Non-volatile storage memory module with physical-to-physical address remapping
A memory module, non-volatile technology used in the field of memory systems to solve problems such as reducing consumer lifespan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
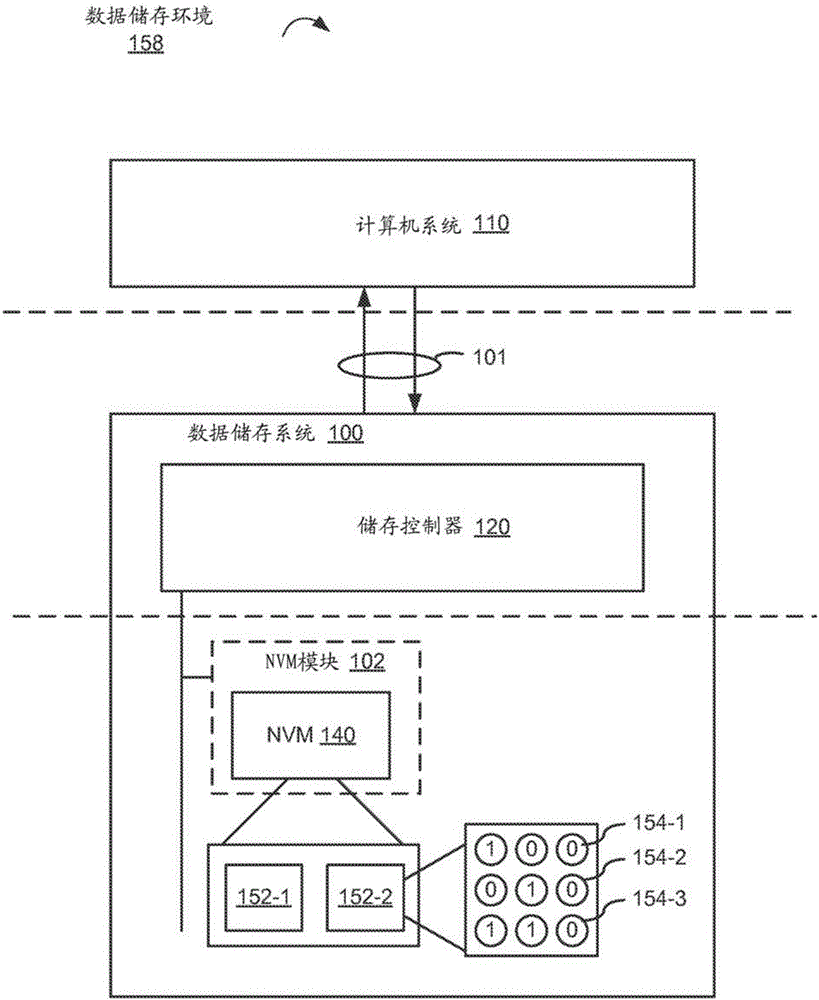
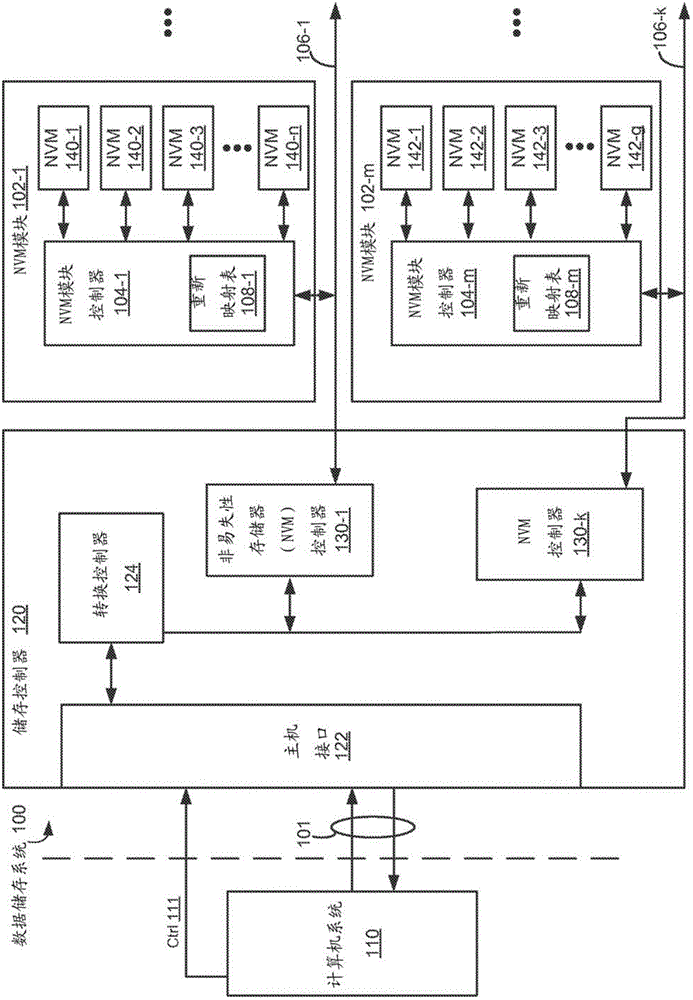
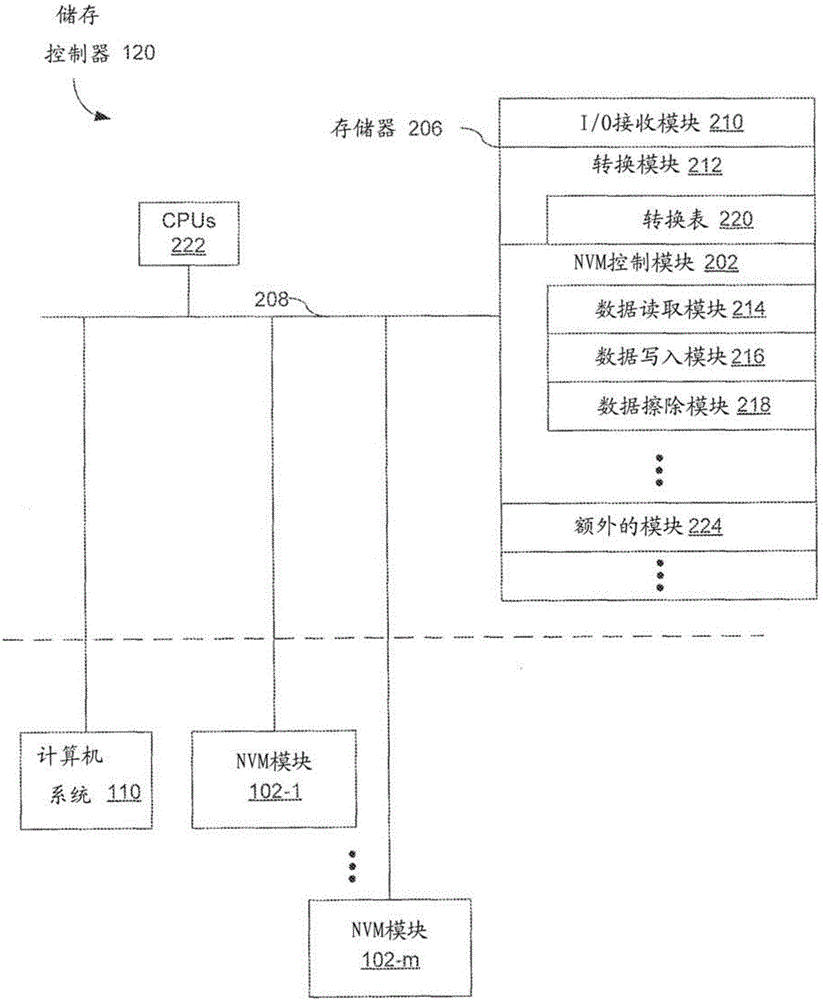
[0017] Regardless of what type of memory element (e.g., individual memory cells in a memory die) is used in a storage system, or how such memory elements are configured (e.g., 2D configuration, 3D configuration), memory elements are sometimes cause failure. The manufacturing process for such memory elements has a certain yield, meaning that some as-manufactured memory elements may be "bad" from the start. Other memory elements are severely damaged after fabrication. In conventional processing, memory dies are integrated before being incorporated into a larger memory device (e.g., memory module 102, Figure 1A ), perform extensive testing to convert the memory die (e.g., NVM die 140, Figure 1A ) into different classes (eg, based on the operating portion or function of the memory elements in such a memory die). For example, severely damaged fabricated memory elements typically often fail the so-called "burn-in" test, rendering portions of the memory die (eg, pages, blocks, die...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com