Treatment technology for antibiotic fungus residues
A technology of antibiotic bacteria residue and treatment process, which is applied to the removal of solid waste, chemical instruments and methods, transportation and packaging, etc. It can solve the problems of releasing unpleasant smell, polluting the surrounding environment, and being difficult to effectively degrade, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
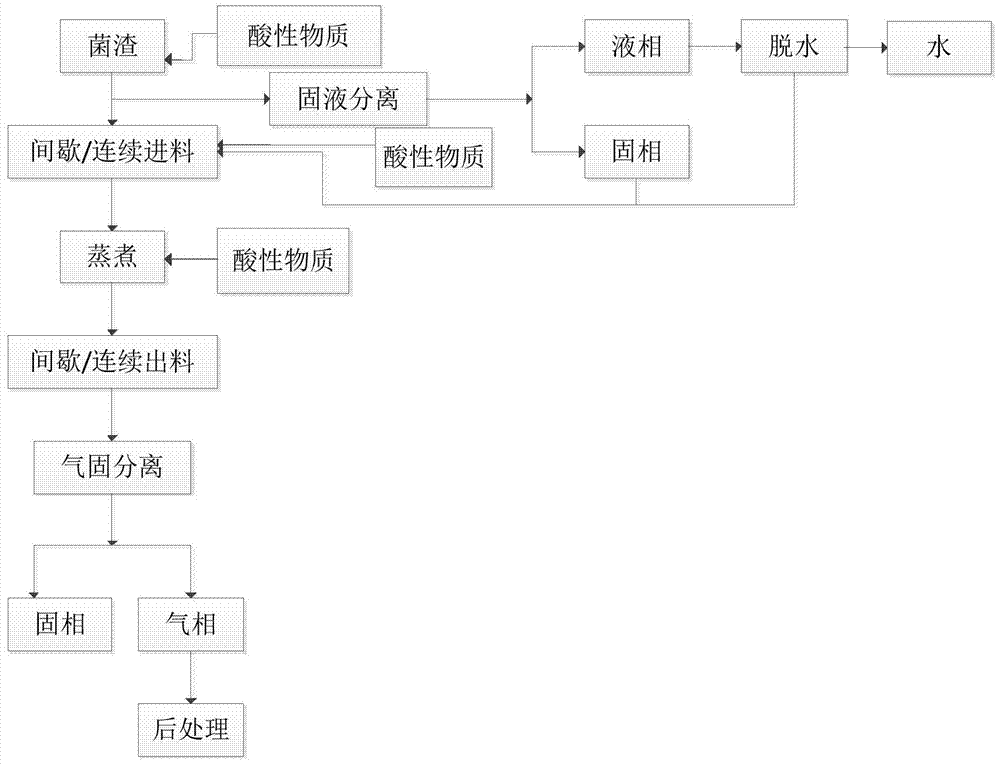
[0047] This embodiment illustrates the treatment process and results of the antibiotic bacteria residue provided by the present invention.
[0048] The penicillin slag to be treated is mixed with citric acid to adjust the acid concentration of the penicillin slag to 0.01M, and the penicillin slag is placed in a batch vertical cooker, and saturated steam is fed into the batch cooker. The saturated vapor pressure is 0.2MPa, and it is degraded under airtight conditions at 120°C and stirring for 15 minutes. The batch digester is quickly depressurized by steam explosion (the pressure difference before and after the decompression is 0.1MPa), the exhaust gas is separated by a cyclone separation device and sent to the gas treatment equipment for post-treatment, and the solid phase degradation products are separated , determined, the residual penicillin in the degradation product was 2.03ppm, and the crude protein content was 45.8% by weight.
Embodiment 2
[0050] This embodiment illustrates the treatment process and results of the antibiotic bacteria residue provided by the present invention.
[0051] The penicillin residue was treated according to the method of Example 1, except that the acidic substance was acetic acid, and the degradation temperature was 180°C. During degradation, the saturated vapor pressure in the digester is 1.0 MPa, and the pressure difference before and after pressure relief is 0.9 MPa. It is determined that the residual penicillin in the degradation product is <0.01ppm, and the crude protein content is 53.9% by weight.
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment illustrates the treatment process and results of the antibiotic bacteria residue provided by the present invention.
[0054] Penicillin scum was treated according to the method of Example 1, except that the degradation temperature was 150°C. During degradation, the saturated vapor pressure in the digester was 0.476MPa, and the pressure difference before and after pressure relief was 0.37MPa. It is determined that the residual penicillin in the degradation product is <0.01ppm, and the crude protein content is 51.4% by weight.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com