Static yaw rotating method based on laser-guided dual-wheel differential AGV
A laser-guided, in-situ technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electrical variable control, instruments, etc., to solve problems such as inappropriateness, limited space, and ignoring object contours and their motion characteristics. The effect of reducing overshoot, saving energy and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] In order to facilitate those of ordinary skill in the art to understand and implement the present invention, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the implementation examples described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
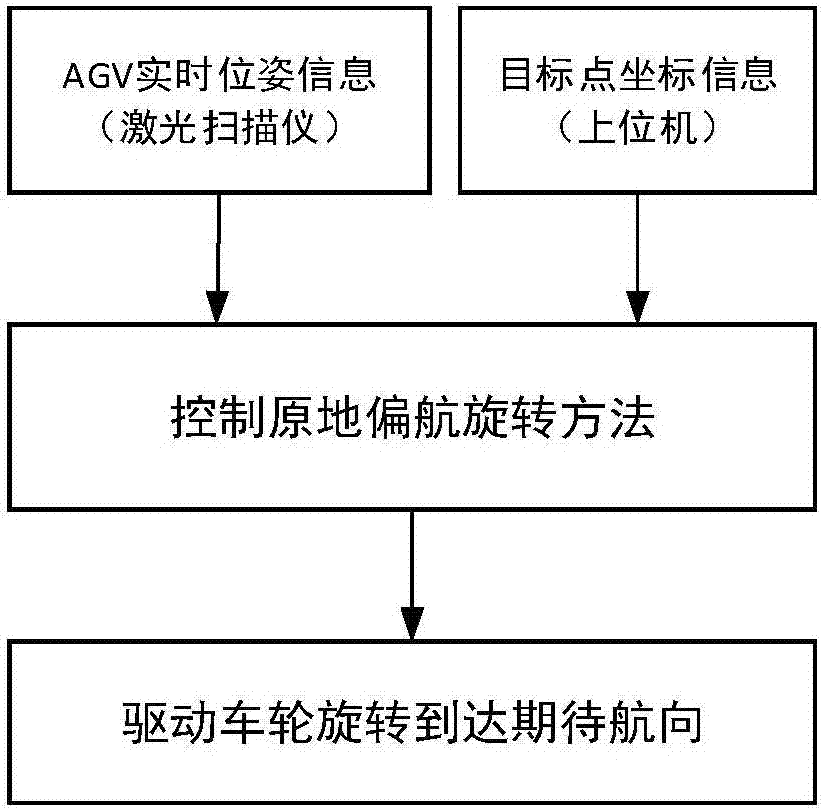
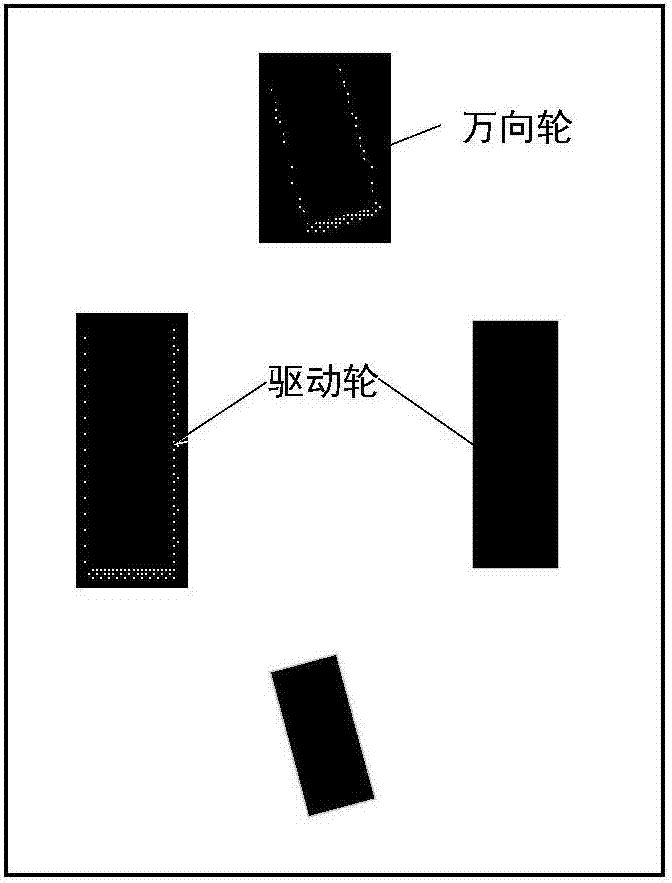
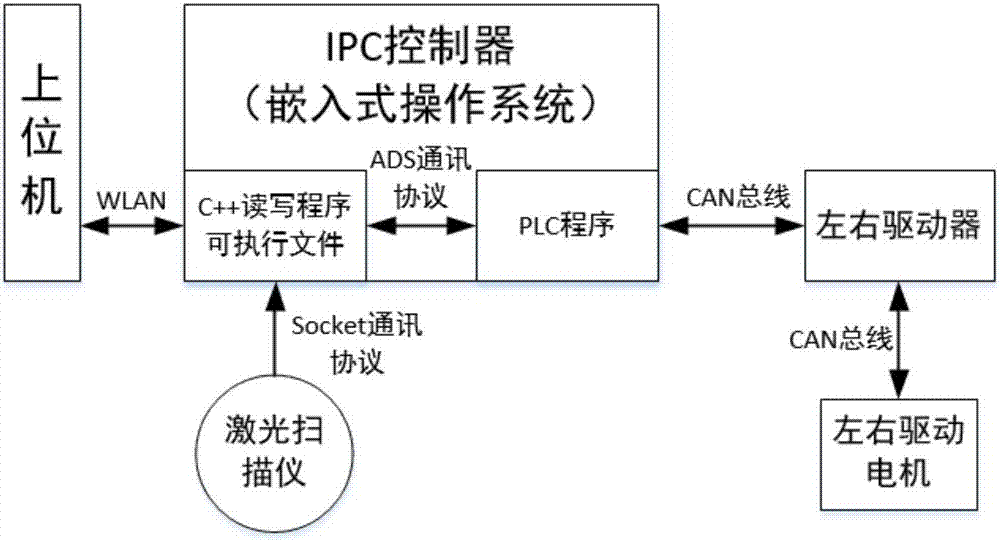
[0058] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides an in-situ yaw rotation method based on a laser-guided two-wheel differential AGV. The real-time pose of the AGV car is continuously obtained through the laser scanner, and is passed to the PLC to execute the program through the intermediate read and write program. At the same time The upper computer communicates the coordinate information of the target point to the vehicle control system through the wireless network. When the AGV needs to move to the next target point after completing the task at a certain point, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com