Dynamic Measurement of Synthesizer Noise Spurs or Phase Noise
A technology of frequency synthesizer and phase noise, applied in noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurement, automatic control of power, measurement device, etc., can solve problems such as unreliable radar measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0038] This process is illustrated for the first embodiment using the equations or process steps described below:
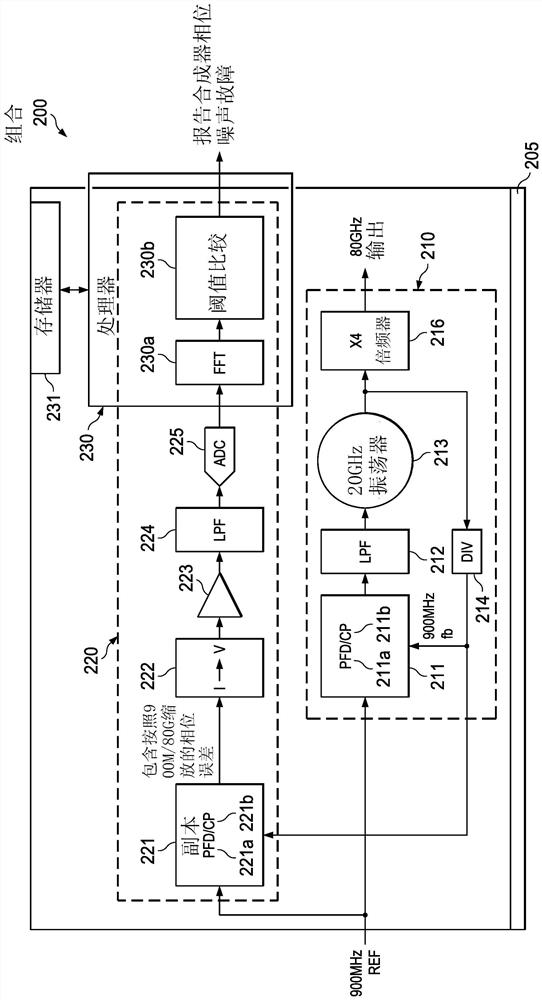
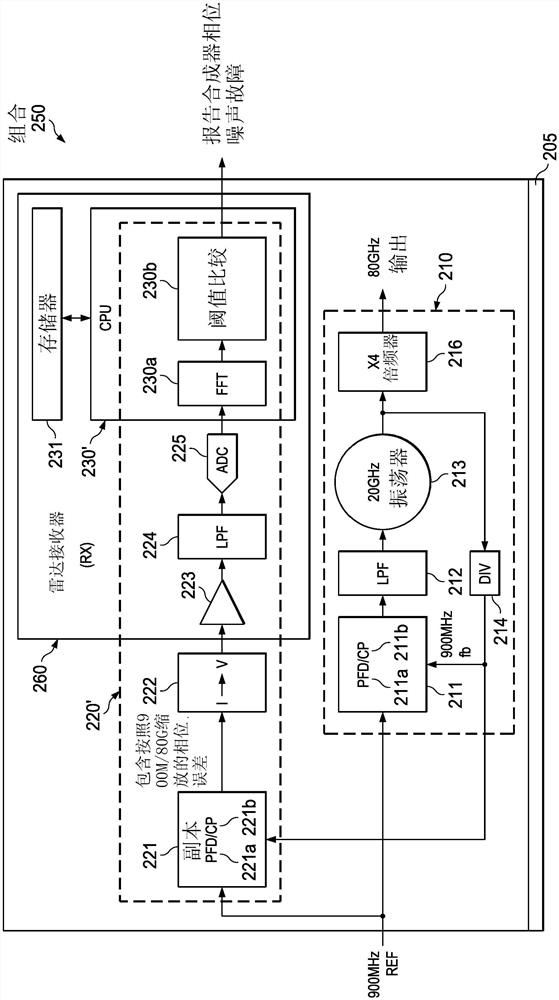
[0039] a. Let x[n] be the digital samples output by the ADC of the PN measurement circuitry. Take N such consecutive samples. Thus, x[n], where n=0 to N-1, can be used as a block sequence of numbers in the processor's memory.
[0040] b. Perform FFT on x[n] to obtain FFT result X[k], where k=0 to N-1.
[0041] c. Find the signal Y[k]=X[k]*X[k], where the operation ".*" means element-wise multiplication. For example, Y[0]=X[0]*X[0], where "*" means multiplication. In other embodiments, Y[k]=|X[k]| may be found to have equivalent PN measurement performance. Here, |X[k}]| denotes the absolute value of the sequence X[k], and the meaning of "absolute value" is well known to mathematicians and engineers.
[0042] d. Optionally, repeat steps a, b, c more (eg L) times (iteration i=1 to L). The digital samples are different for each acquisition because new acquisiti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com