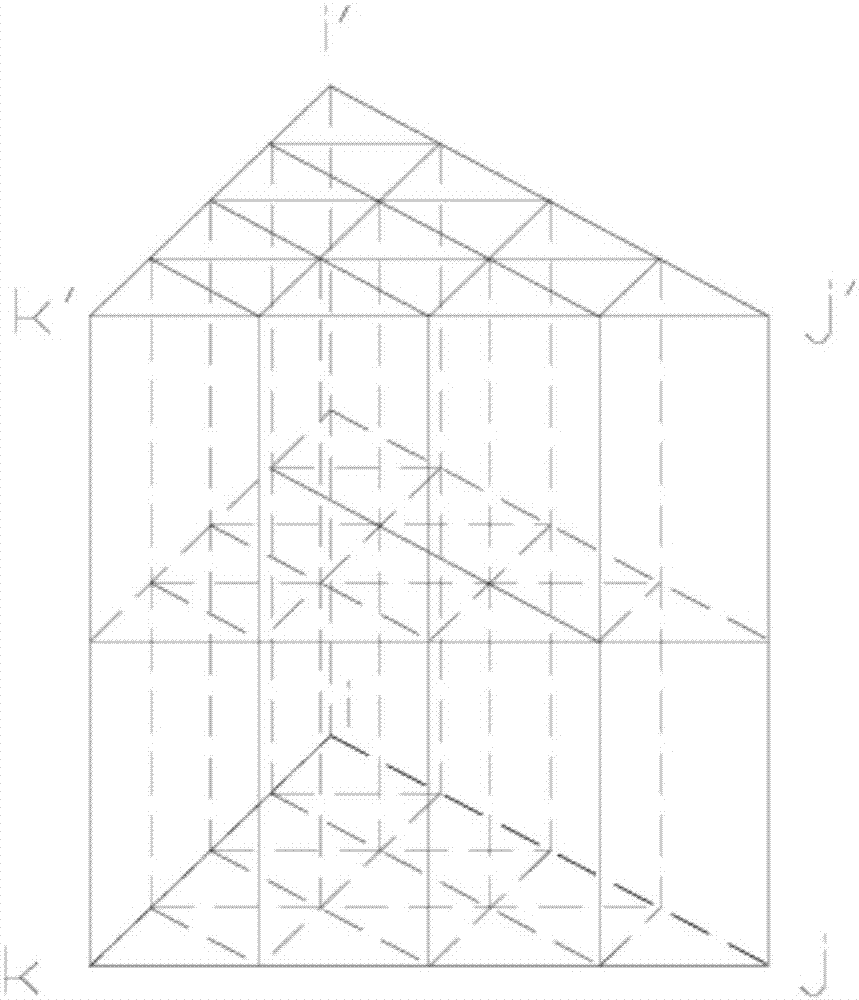
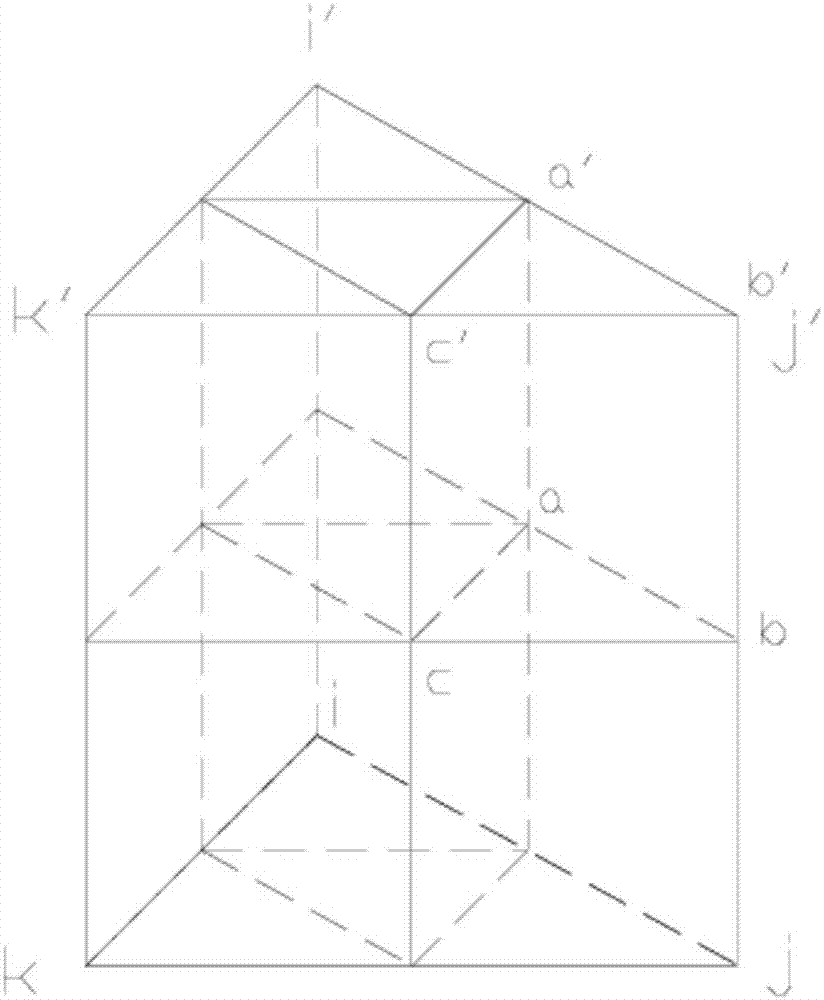
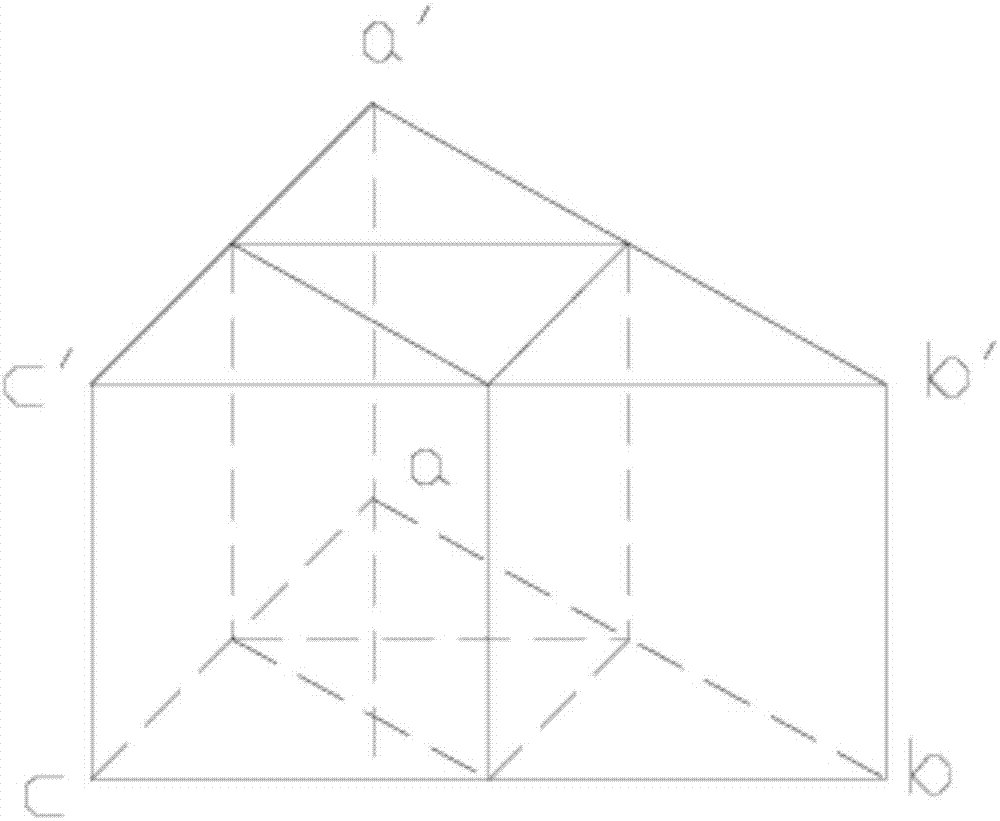
Triple-grid multi-scale finite element method for simulating three-dimensional underground water flow movement
A multi-scale, finite element technology, applied in the field of hydraulics, can solve the problem of low efficiency of three-dimensional multi-scale basis function construction, and achieve the effect of saving calculation consumption, less calculation amount, and ensuring continuity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Embodiment 1: Three-dimensional continuum steady flow model
[0094] The research area Ω is an area of 10km×10km×10m, and the origin is (50m, 50m, 0m) permeability coefficient K x = K y = K z =10 -8 x 2 m / d, the research equation is the steady flow equation:
[0095]
[0096] The boundary conditions and the source-sink term W are determined by the analytical solution H=10 -4 (x 2 +y 2 +z 2 ) is given.
[0097] Sub-example 1.1: Use FEM, MSFEM and ETMSFEM to solve, and divide the study area into the same number of fine units; FEM divides the study area into 120×120×2 grids, and other methods divide the study area into 30 ×30×2 grid; MSFEM divides each coarse unit into a 4×4×1 grid to obtain a fine unit, and ETMSFEM divides each coarse unit into a 2×2×1 grid to obtain a medium unit , and then divide each medium unit into a 2×2×1 grid to obtain fine units.
[0098] figure 2 It is the hydraulic head field of AS, FEM, MSFEM and ETMSFEM on the plane of y=4050...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2: Three-dimensional stochastic logarithmic normal distribution medium steady flow model
