Viral particles as immunogens against enterovirus infection and production thereof
A virus particle, enterovirus technology, applied to induce resistance to enterovirus infection, hand, foot and mouth disease. , or the domain of the immune response to the disease it causes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0113] Example 1: Ideas for developing a HFMD vaccine with multivalent immunogenic components
[0114] A serum-free, Vero cell-based, formalin-inactivated whole-virus EV71 vaccine has been developed and has undergone human clinical trials (Wu et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2007; Liu et al. al., 2011; Chang et al., 2012; Chou et al., 2012; Li et al., 2012; Cheng et al., 2013; Zhu et al., 2013). Surprisingly, unexpected results showed that EV71 vaccine failed to protect against CVA16 infection in cell culture assays (Chou et al., 2013). Our recent studies on the CVA16 vaccine candidate also showed that mouse and rabbit anti-CVA16 antisera were unable to neutralize EV71 (Chong et al., 2012). When the protein sequences of these virus strains ((EV71, CVA6, CVA10 and CVA16) were arranged and analyzed; the similarity of the P1 peptide was found to be 65-80% on the P1 sequence (Table 1). HFMD caused by common enterovirus strains (such as CVA6 and CVA10) is urgently needed to develop a HF...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Example 2: Establishment of a Novel Biological Process for Kexakivirus Group A
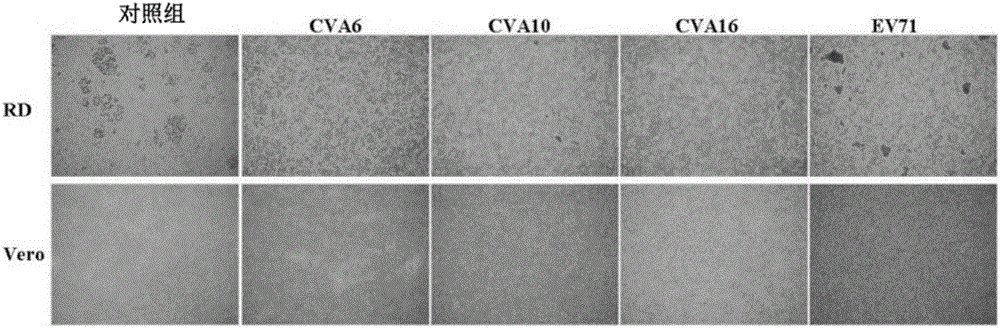
[0118] Biological processes for the manufacture of human multivalent HFMD vaccines have been developed and explored. Based on the existing biological process for the development of EV71 vaccine described in published literature (Liu et al., 2007; Chou et al., 2012), to our surprise, CVA6 and CVA10 can be expressed in Infect and replicate in RD cells, but unable to infect and replicate in Vero cells ( figure 1 ). However, RD cells are not as suitable for production of human vaccines as HEK293 cells. Please refer to Table 2 and Table 3 at the same time.
