Safe Electric Braking Devices for Synchronous Motors
A synchronous motor and mechanical brake technology, applied in the field of rail vehicles, can solve the problems of complicated converter adjustment, difficult and error-free control, etc., and achieve the effects of increased complexity, low complexity, and simple safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
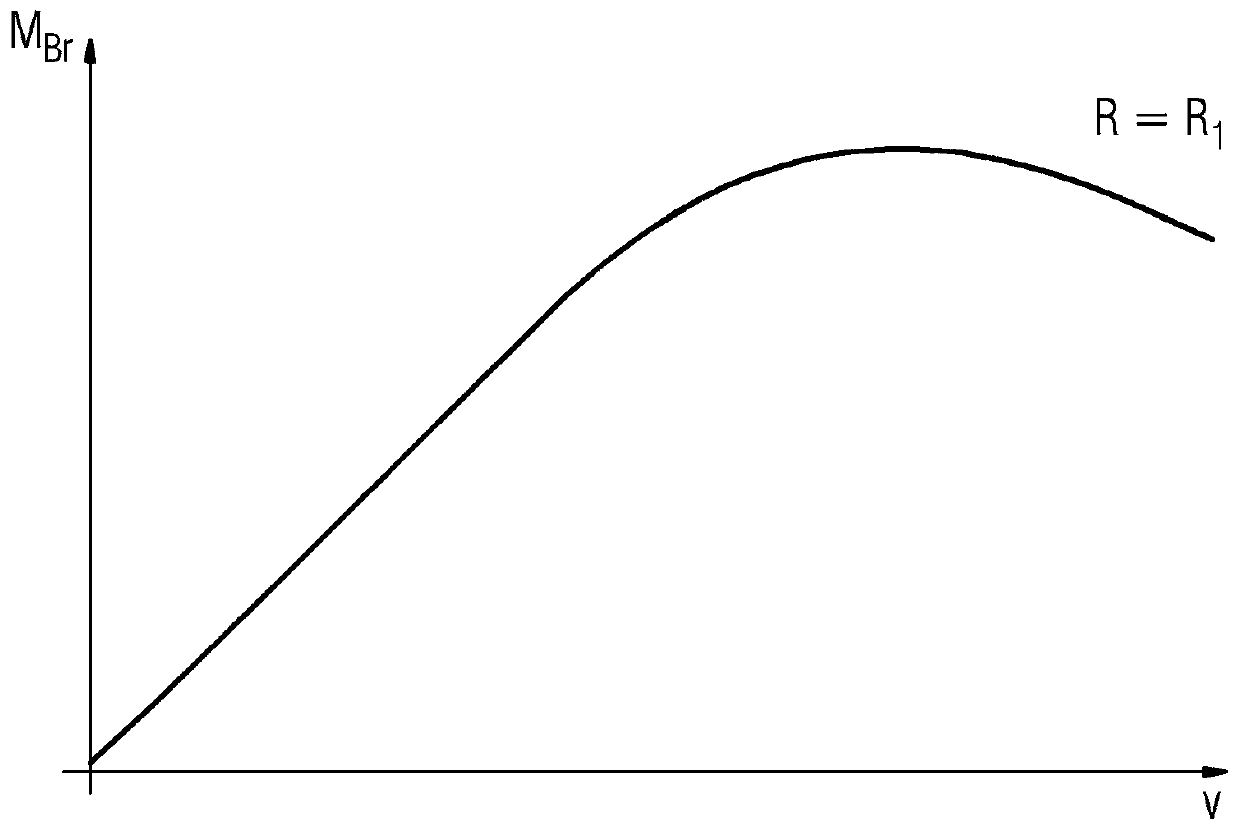
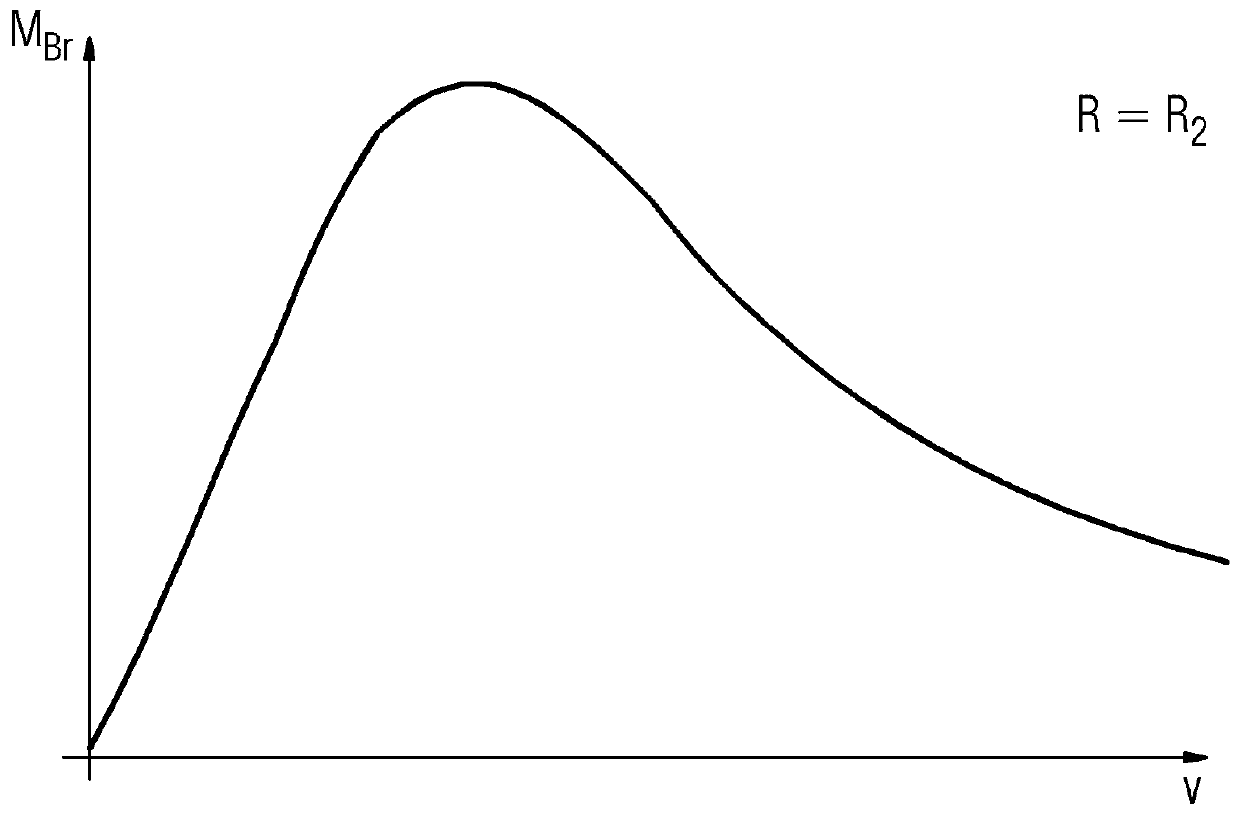
[0031] figure 1 shows the respective electrical connections at the phase connectors 20 with the value R 1 The braking torque M in the case of resistor 4 Br Curves against rotational speed. For values with value R 2 The second resistor 4, where R 2 1 , whose curve is as figure 2 shown. Obviously, for a