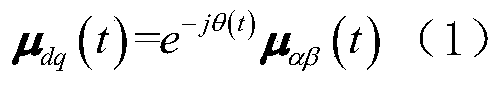A Small-Signal Impedance Modeling Method of Generalized Second-Order Integral Phase-Locked Loop
A modeling method and second-order integration technology, applied in AC network circuits, electrical components, single-network parallel feeding arrangements, etc., can solve the problem of convolution, complex calculation, and inability to truly reflect the impedance characteristics of single-phase phase-locked loops And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
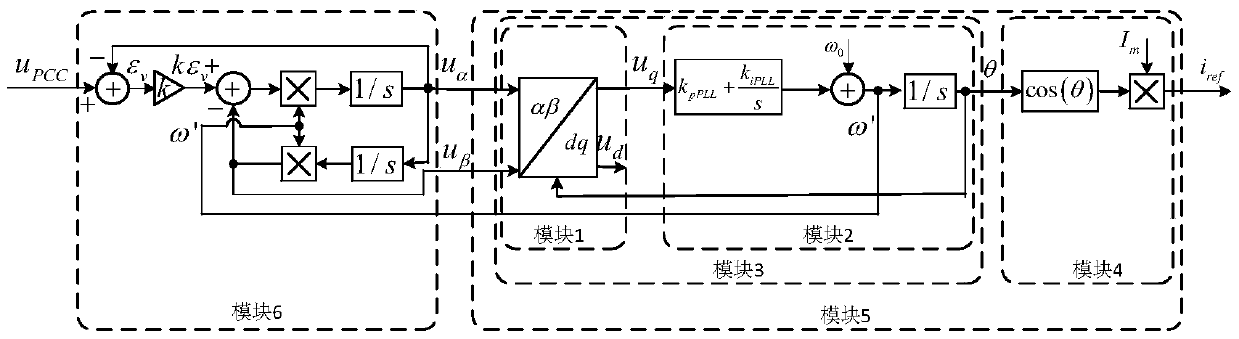
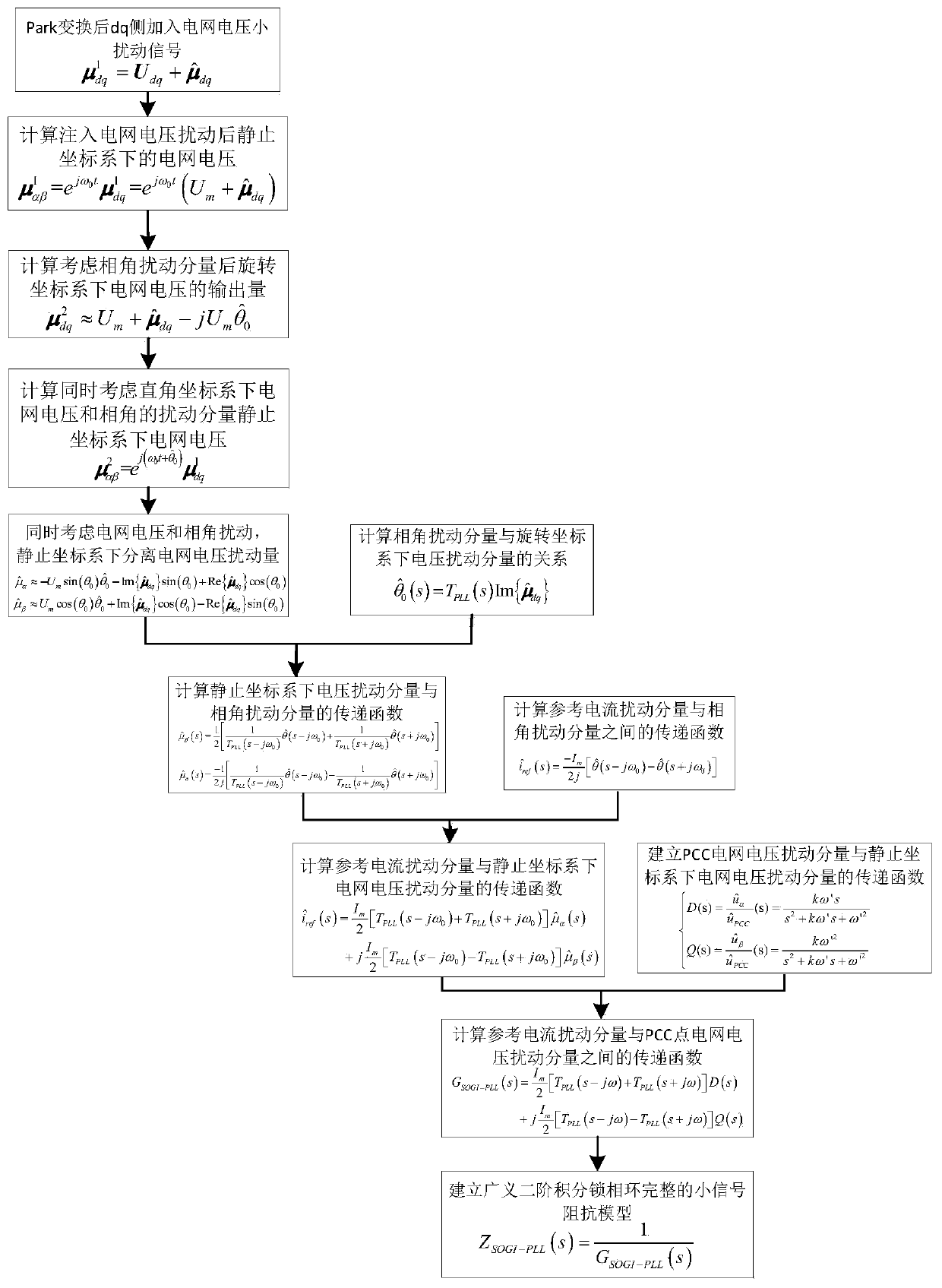
[0082] In order to more specifically illustrate the modeling process of the generalized second-order integral phase-locked loop small-signal model provided by the present invention, it will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0083] Such as figure 2 As shown, the small-signal impedance modeling flowchart of the generalized second-order integral phase-locked loop of the present invention, the modeling method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0084] Step I: Determine the relationship between the input grid voltage in the stationary coordinate system and the small output signal in the rotating coordinate system;
[0085] Step II: Establish the transfer function of the virtual axis output disturbance component and the phase angle disturbance component under the rotating coordinate system;
[0086] Step III: establish the transfer function of the grid voltage disturbance component and the phase angle disturbance component un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com