Method for repairing organotin polluted water by submerged plant
A submerged plant and organotin technology, applied in water pollutants, biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve no secondary pollution, fast growth and reproduction, and strong stress resistance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
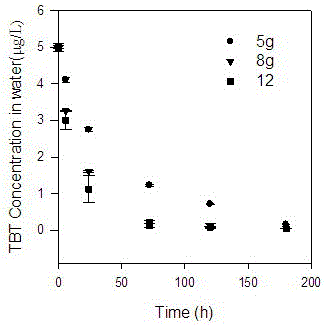
[0029] Put 5g, 8g, and 12g of hornwort into three groups of 2L sewage containing 5 µg / L tributyltin (TBT) (controlling pH = 6). figure 1 . After 5 days, the tin content of hornwort was 0.6mg / kg. The greater the number of hornwort algae, the better the removal effect, but the density should not be too large, 12g in 2L of water is the best. After 5 days, the salvaged hornwort was transferred to a safe place for drying, crushing, incineration, and finally a safe landfill.
Embodiment 2
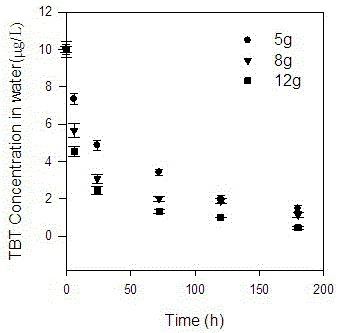
[0031] Put 5g, 8g, and 12g of hornwort into 3 groups of 2L water bodies containing 10µg / L tributyltin (TBT) (controlling pH = 8), respectively. The relationship diagram of the removal effect of tributyltin (TBT) over time is shown in the appendix figure 2 . After 5 days, the tin content of hornwort was 1.1 mg / kg. The greater the number of hornwort algae, the better the removal effect, but the density should not be too large, 12g in 2L of water is the best. After 7 days, the salvaged hornwort was transferred to a safe place for drying, crushing, incineration, and finally a safe landfill.
Embodiment 3
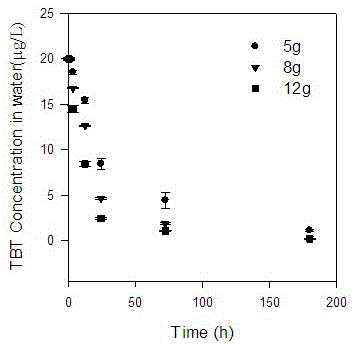
[0033] Put 5g, 8g, and 12g of hornwort into 3 groups of 2L water bodies containing 20µg / L tributyltin (TBT) (controlling pH = 10), respectively, and see the relationship diagram of the removal effect of tributyltin (TBT) with time. image 3 . After 5 days, the tin content of hornwort was 2.1 mg / kg. The greater the number of hornwort algae, the better the removal effect, but the density should not be too large, 12g in 2L of water is the best. Ten days after the hornwort was planted, the salvaged hornwort was transferred to a safe place for drying, crushing, incineration, and finally a safe landfill.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com