Solar cell module with high photoelectric conversion efficiency
A technology of photoelectric conversion efficiency and solar cells, which is applied in the field of solar energy, can solve the problems of cumbersome inversion of series connection and reduce photoelectric conversion efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of series connection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
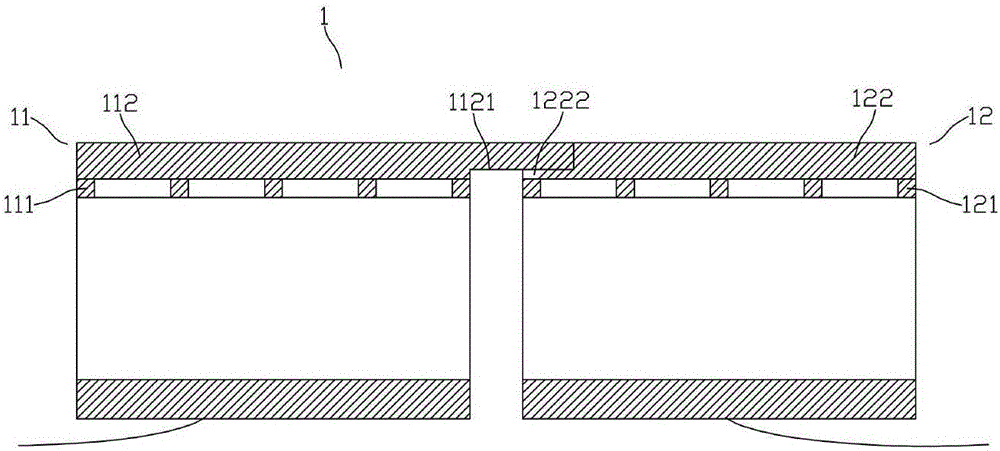
[0030] See figure 1 As shown, the solar cell panel 1 includes a first-type solar cell 11 and a second-type solar cell 12 , the front electrode 111 of the light-receiving surface of the first-type solar cell 11 is an n-type electrode, and the second-type solar cell 12 light-receiving surface front electrode 121 is a p-type electrode, a bus bar electrode 112 is formed on the front electrode of the first type solar cell, a bus bar electrode 122 is formed on the front electrode of the second type solar cell, and a first electrode is formed on one side of the bus bar electrode 112 of the first type solar cell 11 The finger structure 1121, the first electrode of the first type solar cell 11 The finger structure 1121 has a finger thickness smaller than the thickness of the bus bar electrode 112 of the first type solar cell 11, and the side of the second type solar cell 12 close to the first type solar cell 11 is busted The strip electrodes 122 form a second electrode groove 1222 stru...
Embodiment 2
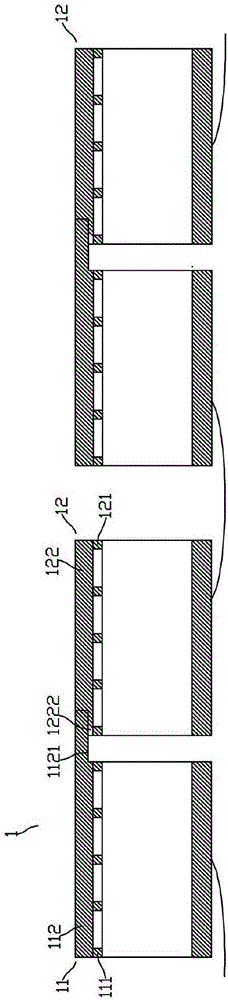
[0032] See figure 2 and image 3As shown, the solar panel 1 includes two first-type solar cells 11 and two second-type solar cells 12 formed side by side, the first-type solar cells 11 and the second-type solar cells 12 are staggered, and the first-type solar cells 11 are arranged side by side. The front electrode 111 of the light-receiving surface is an n-type electrode, the front electrode 121 of the light-receiving surface of the second type of solar cell 12 is a p-type electrode, the bus bar electrode 112 is formed on the front electrode of the first type of solar cell, and the bus bar is formed on the front electrode of the second type of solar cell. The bar electrode 122, the first electrode finger structure 1121 is formed on one side of the bus bar electrode 112 of the first type solar cell 11, and the finger thickness of the first electrode finger structure 1121 of the first type solar cell 11 is smaller than that of the bus bar electrode 112 of the first type solar c...
Embodiment 3
[0034] See Figure 4 As shown, the solar panel 1 includes two first-type solar cells 11 and one second-type solar cell 12 formed side by side, the first-type solar cells 11 and the second-type solar cells 12 are staggered, and the first-type solar cells 11 receive light The front surface electrode 111 is an n-type electrode, the front surface electrode 121 of the light-receiving surface of the second type solar cell 12 is a p-type electrode, a bus bar electrode 112 is formed on the front surface electrode of the first type solar cell, and a bus bar is formed on the front surface electrode of the second type solar cell. Electrode 122, first type solar cell 11 bus bar electrode 112 forms a first electrode finger structure 1121 on one side, and a first electrode groove structure 1122 on the opposite side, the first type solar cell 11 The first electrode finger structure 1121 has a finger thickness and a first The thickness of the electrode groove structure 1122 is smaller than th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com