Alignment system and adjusting method for large-calibre space optical camera lens
A space optics and large-aperture technology, applied in the field of space optics remote sensing, can solve the problems of cantilever effect, sensitivity to gravity changes, optical system optical transfer function and imaging quality degradation, relative position accuracy changes, etc., to achieve the best engineering implementability, installation The effect of small adjustment difficulty and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0060] For a large-aperture space optical camera lens with a diameter of 2.5m, a distance between the primary mirror and the secondary mirror of 3.5m, and a focal length of 30m, the specific process is as follows:
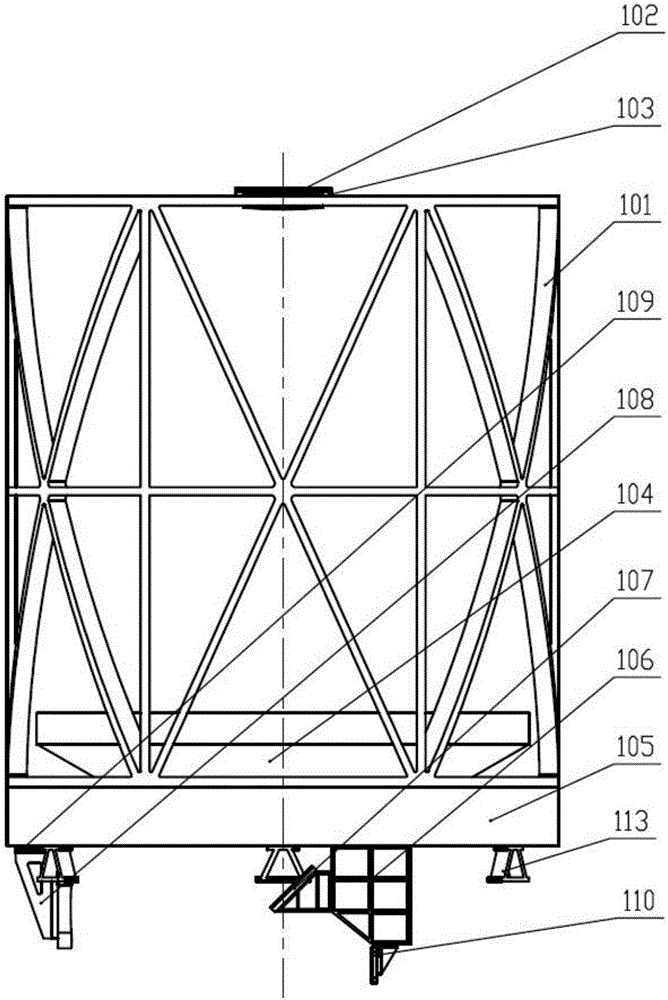
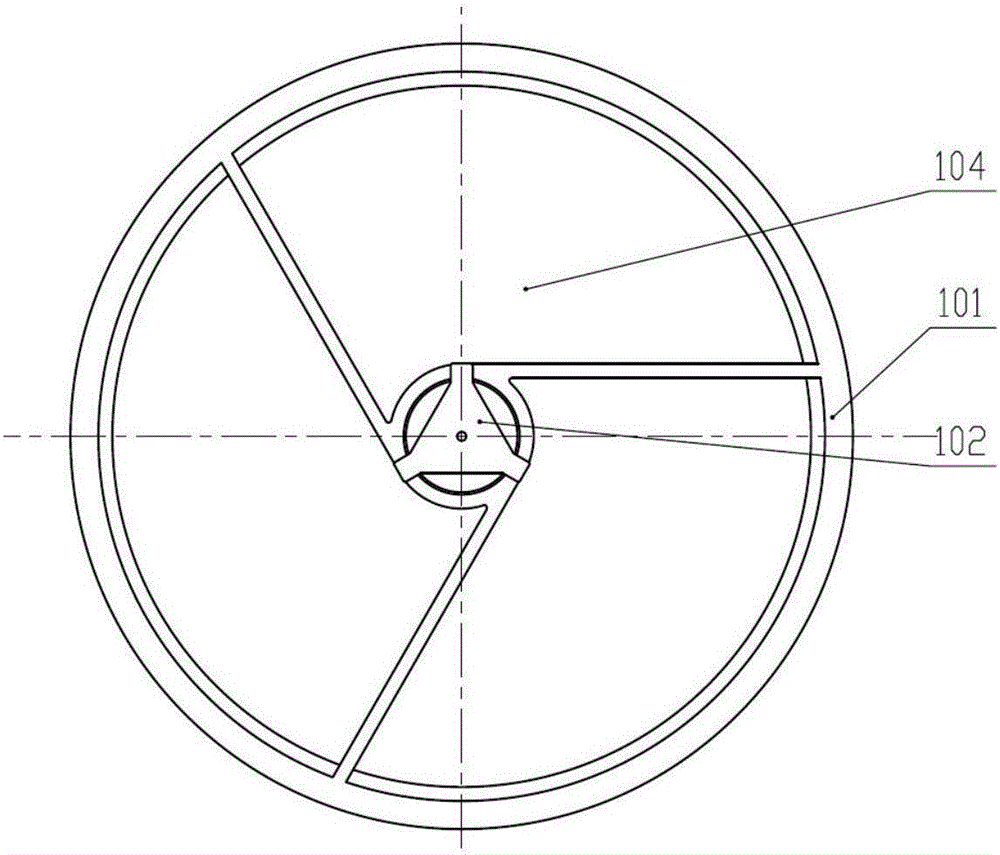
