Underwater vehicle three-dimensional path planning method based on Lazy Theta satellite and particle swarm hybrid algorithm
A particle swarm algorithm and path planning technology, applied in three-dimensional position/channel control and other directions, it can solve problems such as terrain obstacle modeling or complex path search, high blindness, and low adaptability to three-dimensional problem solving, so as to achieve rapid improvement. reliability and reliability, and the effect of reducing computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
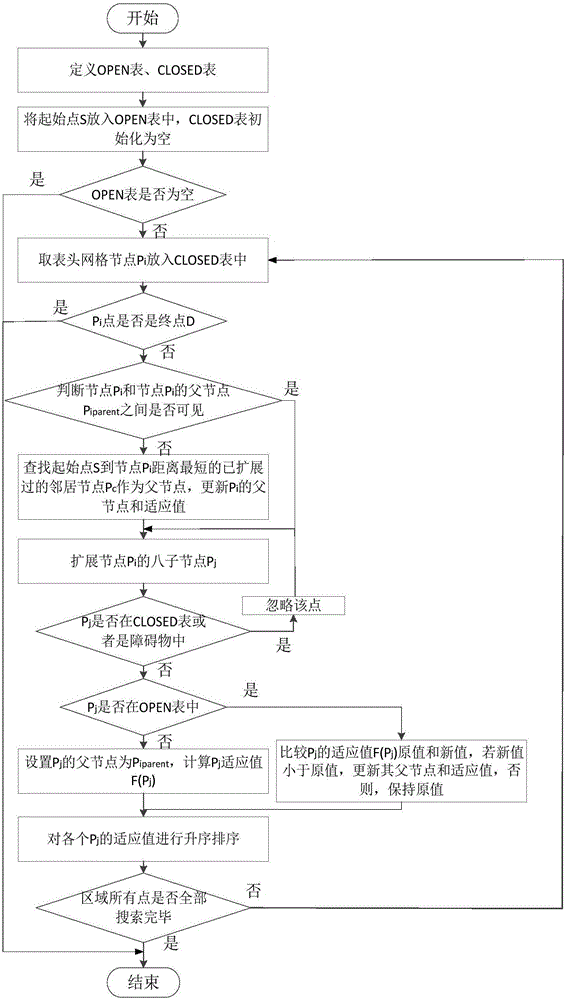
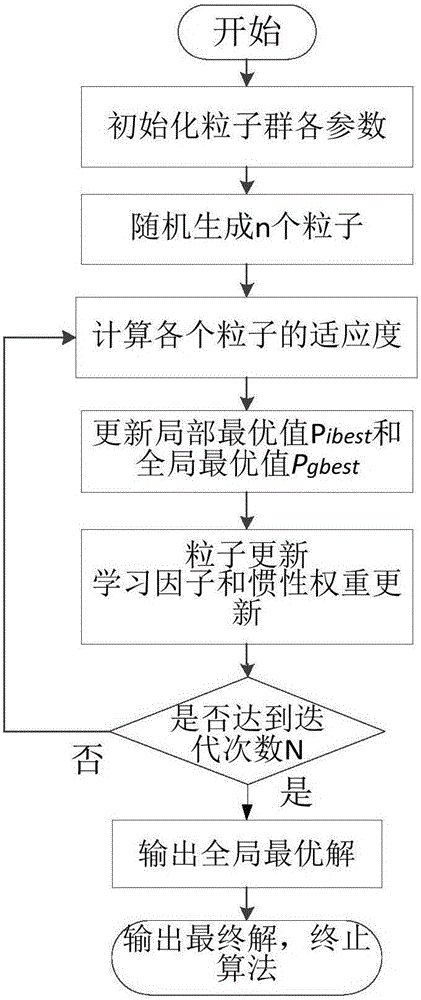
[0039] The present invention first uses the Lazy Theta star to carry out two-dimensional path planning, and then uses the particle swarm algorithm to carry out depth planning on the path in the depth direction to obtain the three-dimensional path of the underwater submersible, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1. Modeling of the navigation space
[0041] Step 1.1. Establishment of navigation space
[0042] The global coordinate system Oxyz is established within the scope of the three-dimensional path planning of the underwater vehicle, and the coordinates are (x s ,y s ,z s ) starting point S and coordinates are (x d ,y d ,z d ) to establish a navigating space at the end point D.
[0043] Step 1.2. Establish a two-dimensional map of the Lazy Theta star algorithm
[0044] In the navigation space established in step 1.1, the minimum safe diving depth z of the underwater submersible safemin Make a horizontal plane for the standard, form z=z s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com