Method for identifying yak meat and cattle meat
A technology of yellow beef and yak, which is applied in the field of identifying the source of yak and yellow beef, can solve the problems of complicated operation, poor repeatability, and low sensitivity, and achieve the effect of good repeatability, high sensitivity, simple and fast operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
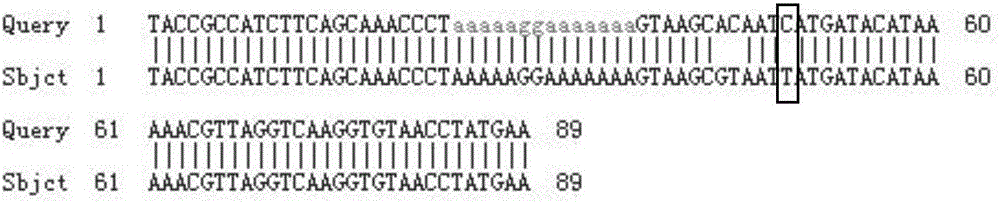
[0040] Primers and probes were designed using the following 89 bp sequence in the yak mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene as the differential site; the sequence of the differential site was as follows:
[0041]
[0042] The marker primer sequences are as follows:
[0043] Upstream primer: 5'-TACCGCCATCTTCAGCAAACC-3'
[0044] Downstream primer: 5'-TTCATAGGTTACACCTTGACCTAAC-3'
[0045] The labeled probe sequence is as follows
[0046] T: 5'-GTATCATGATTGTGCTTACTTTTTTTCC-3'
[0047] 17 test samples from Gannan yak, take 200mg of each test sample, extract the whole genome DNA of the test sample, use the whole genome DNA of the sample as a template, and carry out asymmetric PCR amplification: the amplification system is as follows: upstream primer 1 μL, downstream primer 0.2 μL, probe 1 μL, sample genomic DNA 2 μL, 2×TaqMix 5 μL, ddH 2 O 1.8 μL, LC Green 1 μL. The amplification program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 55...
Embodiment 2
[0050] From 23 samples to be tested of Pingliang Red Bull, 200 mg of each sample to be tested was taken to extract the whole genome DNA of the samples to be tested, and the rest of the method steps were the same as in Example 1.
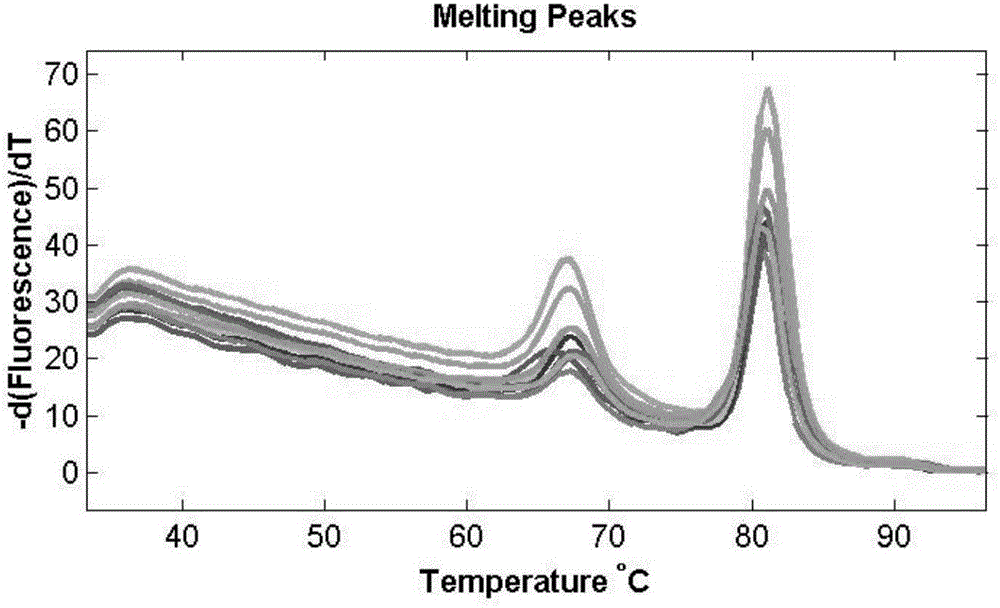
[0051] The solubility curve of the PCR amplification product of described sample to be tested is as follows image 3 shown, according to image 3 As shown, the melting peak is in the temperature range of 65-70°C, thus it can be judged that the sample to be tested is a yellow beef sample.
Embodiment 3
[0053] 21 mixed test samples from Yushu yak and Hexi beef cattle were taken, and 200 mg of each test sample was taken to extract the whole genome DNA of the test sample. The rest of the method steps were the same as in Example 1.
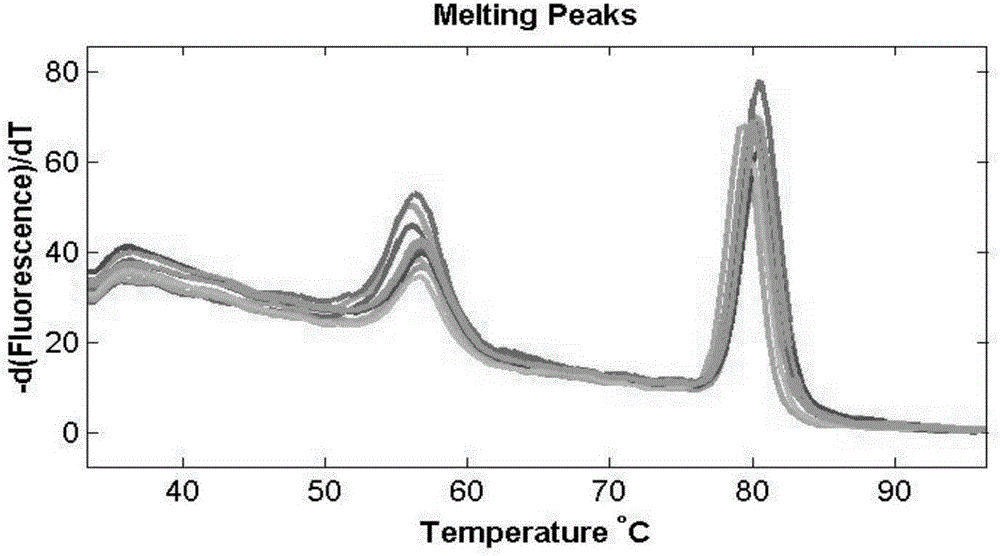
[0054] The solubility curve of the PCR amplification product of described sample to be tested is as follows Figure 4 shown, according to Figure 4 As shown, there are melting peaks in the temperature range of 55-60°C and 65-70°C, so it is judged that the sample to be tested is a mixed sample of yak meat and yellow beef.
[0055] It can be seen from the above examples that the method of the present invention adopts the HRM method to operate simply and quickly, and only needs 2 hours to complete a detection. It has high sensitivity and good repeatability, and can accurately detect a large number of samples at the same time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com