A method for improving the mechanical properties of steel plates through hot forming-sub-temperature quenching-partitioning process
A sub-temperature quenching and hot forming technology, applied in the field of improving the mechanical properties of steel plates, can solve the problems that aluminum and magnesium alloys have not been applied on a large scale, the forming process is complex, and the manufacturing cost is high, so as to save fuel, improve the environment, and improve mechanics. performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
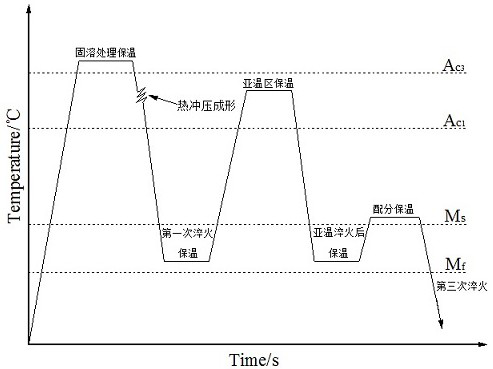
[0012] Example 1 The material used in actual production is C-Si-Mn steel plate, and its production process includes the following steps: (1) Solution treatment: first heat the steel plate at a certain heating rate to Ac 3 Above 150°C, and keep warm for 5min.
[0013] (2) The first quenching: Then the steel plate is transferred to the die for hot stamping, then quenched, and quenched to Q T1 =Ms-170℃, keep warm for 15s.
[0014] (3) Insulation in sub-temperature zone: then quench to Q T1 The steel plate was reheated to Ac 3 -10°C, and keep warm for 3 minutes.
[0015] (4) Sub-temperature quenching: Then immediately quench the steel plate Q T2 = Ms - 180°C, and keep warm for 15s.
[0016] (5) Partitioning and heat preservation: Then heat the steel plate to Ms+10°C and keep it warm for 90s.
[0017] (6) The third quenching: finally quench the steel plate to room temperature.
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2 The material used in actual production is C-Si-Mn steel plate, and its production process includes the following steps: (1) Solution treatment: first heat the steel plate at a certain heating rate to Ac 3 Above 120°C, and keep warm for 8min.
[0019] (2) The first quenching: Then the steel plate is transferred to the die for hot stamping, then quenched, and quenched to Q T1 = Ms - 190°C, keep warm for 15s.
[0020] (3) Insulation in sub-temperature zone: then quench to Q T1 The steel plate was reheated to Ac 3 -20°C, and keep warm for 3 minutes.
[0021] (4) Sub-temperature quenching: Then immediately quench the steel plate Q T2 = Ms - 200°C, and keep warm for 15s.
[0022] (5) Partitioning and heat preservation: Then heat the steel plate to Ms+20°C and keep it warm for 60s.
[0023] (6) The third quenching: finally quench the steel plate to room temperature.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3 The material used in actual production is C-Si-Mn steel plate, and its production process includes the following steps: (1) Solution treatment: firstly, the steel plate is heated to Ac 3 Above 100°C, and keep warm for 10min.
[0025] (2) The first quenching: Then the steel plate is transferred to the die for hot stamping, then quenched, and quenched to Q T1 = Ms - 200°C, keep warm for 15s.
[0026] (3) Insulation in sub-temperature zone: then quench to Q T1 The steel plate was reheated to Ac 3 -10°C, and keep warm for 3 minutes.
[0027] (4) Sub-temperature quenching: Then immediately quench the steel plate Q T2 =Ms-210°C, and keep warm for 15s.
[0028] (5) Partitioning and heat preservation: Then heat the steel plate to Ms+20°C and keep it warm for 45s.
[0029] (6) The third quenching: finally quench the steel plate to room temperature.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com