Method for screening drugs for treating steatohepatitis by taking N-terminal dimerization of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) as target
A steatohepatitis and apoptosis signal technology, applied in the field of medicine for relieving and/or treating steatohepatitis, preparation and prevention, can solve problems such as damage to digestive system function, affect hormone metabolism, reduce human immunity, etc. effect of development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
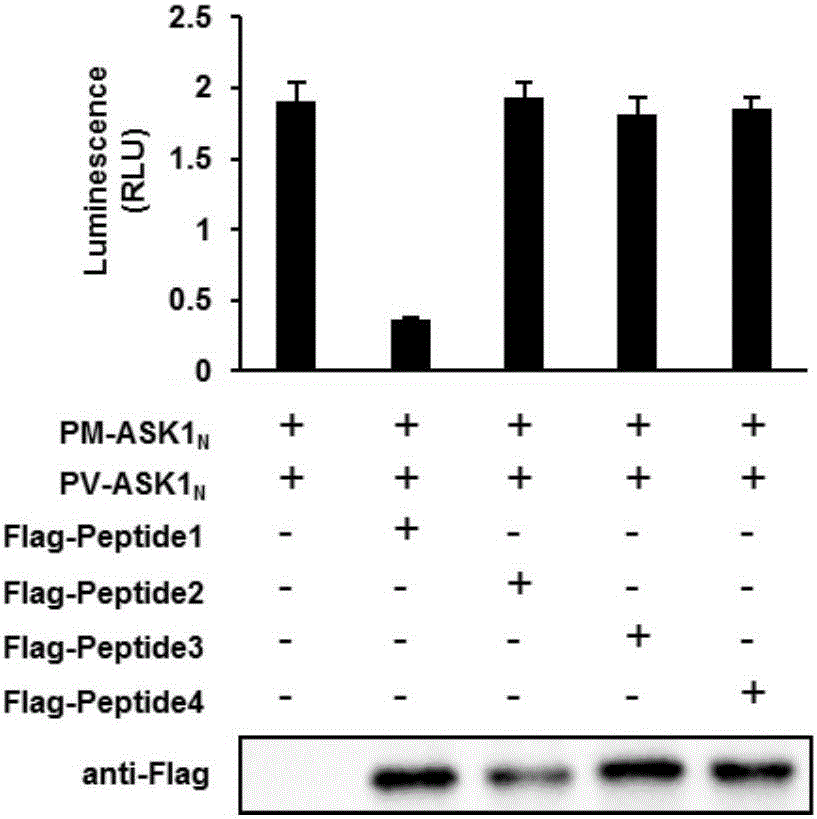
[0134] [Example 1] Screening for polypeptides that can inhibit the N-terminal dimerization of ASK1
[0135] Stable expression of ASK1 N The HEK-293T plasmids for dimerization detection are divided into 5 groups, which are marked as A, B, C, D, and E respectively. In group A, only the pG5luc plasmid is added without the psi-flag-Peptide plasmid when the target polypeptide is transiently transfected. , Groups B, C, D, and E were transfected with psi-flag-Peptide1, 2, 3, 4 plasmids and pG5luc plasmids into HEK-293T cells respectively, that is, the five groups were:
[0136] A: HEK-293T cells (pACT-ASK1 N +pBIND-ASK1 N )+pG5luc
[0137] B: HEK-293T cells (pACT-ASK1 N +pBIND-ASK1 N )+psi-flag-Peptide1+pG5luc
[0138] C: HEK-293T cells (pACT-ASK1 N +pBIND-ASK1 N )+psi-flag-Peptide2+pG5luc
[0139] D: HEK-293T cells (pACT-ASK1 N +pBIND-ASK1 N )+psi-flag-Peptide3+pG5luc
[0140] E: HEK-293T cells (pACT-ASK1 N +pBIND-ASK1 N )+psi-flag-Peptide4+pG5luc
[0141] After addin...
Embodiment 2
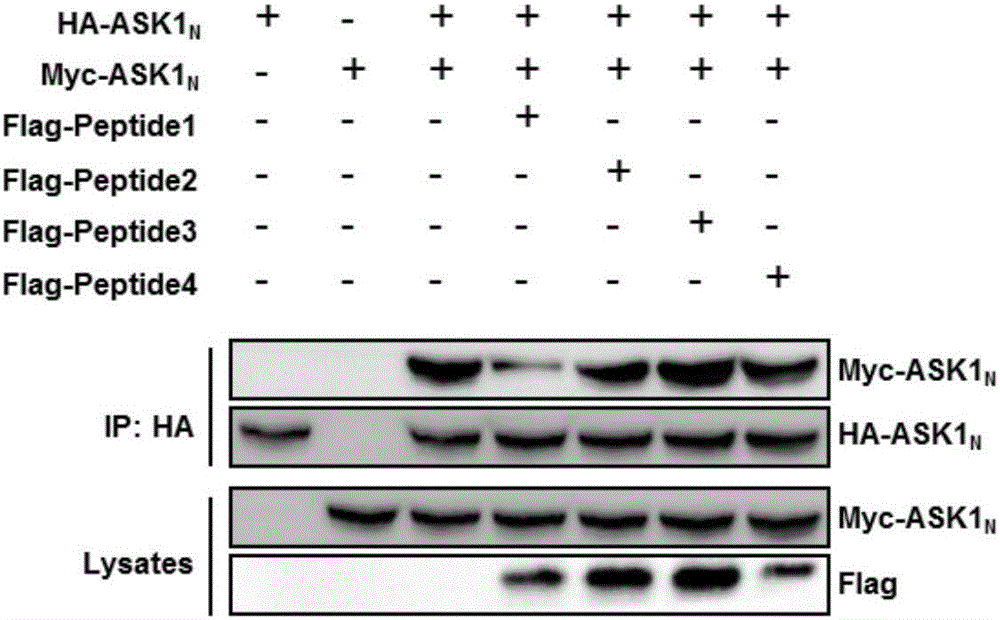
[0143] [Example 2] Co-immunoprecipitation verification of the inhibitory effect of polypeptides on the N-terminal dimerization of ASK1
[0144] HEK-293T cells were divided into 7 groups, coded as A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. Cells in group A and group B were only transfected with HA-ASK1 N or Myc-ASK1 N Plasmid, cells in groups C, D, E, F, and G were simultaneously transfected with HA-ASK1 N and Myc-ASK1 N Two plasmids, positive cells were screened after 48 hours. The resulting cells are as follows:
[0145] Group A: HEK-293T cells (HA-ASK1 N )
[0146] Group B: HEK-293T cells (Myc-ASK1 N )
[0147] C, D, E, F, G groups: HEK-293T cells (HA-ASK1 N +Myc-ASK1 N )
[0148] Afterwards, the transient transfection of the target polypeptide plasmid was carried out. Only the same amount of transfection solution without the target polypeptide plasmid was added to the cells in groups A, B, and C, and the cells in groups D, E, F, and G were respectively added with psi-flag-Peptide1 ...
