A layered control method for nuclear power engineering foundation blasting excavation
A layered control and nuclear power engineering technology, which is applied in blasting, material analysis, solid analysis using sound wave/ultrasonic wave/infrasonic wave, etc. It can solve problems such as difficult coordination of contradictions, unsatisfactory pre-cracking effect, and little damage to underlying bedrock. , to achieve good economic and social benefits, reduce the number of on-site tests, and reduce the workload of the field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
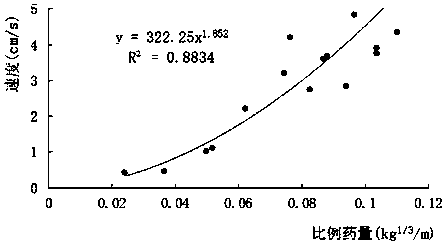
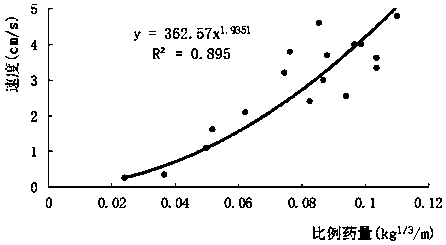
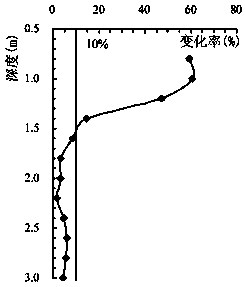
[0057] Example 1, such as figure 1 As shown, a layered control method for nuclear power engineering foundation blasting excavation, the following steps are performed for step blasting and pre-splitting blasting respectively:
[0058] Step 1: Determine the number of excavation layers and the excavation depth according to the foundation negative excavation depth H. Take H as 16.12 meters, then excavate in five layers, and calculate the allowable excavation depths from the first layer to the fifth layer (from top to bottom): 4.8 meters, 4.8 meters, 3.2 meters, 2.0 meters and 1.32 meters .
[0059] The excavation depth of the last layer (ie protective layer) should not exceed 1.50m.
[0060] However, when the last layer of blasting is excavated, a 0.25m air column or sawdust and other flexible cushions are reserved at the bottom of the blast hole without charge, so the allowable depth of blasting damage is 0.25m.
[0061] Step 2. Carry out blasting vibration tests on the site f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com