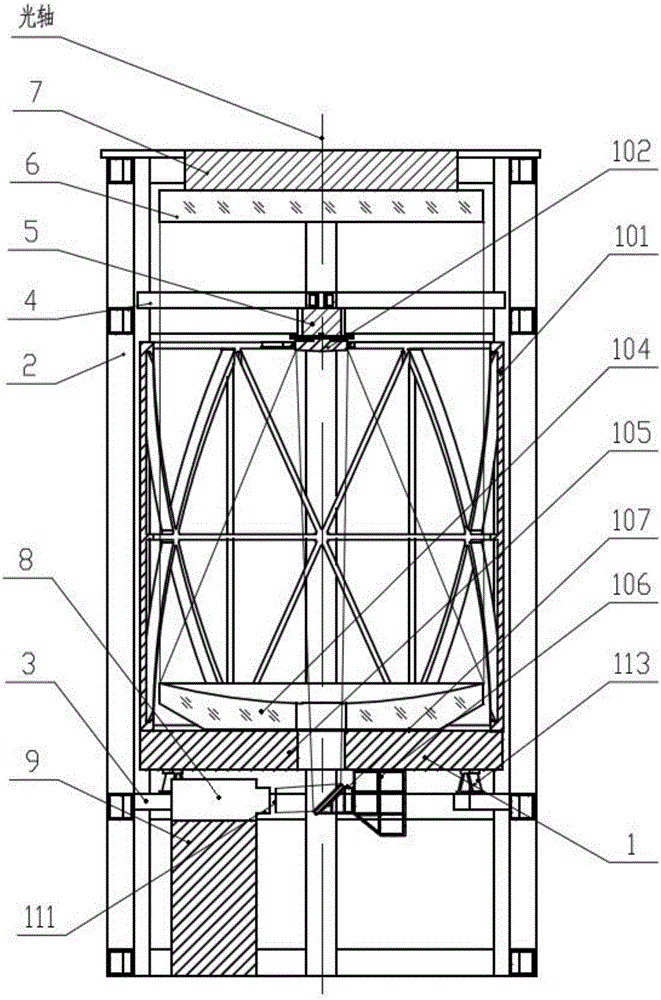
[0061] Step 1. Fix and connect the three connecting supports 113 to the lower surface of the camera substrate 105 by screws, the three connecting supports 113 are evenly distributed along the circumference of the lower surface of the camera substrate 105, and fix the main mirror assembly 104 by screws according to its theoretical position Connect to the upper surface of the camera substrate 105, position the camera frame 101 and the camera substrate 105 through positioning pins, and then fix the camera frame 101 to the edge of the upper surface of the camera substrate 105 by screws.
[0062] Step 2: Fix the three lens connecting seats 3 on the inner wall of the lower end of the lens adjusting frame 2 through screws, distribute the three lens connecting seats 3 evenl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com