Method of using industrial solid slag to produce silicate cement for nuclear power engineering
A portland cement and nuclear power engineering technology, applied in cement production, etc., can solve problems such as high alkali content and inability to produce portland cement that meets market requirements, and achieve the goals of protecting the ecological environment, saving costs, and saving natural raw materials Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
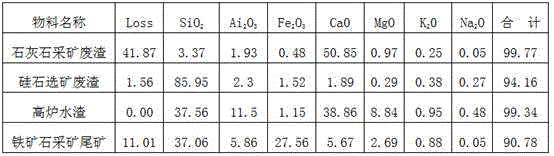
[0029] A method for producing Portland cement for nuclear power engineering from industrial solid waste, using raw materials in proportions by weight: 72.0% of limestone mining waste, 16.0% of silica mining waste, 2.0% of blast furnace slag, and 10.0% of iron ore mining tailings ; After the above raw materials are mixed and ground, they are sequentially subjected to preheater heat exchange, gas-solid separation treatment, decomposition furnace carbonate decomposition, dry rotary kiln calcination, and cooling to obtain Portland cement clinker; the temperature in the middle of the decomposition furnace is 830°C, and the temperature of the tail smoke chamber of the dry rotary kiln is 900°C; the blast furnace water slag is mixed and ground before going through a magnetic separator to remove iron.
Embodiment 2
[0031] A method for producing Portland cement for nuclear power engineering from industrial solid waste, using raw materials in proportions by weight: 75.0% of limestone mining waste, 12.0% of silica mining waste, 1.0% of blast furnace slag, and 12.0% of iron ore mining tailings ; After the above raw materials are mixed and ground, they are sequentially subjected to preheater heat exchange, gas-solid separation treatment, decomposition furnace carbonate decomposition, dry rotary kiln calcination, and cooling to obtain Portland cement clinker; the temperature in the middle of the decomposition furnace The temperature is 850°C, and the temperature of the tail smoke chamber of the dry-process rotary kiln is 950°C; the blast furnace water slag is mixed and ground before going through a magnetic separator to remove iron.
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for producing Portland cement for nuclear power engineering from industrial solid waste residues. The ratio of raw materials used is: limestone mining waste residue 78.0%, silica mining waste residue 9.0%, blast furnace slag 5.5%, iron ore mining tailings 7.5% ; After the above raw materials are mixed and ground, they are sequentially subjected to preheater heat exchange, gas-solid separation treatment, decomposition furnace carbonate decomposition, dry rotary kiln calcination, and cooling to obtain Portland cement clinker; the temperature in the middle of the decomposition furnace The temperature is 870°C, and the temperature of the tail smoke chamber of the dry rotary kiln is 1000°C; the blast furnace slag is mixed and ground before going through a magnetic separator to remove iron.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com