications, transmission systems, etc., to prevent monitoring/eavesdropping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
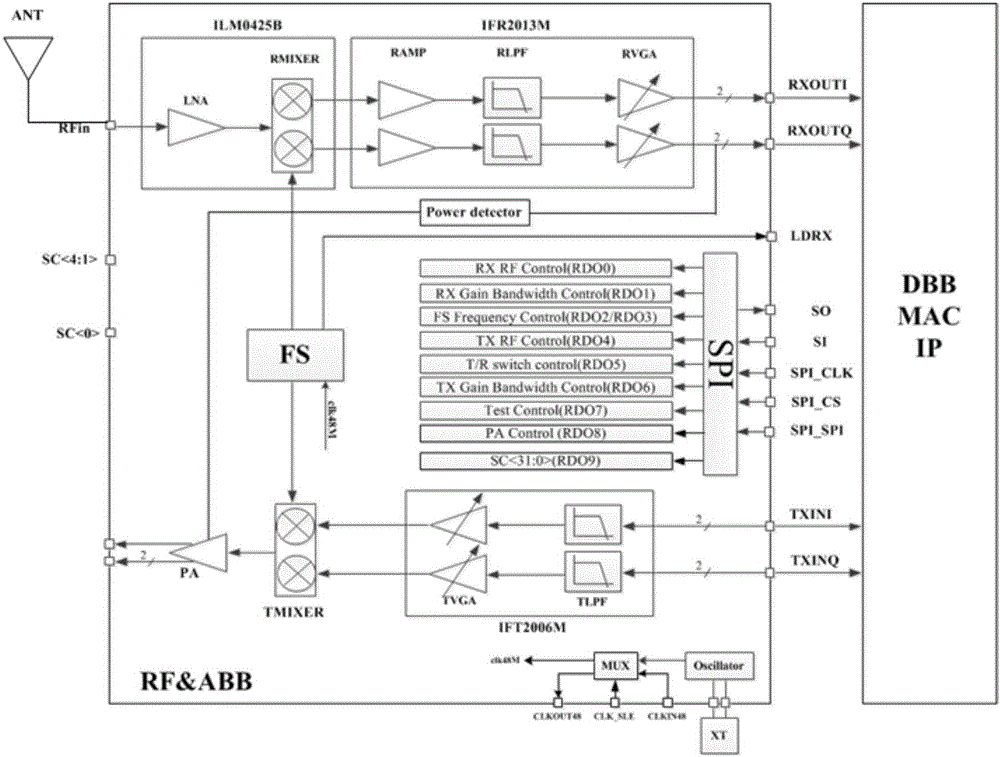
[0030] Such as figure 2 As shown, the RF unit includes: antenna ANT, used to send and receive RF signals; low noise amplifier LNA, used to amplify RF signals; down-mixer RMIXER, used to linearly move RF signals to intermediate frequency signals; frequency synthesizer FS , used to generate a frequency source in a certain frequency range; the up-mixer TMIXER, used to linearly move the intermediate frequency signal to the RF signal; and the power amplifier PA, used to amplify the RF signal and transmit it through the antenna ANT. The RF unit mainly has the following two working modes:
[0031]Signal receiving mode: The signal is input to LNA after being received by the antenna ANT, and then input to RMIXER for linear frequency shift after being amplified by LNA with low noise, and the high frequency is shifted to the intermediate frequency, and then provided to ABB.
[0032] Signal transmission mode: The intermediate frequency signal provided by ABB is input into TMIXER for lin...
Embodiment 2
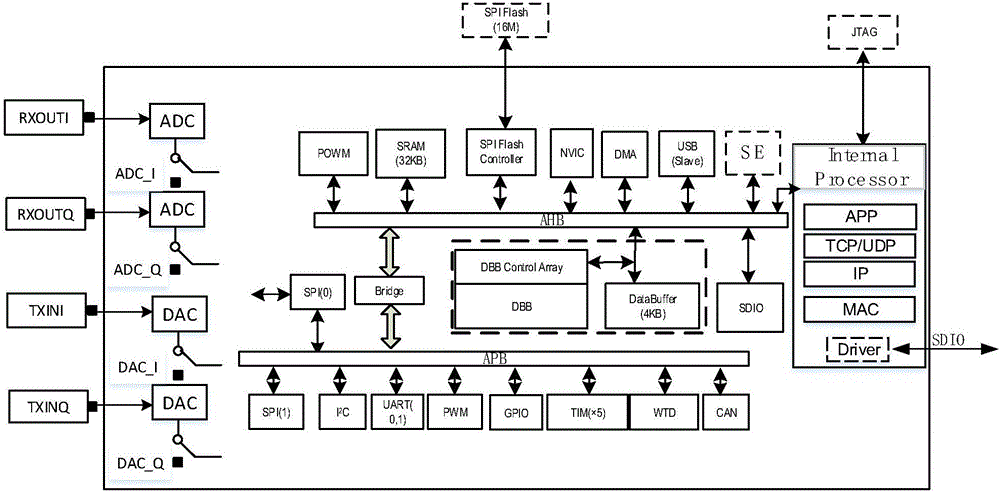
[0042] Such as image 3 and 4 As shown, the digital baseband DBB unit includes: a fast Fourier transform IFFT module 202, which is used to provide the transformation from the frequency domain to the time domain with a variable number of points; a fast Fourier transform FFT module 204, which is used to provide a variable number of points Transformation from time domain to frequency domain; vector mapping modulation and demodulation module 206, used to provide vector-based modulation and demodulation methods, so as to be compatible with multiple modulation and demodulation methods; codec module 208, used to provide multiple codec methods.
[0043] In this embodiment, the FFT and IFFT modules use variable points, thereby solving the problem of inconsistency in the number of subcarriers under different OFDM systems. That is to say, in this application, the number of points of FFT and IFFT is standardized, and then a maximum available number of points is provided. In specific impl...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Such as Figures 5A-5E As shown, the accompanying drawings show various network application examples of the IP over RF network standard of the present invention. Figure 5A It shows a schematic diagram of data sending and receiving for D2D communication, P2P communication or M2M communication in the IP over RF network standard of the present invention. Data can be transferred directly from one device to another.
[0051] Figure 5B A schematic diagram of wireless signal amplification performed by the IP over RF network standard of the present invention is shown. When the two communication targets MA(A) and MA(C) cannot communicate directly due to various reasons (such as too far away, blocked by obstacles, too low transmission power, etc.), they can communicate wirelessly through the intermediate device MS(B). Signal amplification. At this time, the wireless signal is only amplified by the antenna of MS(B), and the received wireless signal is amplified and sent out i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com