A self-test method and device for non-volatile memory
A non-volatile, memory technology, applied in the field of memory, can solve the problems of rising cost of memory products and high testing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
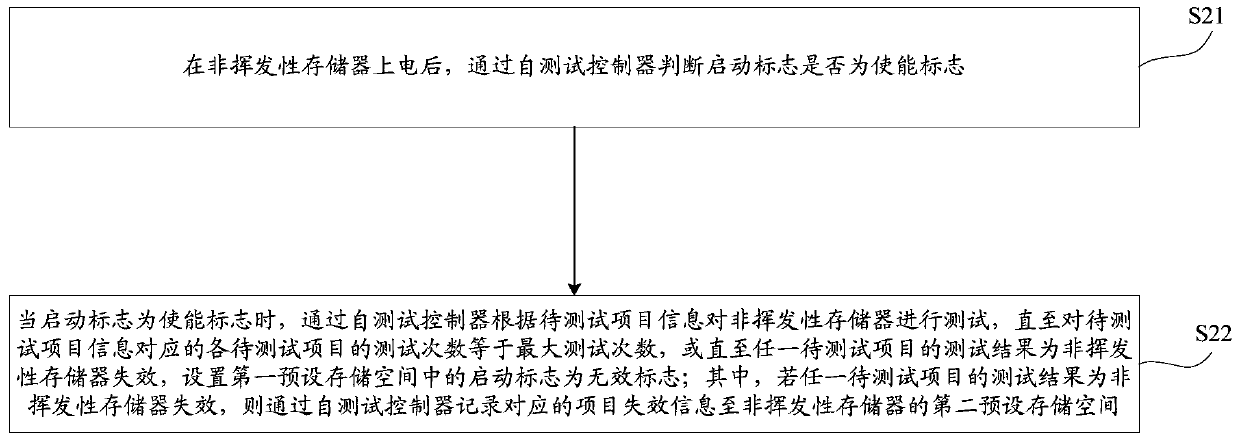
[0025] refer to figure 2 , shows a flow chart of the steps of a non-volatile memory self-test method embodiment of the present invention, the non-volatile memory includes a self-test controller, the self-test controller can be embedded or integrated in the non-volatile memory, the non-volatile memory The first preset storage space of the volatile memory stores the startup sign written by the test equipment, the maximum number of tests and the information of the items to be tested, and the self-test method may specifically include the following steps:
[0026] S21. After the non-volatile memory is powered on, judge whether the start flag is an enable flag through the self-test controller.
[0027] Wherein, a non-volatile memory (NVRAM, Non-volatile memory) refers to a memory in which stored information will not disappear when the system is turned off or there is no power supply. For example, EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory...
Embodiment 2
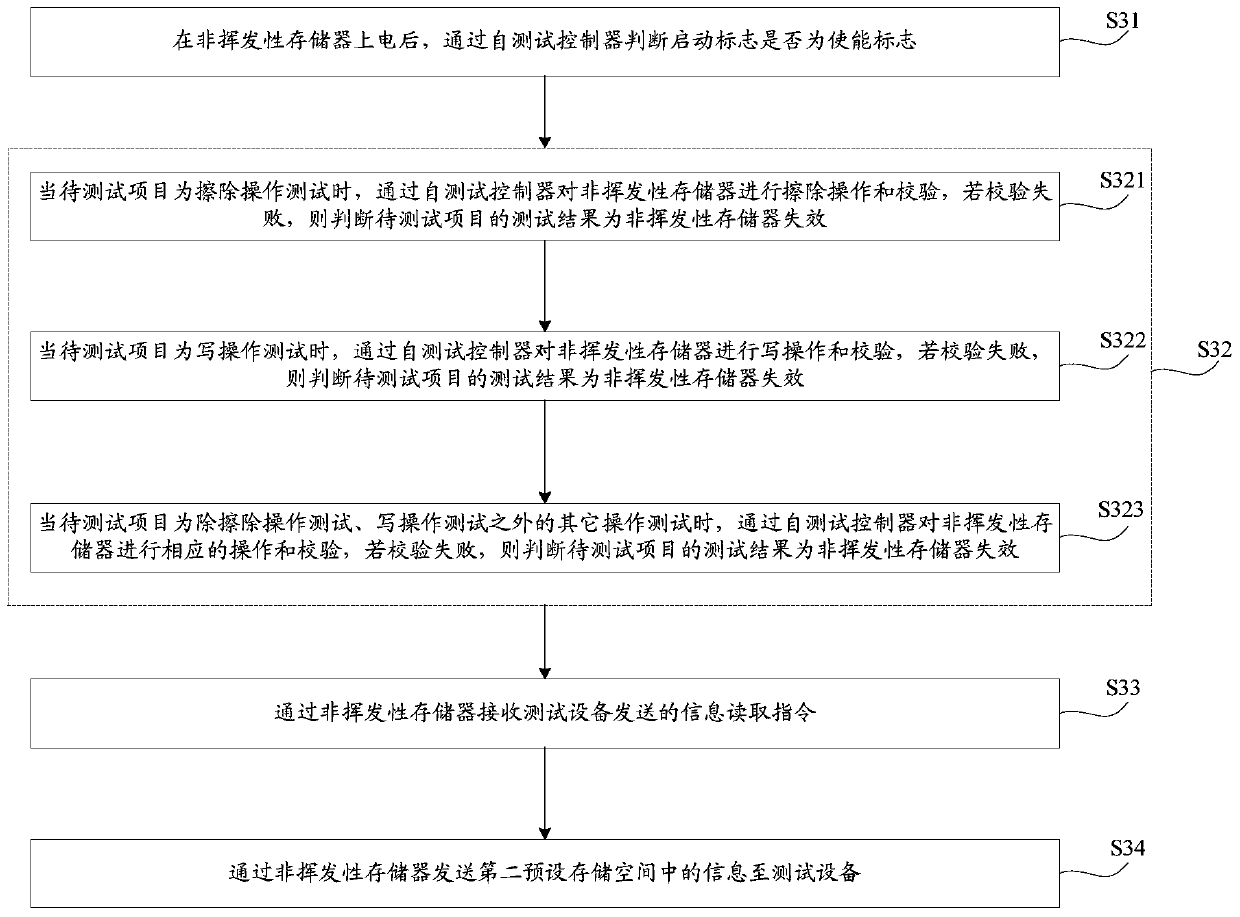
[0040] refer to image 3 , shows a flow chart of the steps of another non-volatile memory self-test method embodiment of the present invention, the non-volatile memory includes a self-test controller, the non-volatile memory is connected with the test equipment, and the first non-volatile memory A preset storage space stores the startup sign written by the test equipment, the maximum number of tests and the information of the items to be tested. The self-test method may specifically include the following steps:
[0041] S31. After the non-volatile memory is powered on, judge whether the startup flag is an enable flag through the self-test controller.
[0042] Wherein, the maximum number of tests and the items to be tested corresponding to the information of the items to be tested may be set during the production of the non-volatile memory according to the characteristics of the non-volatile memory, testing requirements, and the like.
[0043] S32, when the startup flag is the...
Embodiment 3
[0062] refer to Figure 4 , shows a structural block diagram of a self-test device embodiment of a non-volatile memory of the present invention, the non-volatile memory includes a self-test controller, and the first preset storage space of the non-volatile memory stores the data written by the test device The startup flag, the maximum number of tests and the information of the items to be tested, the self-test device can specifically include the following modules:
[0063] The judging module 41 is configured to judge whether the startup flag is an enable flag through the self-test controller after the non-volatile memory is powered on.
[0064] The test module 42 is used to test the non-volatile memory according to the information of the items to be tested by the self-test controller when the start flag is the enable flag, until the number of tests of each item to be tested corresponding to the item information to be tested is equal to the maximum test number of times, or unt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com