Embodiment 3
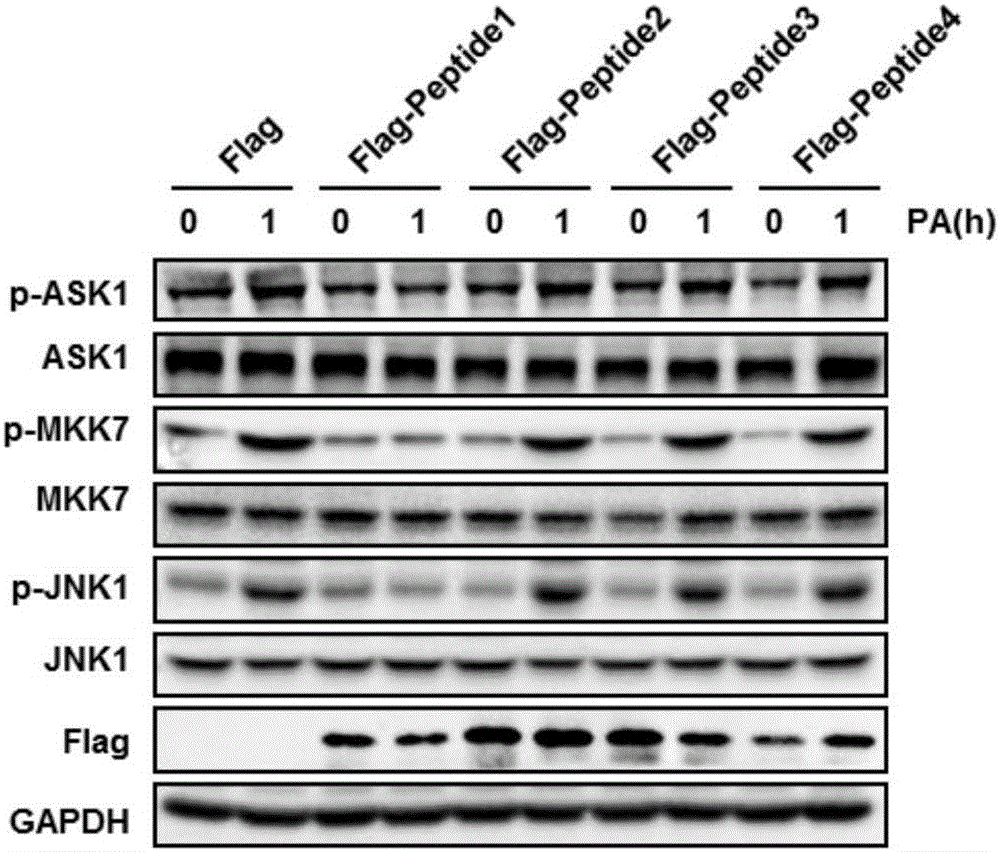
[0159] [Example 3] Inhibiting the N-terminal dimerization of ASK1 can inhibit the ASK1-JNK1 signaling pathway
[0160]Western blot analysis was used to detect the effect of inhibiting the N-terminal dimerization of ASK1 on the intracellular JNK1 signaling pathway. Required primary antibody information: p-ASK1 (Cell Signaling Technology, #3765), ASK1 (GeneTex, #GTX107921), p-MKK7 (Aviva Systems Biology, #OAAF05547), MKK7 (Cell Signaling Technology, #4172), p-JNK1 (NOVUS, #NB100-82009), JNK1 (Abcam, #ab199380), Flag (Sigma, #F3165); required secondary antibody information: HRP AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (Jackson, #111-035 -003), Biotin AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) (Abbkine, A21210).
[0161] L02 cells were divided into 5 groups and cultured in culture dishes, numbered A, B, C, D, E, and cultured at 37°C until the cell density was 70%. Cells in group A were transfected with psi-flag plasmid as a control, and cells in group B, C, and D were cultured in culture ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com