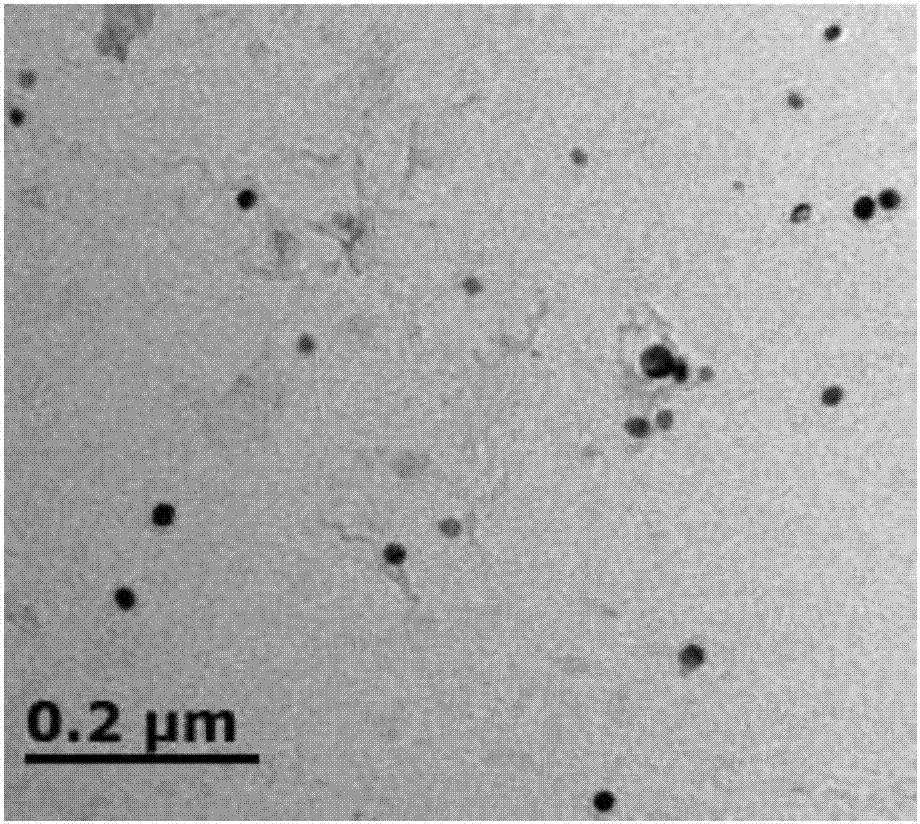
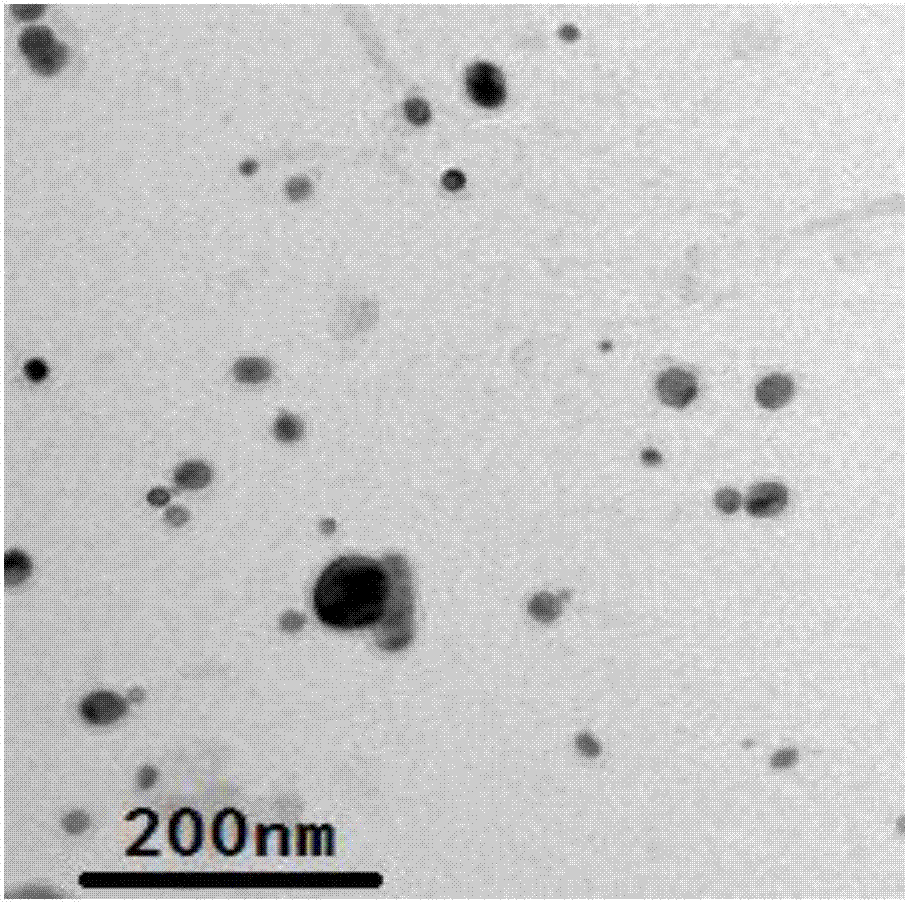
Novel dispersion-strengthened low-activation radiation-resistant martensitic steel and heat treatment technology thereof
A technology of martensitic steel and elements, applied in the field of martensitic steel and its preparation, can solve the problems of small output, poor stability, small size, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] The application also provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned martensitic steel, comprising the following steps:
[0049] A), forging the martensitic steel ingot, the element composition of the martensitic steel ingot is as shown in the above scheme;
[0050] B), the forged martensitic steel ingot is rolled, the rolled martensitic steel is quenched and tempered once, and the martensitic steel ingot after the first tempering is tempered twice .
