Ganoderma undergrowth bionics wild cultivation method
A technology of imitating wild cultivation and Ganoderma lucidum, applied in the field of edible fungus cultivation, can solve the problems of not absorbing natural gas, low yield and poor benefit, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
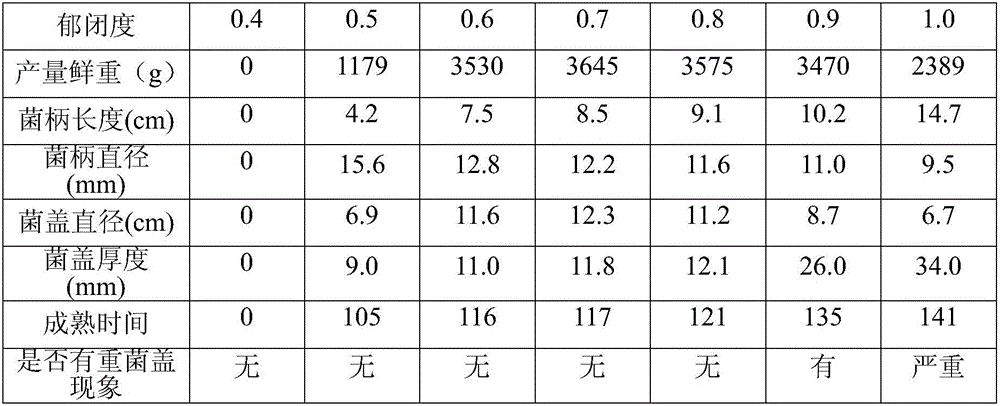
[0049] Embodiment 1: Effect contrast of Ganoderma lucidum cultivation under different canopy density stands
[0050] Test method: Under the same orientation, through selection or thinning or pruning, seven mixed forest plots with canopy density of 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, and 1.0 were selected for Ganoderma lucidum cultivation. The main tree species in the mixed forest are trellis, pine and red cone.
[0051] Understory cultivation time: March 5, 2014.
[0052] Cultivation method: remove the bagged fungus sticks of black Ganoderma lucidum grown with sweetgum, and bury them under the above-mentioned seven gradient forest stands with different canopy density, and cover with fine soil with a thickness of 2 cm. Each canopy density is planted with 40 fungus sticks.
[0053] test results:
[0054] Comparison table of Ganoderma lucidum cultivation effect under different canopy density stand
[0055]
[0056] It can be seen from the above results that the forest stand with...
Embodiment 2
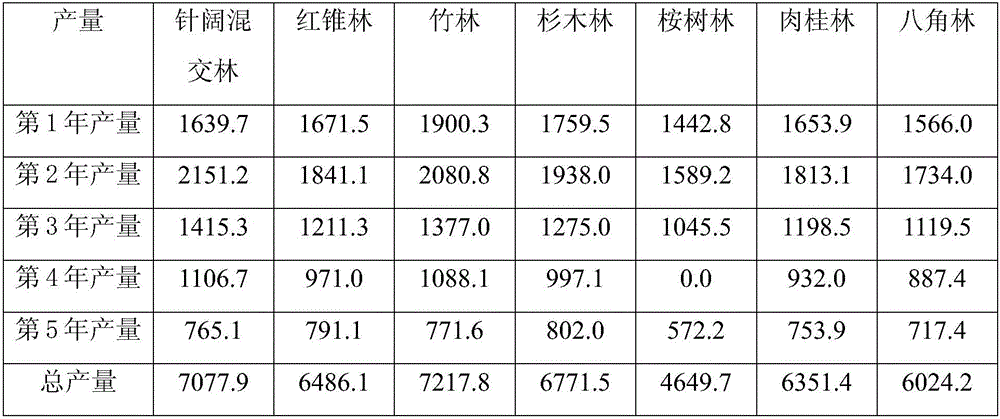
[0057] Example 2: Bionic planting of Ganoderma lucidum in different forests
[0058] 1. Cultivation forest land selection
[0059] Seven kinds of forests, namely mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest, pure red cone forest, bamboo forest, pure Chinese fir forest, pure eucalyptus forest, pure cinnamon forest and pure star anise forest were selected for imitation wild cultivation of Ganoderma lucidum under the forest. Each cultivation point faces south, and the canopy density of the cultivation point is adjusted between 0.7 and 0.8.
[0060] Ganoderma lucidum species: Black Ganoderma lucidum
[0061] Segment tree species: sweetgum tree
[0062] 2. Cultivation method
[0063] In October, the liquidambar tree is cut down as a section. After felling, the main stem and branches with a diameter greater than 2cm are brought back outdoors. In November, when there are small cracks at the trunk end, the section is processed and bagged. Sterilize for 20 hours, inoculate after coolin...
Embodiment 3
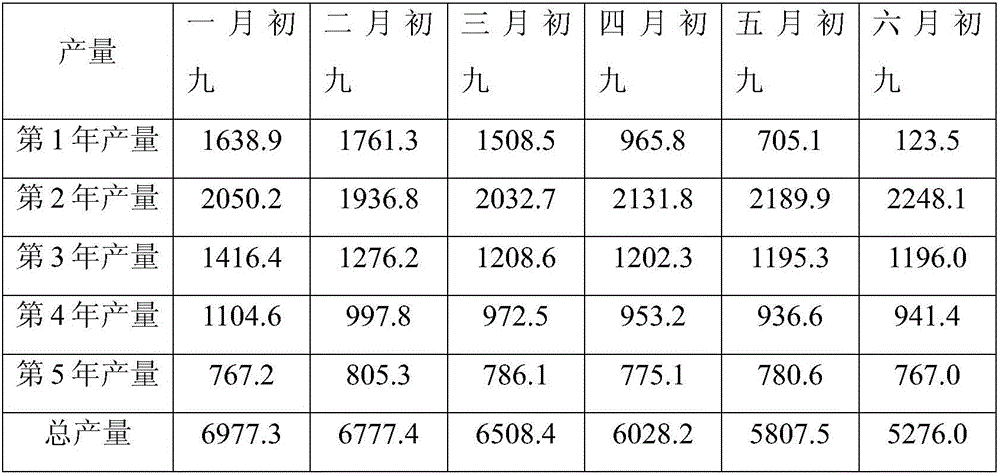
[0071] Example 3: Effects of different burying times on the imitation wild planting of Ganoderma lucidum under the forest
[0072] 1. Planting species and forest land
[0073] The plantation forest land is coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest land with relatively fertile soil. The forest land faces south, with a slope of about 18 degrees, and the canopy density of the forest land is about 0.8. The species of Ganoderma lucidum is purple Ganoderma lucidum, and the tree species of the section wood is sweetgum.
[0074] 2. Cultivation method
[0075] The purple ganoderma lucidum segments that have been cultivated were planted on the same forest land on the ninth day of the first lunar month, the ninth day of February, the ninth day of March, the ninth day of April, the ninth day of May, and the ninth day of June. Bury 30 fungus sticks; harvest the Ganoderma lucidum after it matures, and harvest for 5 years. The retrieved Ganoderma lucidum was baked in a constant temperature...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com