Computer-assisted fracture restitution degree measurement method
A computer-aided, fracture restoration technology, applied in the field of three-dimensional medical image processing, can solve the problem that the restoration progress cannot be measured, and achieve the effect of shortening the time and improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A computer-aided fracture restoration progress measurement method, comprising the following steps:
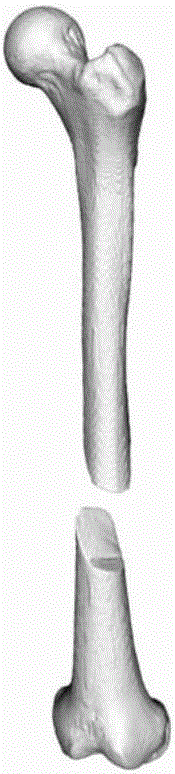
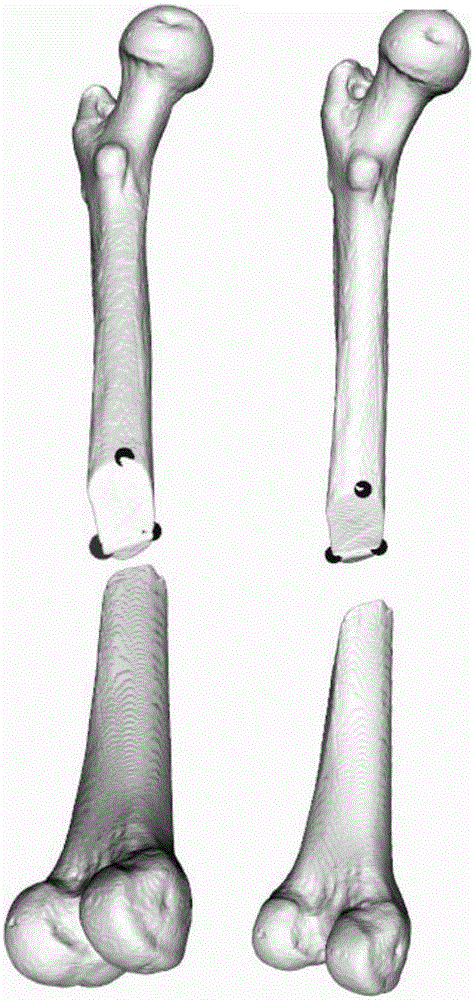
[0027] Step 1, use medical imaging equipment to scan the fracture site, obtain medical images, and perform three-dimensional reconstruction on the fracture site to obtain the surface model of the broken bone (such as figure 1 shown); Manually select feature points on the fracture section of the reconstructed model: take one of the broken bones as the target bone, assuming it is fixed, and manually select n points with obvious features on the target bone section as the target feature point set ,Such as figure 2 As shown; also select n feature points one-to-one corresponding to the target feature point set on the section of another broken bone (that is, the source bone) as the source feature point set.
[0028] Step 2. Use the ICP algorithm to calculate the translation matrix and transformation matrix between the two broken bones, rotate and translate the source bone and...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The specific steps of manually selecting a feature point set in Step 1 of this embodiment are as follows:
[0034] Step 1.1, manual selection of source feature point set:
[0035] Select an appropriate angle for the 3D model of the source bone, select a point on the side or corner with obvious features on the section, select the point with the mouse, and store the point in the source point set to obtain SourcePoint(x i ,y i ,z i ), i=1...n.
[0036] Step 1.2, manual selection of the target feature point set:
[0037] On the cross-section of the target bone 3D model, select the point corresponding to the feature point on the source bone, store it in the target point set, and obtain the corresponding target point set TargetPoint(x i ,y i ,z i ), i=1...n.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Step 2 of this embodiment uses the ICP algorithm to calculate the translation matrix K and rotation matrix L between the target bone and the source bone (at this time, the target bone and the source bone both refer to the three-dimensional model of the broken bone), and the source bone After performing rotation and translation, it docks with the target bone to achieve pre-synthesis and obtain the best restoration position.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com