Method for efficiently reducing content of ginkgolic acid in ginkgo nut
A technology of ginkgo fruit and ginkgolic acid, which is applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of not being able to guarantee the safety and edible properties of the product, not realizing the core removal of ginkgo fruit, and high labor intensity, so as to improve the safety and edibility, the method is simple, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
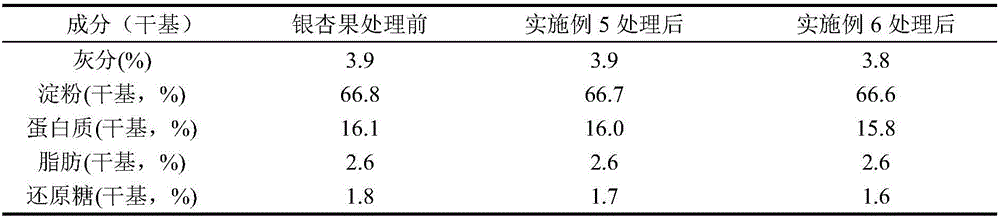
[0015] Take different kinds of fresh Ginkgo biloba (Ma Ling, Yuanzi, and Bergamot), three parts: outer testa, pulp, and fruit core, after drying, crushing, and sieving, measure the water content respectively, calculate the ginkgolic acid content on a dry basis, and prepare To be tested later. The measured testa: Bergamot > Yuanzi > Ma Ling, the content of ginkgolic acid in the testa of the three varieties is 158-211μg / g; in the pulp, the content of ginkgolic acid in the three types of ginkgo fruit is relatively low, all about 80μg / g. Fruit core: Yuanzi > Bergamot > Ma Ling, the content of ginkgolic acid in the core of the three varieties is 3798-4728μg / g. However, the distribution of ginkgolic acid content in different types of ginkgo fruit was the same: fruit core>pericarp>pulp.
Embodiment 2
[0017] Fresh bergamot ginkgo fruit, which is plump and popular in the market, is selected as the experimental object. Ginkgo biloba with a content of 280 μg / g of shelled ginkgo was heated at 80°C, 90°C, and 100°C for 10-30 minutes to remove the hard shell and seed coat. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0018] Table 1 Ginkgo content at different temperatures and times
[0019]
[0020] When the cooking temperature was 100°C, it was found that the shell part of the ginkgo fruit had cracked, and the pulp remained intact. In order to achieve a better dehulling and detoxification effect, and considering energy consumption, a cooking time of 20 minutes and a cooking temperature of 100°C were selected. Before and after cooking, the content of ginkgolic acid decreased from 280 μg / g (dry basis) before heating to 253 μg / g (dry basis).
Embodiment 3
[0022] Take out the shelled ginkgo fruit and peel off the shell. After mechanical coring treatment, before and after coring, the content of ginkgo ginkgolic acid decreased from 280 μg / g (dry basis) before coring to 135 μg / g (dry basis).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com