3D imaging device for surgical microscopes
A technology of an operating microscope and an imaging device, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of high requirements for research and development and manufacturing, no three-dimensional effect, etc., and achieve the effect of simple structure and convenient use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
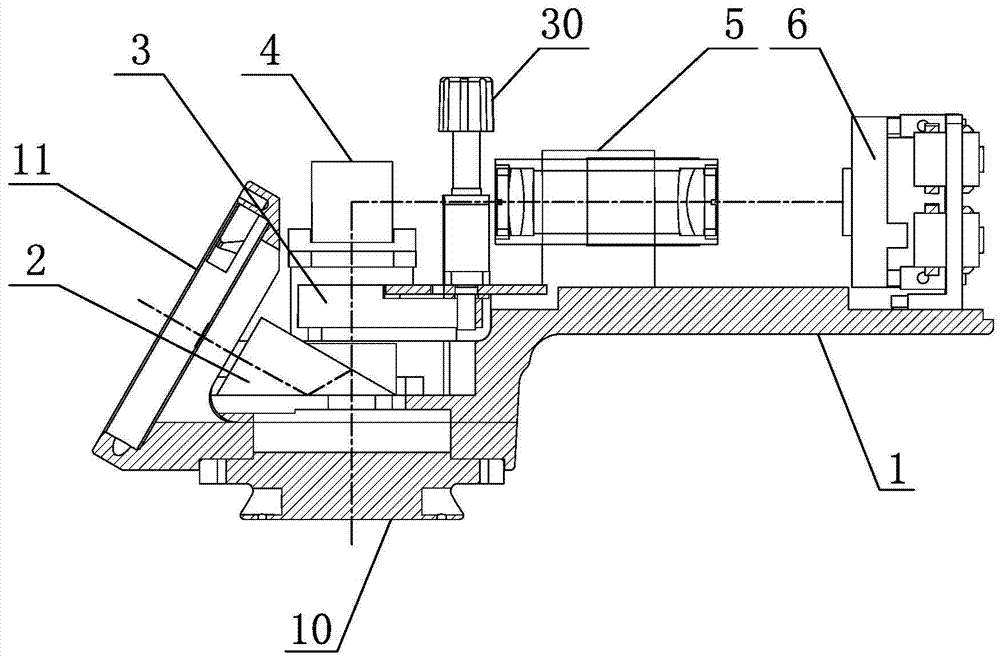
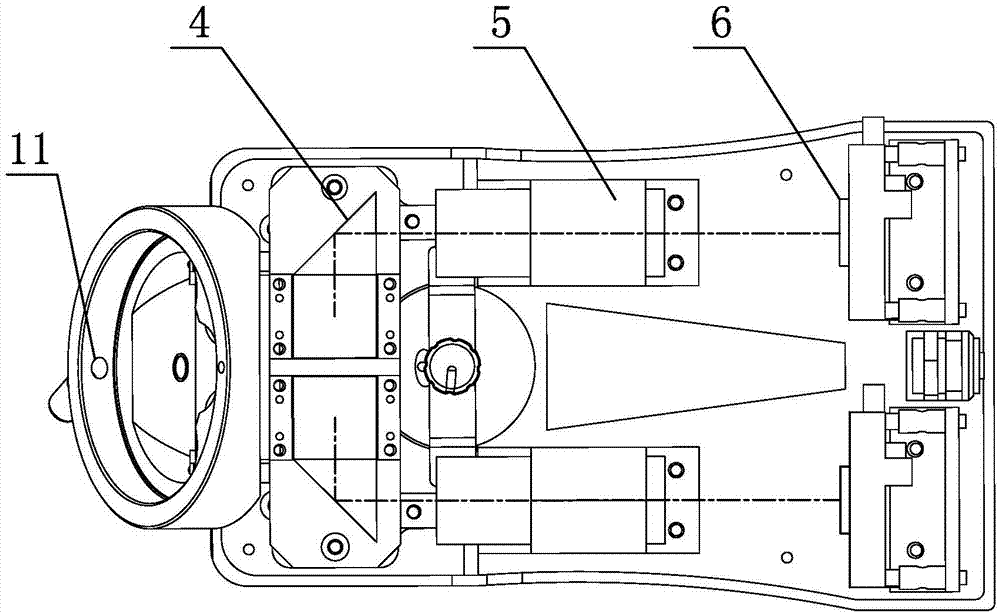
[0029] as shown in the picture 1 、 2 an operating microscope 3D Imaging device, including housing 1 ,case 1 There is a mirror body connection part connected with the main mirror body 10 , the lens barrel connecting part connected with the binocular tube 11 。
[0030] in the shell 1 Built-in beam splitter 2 , variable aperture 3 , left and right steering mirror group 4 , left and right imaging mirror groups 5 and left and right photosensitive elements 6 . Where: Iris diaphragm 3 with adjustment operator 30 , adjust the operating part 30 exposed shell 1 Outside; left and right imaging mirror groups 5 Can use such as flat reflector; left and right photosensitive elements 6 can be CCD or CMOS 。
[0031] It works as follows:
[0032] Through the parallel double beams in the two symmetrical apertures of the main mirror body, through the beam splitter group 2 Divided into two paths, one path of double beams pass...