[0119] Table 2: Viral titers of enteroviruses produced in different cells
[0120] Virus potency (TCID50 / mL)
[0121]
[0122]
[0123] CPE: cytopathic effect
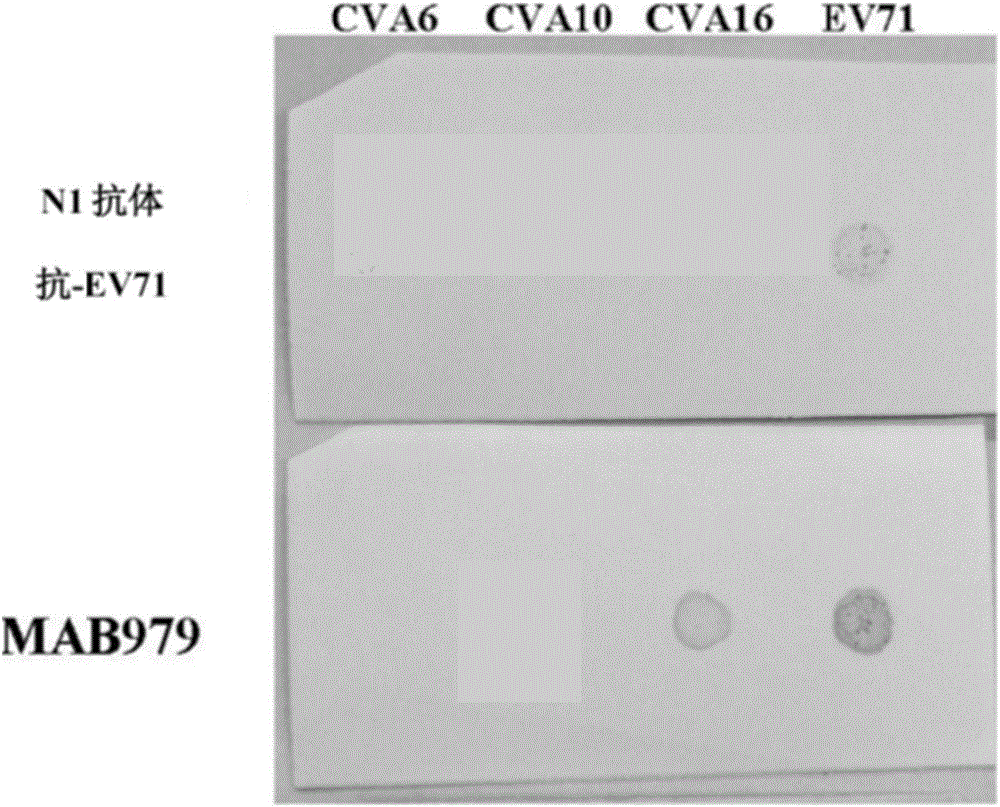
[0124] In order to confirm that no viral protein can be expressed and produced in Vero cell culture, two monoclonal antibodies (N1 and MAB979 can specifically recognize VP1...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Example 3: Using HEK293 cell culture to produce virus
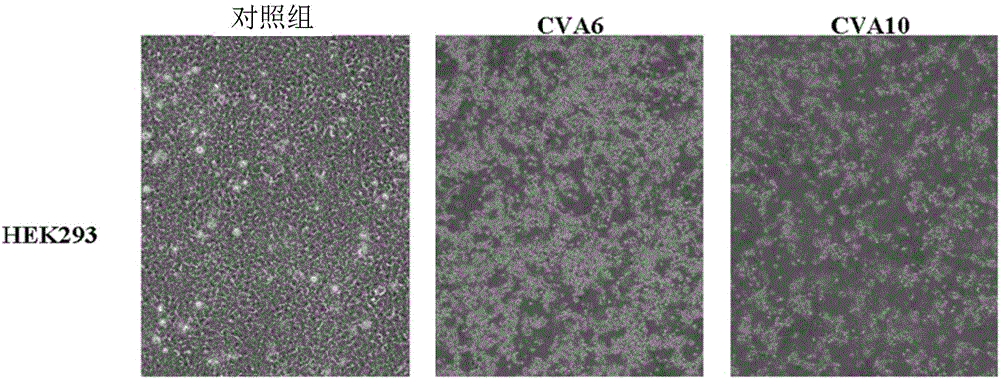
[0126] Since CVA6 and CVA10 cannot infect Vero cells and RD cells and cannot be used for human vaccine production, other possible GMP-certified cell lines, such as MDCK, MRC-5, CHO and HEK293, were tested and used for propagation CVA6 and / or CVA10. To our surprise, both CVA6 and CVA10 could only infect HEK293 cells ( image 3 ).
[0127] To obtain sufficient CVA6 and CVA10 for analysis of biochemical and immunogenic properties, the viruses were cultured in HEK293 cells. After 6 days of culture, the cell density reached 1-2.5×10 per mL 6 cell. cells at an MOI of 10 -2 to 10 -5 concentration for infection. Viruses were harvested and collected from cell culture supernatants at 6 days post infection (DPI). See Table 3.
[0128] Table 3: Viral titers of enteroviruses produced in HEK293 cells
[0129] Virus price
[0130]
[0131] CPE: cytopathic effect
[0132] When EV71 infects HEK293 cells, the virus ti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com