[0051] In the process of preparing martensitic steel, the applicant first prepared a martensitic steel ingot; the preparation of the martensitic steel ingot was prepared according to technical means well known to those skilled in the art, and this application has no special For example, the preparation of the martensitic steel ingot can be carried out by vacuum induction melting first, and then vacuum consumable arc melting; in the process of vacuum induction melting, the easily oxidizable alloying elements are added...
Embodiment 1
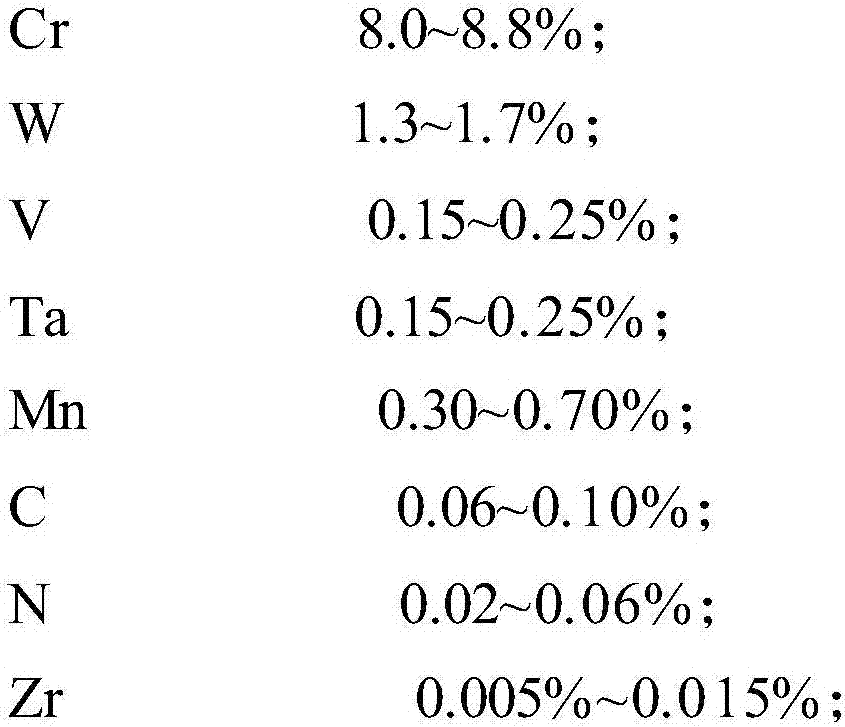
[0060] (1) In terms of mass percentage, according to the composition ratio: Cr 8.5%, W 1.5%, V 0.16%, Ta 0.20%, Mn0.45%, C 0.08%, N 0.02%, Zr 0.005% ~ 0.015%, Si <0.01%, P≤0.005%, S≤0.005%, O≤0.005%, Al≤0.01%, Ni≤0.005%, Nb≤0.001%, Co≤0.005%, Cu≤0.005%, Mo≤0.005% and alloy The burning loss proportioning raw material, wherein C, N, Ta and V satisfy the relational expression of formula (1);
[0061] (2) In the vacuum induction furnace, raw materials are added sequentially according to the burning loss and volatilization characteristics of the alloying elements. The easily oxidized alloying elements are added after they are fully deoxidized, and the volatile alloying elements are added under the protection of the atmosphere or at the end of the smelting process. Ingots with qualified components are prepared after induction melting;
[0062] (3) Melting the prepared ingot by vacuum consumable arc to further purify the material;
[0063] (4) Forging the ingot obtained in step (3)...
Embodiment 2
[0068] (1) In terms of mass percentage, according to the composition ratio: Cr 9.0%, W 1.5%, V 0.11%, Ta 0.25%, Mn0.45%, C 0.08%, N 0.03%, Zr 0.005% ~ 0.015%, Si <0.01%, P≤0.005%, S≤0.005%, O≤0.005%, Al≤0.01%, Ni≤0.005%, Nb≤0.001%, Co≤0.005%, Cu≤0.005%, Mo≤0.005% and alloy The burning loss proportioning raw material, wherein C, N, Ta and V satisfy the relational expression of formula (1);
[0069] (2) In the vacuum induction furnace, add the above-mentioned raw materials in sequence according to the burning loss and volatilization characteristics of the alloy elements. The easy-to-oxidize alloy elements are added after they are fully deoxidized, and the volatile alloy elements are added under the protection of the atmosphere or at the end of the melting process. Ingots with qualified components are prepared after induction melting;
[0070] (3) Melting the prepared ingot by vacuum consumable arc to further purify the material;
[0071] (4) Forging the ingot obtained in step ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com