Embodiment 2
[0034] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that: 3 Shown: the left and right imaging mirrors 5 group including first left and right imaging lenses 50 , the second left and right imaging lenses 51 . Specifically:
[0035] in the shell 1 There is a horizontal beam splitter group inside 20 , beam splitter group 2 , variable aperture 3 , the first left and right imaging lenses 50 , left and right steering mirror group 4 , the second left and right imaging mirror groups 51 and left and right photosensitive elements 6 。
[0036] It works as follows:
[0037] Through the parallel double beams in the two symmetrical apertures of the main mirror body, through the transverse beam splitter group 20 After passing through the beam splitter group 2 Divided into two paths, one path of double beams passes through the binocular tube for the surgeon to observe; the other path of double beams passes through the...
Embodiment 3
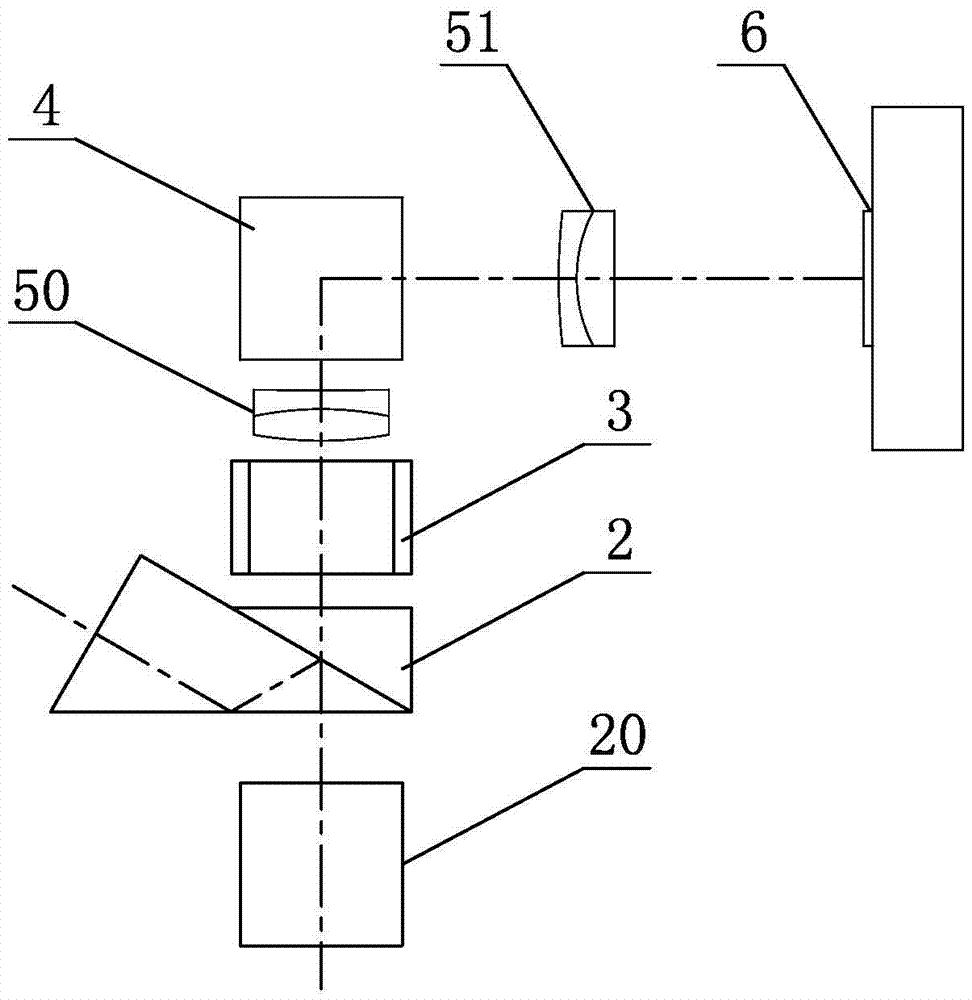
[0040] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that: 4 Shown: the left and right imaging mirrors 5 group including first left and right imaging lenses 50 , the second left and right imaging lenses 51 ;Second left and right imaging lenses 51 , left and right photosensitive elements 6 secondary steering mirror 7 . Specifically:
[0041] in the shell 1 Built-in beam splitter 2 , variable aperture 3 , the first left and right imaging lenses 50 , left and right steering mirror group 4 , the second left and right imaging mirror groups 51 , secondary steering mirror 7 and left and right photosensitive elements 6 . Among them: left and right steering mirror group 4 Right Angle Prism 40 and rhombic prism 41 combination, as shown in the figure 5 shown; secondary steering mirror 7 The right-angle prism is used to turn again, shortening the height of the system, and turning the mirror image ref...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com