Method for identifying bipolar short-circuit fault in direct current line
A bipolar short circuit and fault identification technology, which is applied to fault locations, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the slow speed of bipolar short circuit fault identification and cannot meet application requirements, and meet the requirements of rapidity and avoid misjudgment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The specific implementation manner of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
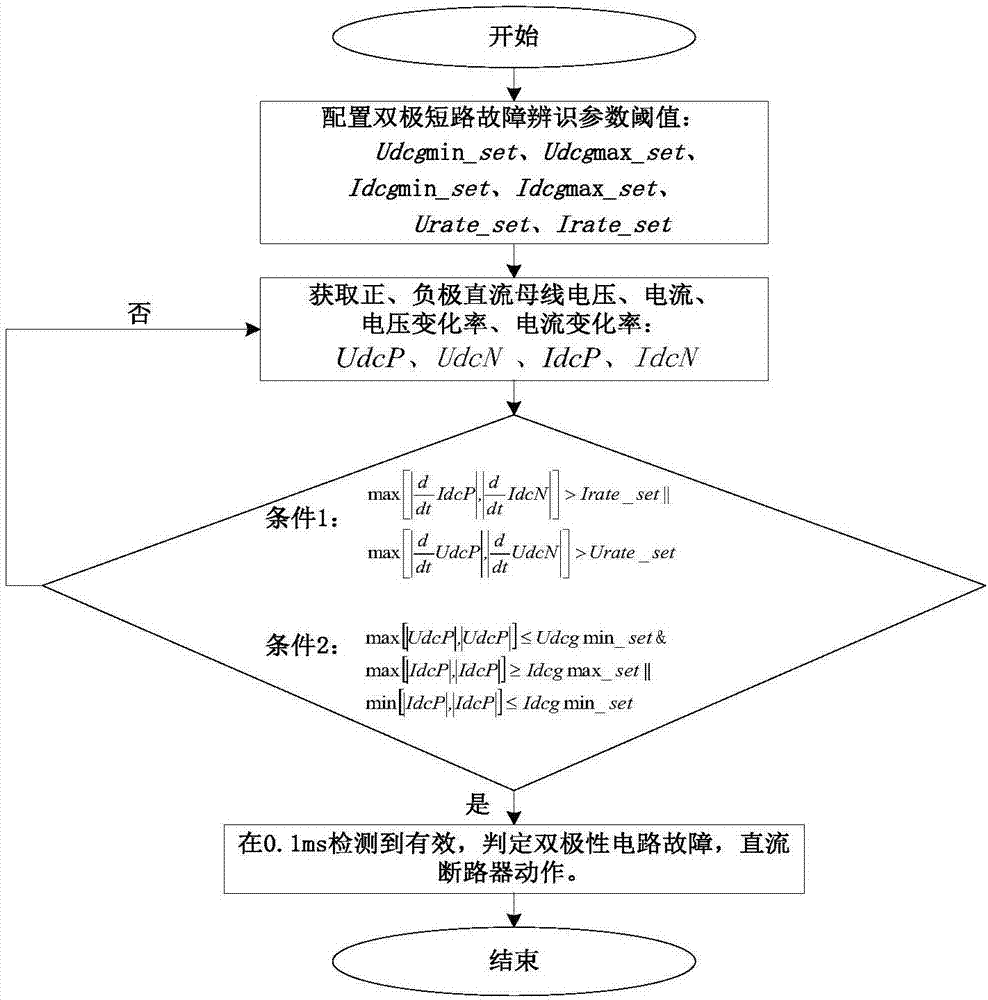
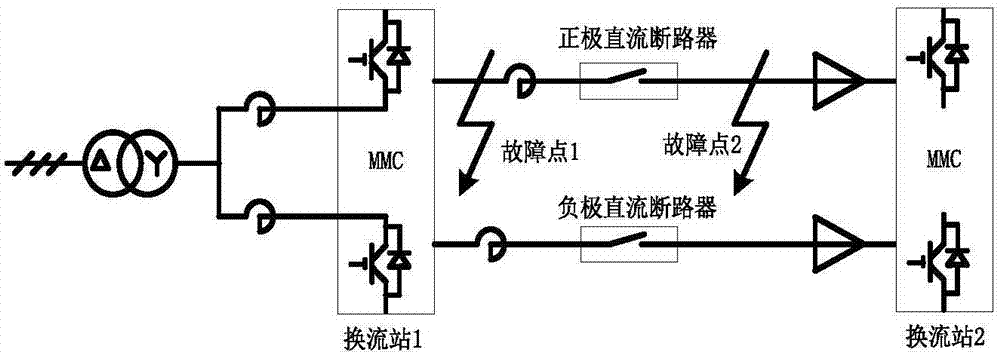
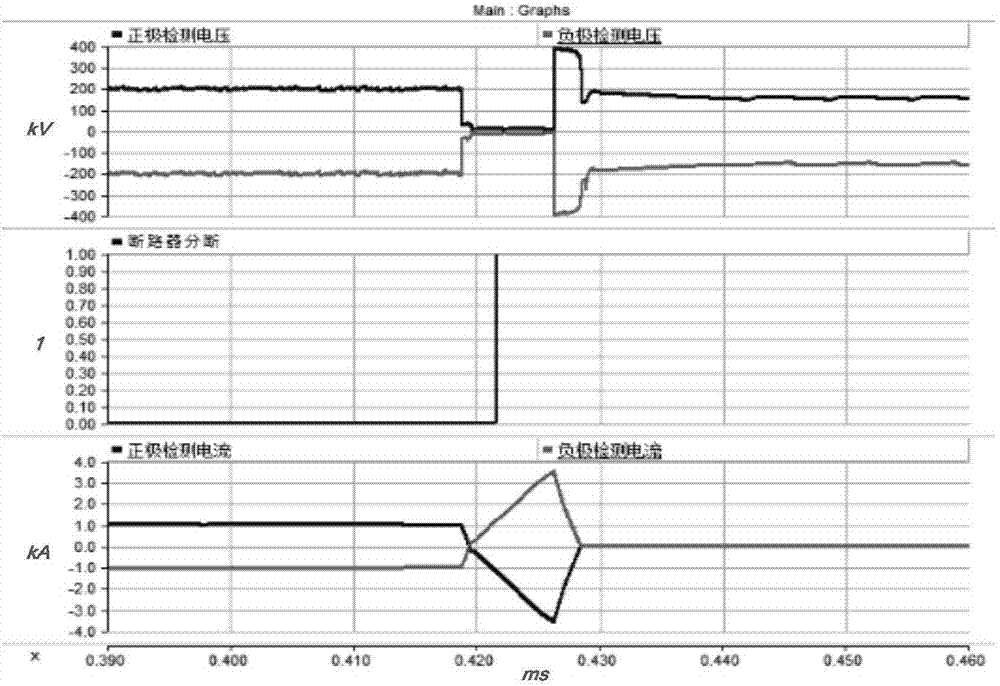
[0024] Such as figure 1 As shown, the identification method of the bipolar short-circuit fault of the DC line includes the following steps:
[0025] Step 1, obtain positive and negative bus voltage, current, voltage change rate and current change rate.
[0026] Specifically, optical transformers are used to obtain identification data such as positive and negative DC bus voltages, currents, voltage change rates, and current change rates. In order to ensure the rapidity of data transmission, in this embodiment, the upload data cycle of optical transformers is 20us .
[0027] Step 2, judging whether the voltage change rate and current change rate of the positive and negative busbars meet the set fault identification and pre-judgment conditions.
[0028] Among them, the pre-judgment conditions for fault identification ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com