smaller resistance 4 a braking torque M occurs at a smaller speed Br the maximum value. At zero rotational speed, no braking torque M can be achieved at the synchronous motor 2 independently of the resistance value Br . In order to be able to apply a braking torque to the drive system in the stationary state, an additional brake, for example a mechanical brake, must be provided in the drive system 1 .
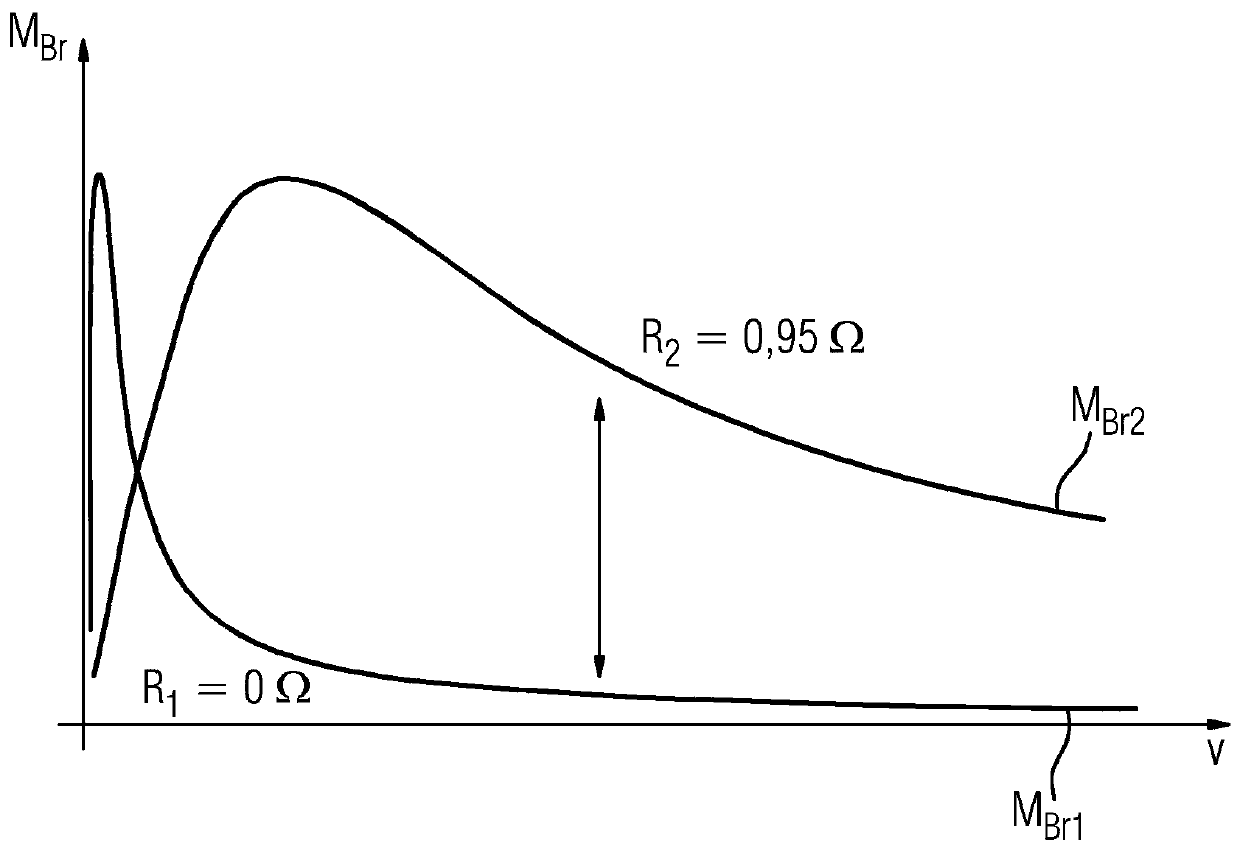
[0032] image 3 shows the first braking torque M Br1 The curve and the second braking torque M Br2 , where the first braking torque occurs when the phase connections 20 of the synchronous machine 2 are short-circuited, and in the case of the second braking torque, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com