[0109] The research area Ω is an area of 1km×1km×120m, and the origin is (0m,0m,0m). Permeability coefficient K x =K y =K z = K, where K is a random log-normally distributed coefficient field generated by the sequential Gaussian simulation method in GSLib (Deutsch and Journal, 1998) on a grid of 400×400×8, the variance of lnK is 4, and the correlation The length is 100m. The left and right boundaries of the study area are constant water head boundaries, which are 16m and 11m respectively, and the other boundaries are separated from water, and the source and sink items are 0.
[0110] MSFEM and ETMSFEM are used to solve this example, and the study area is divided into the same number of fine elements. MSFEM and ETMSFEM divide the study area into a 25×25×2 grid. At the same time, we also use two kinds of coarse unit division, 1: MSFEM divides each coarse unit into a ...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3: Unsteady flow model of medium with three-dimensional horizontal gradient and vertical abrupt change
[0113] Consider the following three-dimensional unsteady flow equation:
[0114]
[0115] The research area Ω is an area of 10km×10km×120m, the origin is (0m, 0m, 0m), and contains 4 aquifers and 4 aquitards; the permeability coefficient K in the aquifer x =K y =1+x / 50m / d, the permeability coefficient K of the aquitard x =K y =0.005+x / 10000m / d, the vertical permeability coefficient is one-tenth of the horizontal direction; the water storage coefficient is S=5×10 -10 x / m, the left and right boundaries are constant water head boundaries, the water head values are 10m and 1m respectively, the other boundaries are water barrier boundaries, the source and sink items are 0, the time step is 1 day, and the total time is 6 days. The water head changes linearly at the initial moment, which is H 0 = 10-x / 10000m.
[0116] MSFEM and ETMSFEM are used to solve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com